Figure 2.
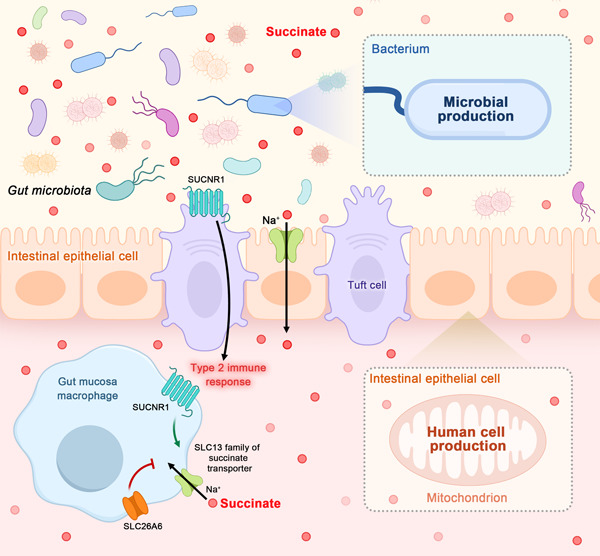
Succinate production and transportation in the human body. Succinate is synthesized by both human cells and gut microbiota. The charged nature of succinate enables its transport across plasma membranes, facilitated by the SLC13 family of Na+‐dependent transport proteins. Notably, the potent suppression of SLC13A2 occurs through the interaction with the SLC26A6 transporter. Furthermore, succinate plays a crucial role in extracellular signaling by stimulating the G protein‐coupled succinate receptor (SUCNR1), which is abundant in various tissues and cells. The uptake of succinate by macrophages can enhance and perpetuate inflammation, while its detection by tuft cells in the small intestine initiates type 2 immunity.
