Figure 1.
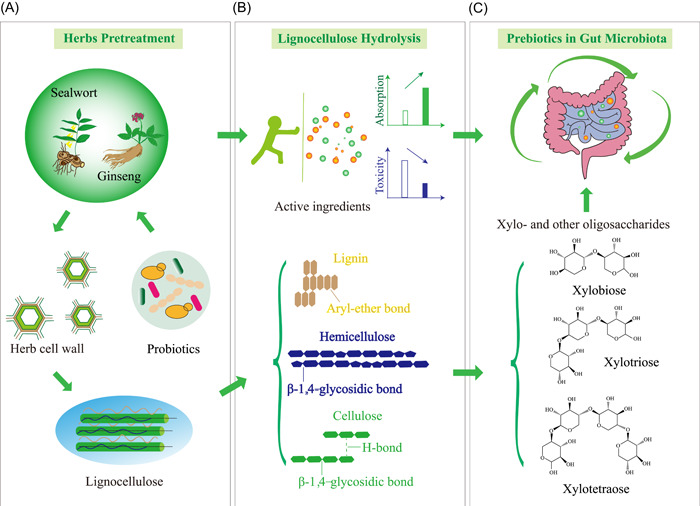
Lignocellulases and their functions in sealwort, ginseng, and other Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) fermentation. (A) The lignocellulose might prevent the release of bioactive ingredients of CHM, and lignocellulases derived from probiotics or other microbes can be used to degrade herb lignocellulose. (B) Lignocellulose hydrolysis releases bioactive ingredients in herbs, and leads to the generation of oligosaccharides prebiotics. (C) Bioactive ingredients and oligosaccharides are beneficial for the gut microbiota of humans and animals.
