Figure 2.
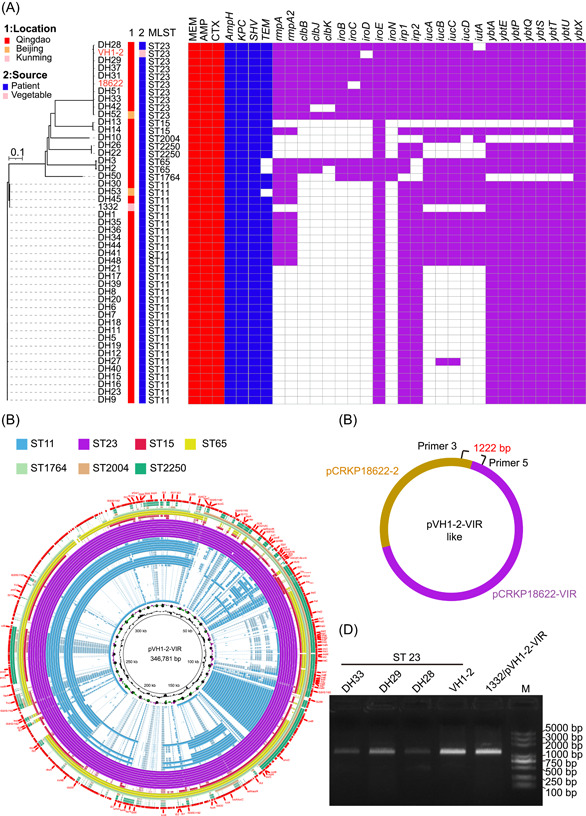
Prevalence of pVH1‐2‐VIR‐like plasmids. (A) Phylogenetic structures, MLST, antibiotic resistance phenotypes, ARGs, and virulence genes of CRKP isolates. Isolate location and sources are indicated. Red and blue squares represent positivity for resistance phenotypes and resistance genes, respectively. Purple squares represent positivity for virulence genes. AMP, ampicillin; CTX, cefotaxime; MEM, meropenem. (B) Sequence alignment of virulence plasmids harboring rmpA and rmpA2 in the 23 clinical CR‐HvKP strains of different STs used in this study. The 346.781 kb virulence plasmid pVH1‐2‐VIR found in this study is used as a reference and genetic regions associated with virulence are highlighted in green. (C) Schematic depicting for investigating potential pVH1‐2‐VIR‐like plasmids. Primers 3 and 5 were used to amplify hybrid regions. (D) PCR confirmed the presence of the pVH1‐2‐VIR‐like plasmids in CRKP isolates. CRKP, carbapenem‐resistant K. pneumoniae.
