Abstract
The gasdermin (GSDM) family has garnered significant attention for its pivotal role in immunity and disease as a key player in pyroptosis. This recently characterized class of pore-forming effector proteins is pivotal in orchestrating processes such as membrane permeabilization, pyroptosis, and the follow-up inflammatory response, which are crucial self-defense mechanisms against irritants and infections. GSDMs have been implicated in a range of diseases including, but not limited to, sepsis, viral infections, and cancer, either through involvement in pyroptosis or independently of this process. The regulation of GSDM-mediated pyroptosis is gaining recognition as a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of various diseases. Current strategies for inhibiting GSDMD primarily involve binding to GSDMD, blocking GSDMD cleavage or inhibiting GSDMD-N-terminal (NT) oligomerization, albeit with some off-target effects. In this review, we delve into the cutting-edge understanding of the interplay between GSDMs and pyroptosis, elucidate the activation mechanisms of GSDMs, explore their associations with a range of diseases, and discuss recent advancements and potential strategies for developing GSDMD inhibitors.
Subject terms: Immunological disorders, Cell biology, Diseases
Introduction
The recently identified gasdermin (GSDM) protein family is pivotal in the modulation of pyroptosis, a specialized form of programmed cell death (PCD). In humans, six paralogous genes have been identified: GSDMA-E, and DFNB59 (Table 1).1,2 The function of GSDMs in pyroptosis is well-established, and GSDMA-E have been shown to undergo proteolytic processing, resulting in the release of N-terminal (NT) fragments that assembles into pores at the plasma membrane (PM).3–6 These GSDM pores possess the ability to perforate both PM and mitochondrial membranes, triggering inflammatory cell death. Additionally, they facilitate the extracellular secretion of cellular elements such as inflammatory cytokines7 and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA),8 which are known to participate in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases. Among the GSDMs, GSDMD has been the subject of extensive research and was initially recognized as a pivotal mediator of inflammasome-triggered pyroptosis. Moreover, it is highly involved in multiple disease-associated inflammations. Upon activation of GSDMD, the linker region can be cleaved by caspase-1/11 (caspase-1/4/5 in human), allowing GSDMD-NT to separate from autoinhibitory structural domain, GSDMD-CT.9 GSDMD-NT forms transmembrane pores, releasing cytokines like interleukin (IL)-1β10 and IL-18,11 disrupting ion and water homeostasis,12 and thereby potentially exacerbating the progression of diverse inflammatory conditions.5
Table 1.
The GSDM family: expression, functions, and implications for disease
| GSDM family | Gene and chromosomal location | Aliases | Activating enzyme | Expression in cells/tissues | Biological function | Associated diseases | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSDMA |
Human: GSDMA (17q21.1) Mouse: Gsdma1–3 (11D) |
GSDM1, FKSG9 |
SpeB caspase-1 (non-mammals) |
Esophagus, prostate, bladder, skin, gastric epithelium, CD4 T | Tumor suppresser; pyroptosis | Systemic sclerosis, IBD, asthma, alopecia | 2,19,145,147,209 |
| GSDMB |
Human: GSDMB (17q21.1) Mouse: None |
GSDML, PP4052, or PRO2521 | Caspase-1, granzyme A | Digestive system, reproductive system, respiratory system, skin, bladder, spleen, NK cells, CD4 T, CD8 T | Tumor suppresser; pyroptosis | Breast cancer, asthma, IBD | 24,36,151,152,155,165–167 |
| GSDMC |
Human: GSDMC (8q24.21) Mouse: Gsdmc1-4 (15D1) |
MLZE | Caspase-8 | Esophagus, vagina, skin, spleen, trachea, small intestine, colon | Pyroptosis | Metastatic melanoma | 17,35,169,176,529 |
| GSDMD |
Human: GSDMD (8q24.3) Mouse: Gsdmd (15D3-E1) |
GSDMDC1, DFNA5L, or FKSG10 | Caspase-1/4/5/11, caspase-8, cathepsin G, neutrophil elastase | The vast majority of human organs and tissues, different types of leukocytes and T cells | Pyroptosis, NETosis, cytokines release | Sepsis, AD, AS, ARDS, IBD, EAE, FMF, HCC | 28,29,42,43,175,176,180,226,258,502 |
| GSDME |
Human: GSDME (7p15.3) Mouse: Gsdme (6B2.3) |
ICERE-1, DFNA5 |
granzyme B Caspase-1/3/7 (teleosts) |
Small intestine, cochlea, placenta, heart, brain, kidney | Pyroptosis, anti-tumor immunity, cytokines release | Deafness, cancer | 16,33,34,47,183–186 |
| DFNB59 |
Human: DFNB59 (2q31.2) Mouse: Dfnb59 (2C3) |
PJVK, GSDMF | Not known | inner ear, liver, intestine, lung, kidney, brain, testis, CD4 T, CD8 T | Not known | Deafness | 20,21,202,203 |
AD Alzheimer’s disease, ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome, AS atherosclerosis, EAE experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, FMF familial Mediterranean fever, HCC hepatocellular carcinoma, IBD inflammatory bowel disease
GSDMs are emerging as attractive checkpoints for immune response, inflammation, cancer, and autoimmune disorders, in addition to their involvement in a multitude of systemic conditions.3,13,14 In recent years, significant strides have been taken in the development of small molecule inhibitors targeting GSDMD. Several GSDMD inhibitors alleviated pathology in preclinical disease models.5 The encouraging results have accelerated the pace of developing GSDMD inhibitors, progressing from preclinical studies to human trials. Consequently, it is both crucial and opportune to examine the functions and mechanisms of novel GSDMs in a spectrum of illnesses and their potential clinical applications. Understanding which GSDMD inhibitors should be prioritized in trials for specific disease indications is becoming particularly urgent.
In the present review, we compile the interplay between GSDMs and pyroptosis, delineate the pyroptosis-independent functions of GSDMs, elucidate the mechanism underlying pore formation by GSDMs, and explore their significance in human health and the pathogenesis of diseases. We also discuss the disease areas where GSDMD inhibitors can be preferentially applied and the advantages and disadvantages of inhibiting GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis.
Research history and milestone events in gasdermins
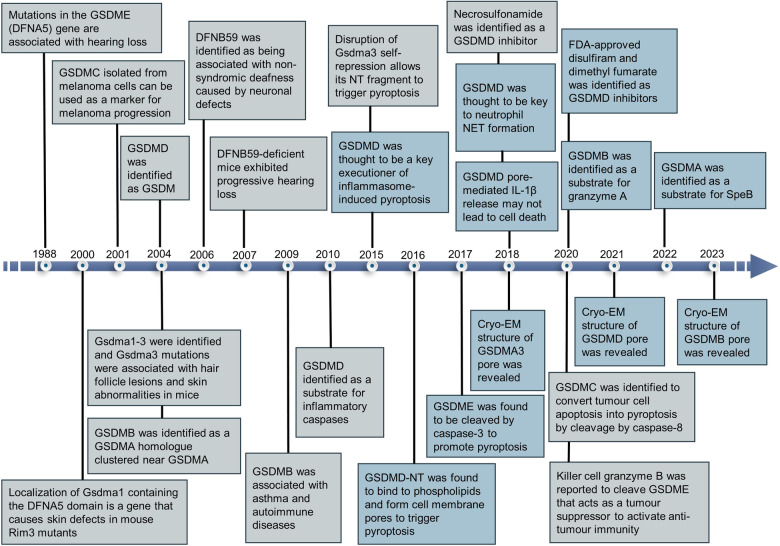
GSDMs represent a gene family with a conserved structural motif. Initial insights into GSDMs emerged in the early 2000s (Fig. 1).15 Saeki and colleagues cloned the mouse gene, GSDM, which bore the signature of the deafness autosomal dominant non-syndromic sensorineural 5 (DFNA5) gene.15 The term GSDM is derived from its selective expression in the mouse gastrointestinal tract and epithelial layers of the skin, an essential step in pinpointing the gene responsible for the Rim3 mutation in mice. The NT region of GSDM exhibited robust sequence similarity to DFNA5. In 1998, Laver et al. revealed an association between DFNA5 gene mutation and non-syndromic hearing loss.16 Following this discovery, the GSDM family expanded to include additional members, alongside proteins exhibiting GSDM-like characteristics.
Fig. 1.
Highlights in the evolution of gasdermins development. Blue boxes denote seminal breakthroughs in gasdermin research
In 2001, researchers isolated GSDMC (also known as MLZE) for the first time from mouse melanoma cells and observed that as the metastatic ability of the tumor increased, the expression of GSDMC rose accordingly,17 a finding that provided insights into the genetic variation underlying the progression of melanoma. Subsequently, in 2004, researchers discovered the Gsdma1–3 genes18 and noted that mutations in Gsdma3 were strongly linked to hair follicle disease and cutaneous anomalies in mice.19 In the same year, GSDMB was identified as a neighboring homolog of GSDMA, while GSDMD was characterized as part of the GSDM family.18 By 2006, the DFNB59 gene was found to be associated with hereditary deafness, and mutations in it may lead to non-syndromic hearing loss.20 In animal models, mice lacking DFNB59 developed progressive hearing loss,21 and analyses of the human genome similarly suggested that mutations in DFNB59 may cause non-syndromic deafness in humans.22,23 In 2009, two genomic studies revealed a link between variants within GSDMB and susceptibility to asthma and autoimmune disorders.24,25 Following this, Agard et al. in 2010 further elucidated the substrates of inflammatory caspases, stating that GSDMD is the most efficient and specific substrate for caspases under inflammatory conditions.26 The terminology of “pyroptosis” was first posited in 2001 to denominate a distinct mode of PCD that is reliant on inflammatory caspase-1. This process is distinctively typified by the induction of pore formation in the cell membrane, subsequent rupture, cellular swelling, and the dispersal of intracellular contents. The contents released during pyroptotic cell demise potentiated the inflammatory response and orchestrated an immune system activation.27 However, the role of GSDMs in pyroptosis remained unresolved.
It was not until 2015 that the relationship between GSDMs, inflammation, and cell death began to become clearer. Three independent studies uncovered the pore-forming capacity of GSDMD, portraying it as a major executor of pyroptosis and fostering inflammatory responses.7,28,29 Moreover, Shi et al. further demonstrated that other proteins within the GSDM family also possess pyroptosis-inducing activity in their conserved NT domains.28 For example, gain-of-function mutation in Gsdma3 lifts self-repression, enabling the NT domain to activate pyroptosis. Subsequently, several investigations in 2016 further revealed that the NT domains of GSDMD are able to create pores by forming oligomers in PM, thereby initiating the process of pyroptosis.9,30–32 As research progressed, GSDME,33,34 GSDMC,35 GSDMB,36–38 and GSDMA39,40 were also found to mediate cell pyroptosis. In 2017, Wang et al. uncovered a novel function for GSDME in the process of pyroptosis. They found that GSDME could transform the caspase-3-mediated apoptotic pathway triggered by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or chemotherapy agents into a pyroptotic pathway.33 Caspase-3 was able to specifically target GSDME for cleavage by cleaving Asp270 in the linker, generating GSDME-NT that forms pores in PM, which triggers pyroptosis.33,34 To delve into the mechanisms underlying GSDM pore formation, Ruan and colleagues conducted cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analyses of mouse GSDMA3-NT pores in 2018.41 The GSDMA3 pore has a 27-fold symmetry and is structured as an intact antiparallel β-barrel consisting of 108 strands of β-strands. Charles L. Evavold et al. discovered that GSDMD can independently facilitate the release of IL-1β without causing cell lysis, implying the presence of a repair mechanism specific to the GSDMD pore. Judy Liberman and Hao Wu’s team hypothesized that the double-ring pore structure formed by GSDMA3 may be associated with pore repair.10 In the same year, the findings of Sollberger and colleagues, as well as Chen and team revealed the function of GSDMD in regulating neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation,42,43 which led to the realization that GSDMD appears to be a more sophisticated modulator of the inflammatory process than had been anticipated. Following this, researchers identified inhibitors of GSDMD, such as necrosulfonamide (NSA),44 as well as existing FDA-approved drugs such as disulfiram (DSF)45 and dimethyl fumarate (DMF).46 The therapeutic efficacy of these compounds in the context of inflammatory disorders has been persuasively demonstrated. In 2020, research highlighted the role of GSDME as a tumor suppressor, which augments anti-tumor immunity through the induction of pyroptosis.47 The role of GSDMC in tumors was also reported. GSDMC was specifically cleaved by caspase-8 to produce GSDMC-NT, which formed pores in PM and converted apoptosis to pyroptosis.35 Meanwhile, GSDME47 and GSDMB36 were identified as substrates for granzyme B and granzyme A, respectively. As of 2022, researchers have revealed the mechanism of GSDMA activation.39,40 It was shown that the SpeB protease of staphylococcal group A (GAS) could cleave at the Gln246 site of GSDMA, releasing the NT domains, which in turn initiate pyroptosis. Beyond their involvement in pyroptosis, GSDMs are also integral to the preservation of tissue homeostasis. For example, in the context of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Rana et al. found that GSDMB regulates the phosphorylation of local adhesion kinases, thereby contributing to epithelial maintenance and damage repair.48 In addition, Zhang et al. reported that GSDMD promoted mucin secretion from goblet cells in the colon, which was essential for maintaining intestinal mucosal homeostasis.49 In 2023, Zhong et al. determined the cryo-EM structure of the 27-fold-symmetric GSDMB pore, revealing that its internal and external pore diameters are ~160 and 270 Å, respectively.38 The GSDMB pore, reminiscent of the architectures observed in GSDMA341 and GSDMD,50 is composed of a coronal ring in addition to a transmembrane β-barrel ring. It is worth pointing out that the cleavage products of GSDMs do not always result in cell death. Specifically, NT domains of GSDMB isoforms 3 and 4 are able to cause pyroptosis, whereas isoforms 1, 2, and 5 are not,37 suggesting that cells may inhibit and evade pyroptosis by generating noncytotoxic isoforms of GSDMB. Ongoing studies of the GSDM family have delved into the mechanisms of PCD and inflammation, highlighting the necessity for comprehensive inquiries into the roles and operational mechanisms of these molecules in both health and disease states.
Mechanisms linking the versatile gasdermins in pyroptosis
Recent investigations have elucidated a pivotal role for GSDMs in managing the intricacies of cell death orchestration, in particular, their remarkable property of regulating pyroptosis through the formation of GSDM pores. It is currently known that in addition to DFNB59, the remaining proteins share similar structures, featuring an NT pore-forming domain and a CT regulatory domain. The NT domains of GSDMA-E are able to penetrate the lipid bilayers and form pores,28,29,33,35,36,39,40 whereas DNFB59 no longer possesses this pore-forming ability, yet it remains responsive to inflammatory and infectious triggers, retaining its activity.51 Moreover, the formation of GSDM pores is intricately linked to a suite of processes, including NETosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and apoptosis. GSDMD cleaved by caspase-11 or neutrophil elastase (NE) is involved in neutrophil NETosis,42,43,52,53 while cathepsin G can also cleave GSDMD, albeit without triggering cell death, instead fostering neutrophil inflammatory responses.53 The activation of GSDMA,54 GSDMD,55,56 and GSDME57 regulates mitochondrial oxidative stress, elucidating their participation in mitophagy. Furthermore, the processing of GSDME by caspase-3 gives rise to the initiation of secondary necrosis in cells undergoing apoptosis.34 The NT domains of GSDMD initiates the liberation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS), triggering pyroptosis through the NLRP3/GSDMD axis or necroptosis along the mixed-lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase (MLKL) pathway.58 Additionally, NT domains of GSDMD and GSDME direct targeting to mitochondria, which aids in the facilitation of the release of cytochrome c, thereby activating caspase-3-mediated apoptosis.59
Overview of pyroptosis
Pyroptosis represents a newly discovered PCD that is critically dependent on PM pores formed by the GSDM family, frequently, although not invariably, following the activation of inflammatory caspases.60,61 The development history of pyroptosis is described in detail by ref. 6 Pyroptosis manifests as a sustained cellular expansion that ultimately culminates in membrane rupture, thereby releasing intracellular contents and eliciting robust inflammatory responses, and is involved in many pathophysiological processes. Specific inflammasomes and inflammatory caspases are triggered by different signals, and caspases execute their function by excising the connecting segment of GSDMs, which disengages the NT and CT domains. This dissociation allows for the modulation of the pore-forming activity of the NT domain that is suppressed by the CT domain at a steady state. In response, the lipophilic NT domain undergoes translocation to the PM, where it associates with acidic phospholipids, like phosphoinositides, within the cytosolic leaflets of PM. This interaction promotes oligomerization, culminating in the assembly of ring-shaped pores. Such GSDM-mediated pores allow the release of cellular contents and cause cell lysis as the pores continue to accumulate. Initially, the researchers reported two pyroptosis pathways: the canonical pathway, which is caspase-1 dependent, and the non-canonical pathway, activated through caspase-4/5/11. With the continued study of GSDMs, two additional pyroptosis pathways, involving the apoptotic caspases and the granzymes, were revealed. Here we focus on the first two pathways, and the latter two can be found in the “Gasdermins and pyroptosis” section.
Canonical pathway
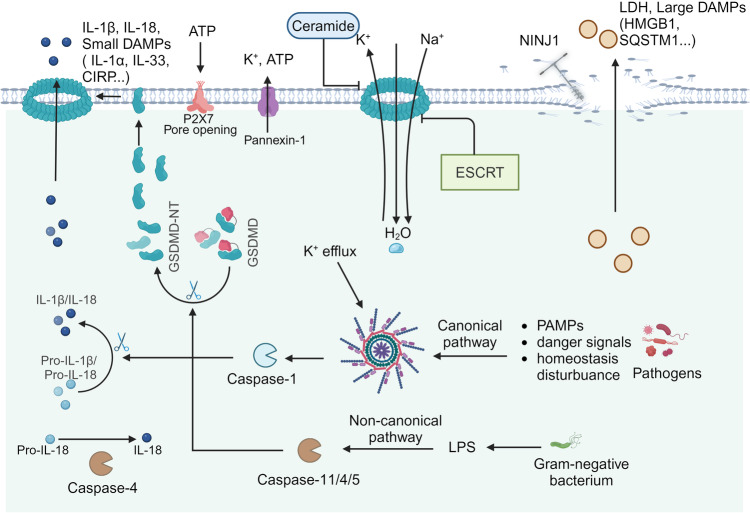
The canonical pyroptosis pathway is triggered by the assembly of the inflammasome, which activates caspase-1. This activation is then propagated through the cleavage of GSDMD, culminating in the release of IL-1β and IL-18 and triggering various physiological responses (Fig. 2).6,62–65 Inflammasomes represent multiprotein complexes activated to protect host cells from certain pathogens and endogenous danger signals (Fig. 3).66–69 The assembly of canonical inflammasomes begins with cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognize pathogen-associated and damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs and DAMPs).70 Activated PRRs promote downstream type I interferon (IFN) production and pro-inflammatory cytokines release.71–74 Upon activation of host cells by bacteria or viruses, and so forth, PRRs such as nod-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), NLR family caspase activation and recruitment structural domain (CARD) containing 4 (NLRC4), NLR family pyrin structural domain containing 1 (NLRP1), Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2), and pyrin, associate with pro-caspase-1 and adapter protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC) to establish the canonical inflammasomes.70,73–77 Subsequently, mature caspase-1 is produced, distinct from the non-canonical pathway.28,78 Upon activation, caspase-1 performs a proteolytic conversion of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 to their mature forms, IL-1β and IL-18, respectively. Complete GSDMD is also rapidly cleaved into two parts, GSDMD-NT and GSDMD-CT, in order to relieve the inhibitory constraint exerted by GSDMD-CT upon GSDMD-NT.7,28,29 GSDMD-NT promotes oligomerization in PM to form pores, triggering cell swelling and subsequent membrane rupture, which exposes the cellular contents and intensifies the inflammatory response.3,30,79,80
Fig. 2.
GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis and rupture of the plasma membrane. DAMPs and PAMPs stimulate inflammasome assemblies formation and caspase-1 activation in the canonical pyroptosis pathway, as well as caspase-11 activation (human caspase-4/5) in the non-canonical pyroptosis pathway. Upon activation, caspase-1/11/4/5 cleaves GSDMD to produce GSDMD-NT. Simultaneously, caspase-1 matures pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18. Moreover, caspase-4 non-canonical inflammasome also matures IL-18. GSDMD-NT assembles into oligomeric pores on the plasma membrane, mediating the release of small molecules such as IL-1β/IL-18, and K+ efflux facilitates NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. Water permeates pyroptotic cells, leading to swelling and NINJ1-dependent PMR. Concurrently, the discharge of large intracellular molecules, including LDH and DAMPs such as HMGB1, is observed. Moreover, the activation of caspase-11 results in the cleavage of Pannexin-1, which in turn facilitates ATP release and orchestrates P2X7-associated cell death. Two mechanisms can repair membrane damage induced by the GSDMD pore: endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT); and ceramide for endocytic repair of the GSDMD pores
Fig. 3.
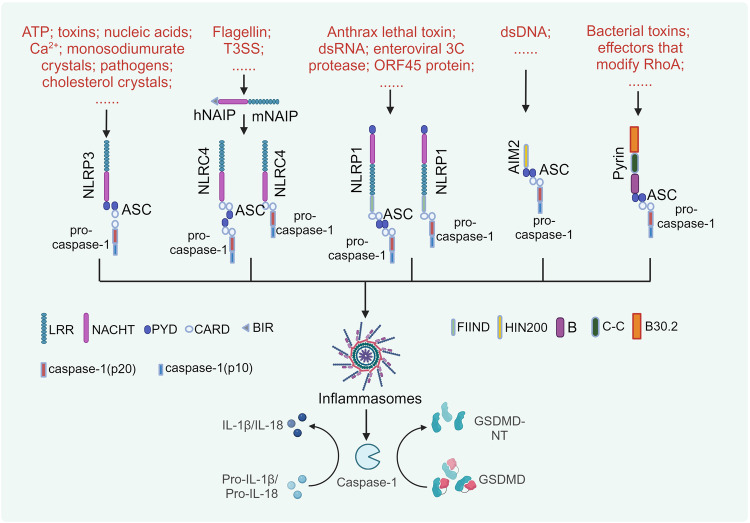
The activation mechanisms of canonical inflammasomes. The convergence of canonical inflammasome components is a crucial step in triggering pyroptosis. A diverse array of PAMPs and DAMPs, such as toxins and nucleic acids, serves as a trigger for NLRP3 inflammasome priming, leading to the recruitment of ASC and pro-caspase-1. The T3SS initiates NLRC4 inflammasome activation via NAIP, and NLRC4 mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by engaging ASC or through direct CARD-CARD domain interactions, which promotes the recruitment of pro-caspase-1 into the assembly complex. Anthrax lethal toxin stimulates the NLRP1 inflammasome, resulting in the activation of pro-caspase-1, which can occur either contingently or independently of ASC recruitment. The AIM2 inflammasome assembles upon detection of dsDNA from host or pathogenic sources. Pyrin inflammasome activation occurs due to bacterial toxins and RhoA-modifying proteins. Both AIM2 and Pyrin engage ASC-mediated signaling to orchestrate the activation of pro-caspase-1. Upon activation, caspase-1 executes its function by cleaving GSDMD and pro-IL-1β/pro-IL-18, thereby facilitating the release of these cytokines via a channel formed by GSDMD-NT
Exposure of inflammasomes to diverse stimuli initiates pyroptosis (Fig. 3). Distinct from other canonical inflammasomes, NLRP3 does not seem to directly identify a particular PAMP or DAMP. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP),74,81 pore-forming toxins (such as nigericin and maitotoxin),82,83 certain exogenous and endogenous particles,84–86 pathogen-associated RNA,87–89 bacterial and fungal toxins and components,90,91 intracellular Ca2+,92–94 and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress95,96 can trigger NLRP3, resulting in a decrease in the intracellular concentration of K+ and the efflux of cytosolic lysates from lysosomes, which in turn trigger mitochondrial dysfunction. The upstream immunosensor proteins for NLRC4 inflammasome activation are NLR family apoptosis inhibitory proteins (NAIPs).97 Investigations to date have revealed that the mouse genome harbors seven distinct NAIPs, whereas the human genome exhibits a singular NAIP gene.98,99 NLRC4 induces pyroptosis independently, dispensing with the requirement for the adapter protein ASC. Nonetheless, the engagement of ASC markedly enhances the propensity for NLRC4-induced pyroptosis.100,101 Bacterial flagellin,102 S. Typhimurium PrgJ, and B. pseudomallei BsaK103 can trigger NLRC4 activation, which are constituent proteins within the type III secretion system (T3SS). The precise mechanism underpinning NLRP1 activation remains elusive, with insights primarily derived from mouse studies.6,104 In contrast to humans that have only one NLRP1 gene, mice express multiple NLRP1 alleles, with NLRP1B being the main subject of study.104 NLRP1 is capable of being triggered by anthrax lethal toxin (LeTx),105,106 dsRNA,107 enteroviral 3C protease,108 ORF45 protein,109 dsDNA mimetic poly (dA:dT),110 ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation and the toxin-induced ribotoxic stress response (RSR).111 Interestingly, the initiation of NLRP1 is highly reliant on the activity of the proteasome, implicating proteolytic degradation as a pivotal process in NLRP1 activation.106,112,113 This is because NLRP1 cleavage releases the carboxyl-terminal effector domain from the inhibition of the amino-terminal effector domain, thereby triggering the formation of ASC specks and the activation of caspase-1.114–117 Self-cleavage of NLRP1 is an indispensable, albeit not standalone, requirement for the activation of NLRP1. The AIM2 inflammasome represents a distinct cytosolic innate immune sensor, variance from the NLR inflammasome, with its activation being predominantly mediated through the HIN200 domain, in response to damaged DNA, endogenous DNA aberrantly present within the cytosolic compartment, and exogenous DNA accumulated in the cytoplasm by intracellular pathogens.118–121 AIM2 does not contain a CARD domain, and thus its activation requires the assistance of ASC.118 Mefv-encoded pyrin functions as a phagocytic inflammasome sensor, responsive to the activation by bacterial toxins that manipulate RhoA. Like AIM2, pyrin plays a pivotal role in triggering inflammasome assembly through binding of the pyrin domain (PYD) to ASC.122–124 Furthermore, beyond the NLRP1 inflammasome, other complexes can participate in the canonical pyroptosis pathway, but do not independently mediate this process. The latest study has identified a pivotal function of NLRP11 in canonical pyroptosis of human macrophages.125 Gangopadhyay et al. found that NLRP11 engaged in a cooperative assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome, with the absence of NLRP11 hindering the initiation of pyroptosis. Notably, the expression of NLRP11 is exclusive to humans, highlighting the distinctive intricacies of human inflammasome regulation.
Non-canonical pathway
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a prototypical PAMP, serves as an effective mediator in the progression of sepsis, which continues to be the principal cause of mortality. Intracellular LPS induces the activation of caspase-11/4/5 by directly binding to the NT CARD of these caspases (Fig. 2).126–130 Upon activation, caspase-11/4/5 cleaves GSDMD, resulting in the production of the GSDMD-NT, thereby forming pores in PM and directly promoting pyroptosis.127,128 Notably, this process can be activated secondarily by the release of IL-1β and IL-18 from NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis, termed non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation.29,131–133 Initially, caspase-11/4/5 lacked the capability to cleave the precursor forms of IL-1β/IL-18127,128; however, recently, Shi et al. demonstrated that caspase-4/5 activated by LPS were capable of cleaving pro-IL-18 at a tetrapeptide cleavage site that coincides with the target site of caspase-1.134 The presence of a cytosolic LPS-specific PPR has emerged only recently. In human macrophages, the process of LPS-activated caspase-4 is dependent on NLRP11, an adapter protein that binds to LPS and caspase-4, thereby facilitating the assembly of a multiprotein complex.135 In addition, Furthermore, NLRP11 plays a role in NLRP3 inflammasome assembly,125 highlighting the intricate mechanisms by which human immune cells modulate the pyroptosis process.
Pannexin-1 stands as a pivotal protein in mediating macrophage death via a caspase-11-dependent non-canonical pathway.136 Cytosolic LPS triggers cleavage of pannexin-1 channels by caspase-11, leading to the subsequent release of ATP, which activates purinergic receptor P2X7 to facilitate the manifestation of cytolytic activity.136 This sequence of events leads to the efflux of intracellular K+, the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and the secretion of IL-1β. Significantly, pannexin-1 modulates the canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome independently of P2X7 via inducing K+ efflux.6,136,137 These observations imply that NLRP3 inflammasome could serve as a pivotal linkage between canonical and non-canonical pyroptosis pathways.
Beyond LPS, evidence exists for the activation of caspase-11 by various additional molecular triggers. Oxidized phospholipid 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine (oxPAPC) specifically promotes pro-inflammatory responses mediated by caspase-11 in dendritic cells (DCs).138,139 However, oxPAPC only triggers the release of IL-1β, leaving the cells in a hyperactivated state without cell death.138,139 The presence of lipophosphoglycan by Leishmania activates caspase-11 in macrophages, which in turn activates NLRP3 and caspase-1.140 Furthermore, secreted aspartyl proteinases (Sap)2 and Sap6 of Candida albicans were previously reported to also activate caspase-11,141,142 but current evidence indicates that this is mediated through the production of type I IFN which modulate caspase-11 expression, as opposed to a direct triggering of caspase-11 activation.141,142
Gasdermins and pyroptosis
Members of the GSDM family display distinct patterns of tissue expression (Table 1). At different body sites, these members show differences in their respective abundance in sensing, recognizing, and defending against infections, especially in specific mucosal tissues.4,15 For example, GSDMA is active mainly in the skin, digestive and urinary systems; GSDMB is predominant in the skin, digestive and respiratory systems, and within immune cell populations; GSDMC exhibits mainly distribution across the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and vaginal epithelium; GSDMD demonstrates a broad distribution across most organs and immune cells; whereas GSDME is primarily localized to the central nervous system (CNS), placenta, heart, and small intestine. In addition, DFNB59 functions mainly in the inner ear and gastrointestinal tract. This variability in expression is closely related to the roles played by the GSDM family in various diseases. For example, GSDMB may be implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma,143 loss of DFNB59 function may lead to hearing loss,16 and widely expressed GSDMD is potentially implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases across multiple organs and systems.1,5,144
Gasdermin A
GSDMA stands as the initial characterized member within the GSDM gene family, mapping to chromosome 17 at location 17q21.1. This gene is associated with defective skin and hair development in mice carrying the Rim3 mutation.97,145 Subsequent studies have revealed that mice with similar skin phenotypes possess three GSDMA homologs (Gsdma1–3), which preferentially specify expression within skin and epithelial tissues, including the epidermis, hair follicles, and gastric epithelium.19,97,146,147 The majority of mutant phenotypes in these mice are attributed to Gsdma3, with mutations in this gene causing intense skin inflammation and alopecia,147 and all of these mutations are localized to Gsdma3-CT, which exhibits gain-of-function mutations, revealing a role for functional NT domain in pyroptosis.32 Researchers elucidated the crystal structure of GSMDA3 pores in 2018, providing key insights into GSDM pore formation.41 GSDMA expression in humans is mainly restricted to esophageal, bladder, and skin epithelial cells, but is frequently extinguished in gastric cancer, implying that DNA methylation may contribute to the suppression of GSDMA transcription.148
GSDMA is associated with autophagy and pyroptosis. Mutations conferring gain-of-function lead to mitochondrial stress and increased ROS, and the NT domain exhibits pro-autophagic activity that induces an increase in LC3-II.149 Distinct from other GSDM family members, the proteases responsible for activating GSDMA-mediated pyroptosis have only recently been characterized, unveiling their important implications in host immune responses.39,40 Group A streptococcus (GAS), represents a pivotal skin pathogen responsible for a substantial burden of morbidity and mortality globally.40 Upon invasion by the GAS pathogen, SpeB undergoes autocatalytic cleavage to generate an active protease that directly proteolytically targets and cleaves GSDMA at the Gln246 site (Fig. 4),39,40 releasing an activated NT domain that promotes pyroptotic cell death in compromised cells. This process results in the initiation of local inflammatory responses and the subsequent eradication of pathogens, highlighting the critical role of GSDMA in host immunity. The absence of Gsdma1 or mutations/suppression of SpeB impedes the activation of GSDMA, triggering a localized immune response that propagates systemically, culminating in multi-organ infections. Investigation into the potential for GSDMA to exert a comparable function in diverse inflammatory disorders would be inquiries worth pursuing. Interestingly, in non-mammals, such as birds, amphibians, and reptiles, GSDMA undergoes cleavage by caspase-1. Consistent with the caspase-1-mediated cleavage of GSDMD in mammals, the tetrapeptide sequence within GSDMA is essential for its processing by caspase-1.150 This has led to a renewed understanding of the precision and complexity of the regulation of the immune system by GSDMs from an evolutionary perspective.
Fig. 4.
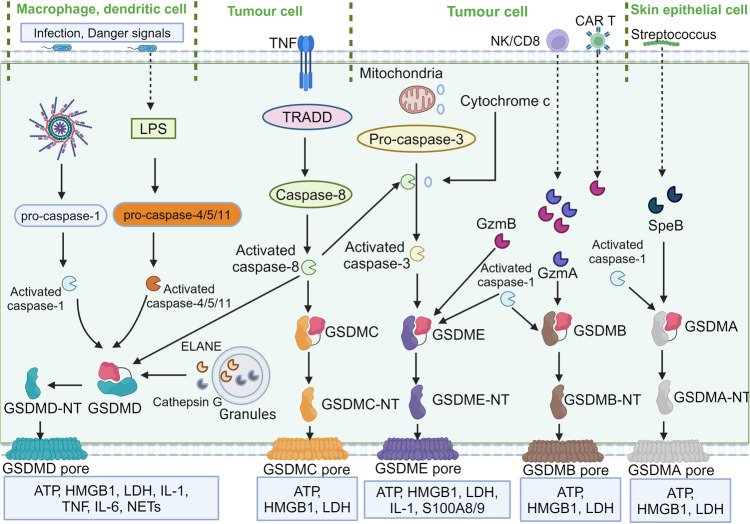
Molecular mechanisms of gasdermins activation. In response to microbial invasion, canonical inflammasomes and in response to LPS, non-canonical inflammasomes, respectively, trigger the activation of inflammatory caspases—caspase-1, -4, -5, and -11, resulting in GSDMD cleavage and generation of GSDMD-NT, followed by the formation of GSDMD pores. GSDMD is also processed by NE and cathepsin G released from neutrophil granules. Yersinia infection initiates caspase-8 to cleave GSDMD. Additionally, the degradation of GSDMC and GSDME is achieved through the action of caspase-8 and caspase-3, respectively, contributing to the transition from apoptotic to pyroptotic cell death. Caspase-8 and cytochrome c are involved in caspase-3 activation. Killer cells secret GzmA and GzmB, which directly cleave GSDMB and GSDME, respectively, to provoke pyroptosis. Secreted by group A Streptococcus, SpeB functions as a cysteine protease that specifically targets GSDMA, thereby initiating the pathological cascade leading to pyroptosis. Caspase-1 can also cleave GSDMB, GSDMA, and GSDME
Gasdermin B
GSDMB, similar to GSDMA, also maps at 17q21.1, but GSDMB has not been identified in rodents.143 Compared to GSDMA, GSDMB exhibits a more extensive expression profile, primarily in airway and gastrointestinal epithelium, esophagus, stomach, liver, small intestine, and immune cells,151–154 but the question of whether these isoforms exhibit tissue- or cell-specific expression patterns remains unresolved. There is a significant correlation between polymorphisms in GSDMB and the propensity to develop chronic inflammatory disorders such as IBD, type I diabetes, and asthma.24,151,155,156
GSDMB enhances caspase-4 activity during non-canonical pyroptosis,156 indicating its potential role in inflammation. Previous evidence suggests that GSDMB could not be cleaved by inflammatory caspases but by apoptotic caspase-3/6/7, and the cleaved NT product may not contain an intact NT domain for pore formation or direct involvement in inflammation.157 In a study published recently, it has been demonstrated that during the process of apoptosis, activated caspase-7 is capable of cleaving the GSDMB protein at residue D91. The cleaved GSDMB fragment (92–417 aa) effectively inhibits the binding of the GSDMB fragment (1–91 aa) to caspase-4, thus preventing non-canonical pyroptosis.158 However, recent studies have presented a different view. In airway epithelial cells, GSDMB is susceptible to cleavage by inflammatory caspase-1, which liberates NT domains capable of triggering pyroptosis159 (Fig. 4). Granzyme A, exuded by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, initiates the cleavage and activation of GSDMB, leading to pyroptotic cell death in tumor cells.36 This suggests additional evidence for its direct involvement in pyroptosis. However, Hansen et al. proposed a mechanism by which the enteropathogen Shigella flexneri secretes IpaH7.8, which is capable of ubiquitinating GSDMB and facilitating its degradation through the 26S proteasome pathway.160 Yin and colleagues delve into the interplay between IpaH7.8 and GSDMB, elucidating the molecular mechanisms underpinning GSDMB ubiquitination and its subsequent inhibition by IpaH7.8.161 This strategy counters the cytolytic effects of granzyme A on GSDMB to offer a protective buffer against bacterial elimination, and instead asserts a microbicidal role by targeting phospholipids on the bacterial plasma membrane. Remarkably, IpaH7.8 is also able to ubiquitinate the human GSDMD protein (but not the mouse) and direct its degradation via the proteasome pathway.162 This property may reveal why Shigella is able to trigger hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in primates but does not show similar symptoms in rodents. In recent times, the structure of the GSDMB-IpaH7.8 complex has been elucidated through the combined efforts of ref. 163 and ref. 38 employing cryo-EM and X-ray crystallography, respectively. This advance may provide insights into the questions posed above. The revealed structure features a complete GSDMB in an autoinhibited conformation, in conjunction with an IpaH7.8 leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain that interacts with the GSDMB-NT. Notably, the IpaH7.8 LRR domain exhibits a specific recognition of an acidic motif within the α1 helix in the C terminus of GSDMB-NT, which includes residues E15, D17, and D21, acting as key structural determinants.
The GSDMB gene in humans gives rise to a family of at least six splice isoforms, each featuring a unique structural blueprint. Isoform 5 is characterized by the presence of the CT domain only, whereas isoforms 1-4 and 6 possess both the NT and CT domains that are conserved across the family. The linker sequences bridging these domains exhibit heterogeneity in length and amino acid composition among the various isoforms. Isoforms 4 and 6, by integrating a consensus sequence derived from exon 6 into their interdomain linkers, demonstrate strong pyroptosis-inducing capabilities. Conversely, isoforms 1, 2, and 3 lack the ability to trigger cell death.163 However, two other studies point out that GSDMB3, like GSDMB4, also has pro-pyroptosis activity, as GSDMB3 also has a stable band motif encoded by exon 6.37,164 These research discrepancies warrant further investigation. However, these findings hold significant value in elucidating the intricate roles of GSDMB isoforms in disease pathogenesis and in informing the future design of targeted GSDMB therapies.
Moreover, increased expression of GSDMB is observed in multiple cancers, spanning cervical, breast, gastrointestinal, and liver cancers, and its high expression is linked to an adverse prognosis,165–167 which may be related to the nuclear translocation and transcriptional regulatory functions of GSDMB,151 which may function independently of its role in pore induction. This phenomenon of acting independently of pyroptosis has also been validated in IBD. Epithelial-derived GSDMB preferentially populates genetic pathways linked to cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion, rather than pyroptosis, and can promote epithelial recovery and mucosal wound healing.48 The differential engagement of GSDMB in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), mediating both pyroptosis and pro-restitution, epitomizes the intricate functional repertoire of a solitary protein within a discrete cellular context. Elucidating the underlying mechanisms of this multifaceted activity presents a compelling target for further investigation.
Gasdermin C
GSDMC, mapping on chromosome 8 (8q24.21), is initially detected in metastatic mouse melanoma cells, functioning as a biomarker indicative of melanoma progression.17,18 There are four Gsdmc homologs (Gsdmc1-4) in the mouse genome.2 GSDMC is expressed within various tissues, including the trachea, small intestine, colon, esophagus, skin, spleen, and vagina.13,14 Downregulation of GSDMC has been shown to inhibit the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells, suggesting a potential role in gastrointestinal cancers.168 In contrast, a separate study revealed that GSDMC was repressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas, suggesting that it may play a tumor-suppressive role.153 Synthetic truncations of GSDMC-NT have been demonstrated to provoke pyroptosis,32 as well as intracellularly GSDMC is cleaved by caspase-8 to generate the GSDMC-NT fragment that induces pyroptosis (Fig. 4).35,169 Hou et al. have uncovered that in breast cancer cells, GSDMC has the capacity to transform apoptosis into pyroptosis, a process that is promotive for tumor necrosis.35 In an oxygen-deprived environment, the p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interacts with PD-L1, culminating in its nuclear translocation and enhancement of GSDMC transcription. As GSDMC expression rose, TNF promotes cleavage of GSDMC by caspase-8, generating GSDMC-NT that facilitates pyroptosis. In addition, the cellular metabolite α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) orchestrates the assembly of the DR6 receptosome in tumor cells, creating a molecular platform that enables efficient proteolysis of GSDMC by activated caspase-8, thereby triggering pyroptosis.169 These findings not only deepen our comprehension of the mechanisms underlying cell death and provide possible potential novel therapeutic tactics for cancer therapeutics.
Moreover, GSDMC participates in type 2 immune responses, as demonstrated by the increased expression of Gsdmcs in an in vivo model of worm-elicited type 2 immunity. Moreover, the overexpression of Gsdmc2 in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells triggers pyroptosis.170 This pyroptotic mechanism could potentially facilitate the release of antiparasitic factors by IECs, aiding in the elimination of worms. This is consistent with the role of the GSDM family as executors of pyroptosis. However, Zhao et al. offered a contrasting perspective, suggesting that although GSDMC gene expression was highly increased in IECs following worm infection, it primarily functioned through a pyroptosis-independent pathway.171 They proposed that STAT6 O-GlcNAcylation regulated membrane pore formation by GSDMC-NT in IECs, which promoted IL-33 unconventional secretion as an alarm response, thereby potentiating the development of type 2 immunity. Notably, this pore-forming but non-lytic feature is different from the non-pore-forming feature of GSDMB found by ref. 48 The proteases that cleave GSDMC and the mechanism prevents intestinal pyroptosis following the formation of GSDMC-NT pores remain to be determined.
Gasdermin D
GSDMD stands out as the most extensively studied member within the GSDM family, being located on chromosome 8 at region 8q24.3.9,172 This protein exhibits broad tissue and immune cell distribution.153,173 GSDMD comprises a 31 kD NT pore-forming domain and a 22 kD CT suppression domain.9,172 An interdomain linker harbors a cleavage site, which is identified as D276 in murine GSDMD and D275 in human GSDMD. Upon activation, this linker is severed, resulting in the dissociation of the GSDMD-NT from the GSDMD-CT.77 Upon release, GSDMD-NT is inserted into the PM and oligomerizes, leading to pore formation, cytokines release, and interference with ion and water regulation.10–12,174 The intact GSDMD protein exhibits an inactive state, which is a consequence of its CT domain interfering with the interaction with its NT domain. However, GSDMD-NT exhibits high toxicity towards bacteria, indicating a potential direct engagement with cell membranes and subsequent lysis.32 This prediction is corroborated by the observation that GSDMD-NT binds with high affinity and specificity to phosphoinositides and cardiolipin, as well as forms extensive pores.9,30–32 Most of the pores feature an inner diameter within the range of 10–14 nm and are composed of roughly 16 symmetrical protomers.32 In contrast to characterized pore-forming proteins, GSDMD is uniquely positioned to induce cell lysis starting from the intracellular compartment of mammalian cells, a property that is linked to the asymmetric distribution of phosphoinositides within the PM.30,32
GSDMD is subject to proteolytic cleavage and subsequent activation by different molecules (Fig. 4). Inflammasome-mediated activation of caspase-1 through diverse canonical pathways, and LPS-mediated caspase-11/4/5 activation result in intense cleavage of GSDMD.63 Under suitable conditions, activated caspase-8 also cleaves GSDMD, a process that can occur in Yersinia spp. infection,175–177 in which the activities of TGFβ-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and IκB kinase (IKK) are blocked. Furthermore, GSDMD can be cleaved by caspase-3. In contrast to the caspases described above, activated caspase-3 targets GSDMD at its NT domain, thereby preventing the assembly of functional GSDMD-NT pores.178 Among these caspases, caspase-1 stands out as the most effective catalyst for GSDMD cleavage, with caspase-8 demonstrating the least impact, possibly functioning as a contingency mechanism when other caspases are compromised.179 Finally, beyond these caspases mentioned above, neutrophils engage in the cleavage and activation of GSDMD through neutrophil elastase (NE) and cathepsin G. Cytosolic protease inhibitors, such as Serpinb1a and Serpinb6a, usually modulate cathepsin G-mediated pro-inflammatory responses by exerting inhibitory control.42,43,53,180 Notably, mutations contribute to GSDMD activation, with alterations in three amino acids within the CT domain that interfaces with the NT domain (L292, Y376, and A380), leading to the autonomous activation of GSDMD and cell death in mice.181,182 The corresponding human amino acids (L290, Y373, and A377) yield similar findings.32
Progressive studies of GSDMD have revealed that its function is not limited to its association with the process of pyroptosis, but that it can also independently carry out various biological roles, such as promoting the unconventional release of cytokines and the formation of NETs. GSDMD has been linked to the development of numerous diseases, and several inhibitors targeting GSDMD have been characterized and shown therapeutic efficacy in disease models. These findings will be discussed in greater detail subsequently.
Gasdermin E
GSDME maps on chromosome 7 (7p15.3), and it is initially perceived to be associated with hereditary hearing loss, devoid of any involvement in inflammatory processes.16,183–185 GSDME mRNA is distributed within various tissues such as the cochlea, placenta, heart, brain, and kidney.16,186 As research advances, GSDME is identified as a regulator of both apoptosis and pyroptosis.33,34,187,188 This protein can be cleaved by caspase-3, with evidence suggesting it plays a role in the induction of secondary necrosis following apoptotic triggers.34,187,188 With the lack of GSDME, cells exhibit a propensity to fragment into minute apoptotic vesicles rather than undergoing complete lysis. Alternatively, GSDME can target the mitochondrial membrane, prompting the efflux of cytochrome c and contributing to the generation of apoptotic cells.59 The above occurs when GSDME is expressed at low levels. However, at high levels of GSDME expression, caspase-3 activation leads to the cleavage of the protein, resulting in cell membrane perforations, cell swelling, rupture, and death.189 One study reveals that in the absence or non-function of caspase-1, pyroptosis in cells can still be triggered, independent of GSDMD activation.190 It is possible that caspase-8 triggers this death by activating caspase-3, which subsequently cleaves GSDME.190,191 Furthermore, in neutrophils, serine protease PR3 released by granules can promote the processing of GSDME by cleaving caspase-3.192 More interestingly, GSDME can serve as a strategic node positioning upstream of caspase-3, bridging exogenous and endogenous apoptotic pathways. This positioning augments caspase-3 activation, establishing a self-amplifying positive feedback loop.189 Interestingly, in teleosts, GSDME is subject to cleavage by caspase-1/3/7,193 where caspase-1-GSDME-mediated pyroptosis is highly efficient, whereas caspase-3/7-GSDME is less efficient in shifting cell death from apoptosis to pyroptosis.
Beyond its cleavage by caspase-1/3/7, GSDME can be activated by granzyme B, a cytotoxic lymphocyte-derived protein that infiltrates tumor cells (Fig. 4).47 This activation results in GSDME cleavage and triggers pyroptosis within the tumor cells. Notably, given that mutations in GSDME can result in hearing loss, the majority of these mutations are associated with the loss of the inhibitory CT domain, potentially leading to the initiation of cell death.33,194 Mechanisms regulating GSDME transcription have been reported recently. For instance, Wei et al. found that oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) stimulates the expression of GSDME in macrophages, leading to pyroptosis. Under the context of atherosclerosis (AS), STAT3 binds to the GSDME promoter, potentiating GSDME transcription and subsequent enhancement of caspase-3 activity, as well as the cleavage of GSDME. Consequently, this promotes the conversion of macrophage apoptosis to pyroptosis.195 Moreover, Pan et al. found that the transcription factor specificity protein 1 (Sp1) is involved in promoting pyroptosis induced by GSDME. Sp1 directly interfaces with the GSDME promoter at the -36 to -28 region, thereby potentiating the transcription of the GSDME gene. The knockdown of Sp1 can reduce cell pyroptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs.196 GSDME also emerge as a potential tumor suppressor,197 serving as a transcriptional target of p53 that is frequently epigenetically silenced through methylation in various malignancies.198–200 The absence of GSDME has been shown to compromise the efficacy of certain chemotherapeutic agents.33,201
DFNB59
As previously mentioned, the majority of GSDMs display a consistent architectural pattern with the exception of DNFB59, which maps on chromosome 2 (2q31.2). This distant relative within the GSDM family exhibits a truncated and non-homologous CT domain, setting it apart from other GSDMs in terms of sequence homology.20,21,202 DNFB59 exhibits widespread expression, with transcripts detected in various organs, including the lung, kidney, brain, inner ear, liver, intestine, and testis.20,203 This protein serves as a peroxisome-associated protein, crucial for the augmented proliferation of peroxisomes under oxidative stress conditions in hair cells and auditory neurons.203 DNFB59 senses sound-induced ROS and activates autophagic mechanisms to degrade damaged peroxisomes.202 The precise nature of DNFB59 remains elusive; whether it acts as a pore-forming protein or is inherently active is yet to be conclusive, attributable to its truncated CT domain, which might insufficiently suppress pore formation. Further exploration deserves to determine whether DNFB59 induces pores in peroxisomal membranes and, subsequently, to investigate whether associating proteins modulate its function by either inhibition or activation.204
Since the uncovering of GSDMs as key executors of pyroptosis, numerous studies have reported evidence linking the activation of GSDMs to various pathological contexts, considering the multiple functions of pyroptosis under different diseases.13,14,63,205–208 Moreover, spontaneous mutations that trigger GSDM activation have been implicated in several disorders, including alopecia (GSDMA),19,147,209–211 asthma (GSDMB),151,155,212–214 and hearing loss (GSDME/DFNB59).16,20,183–185,215–219 Accumulating evidence indicates that GSDMs could potentially participate in the modulation of infection and cancer,35,36,42–47,180,220,221 suggesting an intricate relationship between GSDMs-orchestrated pyroptosis and their non-lytic processes48,52,222–226 in the etiology and progression of these conditions.
Gasdermin pore formation
Structural auto-inhibition in the full-length GSDMs
The latest findings reveal that GSDM-NT binds to phospholipids and triggers pyroptosis, which is not the case for full-length GSDM or GSDM-CT.30,32,227 Increased expression of GSDMD-CT effectively inhibited GSDMD-NT-induced pyroptosis under LPS stimulation.32 The crystal structure of GSDMs elucidates the mechanism of structural auto-inhibition: the CT domain of the full-length GSDMs folds onto the NT domain, preventing lipid interaction and subsequent pore assembly. The crystallographic datasets for mouse GSDMA3, human and mouse GSDMD, and human GSDMB proteins reveal that full-length GSDMs employ a mechanism of auto-inhibition facilitated by the intimate association of the CT domain with the NT domain. This interaction involves the α1 helix and β1–β2 hairpin of the NT domain engaging in extensive electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions with the CT domain, effectively preventing the activation of the GSDMs.38,41,50,227 The aromatic amino acids of the β1–β2 hairpin, Phe49, and Trp50 (Phe48 and Trp49 in mGSDMA3) are embedded into the hydrophobic pocket of the CT domain.227 Notably, GSDMA3 features an auxiliary contact surface that arises from the insertion of the α4 helix within the NT domain into a separate hydrophobic pocket of the CT domain.32,41 Unlike the GSDMD, the NT domain of GSDMB exhibits an elongated β-sheet structure containing ten antiparallel aligned β-strands (β1–β10) and is structurally ordered. α1 helices and their subsequent loops with neighboring β1/β2 hairpins constitute the main interaction interface with the GSDMB-CT domain.38,163 Mutational interference with the NT-CT domain interaction results in constitutive self-activation of the intact protein, implying the presence of a preserved mechanism for structural auto-inhibition within the GSDM family.
GSDMs found in fungi and bacteria (bGSDM) follow a similar strategy, leading to structural auto-inhibition. The short CT domain in fungi GSDMs interacts directly with the α1 helix and β1–β2 hairpin in the NT domain, and removal of the CT domain by caspases or protein hydrolysis leads to cytotoxicity exerted by the NT domain.228 Sequence analysis revealed the presence of 50 bGSDM homologs, distinct from eukaryotic homologs. Although the large α-helical CT domain required for structural auto-inhibition is lacking in Bradyrhizobium tropiciagri and Vitiosangium sp., they contain a structurally similar molecular substitute. The bGSDM caspase system is commonly present in bacteria and archaea, where bGSDM is cleaved by caspase-like proteases. It is worth noting that the pore structures formed by bGSDM are diverse and different in size from those of mammals, which may be products of specific internal substance releases. This reveals the functional conservation of GSDM in all life forms, from prokaryotes to eukaryotes.
Mechanism underlying the formation of GSDM pores
Cleavage by proteases facilitates the release of GSDM-NT, which subsequently translocates to PM and assembles into oligomeric pores. Electron microscopy has elucidated that the pore formed by GSDMD-NT has an inner diameter of ~12–20 nm, exhibits a symmetric subunit structure of approximately 16. Furthermore, GSDMD-NT pores isolated from liposomes are characterized by a molecular weight of approximately 24 kD.9,32 The use of cryo-EM and high-resolution atomic force microscopy (AFM) techniques further validate these data, revealing that the GSDMD-NT pore exhibits an average diameter of 20 nm with symmetry between 15 and 45.31,229 The diameter of the GSDMD-NT pore is appropriately sized to permit the transit of larger molecules, including IL-1 family cytokines and galectins.10,174,225,230–232 Further cryo-EM reveals that the macropore structure formed by human GSDMD-NT consists mainly of 33 (ranging from 31 to 34) subunits. These 33-fold macropores exhibited a full antiparallel β-barrel structure, which modestly exceeds the dimensions of the previously described 26–28-fold GSDMA3 pores and 26–30-fold GSDMB pores.38,41,50,163 Inserted into the membrane, the GSDMD-NT pore, the GSDMA3-NT pore, and the GSDMB-NT pore have a similar structure, all consisting of a coronary ring in conjunction with a transmembrane β-barrel ring. The NT domain is constructed like a left hand, in which the cytosolic globular structural domain serves as the palm, the α1 helix resembles the thumb, and the four protruding β-strands from the dual β-hairpins penetrated into the membrane constitute the fingers.38,41,50,163 The aggregation process of GSDM pores is mainly achieved by the interaction between cytosolic globular structural domains and transmembrane regions via a complex interplay of hydrophobic associations, electrostatic interactions, and hydrogen bonds, especially the α1 helices, which form a helical belt structure with head-to-tail linkages to stabilize the entire pore structure. This oligomerization pattern is retained in all GSDMs containing pore structures, including GSDMD, GSDMA3, and GSDMB.
Recent findings have documented that both GSDMD-NT and GSDMA3-NT can form not only ring-shaped pores in lipid bilayers and liposomes, but also smaller arc-shaped and slit-shaped pores.229,233 These pores composed of as few as two GSDMD-NT molecules are capable of admitting the passage of water and ions, and these assemblies also grow and fuse together.229,233,234 Smaller oligomers have the potential to organize into arc-shaped pores, potentially serving as conduits for the transit of small-molecule proteins across the PM. These arc-shaped channels are susceptible to adopt narrower slit-shaped channels due to the tension exerted by the external lipid bilayers, or they may continue to expand and fuse, eventually forming complete ring-shaped channels. This suggests that GSDMD pores are dynamic and non-homogeneous in structure, and that pore formation may occur along different pathways in parallel.
Previous studies of pore-forming GSDMs have revealed two stable ring-like oligomers that are not inserted into the membrane, termed “prepore”, and found in both GSDMD and GSDMA3.41,50,235–240 Comparison of the structures of GSDMD prepore and pore highlights conservation in diameter, with the precursor being approximately 40 Å shorter in height. This discrepancy is proposed to arise from a conformational change involving the globular domains, which undergo a rigid-body rotation relative to the membrane as the pore is formed.50 The globular domain within the prepore presents an autoinhibited configuration, yet the organized transmembrane region aligns more closely with the conformation observed in the mature pore, suggesting a transition from the prepore to the pore.50 Thus, the presence of GSDMD prepore and GSDMA3 prepore implies that GSDMs may adopt a conserved and simple synergistic mechanism during membrane insertion. However, this unifying mechanism contradicts reports that GSDMDs form arc-like and slit-like assemblies on the membrane.31,229 These observations imply that GSDM-NT may independently insert into PM and subsequently oligomerize within PM, with additional GSDM-NT recruited subsequently to expand these pores. Employing experimental approaches, such as patch-clamp electrophysiology or direct observation of prepores in the membrane, will aid in elucidating the pore-forming mechanism of GSDMs further.
GSDM-mediated cell rupture and membrane repair
GSDM-NT interacts with acidic lipids to generate pores; however, the exact mechanism driving this process is yet to be fully elucidated. Ruan et al. employed cryo-EM to illustrate the formation of single-ring pores of GSDMA3-NT at resolutions of 3.8 and 4.2 Å, respectively, as well as double-ring pores at 4.6 Å resolution.41 The structure of the GSDMA3 pore exhibits similarities to that of the GSDMD pore. The GSDMA3 pore is composed of 26–28 subunits, while the number of subunits in the GSDMD pore is approximately equivalent to that of GSDMA3 and GSDMB. The GSDMD pore exhibits an inner diameter of ~10–14 nm, a measurement that accommodates the release of IL-1β (4.5 nm), along with a subset of other small DAMPs, encompassing IL-18, IL-1α, IL-33, galectin-1/3, ATP, and the cold-inducible RNA binding protein (CIRP). The implications of varying pore architectures and dimensions in dictating the liberation dynamics of diverse cargoes are yet to be fully elucidated. However, it is estimated that assemblies comprising at least 10 GSDMD-NT subunits may suffice to facilitate the transit of IL-1β.234
Subsequent cellular rupture releases larger molecules, including LDH, DNA-binding histones, high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1), sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), and perhaps even organelles, a process mediated by Ninjurin-1 (NINJ1) (Fig. 2).241,242 As an evolutionarily conserved cell surface protein, NINJ1 facilitates cell membrane rupture and the discharge of DAMPs.243 These DAMPs are detected by PRRs, which activates a cascade of immune responses, resulting in the attraction of immune cells and the triggering or augmentation of inflammatory reactions, which can ultimately promote the manifestation of inflammatory diseases. NINJ1 offers insights into the uncoupling of GSDMD-mediated cell death from plasma membrane rupture (PMR). In macrophages from both mouse and human, deletion of NINJ1 does not inhibit GSDMD pore formation, cell swelling, and death, yet PMR is impaired.243,244 The precise mechanism underlying which NINJ1 augments PMR remains undetermined; however, this function is contingent upon an amphipathic α-helix within the NT region of NINJ1 and the assembly of NINJ1 into oligomers.243 Moreover, the triggers for NINJ1-mediated PMR are inconclusive. Dondelinger et al. demonstrated that hypotonicity was sufficient to induce NINJ1 oligomerization and NINJ1-mediated PMR in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), but this in vitro system may not fully mimic the true situation of PMR in vivo.245 Wang et al. hypothesized that the activation signal for NINJ1 might involve a form of membrane modification or ion channel activation rather than osmotic pressure disruption, because NINJ1-mediated PMR plays a global effect, but apoptotic cells do not undergo swelling in the current consensus.246 The phenotype linked to NINJ1 depletion shares similarities with those observed in cells subjected to pyroptosis inducers in an environment containing glycine,10,174,247,248 and one report indicated that glycine administration curtails the assembly of NINJ1 oligomers that are correlative with PMR.244 These results imply that NINJ1 could represent a crucial target through which glycine exerts its protective effects on cellular integrity.244
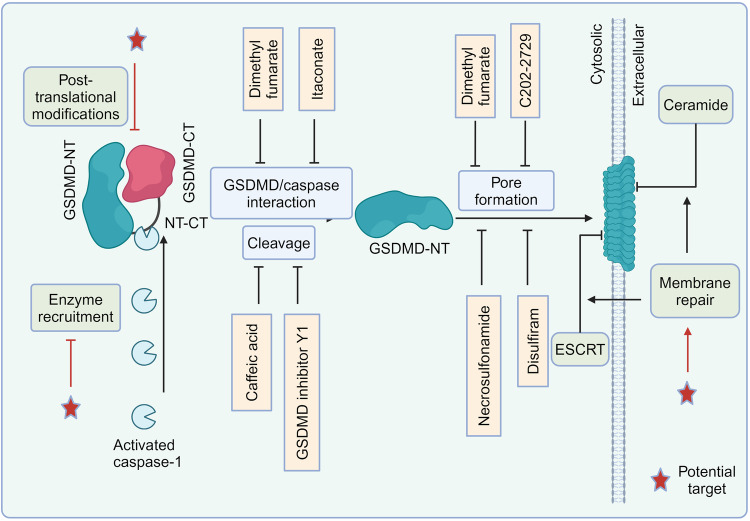
More recently, it has been observed that cells expressing GSDMD-NT do not always undergo cell lysis. Owing to the presence of repair mechanisms for PMR, GSDMD-NT pores do not consistently lead to pyroptosis and may merely release inflammatory cytokines without cell death.10,174,249 The influx of Ca2+ via GSDMD pores functions as a signaling mechanism for cellular initiation of PM repair, recruiting the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) to remove pores from the PM, which are subsequently shed as ectosomes.249 PM repair by ESCRT-III allows for restricted pyroptosis while permitting limited GSDMD-dependent cytokines release. Recent research has uncovered a unique resistance mechanism against cell lysis, where Ca2+ influx prompts lysosomal exocytosis at the site of damage, releasing acid sphingomyelinase (ASM). Caspase-7 mitigates GSDMD pores and maintains cellular integrity by activating ASM, thereby generating substantial ceramide levels. These ceramides facilitate clathrin-independent endocytosis to internalize GSDMD pores and repair damaged membranes.250 Under these conditions, pores fail to trigger pyroptosis but rather facilitate the secretion of IL-1 through them, generating a state of cellular hyperactivation that correlates with an elevated capacity to prime adaptive immune responses.138 The mechanism of PM repair aligns with the function of living cells in releasing inflammatory cytokines, which also corresponds to the observation that hyperactivated cells exhibit fewer GSDMD pores compared to pyroptotic cells.10 Notably, other potential mechanisms exist to promote PM repair. Phospho-MLKL is eliminated from PM via flotillin-driven endocytosis or ALIX-syntenin-1 axis of exocytosis, thereby inhibiting necroptosis. Similar to ESCRT-III- and caspase-7-mediated PM repair,251 these mechanisms may ensure that only signals of sufficient strength lead to necroptosis, but whether they inhibit membrane damage caused by pyroptosis remains to be demonstrated.
Gasdermins and mitochondrial damage
Mitochondria regulate cell death with their diverse metabolic functions and demonstrate an important role in pyroptosis.252 Beyond its established interaction with PM, GSDM-NT is also known to engage with membranes within the interior of the cell.8,42,54,57,59,226,253,254 The NT domains of GSDMD and GSDME are capable of targeting mitochondria, where they interfere with the integrity of both the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes and disrupting their functional roles. This interference results in the production of mtROS, the release of mtDNA, the dissipation of transmembrane potential, and the release of cytochrome c. These cumulative actions ultimately lead to the activation of caspase-3, facilitating the execution of both apoptosis and pyroptosis.8,57,59 Additionally, mtROS is instrumental in fostering RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis,254 while mtDNA promotes GSDMD pore formation,8 further facilitating pyroptosis. Moreover, mtDNA can be sensed by the AIM2 inflammasome, initiating pyroptotic cascades.255 Mitochondrial damage also activates the NLRP10 inflammasome, resulting in ASC specks formation and the release of cytokines, independent of mtDNA.256 These insights underscore the significance of mitochondrial dysfunction in orchestrating immune responses through enhancing pyroptosis, and emphasizes the indispensable roles of GSDMs as proximal executors in multiple pathways of cell death.
The GSDMD-NT demonstrates a marked preference for binding with mitochondrial and bacterial lipids, as well as cardiolipin, exhibiting a significantly stronger binding affinity compared to PM lipids.30,32 Upon activation of GSDMD, the onset of mitochondrial damage precedes damage to PM.8 Similarly, GSDMA-NT tends to accumulate preferentially within mitochondria, with a delayed and diminished presence at PM.253 This distinct subcellular distribution kinetics implies that GSDM-NT may initiate mitochondrial dysfunction prior to their penetration into PM.
Novel pyroptosis-independent functions of GSDMs
A multitude of investigations have centered on the role of GSDMs in pyroptosis, but recently GSDMs have also been reported to act independently of this process. The assembly of GSDM pores is not invariably predictive of pyroptosis occurrence, and cells may survive after moderate GSDM pore formation due to PM repair mechanisms, weak inflammasome activation, and oxidized lipid stimulation.50,249,257 In the following, we present the novel pyroptosis-independent functions of GSDMs from three aspects: GSDMs in IL-1 release, GSDMs in NETosis, and GSDMs in non-immune cells.
GSDMs in IL-1 release
The initial characterization of the functional linkage between pyroptosis and the release of IL-1β was established in macrophages,10,174,258 yet this view has recently been challenged. Evidence has mounted to suggest that in macrophages and neutrophils, IL-1β is discharged via pores formed by GSDMD rather than by pyroptosis, or that the secretion of IL-1β is GSDMD-independent.259 Notably, NINJ1 has been documented to coordinate the ionic and osmotic disruptions triggered by GSDMD pores, facilitating the terminal stages of PMR.243 Despite its pivotal role in PMR, NINJ1 is not required for the formation of GSDMD pores, corroborating the concept of GSDMD as a pivotal player in both pyroptosis induction and the unconventional secretion of IL-1β.
Neutrophils are considered to be complex cells with a range of important specialized functions that serve as first-line weapons in the innate immune system.260 They are the most abundant subtype of granulocytes and are capable of assembling diverse inflammasome platforms to release IL-1β to defense various microbial pathogens.261,262 Unlike macrophages, neutrophils are not susceptible to GSDMD-dependent pyroptotic lysis upon activation of inflammasomes to maintain their vitality for efficient microbial eradication, while still employing a GSDMD-dependent mechanism for the export of IL-1β.42,263,264 However, this was not evident until it is confirmed that GSDMD is a conduit for macrophage IL-1β secretion and pyroptosis. Before these findings, some researchers merely indicated that the engagement of specific inflammasome signaling pathways in neutrophils could result in substantial IL-1β secretion without pyroptosis, as assessed by LDH release.137,263–265 These studies prompt an investigation into GSDMD in neutrophils, ultimately demonstrating a critical function for this protein in the controlled secretion of IL-1β by myeloid leukocytes and revealed pyroptosis as a universally exhibited pro-inflammatory form of PCD.
The mature IL-1β cytokine is generated through the proteolytic cleavage of pro-IL-1β by caspase-1, representing the most conventional pathway for its production. However, neutrophils are rich in azurophilic granules, which opens up the possibility of an abundance of IL-1β precursor protein-cleaving enzymes. Additionally, pro-IL-1β may be cleaved by a spectrum of serine proteases (including NE, cathepsin G) stored in azurophilic granules, thereby yielding a biologically active form of IL-1β.266 The proficiency of neutrophils to produce biologically active IL-1β via the canonical pathway and other serine protease pathways underscores their significance as a prime generator of pro-inflammatory cytokines during diverse innate immune responses. As previously described, GSDMD, which can be cleaved by caspase-1/11/4/5, constitutes a component within various inflammasome signaling pathways. The GSDMD-NT pore, which accumulates on the plasma membrane, is a conduit for the direct release of IL-1β. Significantly, the caspase-4/11-induced aggregation of GSDMD-NT pores on the PM can facilitate K+ efflux, which is sufficient to prompt the secondary assembly and activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes, as well as the caspase-1-dependent cleavage of pro-IL-1β, culminating in the efflux of mature IL-1β through the GSDMD-NT pore.28 Recent electron microscopic and functional assessments of GSDMD-NT pore have revealed a mechanism that prevents pro-IL-1β release, with GSDMD-NT pore mediating mature IL-1β release through electrostatic filtration, thereby hindering pro-IL-1β fluxes.50,225
Nonetheless, an alternative viewpoint has been proposed, with Karmakar et al. reporting that GSDMD-NT was essential for the secretion of IL-1β by human and mouse neutrophils, but it does not migrate to the plasma membrane, nor does it augment membrane permeability or trigger pyroptosis.226 GSDMD-NT produced by activated caspase-1 is trafficked to azurophilic granules, resulting in the deployment of NE into the cytoplasm and the subsequent secondary GSDMD cleavage. These finding suggests that the abundance and compact arrangement of neutrophil granules may function as a diffusion obstacle, impeding the transport of GSDMD-NT to the inner leaflet of the PM. They demonstrated that neutrophils deploy IL-1β secretion through a mechanism that is contingent upon autophagy, based on the observation that neutrophils from autophagy-related 7 (ATG7)-deficient mice exhibited impaired IL-1β secretion.226 It is noteworthy to highlight that the IL-1 family can also be liberated through a pathway that is independent of GSDMD. Monteleone et al. discovered that the initial secretion of IL-1β from mouse neutrophils was facilitated by a mechanism dependent on GSDMD. However, subsequent releases of IL-1β in both in vitro and in vivo settings occurred independently of GSDMD.267 However, inflammasomes accelerate IL-1β release through caspase-1 and GSDMD activation. Many previous investigations have found that macrophages can secrete IL-1β via exosomes,268,269 secretory autophagy,270 or small extracellular vesicles,271 suggesting other novel pathways for IL-1β secretion without pyroptosis. Recently, Ratitong et al. have confirmed that neutrophils utilize exosome secretion as a conduit for the release of IL-1α cytokine,272 which suggests that extracellular vesicles such as exosomes are a critical mechanism for the secretion of IL-1 family by neutrophils.
It is noteworthy that IL-1α and IL-33 are able to be secreted in living cells via the GSDM pores.224,232,273 In human T cells, the GSDME-NT pores mediate the unconventional IL-1α release, with the NLRP3/caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME axis pivotal in this process.273 GSDMD in airway epithelial cells and macrophages is susceptible to cleavage by allergenic proteases to generate a novel fragment, p40 GSDMD-NT (p35 GSDMD-NT in humans), which effectively promotes IL-33 release without accompanying cell death.232 In addition, GSDMs also promote the unconventional release of other inflammatory mediators, including ATP and HMGB1.274,275
GSDMs in NETosis
In 2004, NETs, the nuclear chromatin complexes encompassing DNA, citrullinated histone H3, myeloperoxidase, NE, and cathepsin G, were uncovered and postulated to play a pivotal role in the innate immune response arsenal of neutrophils.276 The process of NETosis, characterized by the deployment of NET structures, marks a significant research front in the domain of neutrophil physiology,277–279 eliciting a robust cellular response that is currently a subject of intense scholarly examination.280,281 NETosis is a multifaceted biological pathway that entails the disruption of both nuclear and granular membranes, the decondensation of chromatin, and its amalgamation with granule components, culminating in the extrusion of condensed chromatin from neutrophils. The combined action of GSDMD and caspase-11 in LPS-induced NETosis drives nuclear membrane breakdown, chromatin relaxation, and rupture of the PM.42,43 GSDMD-NT interacts with azurophilic granules, the releasing granule proteins required for NETosis progression, where NE can further cleave GSDMD. The formation of GSDMD pores within the nuclear membrane permits the rupture of this barrier and the infiltration of caspase-11 into the chromatin, where caspase-11 mediates histone shearing and inactivation to enable DNA amplification. The collaboration of caspase-11 and GSDMD is indispensable for neutrophil PMR, undergone by neutrophils during the terminal stages of NET extrusion.42,43 Sollberger et al. concluded that NET formation did not require caspase-11 activation because the proteolytic activation of GSDMD was independent of caspase-11.43 They proposed that neutrophil serine proteases cleaved GSDMD, releasing activated and toxic NT domains. This finding is consistent with the report of Kambara et al.,180 wherein NE was demonstrated to cleave GSDMD, and together these two studies suggest that GSDMD has additional functions independent of inflammasomes.
In 2022, Chauhan et al. suggested that GSDMD might not be an indispensable factor for PMA-induced NETosis,282 contrary to the view of Sollberger et al. 43 The latter view was proposed in the context of LDC7559 inhibiting PMA-induced NETosis by targeting GSDMD, yet LDC7559 was subsequently demonstrated to inhibit PMA-induced NETosis not by directly targeting and inhibiting GSDMD, but rather by functioning as a potent agonist of the glycolytic enzyme phosphofructokinase-1 liver type (PFKL).283 In 2023, Stojkov et al. discovered that NET formation after C5a or LPS stimulation of mouse neutrophils was GSDMD-independent.284 Neutrophils from both wild-type (WT) and GSDMD−/− mice exhibit equivalent kinetics and magnitude of response to NET-inducing agonists, a process that is independent of cell death. Furthermore, even under conditions of canonical inflammasome activation, which culminates in GSDMD cleavage and prompts NET production, the release of NETs does not necessitate the participation of caspases or GSDMD.284 The differences between these studies described above could be attributed to variations in the stimulation conditions, the timing of NET assembly measurement, and the methodologies utilized for quantifying cell death. In conclusion, these recent reports imply that the role of GSDMD in regulating NETosis is incidental rather than mandatory. Clearly, the relationship between GSDMD and NETs needs further scrutiny due to potential discrepancies in NETosis and NET formation.
GSDMs in non-immune cells
GSDMD in immune cells has received extensive attention for mediating cell death and promoting inflammation that contributes to the manifestation of diverse diseases. Now the function of GSDMD on tissue homeostasis in non-immune cells is gradually being reported. Li et al. discovered that in osteoblasts, GSDMD was cleaved into non-lytic p20 products, a function that serves to forestall bone resorption and preserve bone homeostasis.285 At late stages of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis, GSDMD undergoes cleavage to produce p20 products rather than the canonical p30, a process that is reliant on receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and caspase-8/3. The GSDMD p20 is selectively targeted to early endosomes, where it constrains the maturation of endolysosomes and inhibits bone resorption. This function is mediated by the protein’s propensity for oligomerization and its ability to regulate phosphoinositide turnover by combining with phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI(3)P). GSDMD−/− mice and Gsdmdfl/fl Lyz2Cre+ mice show osteoporosis, exhibiting significant reductions in trabecular bone volume and trabecular number. Zhang et al. reported that GSDMD was pivotal in the secretion of mucin and the establishment of the mucus layer within goblet cells.49 Specific deletion of GSDMD in IECs results in reduced mucus secretion accompanied by loss of the mucus layer, which undermines the integrity of the host-microbial interface and impairs the effectiveness of pathogen clearance from the mucosal surface. The mechanism is that stimulation of NLRP6 in goblet cells activates caspase-1/11, which in turn activates the GSDMD via a mechanism of ROS synthesis. GSDMD-NT facilitates mucin secretion via Ca2+-dependent disassembly of cortical F-actin via the action of scinderin.49 He et al. reported that in IECs, GSDMD was cleaved to a 13 kD NT fragment by caspase-3/7 following exposure to dietary antigens.222 This fragment, distinct from the 30 kD NT fragment, migrates to the nucleus and stimulates the transcription of CIITA and MHCII molecules, which leads to the apoptosis of Tr1 cells in the proximal small intestine. This process enables IECs to foster protective immune responses against pathogens while preserving immune tolerance to dietary antigens.222 In addition, GSDMD also functions in full-length form. Zhang et al. demonstrated that GSDMD could enhance the susceptibility of tumor cells to chemotherapy by inducing ER stress, rather than via pyroptosis.286 This mechanism involves the upregulation of eIF2α binding to p-ERK and promotes the phosphorylation of eIF2α and the induction of ER stress. Following the upregulation of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) protein level, a cascade of events is initiated, leading to the activation of apoptosis-related proteins, including C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP). This activation is proposed to correlate with the susceptibility of the tumor to therapeutic agents, potentially influencing drug response outcomes.286 Similarly, GSDMB can act through the full-length form. In IBD, epithelial-derived GSDMB modulates the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase, thereby enhancing the preservation and regeneration of epithelial tissue.
These studies further sophisticate our current comprehension of the pyroptosis-independent function of GSDMs across various physiological and cellular contexts and suggest potential risks of using GSDMs as a therapeutic target for anti-inflammatory drugs. A pivotal yet intriguing inquiry lies in understanding the diverse responses of various cell types to these structurally akin GSDM-NT pores or full-length GSDM. Future investigations in structural biology might provide insights into this matter. Moreover, we speculate the presence of additional proteins that collaborate in the distinct functionalities of the GSDM-NT pores, as suggested by ref. 243
Regulation of gasdermins
Transcriptional regulation of gasdermins
GSDMs are pivotal in orchestrating cell death and inflammatory responses. The expression level of GSDMs has a direct impact on cellular susceptibility to pyroptosis, where the key lies in whether the formation of GSDM pores is sufficient to overwhelm the repair mechanism of PM, thereby triggering pyroptosis. Thus, regulating the expression of GSDMs becomes an effective strategy to modulate cell death and cytokines release. As investigating into the transcriptional regulators of GSDMs and their participation in pathological conditions deepens, we have gained a preliminary understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of GSDMs at the transcriptional level,80 but further exploration is still needed. Currently, there is a preliminary understanding of the transcriptional regulation of GSDMD, however, little has been explored for other GSDMs.
Recent investigations have elucidated that in mouse macrophages, the manifestation of GSDMD is governed by interferon-regulated factor 2 (IRF2), which acts by selectively combining with the transcription initiation site of GSDMD.80 The absence of IRF2 does not entirely abrogate GSDMD expression but does lead to a marked reduction in GSDMD level, accompanied by decreased release of IL-1β and reduced cell mortality. Conversely, human monocytes do not rely on IRF2 for GSDMD expression regulation.287 Nonetheless, the current understanding of the regulatory mechanisms involving these transcription factors, and their potential interplay with cofactors, remains incomplete.
While the regulatory mechanisms that govern GSDMD expression in homeostatic conditions have been partially elucidated, the comprehension of its transcriptional control during inflammation is still lacking. Upon LPS stimulation, adipocytes engage in GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis, a process mediated by the NF-κB signaling cascade.288 In human septic neutrophils, GSDMD transcription is regulated by STAT3, which involves nuclear PD-L1 translocation.289 STAT3 also regulates the transcription of GSDMC, a process that necessitates the participation of nuclear PD-L1. Upon macrophage-derived TNF-α activation, caspase-8 cleaves GSDMC at the D365 site, generating GSDMC-NT, which ultimately leads to pyroptosis.35 Furthermore, the transcriptional activation of GSDMD in response to cytosolic A. baumannii infection Furthermore, the transcriptional activation of GSDMD in response to cytosolic A. baumannii infection relies on IRF3/7 and IFNAR1.290 Recently, it was found that the Sp1 positively modulates the transcriptional control of GSDME by binding −36–−28 sites in the GSDME promoter, and promotes the pyroptosis of tumor cells.196 A comprehensive investigation into the transcriptional control of GSDMs is anticipated to reveal novel therapeutic approaches for managing this pivotal protein family, and additional studies are needed to pinpoint the pathways that trigger GSDMs expression.
Post-translational modifications of gasdermins
Ubiquitination of gasdermins
Ubiquitination, a pivotal post-translational modification, is integral to the “quantitative” and “qualitative” regulation of proteins in many biological and disease processes.291–293 The process consists of multiple enzyme-catalyzed stages, involving the coordinated activity of ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s) and ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) to ubiquitin ligases (E3s), leading to the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to the target protein.294–296
Inflammasomes regulated by ubiquitination have been extensively studied297–302; however, ubiquitination on GSDMs has been reported less frequently, but recent studies have yielded intriguing insights into this process (Table 2). The human GSDMB and GSDMD are directly implicated in the lysis of incoming bacterial pathogens and the cells they have infected, whereas the bacterial E3 ubiquitin ligase IpaH7.8 can ubiquitinate degradation of human GSDMB and GSDMD, potentially enabling pathogen escape.160,162 The recently published structure for the GSDMB and IpaH7.8 LRR complex has provided valuable insight into the mechanism of this ubiquitination.38,163 The interaction between GSDMB-NT and the IpaH7.8 LRR is mediated by charged and hydrophobic residues, with specific GSDMB residues (E15, D21, L96D, R124, and R208) being essential for this association. It is worth mentioning that the binding of IpaH7.8 to GSDMs is not a universal precursor to ubiquitination or protein degradation. This is exemplified by the fact that IpaH7.8 binds both hGSDMD and mGSDMD proteins, yet it specifically ubiquitinates and degrades only the human protein, sparing the mouse equivalent.38,162,163 This feature may enable mice to capitalize on mGSDMD-induced pyroptosis as a defense mechanism against Shigella infection. Another report also shows that the E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1 engages with GSDMD, mediating the non-proteasomal polyubiquitination of Lys27-linked GSDMD at residues Lys203 and Lys204 in humans (Lys204 and Lys205 in mouse).303 Interestingly, this process promotes pyroptosis rather than inhibition, and the mechanism involved is not known.
Table 2.
PTMs modulating the activities of the GSDM family
| PTM | GSDM family | Modified residue | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lys48-linked polyubiquitination (IpaH7.8) | GSDMB | At least Lys177, Lys190, Lys192 (human) | Promote degradation of GSDMB and directly inhibit pore formation | 38,160–163 |
|
Lys63-linked/ Lys48-linked polyubiquitination (IpaH7.8) |
GSDMD | LysK55, Lys62, Lys203 (human) | Promote degradation of GSDMD | 38,161–163 |
|
Lys27-linked Polyubiquitination (SYVN1) |
GSDMD | Lys203, Lys204/Lys204, Lys205 (human/mouse) | Promote pyroptosis | 303 |
|
Lys48-linked Polyubiquitination (CDC20) |
GSDME | Not mentioned | Promote degradation of GSMDE | 305 |
| Deubiquitination (USP24) | GSDMB | Not mentioned | Increase the stability of GSDMB | 304 |
| Deubiquitination (USP48 and OTUD4) | GSDME | Not mentioned | Increase the stability of GSDME | 306,307 |
| Phosphorylation (AMPK) | GSDME | Thr6 (human) | Prevent pore formation | 59,311 |
| Phosphorylation (PLK1) | GSDMA | Thr8 (human) | Prevent pore formation | 59,312 |
| Phosphorylation | GSDMD | Thr213 (human) | Prevent pore formation | 32 |
| Disulfiram | GSDMD | Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) | Prevent pore formation | 45 |
| Disulfiram | GSDME | Not mentioned | Prevent pore formation | 530 |
| Necrosulfamide | GSDMD | Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) | Prevent pore formation | 44 |
| Succination (fumarate) | GSDMD | Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) | Prevent cleavage and pore formation | 46 |
| Succination (fumarate) | GSDME | Cys45 (mouse) | Prevent pore formation | 46 |
| Itaconation | GSDMD | Cys77 (mouse) | Prevent caspase-1-dependent cleavage | 320 |
| Oxidation | GSDMD | Cys38, Cys56, Cys268, Cys467 (human) |
Promote cleavage by caspase-1 |
323 |
| Palmitoylation (ZDHHC5/9) | GSDMD | Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) | Promote pore formation and pyroptosis | 324,325 |
| Palmitoylation (ZDHHC-2/7/11/15) | GSDME | Cys407/Cys408 (human/mouse) | Promote pore formation and pyroptosis | 326 |
| Palmitoylation | bacterial and fungal GSDMs |
Cys3/Cys3/Cys4/Cys7 (Runella/ Bradyrhizobium/ Vitiosangium/Lysobacter) |
Promote structural stability and pore-forming activity | 228 |
In addition, GSDMB and GSMDE are also regulated by ubiquitination. USP24 interacts with GSDMB and acts as a deubiquitinating enzyme (Dub) to remove polyubiquitin chains from GSDMB,304 increasing the stability of GSDMB in bladder cancer and further promoting downstream phosphorylation of STAT3, which promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation. Caspase-3/GSDME-dependent pyroptosis is a key determinant of anti-tumor immunity. The E3 ubiquitin ligase CDC20 reduces tumor cell pyroptosis through ubiquitinated degradation of GSMDE.305 The Dub USP48 and OTUD4 promote GSDME-mediated pyroptosis by deubiquitinating and stabilizing GSDME, which increases the sensitivity of tumor cells to treatment.306,307 It is clear that we are just beginning to understand the regulatory role of ubiquitination on GSDMs, and the mechanisms of GSDM recognition and ubiquitination remain to be elucidated.
Phosphorylation of gasdermins
Phosphorylation, as a pervasive protein modification mechanism, permeates numerous signaling processes and serves as a pivotal regulator across diverse levels of cellular activity.308,309 Evidence suggests that the operational dynamics of GSDMs may be fine-tuned by this post-translational modification, albeit the underlying mechanics remain largely elusive. Currently, the presence of phosphorylation has only been found in humans for GSDMA, GSDME and GSDMD (Table 2). Analysis of the PhosphoSitePlus mass spectrometry database310 revealed phosphorylation of GSDME at multiple serine (Ser) and threonine (Thr) sites, including Thr6, Ser69, Ser113, Ser114, Thr117, and Ser252.59 In particular, phosphorylation of Thr6 prevents the oligomerization of GSDME in the membrane and its induced pyroptosis,59,311 and a recent report elucidated that adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) acts as its kinase.311 Phosphorylation of the Thr8 site of GSDMA is mediated by polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), a process that, similar to GSDME, prevents the ability of GSDMA from forming pores in PM.59,312 Both Thr8 and Thr6 are situated on the α1 helices of both GSDMA and GSDME, which helices are essential for protein oligomerization, and phosphorylation may produce charge repulsion, thereby hindering the assembly of GSDM pores.313 GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis is attenuated when Ser and Thr residues are converted to Glu residues.314 Gel electrophoretic migration analysis has uncovered that Thr213 serves as the principal phosphorylation site that inhibits GSDMD oligomerization, but the specific kinase is not known. Furthermore, it appears that only in their phosphorylated forms can GSDMD-NT and GSDMA-NT interact with membrane lipids, indicating that alterations in membrane lipid composition, coupled with phosphorylation, represent an additional regulatory mechanism within the pyroptosis process.32 As to whether the remaining GSDMs modulate their function through direct phosphorylation remains unresolved, although each of these proteins harbors at least one Ser or Thr residue within the α1 helix.
The phosphorylation of caspases interacting with GSDMs could potentially serve as a pathway for regulating the activity of GSDMs. Ser376 stands as the sole characterized phosphorylation site on caspase-1, which is essential for its activation.315 Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that the phosphorylation of caspase-3/7/8 modulates their activation processes and/or abilities to recognize substrates.316–319 However, the phosphorylation of caspase-4/5/11 has not been investigated, and a possible explanation is that they have a low activation threshold or do not require phosphorylation modification to trigger pyroptosis.
Cys modifications of gasdermins
In 2016, Liu et al. illuminated the essential function of Cys191 in hGSDMD and Cys192 in mGSDMD in orchestrating the pyroptotic response (Table 2).30 Subsequent investigations revealed that a mutation at Cys191 in hGSDMD can diminish the pyroptotic frequency by half.45,50 Meanwhile, small molecule compounds such as NSA44 and DSF45 have been shown to hinder hGSDMD-mediated apoptosis by covalently modifying Cys191. In addition, the metabolite fumarate irreversibly binds Cys191 of hGSDMD, Cys192 of mGSDMD, and Cys45 of mGSDME in a process known as succination,46 which is effective in inhibiting the cleavage and oligomerization of hGSDMD and the resulting cell death, and has demonstrated therapeutic effects in animal models of lethal endotoxemia. These insights suggest that metabolic shifts, particularly from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis, can regulate the formation of GSDM pores. Recent research further endorses the notion that metabolic transitions exert influence over GSDM-mediated pyroptosis. The accumulated cellular metabolite itaconic in macrophages that are challenged by prolonged LPS stimulation directly interacts with GSDMD at the Cys77 site, thereby preventing GSDMD pore mediated by caspase-1 and making the cells tolerant to prolonged LPS exposure.320 In addition, ROS, which is generated in response to inflammasome stimulation,321,322 can modulate the activity of hGSDMD by directly oxidizing Cys38, Cys56, Cys268, and Cys467 of hGSDMD, and mutation of these residues reduces GSDMD pore formation.313,323
Recent studies have revealed the mechanism by which Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) is essential for GSDMD pores. Post-translational palmitoylation of GSDMD at the Cys191/Cys192 site is a decisive step in the transfer of GSDMD-NT to PM for pore formation, which is facilitated by the palmitoyl acyltransferases ZDHHC5/9 and is potentiated by ROS induced by LPS.324,325 Inhibition of palmitoylation of GSDMD by using the palmitate analog 2-bromopalmitate significantly reduces macrophage pyroptosis and the secretion of IL-1β, thereby alleviating the pathological state in septic mice. In addition to GSDMD, Cys407/Cys408 (human/mouse) of GSDME are also palmitoylated during chemotherapy-induced pyroptosis, and ZDHHC-2/7/11/15 have been identified as the acyltransferases responsible for palmitoylating GSDME.326 This palmitoylation may aid in the separation of GSDME-NT and GSDME-CT without altering the caspase-3-mediated cleavage of GSDME, a process that can be inhibited by 2-bromopalmitate. In addition, palmitoylated cys residues have been found in bacterial and fungal GSDM homologs, contributing to structural stability and maintaining pore-forming activity in anti-phage defense.228 Protein palmitoylation, a widespread form of acylation, represents a fundamental regulatory mechanism governing membrane binding, localization, stability, and protein interactions.327,328 Collectively, Cys modification emerges as a conservative regulatory mechanism of paramount importance in controlling the function of GSDMs.
Gasdermins and diseases
GSDMs have been initially characterized for their involvement in a spectrum of pathologies, encompassing hearing impairment,16,20 asthma,151,212 hair loss,19,209 and cancer.146,153 Despite years of investigation, the specific biological roles of these proteins have remained elusive. Nonetheless, researchers have proposed a connection between GSDMs and inflammation. For instance, mutations in the Gsdma3 gene have been associated with alopecia in mice, a condition that is characterized by the depletion of stem cells, hyperkeratosis, and concurrent inflammation.329 Presently, aggregation of GSDM pores within PM is considered to be a signature feature of pyroptosis. Although this notion somewhat restricts GSDMs primarily to their role in pyroptosis, contemporary research indicates that these proteins may also participate in diverse cellular death mechanisms330 and additional non-lytic pathways, which together mediate inflammatory progression. GSDMs have been involved in a wide array of pathologies, spanning sepsis, viral infections, cancers, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Sepsis
Sepsis is considered a dysregulated immune response to pathogenic challenge, leading to profound and potentially fatal injury to tissues and organs.331–335 The etiology of sepsis is multifaceted and involves numerous aspects of the interaction between the invading microorganism and the host, including persistent excessive inflammation and immunosuppression, as well as an inability to restore homeostasis.336–341 Inflammatory imbalance is the most critical basis underlying the pathogenesis of sepsis, persisting throughout the progression of the disease. GSDMD is a critical regulator of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by immune cells, and recent evidence suggests a pivotal modulatory role for GSDMD in the pathogenesis of sepsis.241,342 Although various sensors and mediators activate pyroptosis, the pore-forming activity of GSDMD-NT emerges as a compelling therapeutic target, as it is a universal terminal step required for pyroptosis and the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to pathogenic or danger-induced signals. GSDMD inhibition or inactivation does prevent lethal bacterial sepsis, with GSDMD−/− mice displaying markedly enhanced survival over WT controls in models of sepsis induced by LPS and cecum ligation and puncture (CLP).7,28,29,180,343–345 GSDMD serves as a crucial mediator in macrophage pyroptosis and the secretion of IL-1β, a classic pro-inflammatory cytokine that initiates the host inflammatory response and amplifies both innate and adaptive immune responses.74 Excessive and persistent IL-1β secretion plays a significant role in the systemic inflammation and organ damage characteristic of severe sepsis,60,346–348 but two phase III clinical trials could not yield beneficial effects of anti-IL-1β receptor antibodies in septic patients.349,350 Consequently, inhibiting GSDMD-mediated cytokine production may represent an effective strategy for treating sepsis. For instance, GSDMD−/− mice are protected against lethal septic shock induced by LPS.28 Kayagaki et al. reported that BMDMs lacking GSDMD are insusceptible to pyroptosis and do not release IL-1β in response to transfection with LPS or synthetic monophosphoryl lipid A. Similarly, GSDMD−/− BMDMs were unresponsive and failed to produce IL-1β upon electroporation with LPS, or when LPS was complexed with cholera toxin B subunit or stimulated with S. typhimurium LPS.28 Consequently, targeting GSDMD inhibition emerges as a promising strategy to mitigate inflammation, as Hu et al. reported that the FDA-approved alcoholism treatment drug DSF effectively inhibited GSDMD pore formation, thereby blocking LPS-induced septic death.45 DSF-induced modification of Cys191 in hGSDMD (Cys192 in mGSDMD) is required to mediate conformational changes in membrane insertion and pore formation. DSF preserves the processing of IL-1β and GSDMD but inhibits the formation of pores, thereby inhibiting the release of IL-1β and the execution of pyroptosis.45 Notably, IL-1β is not uniformly detrimental due to the different triggers of sepsis. Indeed, IL-1β increased host resistance against C. albicans and mitigated diffuse infections caused by this pathogen.351–353 Surprisingly, GSDMD−/− mice are resistant to C. albicans infection and accompanying kidney injury, partly because IL-1β does not rely on GSDMD release to generate antifungal host defense. Another reason is that GSDMD inhibition prevents the escape of C. albicans and promotes the clearance of the fungus.352
Coagulation dysfunction stands as a prevalent and severe manifestation of sepsis, occasionally resulting in disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), which is a pathological state marked by systemic thrombotic activation, microvascular occlusion, organ dysfunction, and death.172,354–356 Abnormalities in the coagulation system play a contributory role in the onset of sepsis, where GSDMD has recently been found to play an important role.357–360 Tissue factor (TF), a critical initiator of the coagulation cascade, plays a decisive role in triggering systemic DIC.361,362 GSDMD knockout attenuates LPS-induced DIC, including blocking thrombin production, fibrin formation, platelet accumulation and microvascular occlusion in the liver, as well as increases in plasma thrombin-antithrombin (TAT), D-dimer and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1).357 Yang et al. documented that caspase-11 triggered GSDMD pores assembly, facilitated Ca2+ influx, and led to phosphatidylserine exposure via the activity of transmembrane protein 16 F, an enzyme involved in Ca2+-mediated phospholipid scrambling. Independent of pyroptosis, enhanced activation of TF promoted the development of DIC.357 As plasma IL-1β concentrations correlate with DIC scores in patients with sepsis, this study suggests that caspase-11/GSDMD signaling may offer new therapeutic avenues for sepsis-associated DIC. Zhang et al. similarly suggested the crucial role of GSDMD in lethal septic DIC.360 TMEM173-dependent increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ drives GSDMD cleavage, thereby initiating the delivery of F3, a critical activator in the blood coagulation cascade. The procoagulant and lethal effects elicited by CLP-, E. coli-, or S. pneumonia are inhibited in mice harboring a mutated GSDMD cleavage site or through the administration of anti-F3 antibodies. Furthermore, platelets, which significantly contribute to DIC, have recently been shown to undergo GSDMD-induced pyroptosis, exacerbating the formation of NETs and inflammation during sepsis. Su et al. demonstrated that platelet pyroptosis fostered inflammation and multi-organ damage in CLP-induced sepsis using platelet-specific GSDMD knockout mice.363 Pyroptotic platelets may release oxidized mitochondrial DNA (ox-mtDNA), which promotes NET formation, exacerbating platelet pyroptosis through the release of S100A8/A9 that targeted toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), creating a self-amplifying cycle that results in excessive cytokines release.
Neutrophils constitute the predominant circulating white blood cells and function as the front-line guardians of the host immune response against invading pathogens.260,277,364–366 During sepsis, activated neutrophils release NETs - complex webs of DNA ensnaring antimicrobial proteins—to facilitate the destruction of pathogens.276 However, an increasing array of findings underscores the detrimental impact of NETs in the progression of sepsis.277,367,368 Recently, evidence has emerged indicating that GSDMD is implicated in the formation and release of NETs42,43 and the development of sepsis.52,289 Silva et al. discovered that GSDMD−/− mice exhibited significantly diminished intravascular NET levels in CLP-induced sepsis, with parallels observed in vitro, where cytosolic LPS failed to prompt NET formation by GSDMD−/− neutrophils.52 GSDMD−/− mice exhibited decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines, improved organ dysfunction, and increased survival in the CLP model. Similar protective effects were observed in WT mice treated with DSF. Transfer of GSDMD-expressing WT neutrophils into GSDMD−/− mice reversed the protective effect of the organs against sepsis and elevated serum NET levels. Septic neutrophils from patients undergoing NETosis display GSDMD expression on PM and are correlated with the formation of prototypical NET structures.52 In addition, our team demonstrated the deleterious role of GSDMD-mediated NET release in sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE), and neutrophil-specific GSDMD knockout reduced plasma and hippocampal NET levels as well as ameliorated inflammatory injury in a murine model of SAE.289 Neutrophil PD-L1 can be translocated to the nucleus, aided by the help of p-Y705-STAT3, to constitute the nPD-L1/p-Y705-STAT3 complex, which promotes the transcription of GSDMD. Consequently, they and we propose that therapeutically targeting GSDMD to directly inhibit NETosis, or targeting upstream regulators of GSDMD to indirectly inhibit NETosis, may represent an efficacious strategy for the treatment of sepsis. In contrast, Liu et al. reported that the occurrence of sepsis induced by CLP in neutrophil-specific GSDMD knockout mice strikingly increased inflammatory cytokine levels, promoted tissue damage, and reduced survival, suggesting that the absence of neutrophil GSDMD does not provide protection against polymicrobial sepsis but rather predisposes mice to a more severe manifestation of the disease.223 This is contrary to the findings of previous studies.52,289 They agree that systemic ablation of GSDMD confers protection against lethal sepsis in mice and that NET release from GSDMD−/− neutrophils in vitro is indeed reduced, but they also confirm that neutrophil-specific GSDMD knockout mice have higher inflammatory cytokines, higher bacterial loads, and higher mortality rates, as well as no reduction in NET levels in vivo.223 They suggest that depletion of GSDMD in neutrophils may impair their bactericidal activity, so that neutrophils lose the ability to remove replicative ecological niches of pathogens, and pathogens are no longer readily engulfed and killed by secondary phagocytes. This exacerbates infections, which subsequently triggers an increased production of cytokines by myeloid cells, resulting in hyperinflammation in CLP mice. The establishment of a GSDMD-dependent positive feedback loop involving platelets and NETs proposed by ref. 363 may be an explanation for the absence of reduced NETs in neutrophil-specific GSDMD knockout mice. This implies that in addition to regulating NETs, GSDMD may be involved in sepsis through other mechanisms. Recently, Pruenster et al. discovered that E-selectin triggers the prompt secretion of S100A8/S100A9 from neutrophils through a reversible activation mediated by the NLRP3/GSDMD axis.369 This rapid activation process is not dependent on the involvement of TLR4, and is followed by the prompt assembly of the ESCRT-III PM repair mechanism, which coincides with the rapid formation of GSDMD pores mediated by E-selectin. Neutrophils may be involved in sepsis through the mechanisms dependent on GSDMD but unrelated to NETs. Collectively, these investigations underscore that GSDMD indeed plays a crucial role in sepsis pathology. Nonetheless, the function of GSDMD in pyroptosis, NET release, and the onset of sepsis is complex, necessitating additional studies to comprehensively delineate its mechanisms of action.
Virus infection
With the growing understanding of pyroptosis, the phenomenon that various virus infections can trigger pyroptosis has come to the forefront. During human adenovirus (HAdVs) infection, the HAdVs genome 36 kb dsDNA is detected by AIM2, which initiates the assembly of an inflammasome complex. Subsequent caspase-1 activation, GSDMD cleavage, and IL-1β release result in the pyroptotic death of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs),370 which is a pivotal component of the innate immune response elicited by viral infection. During human norovirus (HuNoV) infection, the nonstructural protein P22 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in enteric stem cell-derived human intestinal enteroids (HIEs), contributing to pyroptosis, and GSDMD pore-released IL-1β and IL-18 promotes inflammation in virus infections.371 Rotavirus infection also leads to pyroptosis in IECs. Specific expression of a novel NLR inflammasome in IECs, NLRP9b, recognizes short dsRNA stretches by the RNA helicase Dhx9, assembling an inflammasome containing the adapter protein ASC and the cysteine protease caspase-1 to promote GSDMD-induced pyroptosis and IL-18 release.372 This is particularly critical for host defense to limit rotavirus replication by triggering the premature death of infected IECs while preserving gut homeostasis. Previously, the lethal attack of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) on its primary cellular target, CD4 T cells, was usually attributed to apoptosis. It is now believed that caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis appears to be the primary cause of CD4 T cell death driven by HIV infection of lymphoid tissues. This results in substantial secretion of IL-1β, which may further exacerbate chronic inflammation.373–375 In addition, intestinal mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells from patients infected with HIV-1 show robust GSDMD-driven pyroptotic signals adjacent to the luminal side, indicating that MAIT cells undergo pyroptosis within the colorectal mucosa, which promotes an increase in inflammatory cytokines and may exacerbate disease progression and hinder effective immune reconstitution.376 It comes as no surprise that GSDMD is implicated in the progression of virus infections as a prominent agent of pyroptosis, while IL-1β and IL-18 contribute to antiviral immunity. Notwithstanding, the function of GSDMD in virus infections remains obscure, despite extensive research into its regulatory functions within the inflammasome framework in response to cytosolic bacteria or LPS activation.
Recently, with the outbreak and epidemic of COVID-19, the study of coronavirus pathogenesis has deepened, and the significance of GSDMD in virus infections has gained new understanding. SARS-CoV-2, the virus linked to COVID-19, is an enveloped RNA virus comprising multiple proteins, including nucleocapsid, matrix, envelope, and spike.377–379 COVID-19 typically presents as a respiratory disease with severe inflammation of the lungs in critically ill individuals, potentially leading to multi-organ dysfunction and mortality in geriatric and comorbid patient populations.380,381 According to Junqueira et al., ~10% of monocytes and 8% of lung macrophages from individuals with COVID-19 were found to be infected with SARS-CoV-2, and pyroptosis pathways were activated, contributing to cell death and inflammatory mediators release, which in turn caused cytokine storms.382 This study also suggests that the internalization of virus-antibody complexes by monocyte-dependent Fcγ receptor results in GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis, which potentially represents a substantial mechanism underlying the severe inflammatory sequelae, leading to vascular leakage, acute lung injury, and multi-organ damage in severe cases.382 Two currently FDA-approved GSDMD inhibitors, DSF (Antabuse)45 and dimethyl fumarate (DMF, tecfidera),46 are undergoing evaluation in clinical trials to assess their protective effects against COVID-19 (NCT04485130, NCT04594343, and NCT04381936), which further indicates that inhibition of GSDMD in the COVID-19 may be of therapeutic significance (Table 3). The researchers did not detect infected neutrophils in COVID-19 patients, suggesting that neutrophil infection may not be a central mechanism in pathogenesis, although NETosis induced by GSDMD may be an essential driver.382 Conversely, Silva et al. reported a significant role for GSDMD-dependent NETosis in the immunopathology of COVID-19, proposing that interventions targeting GSDMD could represent a novel strategy for enhancing therapeutic approaches to the disease.383 They observed that serum NET and GSDMD levels were elevated and positively correlated with severe cases of COVID-19. The activation of GSDMD-mediated NET in neutrophils requires caspase-1/4 and SARS-CoV-2, which can be abrogated by DSF treatment. In a mouse model infected with SARS-CoV-2, DSF treatment inhibits NET release and attenuates lung damage.383 Similarly, our team demonstrated that peripheral blood neutrophil NET release correlated with GSDMD in patients experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).384 Using an intratracheal LPS-induced mouse model of ARDS, lung NET accumulation and ARDS injury were significantly attenuated in neutrophil-specific GSDMD knockout mice or DSF-treated WT mice, demonstrating a significant association between the progression of lung injury in ARDS and the accumulation of NETs mediated by GSDMD. In combination with the study of ref.,52 GSDMD-induced NETosis emerges as a pivotal mechanism in the development of lung injury. Moreover, Ma et al. illustrated that after infection, the nucleocapsid of SARS-CoV-2 could inhibit host pyroptosis and counteract cellular inflammatory responses by blocking the cleavage of GSDMD.385 The nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds to the GSDMD linker region in infected monocytes and hinders caspase-1-mediated processing of GSDMD, restraining GSDMD cleavage and leading to reduced IL-1β secretion, despite enhanced IL-1β expression at this time. This further explains the close association of GSDMD with anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity, as the virus has also evolved this mechanism to avoid GSDMD cleavage.
Table 3.
FDA-approved drugs and clinical trials related to gasdermins
| Clinical trial | FDA-approved drugs | Dose and schedule | Indication | Enrollment | Study Start/ Completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04594343 (phase 2) | Disulfiram | 500 mg disulfiram orally or enterally daily for 14 days | Hospitalized subjects over the age of 50 with a diagnosis of moderate COVID-19 | 140 | 2020-11-20/2021-09-25 |
| NCT04485130 (phase 2) | Disulfiram | Oral disulfiram for 5 consecutive days (cohort 1, 1000 mg/day; cohort 2, 2000mg/day) | COVID-19 patients with early mild to moderate symptoms | 11 | 2021-08-18/2022-02-28 |
| NCT04381936 (phase 2/3) | Including but not limited to dimethyl fumarate | Not mentioned | COVID-19 Inpatients | 50,000 (estimated) | 2020-03-19/ 2032-11 (estimated) |
In NCT04381936, dimethyl fumarate has been shown to have no beneficial effect on COVID-19 inpatients and recruitment for this drug has been stopped
In addition to the widely publicized SARS-CoV-2, the function of GSDMD in swine enteric coronavirus infections has been tentatively explored, such as enteric coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV), and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV). TGEV and PDCoV upregulate and activate GSDMD, leading to post-infectious pyroptosis.386 Knockdown of GSDMD or pharmacological inhibition of GSDMD reduces IFN-β release, suggesting that GSDMD is associated with its ability to facilitate the non-conventional secretion of IFN-β, which enhances the IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) response. The 3C-like protease Nsp5 of PEDV is capable of cleaving porcine GSDMD at the Q193-G194 site to generate two fragments that lack the capacity to initiate pyroptosis, thereby promoting the propagation of the virus at the initial stage and sustaining PEDV infection.387 Notably, GSDMD also serves a critical role in non-coronavirus infection. The protein S273R encoded by the African swine flu virus (ASFV) specifically cuts GSDMD at the G107-A108 site, producing a short segment of the GSDMD-NT domain (GSDMD-N1-107) composed of residues 1 to 107, which fails to activate pyroptosis or curtail the replication of ASFV.388 When infected with enterovirus 71 (EV71), the viral protease 3C specifically targets Q193-G194 sites on GSDMD, facilitating proteolytic cleavage, which is protease-dependent and produces a short N-terminal segment across aa 1–193 (GSDMD1-193) that lacks the ability to elicit cell death or impede the replication of EV71.389 These studies reveal a possible mechanism by which ASFV and EV71 evade antiviral responses.
Excessive inflammatory response and damage to tissues under influenza virus attack may progress to severe lung disease.390 Influenza A virus (IAV) triggers activation of GSDMD in lung epithelial cells, exacerbating pathological changes in the lungs and accumulation of immune cells. GSDMD−/− mice show greater resistance to IAV infection, as evidenced by attenuated neutrophil recruitment and chemotaxis, reduced epithelial damage and cell death, and increased survival.391,392 In addition, the H7N9 influenza virus is able to activate GSDME, leading to pyroptosis of alveolar epithelial cells and triggering cytokine storms in the lung.393 Through the targeted deletion of GSDME, the cell death mechanism in alveolar epithelial cells infected with the H7N9 virus is transformed from pyroptosis to apoptosis. GSDME−/− mice results in a notable reduction in lung inflammation and a substantial increase in survival rates when exposed to a lethal dose of the H7N9 virus.393 Recently, activation of GSDME has also been found to be associated with Zika virus (ZIKV), foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), and oncolytic parapoxvirus ovis (ORFV) infections. ZIKV activates GSDME via TNF-α/caspase-8/caspase-3, causing a significant increase in GSDME activation and in placental cell pyroptosis.394 FMDV 3Cpro cleaves the Q271-G272 junction of porcine GSDME to trigger pyroptosis, a pathway that is not contingent upon caspase-3.395 ORFV attack activates GSDME-induced pyroptosis by decreasing the ubiquitination of GSDME.396 Reducing the expression of GSDME both reduces these virus-induced pyroptosis and improves the disease phenotype.
The above findings hint that the pore-forming activity of GSDMs can effectively inhibit virus replication and immune escape in various virus infections, thus accounting for the evolutionary adaptation of viruses to deploy various strategies to evade GSDM activation. GSDMs may represent a novel therapeutic candidate for refining the management of virus infections, but the precise mechanisms require comprehensive further investigation.
Cancers
There is mounting evidence supporting the potential involvement of GSDMD in diverse cancers. NLRP3/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis pathway has been implicated in the progression of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC),397,398 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC),399 ovarian cancer,400 and colorectal cancer.401,402 GSDMD is observed in differentiated cells of gastric cancer (GC) and exhibits colony formation inhibitory activity, potentially inhibiting cell proliferation.153 GSDMD is also implicated in the invasive and metastatic potential of colorectal cancer cells and is a negative regulator.403 Moreover, GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis has an immunostimulatory effect, being essential for enhanced spontaneous anti-tumor immune responses and increased sensitivity to anti-PD-1 blockade in mixed-lineage leukemia 4 (Mll4)−/− melanoma.404 The underlying mechanism of GSDMD-mediated anti-tumor activity has been partially elucidated. According to Wang et al., silencing GSDMD expression in gastric cancer (GC) cells enhanced their proliferation and tumourigenesis in nude mice. This downregulation activated the PI3K/AKT, STAT3, and ERK1/2 signaling cascades, which in turn modulated the expression of CDK-2 and cyclin A2, leading to an acceleration of the S/G2 cell cycle transition. These findings suggest that GSDMD functions as a suppressor of GC cell proliferation.405 Xi et al. demonstrated that GSDMD facilitates the cytotoxic activity of T lymphocytes (CTLs) against cancer cells, primarily by delivering the contents of cytotoxic granules into the immune synapse established with the tumor cells.406 Elevated levels of GSDMD processing within CTLs, concomitant with the proximity of GSDMD to granzyme B, are detected in the perimeters of the immune synapse, and GSDMD knockdown decreases cytotoxicity of CTLs. They propose that GSDMD may be essential for the robust activation of CTLs against cancer cells, although the role of GSDMD in CTL remains undefined.406 Remarkably, GSDMD also exhibits pyroptosis-independent roles in the context of cancer. Peng et al. suggested that under specific stress conditions, such as hypoxia or cytotoxic treatment, GSDMD is directed to the nucleus to promote apoptosis, which has been correlated with positive clinical outcomes in cases of colorectal cancer. After nuclear translocation, GSDMD engages in a complex with poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1), significantly suppressing the function of PARP-1 on DNA damage repair, thereby functioning as a tumor suppressor to enhance apoptosis in cancer cells.407 They concluded that the subcellular distribution of GSDMD could potentially help guide the treatment of colorectal cancer.
Conversely, GSDMD is prominently enhanced in NSCLC and is thought to initiate cancer. Knockdown of GSDMD inhibits cancer growth in vivo and in vitro, concurrent with the activation of caspase-3 and PARP cleavage, and enhances cancer cell death via the mitochondrial intrinsic apoptotic pathway.408 Furthermore, high GSDMD expression in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) implies a poor prognosis relative to lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). Lv et al. identified high GSDMD expression as a promoter of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development.409 The HMGB1/TLR4/caspase-1 pathway is involved in the upregulation and processing of GSDMD. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) activation is inhibited by GSDMD-NT through the efflux of K+ to promote autophagy, and by histone deacetylase/STAT1 through the influx of Ca2+ to induce transactivation of PD-L1 to promote PD-L1 expression. GSDMD−/− or WT mice treated with a combination of the GSDMD inhibitor DMF and an anti-PD-1 antibody showed reduced liver tumors and decreased PD-L1 expression.409 Consequently, the authors proposed that an approach encompassing both anti-PD-1 and GSDMD inhibitors could be effective in treating HCC with upregulated GSDMD. Similarly, a combined GSDMD/PD-L1 suppressive immunotherapy in improving anti-tumor immunity was also suggested by Jiang and colleagues.410
GSDMD is enriched in TME antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and is associated with immune checkpoint characteristics. By conditionally deleting GSDMD, Jiang et al. demonstrated that GSDMD within APCs limited anti-tumor immunity when PD-L1 was inhibited, suppressed ISG expression through targeting the cGAS signaling, and thus inhibited the capacity of macrophages and DCs in presenting tumor-related antigens as well as CD8 T cell activity. Pharmacological inhibition of GSDMD with DMF in conjunction with anti-PD-L1 treatment markedly reduces tumor load and improves survival in melanoma mice.410 These studies provide new insights for combination therapy for cancers that, while anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 therapy is effective, numerous patients do not respond to this treatment.
IL-33 is recognized as a tumor-promoting cytokine, and Yamagishi et al. elucidated the mechanism underlying which IL-33 was exported from senescent hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) through the GSDMD pores in a mouse model of HCC induced by obesity.224 In the tumor microenvironment, caspase-11 cleavage is induced by lipoteichoic acid (LTA) in senescent HSCs, and GSDMD-NT forms pores in PM, releasing IL-33 and IL-1β. IL-33 cleaved by elastase CELA1 promotes the development of HCC through the activation of ST2-positive Treg cells.224 DSF treatment markedly curtails the secretion of IL-1β and IL-33 and suppresses hepatic tumor formation, suggesting the potential of inhibitors targeting the pore-forming process of GSDMD in the treatment of HCC.
Other GSDMs have been shown to be potentially associated with a multitude of cancers.411,412 Analyses of multiple bioinformatics databases demonstrate the involvement of GSDMs in HCC and clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), with increased expression of GSDME correlating significantly with reduced overall survival in HCC and ccRCC patients.411,412 Studies have highlighted the engagement of GSDME in the pyroptotic demise of melanoma cells. Inhibition of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF-2K) can inhibit autophagy and promote GSDME-mediated pyroptosis, which in turn modulates the susceptibility of melanoma cells to doxorubicin.413 ROS in the presence of iron have been implicated in triggering pyroptosis in melanoma cells via the Tom20-Bax-caspase-GSDME pathway.187 Inducing tumor pyroptosis to promote anti-tumor immunity is a potential cancer treatment strategy. Various drugs for cancer treatment act in part through caspase-3/GSDME-mediated tumor cell pyroptosis, including triptolide,414 mesothelin-targeting antibody-drug conjugate,415 apoptin,416 platinum-based drugs,417,418 tetraarsenic hexoxide,419 and alantolactone.420 GSDME knockout or knockdown may mitigate the anti-tumor potency of these agents. Similarly, GSDME-mediated pyroptosis also determines the effectiveness of radiotherapy for cancer treatment.421 Remarkably, cancer cells also use GSDME for their own survival strategies. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), cells deploy GSDME to enhance mucin 1 and mucin 13 secretion, effectively establishing a protective barrier against the digestion enzyme chymotrypsin.422 This regulatory function of GSDME is distinct from its pyroptosis-inducing function, instead involving a regulatory mechanism where it interacts with and facilitates the nuclear translocation of the transcription factor Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1), which then directly enhances the expression of mucins.
In addition, researchers have uncovered a pivotal role for the post-translational modifications of GSDME in therapeutic interventions. Examination of multiple prostate cancer cohorts reveals that CDC20 interacts with GSDME and undergoes ubiquitination-mediated protein hydrolysis to negatively regulate tumor cell pyroptosis.305 The CDC20 small molecule inhibitor apcin exhibits synergistic effects with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. The Dub USP48 promotes pyroptosis and enhances anti-tumor immunity by stabilizing GSDME. Mechanistically, USP48 binds GSDME and removes the k48-linked ubiquitination marks at positions K120 and K189. Pharmacological modulation of USP48 could represent a potent approach to trigger tumor cell pyroptosis.307 Similarly, OTUD4 deubiquitinates and stabilizes GSDME to enhance the sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiotherapy by promoting pyroptosis.306 These insights underscore the critical function of pyroptosis in the body’s offensive against tumors. However, the very mechanisms that make pyroptosis a potent anti-tumor weapon—its ability to eliminate tumor cells—also pose a challenge. The activation of this pathway by chemotherapeutic agents can lead to unwanted collateral damage to healthy tissues. Ai et al. reported that during chemotherapy, mannose activates AMPK to inhibit GSDME-mediated pyroptosis, exerting a protective effect in the kidney and small intestine. Activated AMPK subsequently phosphorylates the Thr6 site of GSDME, thereby blocking the cleavage of GSDME induced by caspase-3 and thus inhibiting pyroptosis.311 This provides a new target for mitigating adverse reactions induced by chemotherapy in the clinic.
Downregulation of GSDMA significantly enhances the proliferation and invasive potential of esophageal cancer cells, a phenomenon that is intricately linked to changes in cell sensitivity to cisplatin.423 In individuals with HER2+ breast cancer, elevated levels of GSDMB correlate with reduced survival rates and an increased propensity for metastatic progression.165,166 It is shown that upregulation of GSDMB can confer resistance to therapeutic interventions in HER2+ cancer cells through activation of the protective autophagy pathway, in which the interaction of GSDMB-NT with LC3B and Rab7 is critical for the activation of pro-survival autophagy.424 Intracellular delivery of antibodies targeting GSDMB using hyaluronan-coated nanoparticles reduces the invasiveness of HER2+ breast cancer.425 Similarly, GSDMC may act as an oncogene, and its expression is upregulated in lung adenocarcinoma, melanoma, and colorectal cancer, promoting tumor progression and spread.17,168,426 However, it has also been suggested that GSDMC-mediated pyroptosis can exert anti-tumor activity.35 Collectively, the above findings suggest that GSDMs function in the development of various cancers, whether it plays an inhibitory or promotional role. The role played by GSDMs in cancer varies according to the environment, varying among different GSDM isoforms and cancer entities, underscoring the complex interplay between inflammation and tumourigenesis, cell proliferation, as well as anti-tumor immune responses.427,428 Further understanding of the functions of GSDMs, both pyroptosis-dependent and pyroptosis-independent, as well as its role in tumor immune checkpoints such as PD-1/PD-L1, may potentially impact the combination therapy strategies for tumor.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases have also been linked to inflammasome activation and GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis.429,430 AS is a chronic condition characterized by dysregulated inflammation, lipid accretion, plaque development, and intimal hypertrophy, with a complex pathogenesis in which inflammation is fundamentally involved in the formation of AS.431,432 Inflammation inhibits reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) to promote AS, and interventions targeting IL-1β have demonstrated potential in mitigating cardiovascular disease risks in clinical settings.433 Opoku et al. suggested that GSDMD inhibited RCT and promoted AS in hyperlipidemic mice, and the possible mechanism is that macrophage GSDMD accelerated the formation of foam cells through an IL-1β-dependent manner. GSDMD−/− macrophages maintain high cholesterol efflux activity through reducing IL-1β release and translocation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P(2)) to the cell surface, as well as reducing pyroptosis, and potentially tipping the equilibrium toward a more beneficial apoptotic cell death pathway.434 In addition, macrophage GSDME is involved in the pathogenesis of AS. ox-LDL stimulates GSDME expression, possibly by a mechanism whereby STAT3 binds to the GSDME promoter and activates its transcription. Subsequently, caspase-3-mediated cleavage of GSDME promotes pyroptosis and inflammation. GSDME deficiency attenuates macrophage pyroptosis and AS lesions.195
Not only macrophage pyroptosis is implicated in the initiation and advancement of AS, but endothelial dysfunction due to endothelial cell pyroptosis is also part of the pathogenesis of AS. For example, ox-LDL-induced upregulation of Hsa_circ_0090231 (circ-USP9×) levels within endothelial cells cytoplasm leads to pyroptosis. The interaction between circ-USP9× and EIF4A3 in the cytoplasm enhances the stability of GSDMD mRNA, which increases GSDMD expression and promotes endothelial cell pyroptosis. Knockdown of circ-USP9× expression using siRNA inhibits pyroptosis through eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III (EIF4A3)-mediated GSDMD.435 Fan et al. reported that in endothelial cells, activation of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway triggers GSDMD-driven pyroptosis, promoting the development of AS.436 NLRP3 inflammasome signaling activates the non-canonical NF-κB transcription factor complex RelB/p52 to potentiate the expression of IRF1. IRF1 interacts with the GSDMD promoter-526/515 sites and caspase-1 promoter-11/10 sites to enhance the expression of GSDMD and its activation mediated by caspase-1.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a prevalent vascular condition marked by cellular physiological modifications driven by active metabolites.437,438 Gao et al. demonstrated that vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC)-specific GSDMD defects reduced the incidence of AAA in a mouse model.439 Mechanistically, GSDMD enhances ER stress-CHOP signaling, which subsequently stimulates the expression of ornithine decarboxylase 1 (ODC1), an enzyme that mediates an increase in putrescine levels. High putrescine triggers a pro-inflammatory switch in VSMCs and increases the vulnerability of mice to the development of Ang II-induced AAA. This reveals that GSDMD affects VSMC activity through a novel mechanism that is independent of pyroptosis, as GSDMD siRNA does not alter LDH release.439 They suggest that targeting GSDMD and putrescine may represent a novel therapeutic avenue for the treatment of AAA.
Cardiomyocyte injury can result from numerous factors, including endotoxin-induced inflammation, myocardial infarction (MI), ischemia/reperfusion (I/R), and doxorubicin (Dox) administration.440 In LPS and Nigerian bacteriocin-stimulated cardiomyocytes, Yu et al. suggested that GSDMD-NT translocated from mitochondria to cytoplasmic membranes in a time-dependent manner.56 In mitochondria, GSDMD-NT is capable of binding to LC3B, and GSDMD-induced mitochondrial damage results in inhibition of autophagic fluxes. Enhanced mitophagy in GSDMD−/− cardiomyocytes provides protection against LPS-induced cardiomyocyte damage. They propose that GSDMD-NT-induced mitochondrial injury could be attenuated by mitophagy-mediated mitochondrial quality control, and that inhibition of GSDMD or enhancement of autophagy might serve as viable therapeutic targets for the amelioration of inflammatory cardiopathy.56
MI remains a significant contributing factor to global mortality.441 Although the prompt reinstatement of blood supply to ischemic myocardial tissue effectively reduces infarct size in MI patients, the benefits of reperfusion therapy are potentially attenuated by the deleterious effects of myocardial I/R injury.442 The efflux of cytokines from pyroptotic cardiomyocytes has the capacity to stimulate innate immune signaling pathways and trigger a potent inflammatory reaction. Shi et al. identified the caspase-11/GSDMD pathway, but not the caspase-1/GSDMD pathway, as a critical event in MI injury.442 Cardiac-specific GSDMD knockout significantly reduces myocardial infarct size in a mouse I/R model. Unexpectedly, oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis releases IL-18 rather than IL-1β. They and Kawaguchi et al. suggested that IL-1β expression originated mainly from fibroblasts.442,443 However, a different view was presented by Jiang et al.444 They suggested that GSDMD is predominantly expressed in leukocytes within the heart tissue, as opposed to other cell populations. Activation of GSDMD occurs early following AMI and is instrumental in enhancing neutrophil synthesis and recruitment to the site of myocardial damage. Elimination of GSDMD through genetic knockout or pharmacological intervention in murine models has been shown to lessen myocardial damage, decrease the size of the infarct, and enhance cardiac function and survival rates. The production and activation of bone marrow-derived neutrophils, which are GSDMD-dependent, are implicated in the detrimental immunopathology that follows AMI.444 The findings imply that GSDMD could represent a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Zhong et al. employed a combination of virtual screening, followed by pharmacological assays, and subsequent pharmacological validation to initially identify a novel GSDMD inhibitor, termed GSDMD inhibitor Y1 (GI-Y1), which was recognized to shield cardiomyocytes from pyroptotic cell death and dysfunction, effectively inhibiting myocardial I/R injury and exerting cardioprotective effects on cardiac remodeling.445 GI-Y1 interacts with GSDMD and prevents the lipid-binding and pore-forming activity of GSDMD-NT by targeting the Arg7 residue, and may also attenuate mitochondrial damage by blocking the induced mitochondrial pore formation by GSDMD-NT.
Dox has been widely used in the treatment of numerous human malignancies, and has seen its broad application hindered due to side effects such as doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC).446 Dox significantly triggers GSDMD expression and cleavage in cardiac tissues. The absence of GSDMD has been observed to mitigate DIC in mice.446,447 Two studies suggested different mechanisms, with Ye et al. suggesting that Dox could directly engage with GSDMD, enhancing pyroptosis facilitated by GSDMD-NT, or indirectly prompt GSDMD-NT production and pyroptosis by stimulating caspase-1/11. In addition, Dox also induces mitochondrial damage and mitochondrial perforation in cardiomyocytes through Bnip3.446 Qu et al. illustrated that GSDMD-NT could form pores within ER, activating ER stress, which in turn, regulated the reticulophagy receptor FAM134B, interacting with the autophagy protein LC3 to instigate cardiac autophagy, accelerate cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and exacerbate DIC.447 Their studies confirm that GSDMD targeting and regulation may present an innovative therapeutic avenue for the prophylaxis and therapy of DIC.
Considering the above findings, it becomes evident that GSDMD exerts a crucial role in cardiovascular diseases, emerging as a promising therapeutic candidate. There is significant potential to explore the upstream transcription factors or inhibitors of GSDMD as well as the relationship between GSDMD and mitophagy and ER stress.
Neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative disorders encompass a spectrum of neurological disorders marked by a gradual erosion of neuronal architecture and function.448,449 The pathogenesis is intricate, with neuroinflammation acknowledged as a crucial driver. The elucidation of pyroptosis mechanisms has drawn attention to the connection between inflammation associated with GSDMD and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases.450,451 Notable neurodegenerative diseases encompass Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD).449 Pyroptosis is implicated in the initiation of amyloid β-protein (Aβ) aggregation and neuronal death in AD, contributing to the onset and advancement of this disorder.452 Caspase-1 inhibition by administration of VX-765 attenuates cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation in an animal model. Additionally, VX-765 prevents neuronal degeneration in vitro.453 IL-1β is intimately involved in CNS inflammation, and pyroptosis triggered by GSDMD is upregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of AD patients, releasing substantial amounts of IL-1β and exacerbating AD. DSF mitigates systemic inflammation and microglia activation in mice with LPS-induced AD, lowering peripheral blood IL-1β levels and exhibiting a significant protective effect.454 A clinical study demonstrated that GSDMD levels were elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of individuals with AD, potentially serving as a diagnostic biomarker.455 In addition, analysis of postmortem brain tissue shows that the expression of GSDMD is across a diverse array of brain cell types, including microglia, astrocytes, and neurons, and that GSDMD is cleaved not only in microglia by caspase-1, but also in astrocytes and neurons, probably through caspase-8 and caspase-4, respectively. Encountering GSDMD-NT expression in microglia and astrocytes in the immediate vicinity of Aβ deposits implies a potential influence of Aβ on the processing of GSDMD.456 These findings suggest that inflammasomes and GSDMD are involved in neuroinflammation in AD, but the roles and mechanisms of GSDMD in various cell types in AD remain unclear due to its complex pathogenesis. Investigating the intricacy and variability within the neuroinflammatory response in patients with AD could shed light on its functional implications.
The fundamental pathological feature of PD is the irreversible destruction of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons, a complexity of which remains elusive.457 GSDMD-mediated neuroinflammation, an influential contributor to PD, has lately been spotlighted. Prussian blue nanozyme (PBzyme), recently recognized as an inhibitor of pyroptosis, exhibits exceptional ROS-scavenging abilities. It inhibits the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome, lessens activated caspase-1, downregulates GSDMD cleavage and inflammatory agent release, and impedes microglia pyroptosis in PD cellular and mouse models. Consequently, it effectively mitigates motor deficit and nigral striatal neuron impairment in a mouse model of PD.458 IL-1β is able to permeate the CNS parenchyma to exacerbate neuroinflammation. In a PD experimental model, peripheral myeloid cell-derived GSDMD boosts microglial immune training via a mechanism where IL-1β, crossing the blood-brain barrier, triggers microglial cell polarization, thereby amplifying neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Moreover, inhibition of GSDMD with DSF attenuates the bacterial infection-associated PD behavioral phenotype and dopaminergic neuron loss.459 These results suggest that GSDMD represents a promising new therapeutic target for PD, but further studies are needed to confirm its therapeutic potential and to elucidate the precise mechanisms underlying its action.
Metabolic diseases
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) represents a widespread chronic liver disorder, frequently coexisting with metabolic syndrome, including hyperlipidemia, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).460–462 Several reports have suggested that NLRP3 inflammasome plays a role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD.69,463–465 GSDMD may also contribute to its progression. Xu et al. elucidated the critical role of GSDMD in the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) by mediating lipogenesis and NF-κB signaling pathway.466 GSDMD-NT expression is positively associated with the activity score and fibrosis in NAFLD. Compared to controls, patients with NAFLD/NASH exhibit elevated levels of hepatic GSDMD and GSDMD-NT proteins, with particularly heightened expression of GSDMD-NT observed in those with NASH. GSDMD silencing attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation, steatosis, necroinflammation, and fibrosis.466 These data emphasize the importance of GSDMD in the pathological progression of steatohepatitis.
IL-1β has emerged as a key driver in the exacerbation of hepatic inflammation, steatosis, injury, and fibrosis, and promotes significant production of TNF-α and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), collectively contributing to the development of NAFLD/NASH.463,467–469 In the mouse model, hepatic production of MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-1β is significantly reduced in GSDMD−/− mice. As NF-κB serves as a critical upstream controller of MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-1β expression, NF-κB signaling is inhibited in GSDMD−/− mice.466 Furthermore, GSDMD−/− mice show reduced expression of genes involved in lipogenesis and enhanced expression of genes associated with lipolysis, which attenuates hepatic steatosis.466 It is thus known that the mechanism of inhibiting GSDMD to control disease progression includes control of cytokines secretion, NF-κB activation, and lipogenesis.
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) occurs in about 40% of diabetes patients and is the primary cause of microvascular complications and end-stage renal disease.470 Numerous reviews have concluded that pyroptosis participates in the onset and progression of DN,471–474 and to a significant degree, inhibiting pyroptosis is tantamount to mitigating the harm caused by DN, and GSDMD inhibition might be an essential target. Increased expression of TLR4 and GSDMD has been observed in both patients with DN and corresponding animal models, and suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascade reduces the expressions of caspase-1 and GSDMD, indicating its involvement in GSDMD-associated pyroptosis in DN.475,476 Moreover, TLR4 can exacerbate DN tubular injury and fibrosis through the canonical pyroptosis pathway. GSDMD activation inhibits apoptosis and induces pyroptosis, potentially representing a switch mechanism between switch between TLR4-induced pyroptosis and apoptosis in the context of DN.476
Podocytes are an important target of injury in the early stages of DN, with their degeneration and loss being intimately linked to the manifestation of proteinuria.477 In diabetic mice, renal podocytes exhibit markedly heightened expression levels of caspase-11 and GSDMD-NT, concomitant with an amplified release of IL-1β and IL-18. The alterations observed in diabetic mice are mitigated by the genetic ablation of caspase-11 or GSDMD. Conversely, the silencing of caspase-4 or GSDMD via siRNA significantly reduces pyroptosis-associated modifications in vitro.478 Compared to WT mice, GSDMD−/− mice showed reduced pyroptosis and improved kidney injury-related indices.478,479 In addition, glomerular endothelial cell (GECs) injury emerges as a pivotal pathological process during the early stages of DN. The non-canonical pyroptosis pathway leads to GECs damage and further aggravates the development of DN. Interference with GSDMD expression ameliorates renal pathology.480 These studies highlight the involvement of GSDMD in pyroptosis-induced DN, but the specific mechanisms deserve further exploration.
Autoimmune diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), including conditions such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, represent chronic inflammatory conditions that primarily impact the gastrointestinal axis.481 IBDs are believed to arise from inappropriate and sustained inflammatory responses to commensal microorganisms in genetically susceptible hosts.481,482 Some evidence suggests the involvement of pyroptosis in IBDs. In the model of colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS), NLRP3 inflammasome emerges as a central regulator driving intestinal inflammation. TLR4/NF-κB activation triggers NLRP3 inflammasome activation, which regulates pyroptosis of IECs and DSS-induced chronic colitis in mice.483 Elevated expression of epithelial-derived GSDMD has been detected in both IBD patients and experimental colitis.271 In colitis models, knockout of GSDMD or pharmacological inhibition of GSDMD attenuates colitis severity compared to WT mice.271,483–486 GSDMD is expressed in colitis IECs, and GSDMD-NT fosters IL-18 release, resulting in the loss of cupped cells and induction of colitis.483 The non-pyroptotic function of full-length GSDMD in guiding the generation of small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) enriched for IL-1β in IECs has been suggested as a contributory factor in intestinal inflammation, and this GSDMD-dependent non-pyroptotic role appears to be coupled with the activation of caspase-8.271 Moreover, inhibition of caspase-8/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis of epithelial cells has a preventive effect on intestinal inflammation.484 It has been proposed that the efficacy of colitis treatment can only be optimized by concurrently disrupting both GSDMD and GSDME.485 Paradoxically, Ma et al. reported that macrophage-specific GSDMD deficiency, but not epithelial cell-specific GSDMD deficiency, exacerbated experimental colitis.487 The mechanism may be that GSDMD acts as a negative modulator within macrophages to control cGAS-dependent inflammation, thereby preventing colitis. Furthermore, GSDMB also acts as a pivotal player in the pathology of IBD. It serves as a crucial element in reestablishing epithelial barrier integrity and reducing inflammatory responses.48 Interestingly, its function in this context is not dependent on pyroptosis. The absence of GSDMB results in enhanced cellular adhesion, an issue that hinders the vital processes of epithelial restoration and repair, fundamental to mucosal wound healing. The underlying mechanism involves the GSDMB knockout-induced inactivation of FAK through PDGF-A-dependent pathways, leading to an upsurge in the formation of actomyosin stress fibers.48 FAK stands as a critical tyrosine kinase governing the transition of focal adhesions and their engagement with the cytoskeleton, whereas PDGF-A regulates FAK phosphorylation.488–491 These results suggest a role for GSDMs in the pathogenesis of IBD, but the functional mechanisms may differ among various cell types, warranting further investigation.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the joints that results in erosion of cartilage and bone, culminating in disability. Excessive inflammatory cytokines contribute to the pathogenesis of RA.492,493 In patients with RA, synovial fluid exhibits heightened concentrations of IL-1β and IL-18, with macrophages displaying increased expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and GSDMD-NT.494 Furthermore, the NLRP3 inflammasome within monocytes is triggered in patients with RA, inducing GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis and the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. In turn, IL-6 exacerbates RA-derived monocyte pyroptosis.495 Although the understanding of NLRP3 activation in RA pathogenesis has been summarized,496 the function and underlying mechanisms of GSDMD in this context are still elusive.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, inflammatory, and demyelinating disorder of CNS, whose exact etiology is yet to be fully understood. It represents the most prevalent non-traumatic cause of disability among young adults.497,498 Its pathogenesis is complex, and recent evidence suggests that pyroptosis-driven inflammation may be critical in MS.497,499–501 GSDMD-mediated inflammasome activation and pyroptosis can occur in myelin-forming oligodendrocytes (ODCs) and microglia within the CNS of MS individuals, as well as in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model.500 The administration of VX-765 to EAE models reduces pyroptosis-related protein levels within the CNS, prevents axonal damage, and improves neurological function.500 GSDMD−/− mice are protected from EAE, with the absence of GSDMD in peripheral myeloid cells of EAE mice significantly impeding the migration of immune cells into the CNS. Consequently, this results in attenuated neuroinflammation and demyelination.502 Three inhibitors of GSDMD protect against EAE. DSF treatment inhibits the progression of EAE and greatly reduces clinical and histopathological scores.502 DMF impedes the development of EAE and reduces neuropathology and demyelination.46 C202-2729, a recently identified GSDMD inhibitor, significantly inhibits the aggregation of immune cells and demyelination within the spinal cord of EAE.503 These investigations corroborate the concept that GSDMD-induced pyroptosis serves as a determinant in the pathogenesis of MS.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) represents a complex autoimmune condition marked by the breakdown of tolerance to nucleic acids, resulting in widespread damage to peripheral organs throughout the body.504,505 Robust increases in the expression of GSDMD and IL-1β mRNA are observed in PBMCs from patients with SLE. DSF treatment potently inhibits serum from SLE patients-induced THP-1 pyroptosis.506 DSF mitigates elevated levels of serum IL-1β and GSDMD-mediated glomerular macrophage pyroptosis as well as the infiltration of inflammatory cells, proliferation of tethered cells, and structural disorders of renal tubules in pristane-induced lupus (PIL) mice.506 In addition, neutrophil NET promotes the development of SLE. In neutrophils, SLE serum immune complexes (ICs) and IFN-γ promote GSDMD activation through the serpinb1 and caspase-1/11 pathway. Simultaneously, these ICs induce mitochondrial stress and the extrusion of ox-mtDNA into the cytoplasm. Cytosolic ox-mtDNA binds to GSDMD-NT, promoting its oligomerization and pore formation. This sequence of events ultimately contributes to the pathogenesis of SLE through the externalization of NETs and mtDNA. The abrogation of neutrophil-specific GSDMD or the therapeutic administration of DSF substantially mitigates disease severity in the PIL mouse model.254 However, there are conflicting perspectives. Wang et al. suggested that GSDMD deficiency resulted in higher mortality, exacerbated renal and pulmonary inflammation, and increased production of autoantibodies within PIL mice.507 GSDMD negatively regulates auto-antigen production and immune dysregulation following organ damage, potentially exerting a previously unrecognized protective influence on systemic autoimmunity.
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) represents the prototypical monogenic autoinflammatory disorder, arising from a missense alteration in the Mefv gene that triggers the pyrin inflammasome. In a mouse FMF model, GSDMD−/− mice exhibited complete protection from systemic inflammatory cytokines production, weight loss, splenomegaly, and liver damage,258 and pharmacological inhibition of GSDMD achieved similar protective effects.46
Therapeutic targets regarding gasdermins
GSDMD inhibitors
As previously described, the silencing or knockout of GSDMD has been demonstrated to exert a protective effect across diverse animal models of inflammatory disorders. In comparison to the selective inhibition of NLRP3 or inflammatory caspases or IL-1β, the inhibition of GSDMD may prove to be more efficacious in inflammatory diseases due to its ability to prevent the subsequent pyroptosis of all inflammasomes. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of pyroptosis mediated by GSDMD could emerge as a promising strategy for the amelioration and control of inflammatory diseases. Here, we provide an overview of several GSDMD inhibitors (Table 4) that have different mechanisms (Fig. 5).
Table 4.
GSDMD inhibitors
| Inhibitor | IC50 | Mechanisms of action | Off-target effects | GSDMD-related disease model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Necrosulfonamide (NSA)44,509–511 | ~10 μM | Binding directly to Cys191 of GSDMD and inhibiting the oligomerization of GSDMD-NT | Binding to Cys86 of MLKL and blocking necroptosis | LPS-induce sepsis, AD, AS, ALF |
| Disulfiram (DSF).45,52,383,384,514,516–519. | ~10 μM | Modifying Cys191 of GSDMD and inhibiting the oligomerization of GSDMD-NT |
Modifying Cys133 in the TLR-binding partner MD-2 and preventing LPS recognition; Inhibiting NLRP3 signaling |
LPS/CLP-induced sepsis, ulcerative colitis, AS, obesity and metabolic dysfunction, SARS-CoV-2 infection, ARDS, DN, NAFLD |
| Dimethyl fumarate (DMF)46,409 | <10 μM | Succinating Cys191 of GSDMD, blocking caspase-GSDMD interactions and inhibiting the oligomerization of GSDMD-NT | Succinating GSDME at Cys45; dopamine beta-hydroxylase; caspase-1; caspase-3 | LPS-induced sepsis, FMF, EAE, HCC |
| Itaconate320,523,531–533 | Not known | Binding to GSDMD via Cys77 and blocking caspase-GSDMD interactions | Inhibiting NLRP3 and caspase-1 | ARDS, IBD, LPS-induced sepsis |
| C202-2729503 | Not known | Binding directly to the GSDMD-NT and inhibiting the oligomerization of GSDMD-NT | Not known | EAE |
| Caffeic acid (CA)522 | Not known | Binding directly to GSDMD and blocking GSDMD cleavage | Not known | LPS-induced sepsis |
| GSDMD inhibitor Y1 (GI-Y1)445 | Not known | Binding to GSDMD via Arg7 and inhibiting the oligomerization of GSDMD-NT | Not known | Myocardial I/R injury |
AD Alzheimer’s disease, AS atherosclerosis, ALF acute liver failure, ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome, CLP cecum ligation and puncture, DN diabetic nephropathy, EAE experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, FMF familial Mediterranean fever, HCC hepatocellular carcinoma, IBD inflammatory bowel disease, I/R ischemia/reperfusion, LPS lipopolysaccharide
Fig. 5.
Strategies for managing GSDMD-related disorders. The activation targeting steps of GSDMD and the functioning mechanisms of existing GSDMD inhibitors are illustrated. Three potential approaches to suppress GSDMD activation are suggested: (i) preventing mutual recruitment of GSDMD and inflammatory caspases; (ii) degrading GSDMD through post-translational modifications; (iii) eliminating GSDMD pores from cell membranes to promote membrane repair. Further details can be found in the text
Necrosulfonamide
NSA is the first demonstrated inhibitor that directly targets GSDMD,44 although it was initially discovered to bind to Cys86 of MLKL, disrupting the disulfide bond and thereby blocking MLKL-associated necroptosis.508 NSA inhibits inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis by directly combining with GSDMD Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) and inhibiting the oligomerization of GSDMD, without affecting GSDMD cleavage or initial dimerization. A noteworthy observation is that NSA treatment is more effective than the Cys191Ala mutation, possibly because NSA activity refers to potential steric interference to oligomerization.44 Furthermore, follow-up studies in other models have demonstrated that NSA can also suppress the proximal events of pyroptosis, including LPS-induced gene transcription and caspase-1 activation,45,259 indicating that it is not entirely specific for GSDMD. The administration of NSA effectively diminishes the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and enhances survival in mice subjected to endotoxin shock.44 The inhibitory effects of NSA have been the subject of comprehensive investigation in various disease models, yielding promising outcomes.509–513 Nonetheless, the prolonged utilization of NSA, beyond its role as a research tool, is curtailed by several potential factors, including its unique mechanism of action, its capacity to inhibit necroptosis in mice, and the challenges in obtaining clinical approval.
Disulfiram
DSF, a therapeutic agent employed for managing chronic alcoholism through targeting aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), has established a robust safety profile over numerous decades of utilization and is currently being actively considered for repurposing. Hu et al. employed a high-throughput screening approach, utilizing a fluorescent liposome leakage assay, to explore the possibility that DSF might serve as a GSDMD inhibitor, thereby preventing the onset of pyroptosis.45 The cellular IC50 values of DSF for inhibition of human canonical pyroptosis and mouse non-canonical pyroptosis are 7.7 ± 0.3 μM and 10.3 ± 0.5 μM, respectively. DSF potently inhibits the formation of GSDMD pores both in vitro and in vivo, as well as intracellularly, while exhibiting minimal influence on the early stages of pyroptosis. Notably, DSF does not inhibit GSDMD or IL-1β cleavage. Mechanistically, DSF modifies Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) to render GSDMD-NT incapable of pore-forming. Modification of other cellular targets by DSF does not result in significant clinical toxicity, and thus numerous studies have reported its potential application in inflammatory diseases. DSF has demonstrated its therapeutic utility across diverse animal disease models, including LPS/CLP-induced sepsis,45,52,514 ulcerative colitis,514,515 AS,516 obesity and metabolic dysfunctions,517 SARS-CoV-2 infection,383 ARDS,384 DN,518 and NAFLD.519 Furthermore, certain clinical trials have substantiated the anti-inflammatory attributes of DSF. In a self-controlled clinical trial (ChiCTR2100048035), DSF demonstrated an ability to modulate the human gut microbiota.519 Additionally, DSF potentially mitigated the occurrence and the extent of COVID-19, resulting in its evaluation in two subsequent phase II clinical trials (NCT04485130 and NCT04594343, Table 3).520 It is noteworthy that DSF exerts its effects not only by inhibiting GSDMD pore formation but also by altering Cys133 in MD-2, a TLR-binding partner, thereby preventing LPS recognition.521 Consequently, DSF robustly inhibits both extracellular and intracellular LPS-triggered innate immune responses.
Dimethyl fumarate
DMF, approved by the FDA for the therapeutic intervention of MS, has recently been demonstrated to be a GSDMD inhibitor, but it was previously considered not to modulate GSDMD-mediated lipid permeability.45 Humphries et al. demonstrated that the introduction of DMF into cells or the endogenous presence of DMF impedes the assembly of GSDMD pores and thus inhibited pyroptosis.46 The underlying mechanism involves DMF binding to GSDMD Cys191/Cys192 (human/mouse) and preventing caspase-1/GSDMD interaction rather than caspase-1 cleavage, ultimately blocking GSDMD cleavage, oligomerization, and cell death. DMF treatment also modifies other GSDMD cys residues, suggesting that succination may have additional off-target effects. In addition to inhibiting GSDMD, DMF also succinates GSDME at the Cys45 site to block GSDME cleavage and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis. DMF has been used across a spectrum of animal models of inflammatory diseases to reduce the severity, including LPS-induced sepsis,46,522 FMF,46 EAE,46 and HCC.409
Itaconate
Itaconate emerges as a distinct regulatory metabolite in myeloid cells following TLR activation, functioning as an intrinsic modulator that curtails the progression of inflammasome activation and pyroptotic cell death. The post-translational modification function of endogenous itaconate on GSDMD was elucidated by Bambouskova et al. Itaconate blocks caspase-1 activation and GSDMD cleavage and enhances cellular tolerance to prolonged LPS stimulation.320 Mechanistically, itaconate binds to GSDMD via Cys77, which has previously been shown to be essential for the oligomerization process and may interfere with caspase/GSDMD interactions, thereby inhibiting pyroptosis. However, research has also demonstrated that itaconate inhibited NLRP3523 and caspase-1,320 suggesting that its inhibitory effects on pyroptosis are non-specific and may not solely target GSDMD.
C202-2729
C202-2729, an unreported small molecule, has recently been recognized as an inhibitor of pyroptosis. A virtual screen of ChemDiv compounds conducted by Cao et al. revealed that C202-2729 potently inhibits inflammation, manifesting robust anti-inflammatory activity in mouse models of endotoxin shock and EAE.503 C202-2729 does not affect either the cleavage of GSDMD or the initiation of inflammasome activation upstream. Instead, it physically associates with the GSDMD-NT, preventing its movement to the PM and the subsequent formation of pores, thereby inhibiting the release of mature IL-1β. The proposed mechanism suggests that C202-2729 could engage with the GSDMD-NT through interactions with Tyr-54 and Lys-235, although this has not been experimentally confirmed.
Caffeic acid
Considering the effectiveness and relative safety of natural compounds, Liu et al. explored the effects of natural compounds on pyroptosis. They found that caffeic acid (CA) inhibited canonical pyroptosis and non-canonical pyroptosis, contributing to the mitigation of LPS-induced sepsis in mice.522 The inhibitory effect of CA on pyroptosis is not contingent upon its influence on cellular lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial functionality, or the expression of genes pertinent to pyroptosis. Mechanistically, CA prevents pyroptosis by directly binding to and blocking the processing of GSDMD, thereby diminishing the formation of GSDMD pores and the subsequent release of cellular contents. CA interacts with GSDMD-NT, possibly through the formation of hydrogen bonds with key residues, such as Asp22, Lys52, Tyr55, and Arg54.
GI-Y1
GSDMD inhibitor Y1 (GI-Y1), named by Zhong et al., was screened for pyroptosis inhibition from a library of seven commercial compounds using virtual and pharmacological screening and subsequent in vitro and in vivo pharmacological validation.445 GI-Y1 demonstrates selectivity for GSDMD, inhibiting GSDMD cleavage and membrane binding of GSDMD-NT, without affecting caspase-1, caspase-11, or GSDME activation. By targeting Arg7 residues, GI-Y1 inhibits the interaction between PM and GSDMD-NT and decreases the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, thereby increasing the sepsis survival rate and providing protection against myocardial I/R injury and cardiac remodeling in mice. Furthermore, GSDMD-NT interacts with mitochondria and causes mitochondrial permeabilization, leading to mitochondrial oxidative stress,524 and GI-Y1 effectively inhibit mitochondrial binding and mitochondrial damage by GSDMD-NT.
The discovery of the above inhibitors and animal studies indicate that blocking pyroptosis associated with GSDMD can effectively improve diverse disease models, thus corroborating GSDMD as a prospective drug target. Since 2018, at least three direct pharmacological inhibitors (NSA, DSF, DMF) have been demonstrated to suppress pyroptosis and subsequent inflammation via modulating GSDMD cleavage or interfering with GSDMD pore formation, which are predominantly mediated by covalent modification of residue Cys191. Nonetheless, these three extensively studied molecules exhibit a lack of specificity, as numerous proteins have active sulfhydryl groups in vivo. Consequently, covalent modification of sulfhydryl groups on various targets, in addition to upstream caspases and GSDMD, could potentially result in deleterious side effects. This limitation could potentially curtail their future application. It is likely that other mechanisms for inhibiting the binding of GSDMD and inflammatory caspases, post-translational modifications to degrade GSDMD, and modulation of GSDMD pore formation are plausible avenues for discovery, which could yield attractive drug targets (Fig. 5).
Furthermore, the development of GSDMD inhibitors might be encumbered by several drawbacks: (i) GSDMD typically operates as a non-singular pivotal signaling node in the inflammasome activation pathway or pyroptosis. As previously discussed, GSDMD possesses non-pyroptosis functions, such as ion and cytokine channels, which concurrently contribute significantly to disease progression. Therefore, experimental inhibition of GSDMD should take these factors into consideration; (ii) GSDME has been demonstrated to encompass numerous functions similar to those of GSDMD, suggesting that only inhibition of the associated effector cell GSDMD might not yield optimal results. Consistent with the requirement of both GSDMD and GSDME for the release of IL-1β by NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes,525 the concurrent inhibition of these two proteins is essential to optimize therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of colitis.485 When investigating GSDMD inhibitors, it is crucial to account for the possibility of other GSDMs acting as reservoirs of GSDMD activity; (iii) The current investigation of GSDMD inhibitors is overwhelmingly centered on a single pyroptosis pathway involving caspases and GSDMD, which, admittedly, represents the most straightforward and efficient strategy. However, emerging studies suggest robust interplay among pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and other types of PCD, and in particular, the concept of PANoptosis has been proposed.526 GSDMD inhibitors deserve further scrutiny in the overall view of cell death.
Manipulating intracellular gasdermins expression
Modulating the expression of intracellular GSDMs is gaining traction as a prospective therapeutic approach for treating diseases. Wang et al. have shown that the combination of phenylalanine trifluoroborate (Phe-BF3) with nanoparticles is able to preferentially deliver GSDMA3 to tumor cells, triggering pyroptosis via Phe-BF3-mediated desilylation.527 In experimental settings, the activation of pyroptosis in a subset of tumor cells, as low as 15%, has been shown to be efficacious in curtailing tumor growth, which is correlated with enhanced anti-tumor immune responses, and it could potentially synergize with immune checkpoint blockade therapy.527 Zhong et al. developed nanoliposomes encapsulating GSDME plasmids and manganese carbonyl (MnCO), which upon entry into tumor cells, facilitated CO/caspase-3/GSDME-mediated pyroptosis.528 Additionally, Mn2+ can activate the STING signaling pathway, potentiating the therapeutic effects of tumor immunotherapy when combined with inflammation induced by pyroptosis.528 These studies lay the groundwork for targeted GSDM-based cancer therapies. However, it is crucial to exercise caution to prevent the onset of hyper-pyroptosis, which may pose toxicity to healthy cells or lead to an uncontrolled release of cytokines and systemic consequences. This approach holds potential for broader applications in the treatment of inflammatory disorders.
Conclusions and future perspectives
Ever since the groundbreaking identification of GSDMD as a target for inflammatory caspases, a growing body of research has fueled interest and ignited investigation into GSDMs. As the crucial executor of diverse pyroptosis pathways, GSDMs have gained prominence in various inflammatory diseases, including sepsis, virus infections, AS, T2DM, NASH, and several neurodegenerative diseases, including AD. Over the past few years, research on GSDMD has contributed invaluable insights: (i) In addition to the inflammatory caspases, apoptotic caspase-8, as well as cathepsin G and NE, are implicated in the cleavage of GSDMD and the subsequent formation of pores; (ii) Interplay between apoptotic and pyroptotic pathways suggests a sophisticated network of interactions within the cell death machinery. For example, caspase-3 and caspase-7 independently cleave GSDMD at the Asp residue, generating an inactive NT fragment (p45) that serves to specifically inhibit the activation of GSDMD; (iii) The generation of GSDMD pores is not invariably predictive of cytolysis. ESCRT-III dynamically repairs GSDMD pores, delaying or preventing the pyroptotic process. Moreover, GSDMD can serve as a channel for ions or inflammatory cytokines but is not accompanied by cell lysis; (iv) GSDMD inhibitors, such as NSA, DSF, and DMF, have shown promising outcomes in mouse models of inflammatory diseases, and an array of novel inhibitors is being identified.
However, despite extensive research, there are still numerous questions surrounding GSDMD that need to be addressed: (i) The destiny of GSDMD exhibits variability across diverse cell types and in various physiological or pathological contexts. For instance, macrophage GSDMD exacerbates inflammatory progression, and augments mortality in sepsis, yet GSDMD is emerging as a critical player in the physiological role of epithelial cells in maintaining intestinal mucosal homeostasis. The elucidation of additional physiological roles for GSDMD remains an open question; (ii) At present, although proteases such as apoptotic caspases, NE, and cathepsin G are known to cleave GSDMD, the mechanism by which they are recognized and cleaved remains obscure; (iii) How the non-pyroptosis function of GSDMD is realized remains not yet fully understood. An associated issue is whether the modulation of GSDMD activation results in lysogenic cell death or an excessive response devoid of accompanying cell mortality; (iiii) More recently, GSDMD inhibitors have been reported, yet they suffer from a lack of specificity, and the unknown risk of toxicological consequences limits their further clinical utility. The identification of GSDMD inhibitors and their implementation into the treatment of relevant inflammatory conditions presents an ongoing challenge. It remains unclear whether studies of the molecular mechanisms of pore formation and cell lysis, which follow pyroptosis, will yield novel therapeutic approaches, including the targeting of NINJ1.
In summary, pyroptosis, as a manner of PCD, is pertinent to a variety of inflammatory conditions. With GSDMs representing a burgeoning area of study, more specific functions of GSDMs in inflammation and corresponding diseases remain to be illuminated. Consequently, additional animal experiments and clinical trials are requisite to further investigate and corroborate the role and underlying mechanism of GSDMs. Moreover, it would be both advantageous and enlightening to take into account more intricate factors in the pursuit of discovering and developing more potent GSDM inhibitors.
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670072, 82272205, 81871253, and 82371782), and the Shanghai Municipal Committee of Science and Technology (20XD1434400). Figures 2–5 in this work were made by BioRender (https://app.biorender.com/).
Author contributions
C.Z., S.X., and R.J. contributed to the manuscript writing and figure preparation, C.Z., Y.Y., J.B., and Z.Z. designed the work, Y.Y., J.B., and Z.Z. supervised the work. All authors have read and approved the article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally: Chenglong Zhu, Sheng Xu, Ruoyu Jiang
Contributor Information
Yizhi Yu, Email: yuyz@immunol.org.
Jinjun Bian, Email: jinjunbian@smmu.edu.cn.
Zui Zou, Email: zouzui@smmu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Burdette BE, Esparza AN, Zhu H, Wang S. Gasdermin D in pyroptosis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2021;11:2768–278. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tamura M, et al. Members of a novel gene family, Gsdm, are expressed exclusively in the epithelium of the skin and gastrointestinal tract in a highly tissue-specific manner. Genomics. 2007;89:618–629. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shi J, Gao W, Shao F. Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017;42:245–25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liu X, Lieberman J. Knocking ‘em dead: pore-forming proteins in immune defense. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020;38:455–485. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-111319-023800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Coll RC, Schroder K, Pelegrín P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022;43:653–668. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yu P, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021;6:128. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.He WT, et al. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1β secretion. Cell Res. 2015;25:1285–1298. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Miao R, et al. Gasdermin D permeabilization of mitochondrial inner and outer membranes accelerates and enhances pyroptosis. Immunity. 2023;56:2523–2541.e2528. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aglietti RA, et al. GsdmD p30 elicited by caspase-11 during pyroptosis forms pores in membranes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:7858–7863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1607769113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Evavold CL, et al. The pore-forming protein gasdermin D regulates interleukin-1 secretion from living macrophages. Immunity. 2018;48:35–44.e36. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.11.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xiao J, et al. Gasdermin D mediates the pathogenesis of neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease in mice. PLoS Biol. 2018;16:e300004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Banerjee I, et al. Gasdermin D restrains type I interferon response to cytosolic DNA by disrupting ionic homeostasis. Immunity. 2018;49:413–426.e41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Broz P, Pelegrín P, Shao F. The gasdermins, a protein family executing cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020;20:143–15. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu X, Xia S, Zhang Z, Wu H, Lieberman J. Channelling inflammation: gasdermins in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021;20:384–405. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00154-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Saeki N, Kuwahara Y, Sasaki H, Satoh H, Shiroishi T. Gasdermin (Gsdm) localizing to mouse Chromosome 11 is predominantly expressed in upper gastrointestinal tract but significantly suppressed in human gastric cancer cells. Mamm. Genome. 2000;11:718–724. doi: 10.1007/s003350010138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Van Laer L, et al. Nonsyndromic hearing impairment is associated with a mutation in DFNA5. Nat. Genet. 1998;20:194–197. doi: 10.1038/2503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Watabe K, et al. Structure, expression and chromosome mapping of MLZE, a novel gene which is preferentially expressed in metastatic melanoma cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2001;92:140–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2001.tb01076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Katoh M, Katoh M. Identification and characterization of human DFNA5L, mouse Dfna5l, and rat Dfna5l genes in silico. Int. J. Oncol. 2004;25:765–770. doi: 10.3892/ijo.25.4.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Runkel F, et al. The dominant alopecia phenotypes Bareskin, Rex-denuded, and reduced Coat 2 are caused by mutations in gasdermin 3. Genomics. 2004;84:824–835. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2004.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Delmaghani S, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding pejvakin, a newly identified protein of the afferent auditory pathway, cause DFNB59 auditory neuropathy. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:770–778. doi: 10.1038/ng1829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schwander M, et al. A forward genetics screen in mice identifies recessive deafness traits and reveals that pejvakin is essential for outer hair cell function. J. Neurosci. 2007;27:2163–2217. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4975-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Collin RW, et al. Involvement of DFNB59 mutations in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. Hum. Mutat. 2007;28:718–772. doi: 10.1002/humu.20510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ebermann I, et al. Truncating mutation of the DFNB59 gene causes cochlear hearing impairment and central vestibular dysfunction. Hum. Mutat. 2007;28:571–57. doi: 10.1002/humu.20478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wu H, et al. Genetic variation in ORM1-like 3 (ORMDL3) and gasdermin-like (GSDML) and childhood asthma. Allergy. 2009;64:629–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Verlaan DJ, et al. Allele-specific chromatin remodeling in the ZPBP2/GSDMB/ORMDL3 locus associated with the risk of asthma and autoimmune disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;85:377–393. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Agard NJ, Maltby D, Wells JA. Inflammatory stimuli regulate caspase substrate profiles. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2010;9:880–893. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900528-MCP200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cookson BT, Brennan MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:113–114. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(00)01936-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kayagaki N, et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature. 2015;526:666–671. doi: 10.1038/nature15541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shi J, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015;526:660–665. doi: 10.1038/nature15514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liu X, et al. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature. 2016;535:153–158. doi: 10.1038/nature18629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sborgi L, et al. GSDMD membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic cell death. EMBO J. 2016;35:1766–1778. doi: 10.15252/embj.201694696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ding J, et al. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 2016;535:111–116. doi: 10.1038/nature18590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang Y, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017;547:99–103. doi: 10.1038/nature22393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rogers C, et al. Cleavage of DFNA5 by caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:14128. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hou J, et al. PD-L1-mediated gasdermin C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020;22:1264–1275. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0575-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhou Z, et al. Granzyme A from cytotoxic lymphocytes cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis in target cells. Science. 2020;368:eaaz7548. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz7548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kong Q, et al. Alternative splicing of GSDMB modulates killer lymphocyte-triggered pyroptosis. Sci. Immunol. 2023;8:eadg3196. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adg3196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhong X, et al. Structural mechanisms for regulation of GSDMB pore-forming activity. Nature. 2023;616:598–605. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Deng W, et al. Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B cleaves GSDMA and triggers pyroptosis. Nature. 2022;602:496–502. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04384-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.LaRock DL, et al. Group A Streptococcus induces GSDMA-dependent pyroptosis in keratinocytes. Nature. 2022;605:527–531. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04717-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ruan J, Xia S, Liu X, Lieberman J, Wu H. Cryo-EM structure of the gasdermin A3 membrane pore. Nature. 2018;557:62–67. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0058-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chen, K. W. et al. Noncanonical inflammasome signaling elicits gasdermin D-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps. Sci. Immunol.10.1126/sciimmunol.aar6676 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Sollberger G, et al. Gasdermin D plays a vital role in the generation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Sci. Immunol. 2018;3:aar6689. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aar6689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rathkey JK, et al. Chemical disruption of the pyroptotic pore-forming protein gasdermin D inhibits inflammatory cell death and sepsis. Sci. Immunol. 2018;3:aat2738. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hu JJ, et al. FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation. Nat. Immunol. 2020;21:736–745. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0669-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Humphries F, et al. Succination inactivates gasdermin D and blocks pyroptosis. Science. 2020;369:1633–1637. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhang Z, et al. Gasdermin E suppresses tumour growth by activating anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2020;579:415–420. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2071-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rana N, et al. GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis. Cell. 2022;185:283–29. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang J, et al. Epithelial gasdermin D shapes the host-microbial interface by driving mucus layer formation. Sci. Immunol. 2022;7:eabk2092. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abk2092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Xia S, et al. Gasdermin D pore structure reveals preferential release of mature interleukin-1. Nature. 2021;593:607–611. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03478-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Angosto-Bazarra D, et al. Evolutionary analyses of the gasdermin family suggest conserved roles in infection response despite loss of pore-forming functionality. BMC Biol. 2022;20:9. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01220-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Silva CMS, et al. Gasdermin D inhibition prevents multiple organ dysfunction during sepsis by blocking NET formation. Blood. 2021;138:2702–2713. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Burgener SS, et al. Cathepsin G inhibition by Serpinb1 and Serpinb6 prevents programmed necrosis in neutrophils and monocytes and reduces GSDMD-driven inflammation. Cell Rep. 2019;27:3646–365. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lin PH, Lin HY, Kuo CC, Yang LT. N-terminal functional domain of gasdermin A3 regulates mitochondrial homeostasis via mitochondrial targeting. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015;22:44. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0152-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Platnich JM, et al. Shiga toxin/lipopolysaccharide activates caspase-4 and gasdermin D to trigger mitochondrial reactive oxygen species upstream of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Rep. 2018;25:1525–1536. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yu Z, et al. Translocation of gasdermin D induced mitochondrial injury and mitophagy mediated quality control in lipopolysaccharide related cardiomyocyte injury. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022;12:e1002. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Neel DV, et al. Gasdermin-E mediates mitochondrial damage in axons and neurodegeneration. Neuron. 2023;111:1222–1240. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.02.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Weindel CG, et al. Mitochondrial ROS promotes susceptibility to infection via gasdermin D-mediated necroptosis. Cell. 2022;185:3214–3323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rogers C, et al. Gasdermin pores permeabilize mitochondria to augment caspase-3 activation during apoptosis and inflammasome activation. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1689. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09397-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Man SM, Karki R, Kanneganti TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017;277:61–75. doi: 10.1111/imr.12534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Man SM, Kanneganti TD. Converging roles of caspases in inflammasome activation, cell death and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016;16:7–21. doi: 10.1038/nri.2015.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Frank D, Vince JE. Pyroptosis versus necroptosis: similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:99–114. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0212-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Orning P, Lien E, Fitzgerald KA. Gasdermins and their role in immunity and inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2019;216:2453–2465. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Vanaja SK, Rathinam VA, Fitzgerald KA. Mechanisms of inflammasome activation: recent advances and novel insights. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25:308–315. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hou J, Hsu JM, Hung MC. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis in inflammation and antitumor immunity. Mol. Cell. 2021;81:4579–4590. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.de Vasconcelos NM, Lamkanfi M. Recent insights on inflammasomes, gasdermin pores, and pyroptosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020;12:a036392. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fang Y, et al. Pyroptosis: a new frontier in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020;121:109595. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.He Y, Hara H, Núñez G. Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016;41:1012–1021. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.de Carvalho Ribeiro M, Szabo G. Role of the inflammasome in liver disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022;17:345–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-032521-102529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Strowig T, Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Flavell R. Inflammasomes in health and disease. Nature. 2012;481:278–286. doi: 10.1038/nature10759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Chen GY, Nuñez G. Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010;10:826–837. doi: 10.1038/nri2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Place DE, Kanneganti TD. Recent advances in inflammasome biology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018;50:32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rathinam VA, Fitzgerald KA. Inflammasome complexes: emerging mechanisms and effector functions. Cell. 2016;165:792–800. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 2014;157:1013–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Abderrazak A, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome: from a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 2015;4:296–307. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Latz E, Xiao TS, Stutz A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:397–411. doi: 10.1038/nri3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Broz P, Dixit VM. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016;16:407–420. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Rathinam VA, et al. TRIF licenses caspase-11-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation by gram-negative bacteria. Cell. 2012;150:606–619. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ramos-Junior ES, Morandini AC. Gasdermin: a new player to the inflammasome game. Biomed. J. 2017;40:313–316. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2017.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kayagaki N, et al. IRF2 transcriptionally induces GSDMD expression for pyroptosis. Sci. Signal. 2019;12:eaax4917. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aax4917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Elliott EI, Sutterwala FS. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly. Immunol. Rev. 2015;265:35–52. doi: 10.1111/imr.12286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021;18:2114–2127. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kelley N, Jeltema D, Duan Y, He Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: an overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:3328. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hornung V, et al. Silica crystals and aluminum salts activate the NALP3 inflammasome through phagosomal destabilization. Nat. Immunol. 2008;9:847–856. doi: 10.1038/ni.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Dostert C, et al. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science. 2008;320:674–677. doi: 10.1126/science.1156995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Martinon F, Pétrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006;440:237–241. doi: 10.1038/nature04516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Kanneganti TD, et al. Bacterial RNA and small antiviral compounds activate caspase-1 through cryopyrin/Nalp3. Nature. 2006;440:233–236. doi: 10.1038/nature04517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gupta R, et al. RNA and β-hemolysin of group B Streptococcus induce interleukin-1β (IL-1β) by activating NLRP3 inflammasomes in mouse macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2014;289:13701–13705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C114.548982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Sha W, et al. Human NLRP3 inflammasome senses multiple types of bacterial RNAs. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:16059–16064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1412487111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Mathur A, et al. A multicomponent toxin from Bacillus cereus incites inflammation and shapes host outcome via the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Microbiol. 2019;4:362–374. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0318-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Rogiers O, et al. Candidalysin crucially contributes to Nlrp3 inflammasome activation by Candida albicans hyphae. mBio. 2019;10:e02221–18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02221-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Brough D, et al. Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ entry differentially contribute to the release of IL-1 beta and IL-1 alpha from murine macrophages. J. Immunol. 2003;170:3029–3036. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.6.3029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Feldmeyer L, et al. The inflammasome mediates UVB-induced activation and secretion of interleukin-1beta by keratinocytes. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:1140–1145. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Chu J, et al. Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins induce rapid release of mature IL-1beta from murine macrophages in a NLRP3 inflammasome and cathepsin B-dependent manner. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009;86:1227–1238. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0309164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Lerner AG, et al. IRE1α induces thioredoxin-interacting protein to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote programmed cell death under irremediable ER stress. Cell Metab. 2012;16:250–264. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Oslowski CM, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates ER stress-induced β cell death through initiation of the inflammasome. Cell Metab. 2012;16:265–273. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Endrizzi MG, Hadinoto V, Growney JD, Miller W, Dietrich WF. Genomic sequence analysis of the mouse Naip gene array. Genome Res. 2000;10:1095–1102. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.8.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Sundaram B, Kanneganti TD. Advances in understanding activation and function of the NLRC4 inflammasome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:1048. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Duncan JA, Canna SW. The NLRC4 inflammasome. Immunol. Rev. 2018;281:115–123. doi: 10.1111/imr.12607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Mariathasan S, et al. Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors ASC and Ipaf. Nature. 2004;430:213–218. doi: 10.1038/nature02664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Miao EA, et al. Cytoplasmic flagellin activates caspase-1 and secretion of interleukin 1beta via Ipaf. Nat. Immunol. 2006;7:569–575. doi: 10.1038/ni1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kofoed EM, Vance RE. Innate immune recognition of bacterial ligands by NAIPs determines inflammasome specificity. Nature. 2011;477:592–595. doi: 10.1038/nature10394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zhao Y, et al. The NLRC4 inflammasome receptors for bacterial flagellin and type III secretion apparatus. Nature. 2011;477:596–600. doi: 10.1038/nature10510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Fenini G, Karakaya T, Hennig P, Di Filippo M, Beer HD. The NLRP1 inflammasome in human skin and beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:4788. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Rathinam VA, Vanaja SK, Fitzgerald KA. Regulation of inflammasome signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2012;13:333–342. doi: 10.1038/ni.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Fink SL, Bergsbaken T, Cookson BT. Anthrax lethal toxin and Salmonella elicit the common cell death pathway of caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis via distinct mechanisms. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:4312–4317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707370105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Bauernfried S, Scherr MJ, Pichlmair A, Duderstadt KE, Hornung V. Human NLRP1 is a sensor for double-stranded RNA. Science. 2021;371:abd0811. doi: 10.1126/science.abd0811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Robinson KS, et al. Enteroviral 3C protease activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome in airway epithelia. Science. 2020;370:aay2002. doi: 10.1126/science.aay2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Yang X, et al. KSHV-encoded ORF45 activates human NLRP1 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2022;23:916–926. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Zhou JY, et al. Activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome in human keratinocytes by the dsDNA mimetic poly(dA:dT) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2023;120:e2213777120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2213777120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Robinson KS, et al. ZAKα-driven ribotoxic stress response activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome. Science. 2022;377:328–335. doi: 10.1126/science.abl6324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Squires RC, Muehlbauer SM, Brojatsch J. Proteasomes control caspase-1 activation in anthrax lethal toxin-mediated cell killing. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:34260–34267. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705687200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Wickliffe KE, Leppla SH, Moayeri M. Anthrax lethal toxin-induced inflammasome formation and caspase-1 activation are late events dependent on ion fluxes and the proteasome. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10:332–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Mitchell PS, Sandstrom A, Vance RE. The NLRP1 inflammasome: new mechanistic insights and unresolved mysteries. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2019;60:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2019.04.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Sandstrom A, et al. Functional degradation: a mechanism of NLRP1 inflammasome activation by diverse pathogen enzymes. Science. 2019;364:aau1330. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Chui AJ, et al. N-terminal degradation activates the NLRP1B inflammasome. Science. 2019;364:82–85. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Xu H, et al. The N-end rule ubiquitin ligase UBR2 mediates NLRP1B inflammasome activation by anthrax lethal toxin. EMBO J. 2019;38:e101996. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Lugrin J, Martinon F. The AIM2 inflammasome: sensor of pathogens and cellular perturbations. Immunol. Rev. 2018;281:99–114. doi: 10.1111/imr.12618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hornung V, et al. AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature. 2009;458:514–518. doi: 10.1038/nature07725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Sharma BR, Karki R, Kanneganti TD. Role of AIM2 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases, cancer and infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019;49:1998–2011. doi: 10.1002/eji.201848070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Fidler TP, et al. The AIM2 inflammasome exacerbates atherosclerosis in clonal haematopoiesis. Nature. 2021;592:296–301. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03341-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Yu JW, et al. Cryopyrin and pyrin activate caspase-1, but not NF-kappaB, via ASC oligomerization. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:236–249. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Xu H, et al. Innate immune sensing of bacterial modifications of Rho GTPases by the Pyrin inflammasome. Nature. 2014;513:237–241. doi: 10.1038/nature13449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Malik HS, Bliska JB. The pyrin inflammasome and the Yersinia effector interaction. Immunol. Rev. 2020;297:96–107. doi: 10.1111/imr.12907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gangopadhyay A, et al. NLRP3 licenses NLRP11 for inflammasome activation in human macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2022;23:892–903. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01220-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Shi J, et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature. 2014;514:187–192. doi: 10.1038/nature13683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kayagaki N, et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature. 2011;479:117–121. doi: 10.1038/nature10558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Downs KP, Nguyen H, Dorfleutner A, Stehlik C. An overview of the non-canonical inflammasome. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020;76:100924. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Matikainen S, Nyman TA, Cypryk W. Function and regulation of noncanonical caspase-4/5/11 inflammasome. J. immunol. 2020;204:3063–3069. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Pfalzgraff A, Weindl G. Intracellular lipopolysaccharide sensing as a potential therapeutic target for sepsis. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2019;40:187–197. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Baker PJ, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of cytoplasmic LPS recognition by both caspase-4 and caspase-5. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015;45:2918–2926. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Schmid-Burgk JL, et al. Caspase-4 mediates non-canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in human myeloid cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015;45:2911–2917. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Rühl S, Broz P. Caspase-11 activates a canonical NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting K(+) efflux. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015;45:2927–2936. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Shi X, et al. Recognition and maturation of IL-18 by caspase-4 noncanonical inflammasome. Nature. 2023;624:442–450. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Rojas-Lopez M, et al. NLRP11 is a pattern recognition receptor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide in the cytosol of human macrophages. Sci. Immunol. 2023;8:eabo4767. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abo4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Yang D, He Y, Muñoz-Planillo R, Liu Q, Núñez G. Caspase-11 requires the pannexin-1 channel and the purinergic P2X7 pore to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock. Immunity. 2015;43:923–932. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Karmakar M, Katsnelson MA, Dubyak GR, Pearlman E. Neutrophil P2X7 receptors mediate NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1β secretion in response to ATP. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:10555. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Zanoni I, et al. An endogenous caspase-11 ligand elicits interleukin-1 release from living dendritic cells. Science. 2016;352:1232–1236. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Chu LH, et al. The oxidized phospholipid oxPAPC protects from septic shock by targeting the non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:996. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03409-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.de Carvalho RVH, et al. Leishmania lipophosphoglycan triggers caspase-11 and the non-canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Rep. 2019;26:429–437. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Gabrielli E, et al. Induction of caspase-11 by aspartyl proteinases of Candida albicans and implication in promoting inflammatory response. Infect. Immun. 2015;83:1940–1948. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02895-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Pietrella D, et al. Secreted aspartic proteases of Candida albicans activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013;43:679–692. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Chao KL, Kulakova L, Herzberg O. Gene polymorphism linked to increased asthma and IBD risk alters gasdermin-B structure, a sulfatide and phosphoinositide binding protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E1128–e1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616783114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Newton K, Dixit VM, Kayagaki N. Dying cells fan the flames of inflammation. Science. 2021;374:1076–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.abi5934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Sato H, et al. A new mutation Rim3 resembling Re(den) is mapped close to retinoic acid receptor alpha (Rara) gene on mouse chromosome 11. Mamm. Genome. 1998;9:20–25. doi: 10.1007/s003359900673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Saeki N, et al. GASDERMIN, suppressed frequently in gastric cancer, is a target of LMO1 in TGF-beta-dependent apoptotic signalling. Oncogene. 2007;26:6488–6498. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Li J, et al. Gsdma3 is required for hair follicle differentiation in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;403:18–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.10.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Moussette S, et al. Role of DNA methylation in expression control of the IKZF3-GSDMA region in human epithelial cells. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0172707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Shi P, et al. Loss of conserved Gsdma3 self-regulation causes autophagy and cell death. Biochem. J. 2015;468:325–336. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Billman ZP, et al. Caspase-1 activates gasdermin A in non-mammals. ELife. 2024;12:PR92362. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92362.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Das S, et al. GSDMB induces an asthma phenotype characterized by increased airway responsiveness and remodeling without lung inflammation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:13132–13137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610433113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hu Y, Jin S, Cheng L, Liu G, Jiang Q. Autoimmune disease variants regulate GSDMB gene expression in human immune cells and whole blood. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E7860–e7862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1712127114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Saeki N, et al. Distinctive expression and function of four GSDM family genes (GSDMA-D) in normal and malignant upper gastrointestinal epithelium. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:261–271. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Carl-McGrath S, Schneider-Stock R, Ebert M, Röcken C. Differential expression and localisation of gasdermin-like (GSDML), a novel member of the cancer-associated GSDMDC protein family, in neoplastic and non-neoplastic gastric, hepatic, and colon tissues. Pathology. 2008;40:13–24. doi: 10.1080/00313020701716250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Kang MJ, et al. GSDMB/ORMDL3 variants contribute to asthma susceptibility and eosinophil-mediated bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Hum. Immunol. 2012;73:954–959. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2012.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Chen Q, et al. GSDMB promotes non-canonical pyroptosis by enhancing caspase-4 activity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019;11:496–508. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Komiyama H, et al. Alu-derived cis-element regulates tumorigenesis-dependent gastric expression of GASDERMIN B (GSDMB) Genes Genet. Syst. 2010;85:75–83. doi: 10.1266/ggs.85.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Li X, et al. Apoptotic caspase-7 activation inhibits non-canonical pyroptosis by GSDMB cleavage. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30:2120–2134. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01211-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Panganiban RA, et al. A functional splice variant associated with decreased asthma risk abolishes the ability of gasdermin B to induce epithelial cell pyroptosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018;142:1469–1478.e1462. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.11.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Hansen JM, et al. Pathogenic ubiquitination of GSDMB inhibits NK cell bactericidal functions. Cell. 2021;184:3178–3191. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Yin H, et al. Insights into the GSDMB-mediated cellular lysis and its targeting by IpaH7.8. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:61. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35725-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Luchetti G, et al. Shigella ubiquitin ligase IpaH7.8 targets gasdermin D for degradation to prevent pyroptosis and enable infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29:1521–1530. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Wang C, et al. Structural basis for GSDMB pore formation and its targeting by IpaH7.8. Nature. 2023;616:590–597. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05832-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Oltra SS, et al. Distinct GSDMB protein isoforms and protease cleavage processes differentially control pyroptotic cell death and mitochondrial damage in cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30:1366–1381. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01143-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Hergueta-Redondo M, et al. Gasdermin B expression predicts poor clinical outcome in HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:56295–56308. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hergueta-Redondo M, et al. Gasdermin-B promotes invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e90099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Sun Q, et al. Expression of GSDML associates with tumor progression in uterine cervix cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2008;1:73–83. doi: 10.1593/tlo.08112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Miguchi M, et al. Gasdermin C is upregulated by inactivation of transforming growth factor β receptor type II in the presence of mutated Apc, promoting colorectal cancer proliferation. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Zhang JY, et al. The metabolite α-KG induces GSDMC-dependent pyroptosis through death receptor 6-activated caspase-8. Cell Res. 2021;31:980–997. doi: 10.1038/s41422-021-00506-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Xi R, et al. Up-regulation of gasdermin C in mouse small intestine is associated with lytic cell death in enterocytes in worm-induced type 2 immunity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2021;118:e2026307118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026307118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Zhao M, et al. Epithelial STAT6 O-GlcNAcylation drives a concerted anti-helminth alarmin response dependent on tuft cell hyperplasia and Gasdermin C. Immunity. 2022;55:623–638. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.03.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wu C, et al. Inflammasome activation triggers blood clotting and host death through pyroptosis. Immunity. 2019;50:1401–1411. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Rieckmann JC, et al. Social network architecture of human immune cells unveiled by quantitative proteomics. Nat. Immunol. 2017;18:583–593. doi: 10.1038/ni.3693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Heilig R, et al. The gasdermin-D pore acts as a conduit for IL-1β secretion in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018;48:584–592. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Orning P, et al. Pathogen blockade of TAK1 triggers caspase-8-dependent cleavage of gasdermin D and cell death. Science. 2018;362:1064–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.aau2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Sarhan J, et al. Caspase-8 induces cleavage of gasdermin D to elicit pyroptosis during Yersinia infection. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:E10888–e10897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1809548115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Kang TB, Yang SH, Toth B, Kovalenko A, Wallach D. Caspase-8 blocks kinase RIPK3-mediated activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Immunity. 2013;38:27–40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Taabazuing CY, Okondo MC, Bachovchin DA. Pyroptosis and apoptosis pathways engage in bidirectional crosstalk in monocytes and macrophages. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017;24:507–514. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.03.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Ramirez MLG, et al. Extensive peptide and natural protein substrate screens reveal that mouse caspase-11 has much narrower substrate specificity than caspase-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2018;293:7058–7067. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Kambara H, et al. Gasdermin D exerts anti-inflammatory effects by promoting neutrophil death. Cell Rep. 2018;22:2924–2936. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Liu Z, et al. Structures of the gasdermin D C-terminal domains reveal mechanisms of autoinhibition. Structure. 2018;26:778–784. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Rathkey JK, et al. Live-cell visualization of gasdermin D-driven pyroptotic cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2017;292:14649–14658. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.797217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Yu C, et al. A 3-nucleotide deletion in the polypyrimidine tract of intron 7 of the DFNA5 gene causes nonsyndromic hearing impairment in a Chinese family. Genomics. 2003;82:575–579. doi: 10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Park HJ, et al. Evidence for a founder mutation causing DFNA5 hearing loss in East Asians. J. Hum. Genet. 2010;55:59–62. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2009.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Li-Yang MN, et al. IVS8+1 DelG, a novel splice site mutation causing DFNA5 deafness in a Chinese family. Chin. Med. J. 2015;128:2510–2515. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.164980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Thompson DA, Weigel RJ. Characterization of a gene that is inversely correlated with estrogen receptor expression (ICERE-1) in breast carcinomas. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998;252:169–177. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Zhou B, et al. Tom20 senses iron-activated ROS signaling to promote melanoma cell pyroptosis. Cell Res. 2018;28:1171–1185. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0090-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Orzalli MH, et al. Virus-mediated inactivation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members promotes Gasdermin-E-dependent pyroptosis in barrier epithelial cells. Immunity. 2021;54:1447–1462. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Jiang M, Qi L, Li L, Li Y. The caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:112. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00349-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Schneider KS, et al. The inflammasome drives GSDMD-independent secondary pyroptosis and IL-1 release in the absence of caspase-1 protease activity. Cell Rep. 2017;21:3846–3859. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Chen KW, et al. RIPK1 activates distinct gasdermins in macrophages and neutrophils upon pathogen blockade of innate immune signaling. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2021;13:e2101189118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2101189118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Ma F, et al. Gasdermin E dictates inflammatory responses by controlling the mode of neutrophil death. Nat. Commun. 2024;15:386. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44669-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Jiang S, Gu H, Zhao Y, Sun L. Teleost gasdermin E is cleaved by caspase 1, 3, and 7 and induces pyroptosis. J. Immunol. 2019;203:1369–1382. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Op de Beeck K, et al. The DFNA5 gene, responsible for hearing loss and involved in cancer, encodes a novel apoptosis-inducing protein. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;19:965–973. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Wei Y, et al. GSDME-mediated pyroptosis promotes the progression and associated inflammation of atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36614-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Pan J, et al. Transcription factor Sp1 transcriptionally enhances GSDME expression for pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15:66. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06455-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Yokomizo K, et al. Methylation of the DFNA5 gene is frequently detected in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:1319–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Masuda Y, et al. The potential role of DFNA5, a hearing impairment gene, in p53-mediated cellular response to DNA damage. J. Hum. Genet. 2006;51:652–664. doi: 10.1007/s10038-006-0004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Akino K, et al. Identification of DFNA5 as a target of epigenetic inactivation in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:88–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Kim MS, et al. Aberrant promoter methylation and tumor suppressive activity of the DFNA5 gene in colorectal carcinoma. Oncogene. 2008;27:3624–3634. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1211021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Lage H, Helmbach H, Grottke C, Dietel M, Schadendorf D. DFNA5 (ICERE-1) contributes to acquired etoposide resistance in melanoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2001;494:54–59. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02304-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Defourny J, et al. Pejvakin-mediated pexophagy protects auditory hair cells against noise-induced damage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:8010–8017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821844116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Delmaghani S, et al. Hypervulnerability to sound exposure through impaired adaptive proliferation of peroxisomes. Cell. 2015;163:894–906. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Harris SL, et al. Conditional deletion of pejvakin in adult outer hair cells causes progressive hearing loss in mice. Neuroscience. 2017;344:380–393. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.12.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Elias EE, Lyons B, Muruve DA. Gasdermins and pyroptosis in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023;19:337–350. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00662-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Privitera G, Rana N, Armuzzi A, Pizarro TT. The gasdermin protein family: emerging roles in gastrointestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023;20:366–387. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00743-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Zou J, et al. The versatile gasdermin family: their function and roles in diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021;12:751533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.751533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Hou J, Li T, Hsu JM, Zhang X, Hung MC. Gasdermins and cancers. Semin. Immunol. 2023;70:101833. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Lunny DP, et al. Mutations in gasdermin 3 cause aberrant differentiation of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2005;124:615–621. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Tanaka S, et al. A new Gsdma3 mutation affecting anagen phase of first hair cycle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007;359:902–907. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Kumar S, et al. Gsdma3(I359N) is a novel ENU-induced mutant mouse line for studying the function of Gasdermin A3 in the hair follicle and epidermis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012;67:190–192. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2012.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Yu J, et al. Polymorphisms in GSDMA and GSDMB are associated with asthma susceptibility, atopy and BHR. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011;46:701–708. doi: 10.1002/ppul.21424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Zhao CN, et al. The association of GSDMB and ORMDL3 gene polymorphisms with asthma: a meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015;7:175–185. doi: 10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Li X, et al. Genetic analyses identify GSDMB associated with asthma severity, exacerbations, and antiviral pathways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021;147:894–909. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Bischoff AM, et al. A novel mutation identified in the DFNA5 gene in a Dutch family: a clinical and genetic evaluation. Audio. Neurootol. 2004;9:34–46. doi: 10.1159/000074185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Cheng J, et al. A novel DFNA5 mutation, IVS8+4 A>G, in the splice donor site of intron 8 causes late-onset non-syndromic hearing loss in a Chinese family. Clin. Genet. 2007;72:471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Nishio A, et al. A DFNA5 mutation identified in Japanese families with autosomal dominant hereditary hearing loss. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2014;78:83–91. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Mansard L, et al. Identification of the first single GSDME exon 8 structural variants associated with autosomal dominant hearing loss. Diagnostics. 2022;12:207. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Cheng J, et al. Novel, pathogenic insertion variant of GSDME associates with autosomal dominant hearing loss in a large Chinese pedigree. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023;10:18004. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Cerqueira DM, et al. Guanylate-binding protein 5 licenses caspase-11 for Gasdermin-D mediated host resistance to Brucella abortus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14:e1007519. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Gonçalves AV, et al. Gasdermin-D and caspase-7 are the key caspase-1/8 substrates downstream of the NAIP5/NLRC4 inflammasome required for restriction of Legionella pneumophila. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15:e1007886. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.He K, et al. Gasdermin D licenses MHCII induction to maintain food tolerance in small intestine. Cell. 2023;186:3033–3048. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Liu F, et al. Neutrophil-specific depletion of gasdermin D does not protect against murine sepsis. Blood. 2023;141:550–554. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Yamagishi R, et al. Gasdermin D-mediated release of IL-33 from senescent hepatic stellate cells promotes obesity-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Immunol. 2022;7:eabl7209. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl7209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Xie WJ, Xia S, Warshel A, Wu H. Electrostatic influence on IL-1 transport through the GSDMD pore. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2022;119:e2120287119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2120287119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Karmakar M, et al. N-GSDMD trafficking to neutrophil organelles facilitates IL-1β release independently of plasma membrane pores and pyroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:2212. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16043-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Liu Z, et al. Crystal structures of the full-length murine and human gasdermin D reveal mechanisms of autoinhibition, lipid binding, and oligomerization. Immunity. 2019;51:43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Johnson AG, et al. Bacterial gasdermins reveal an ancient mechanism of cell death. Science. 2022;375:221–225. doi: 10.1126/science.abj8432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Mulvihill E, et al. Mechanism of membrane pore formation by human gasdermin-D. EMBO J. 2018;37:e98321. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Russo AJ, et al. Intracellular immune sensing promotes inflammation via gasdermin D-driven release of a lectin alarmin. Nat. immunol. 2021;22:154–165. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00844-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Chen Y, et al. Gasdermin D drives the nonexosomal secretion of galectin-3, an insulin signal antagonist. J. Immunol. 2019;203:2712–2723. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Chen W, et al. Allergen protease-activated stress granule assembly and gasdermin D fragmentation control interleukin-33 secretion. Nat. immunol. 2022;23:1021–1030. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01255-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Mari SA, et al. Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along variable pathways. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:2609. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30232-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Schaefer SL, Hummer G. Sublytic gasdermin-D pores captured in atomistic molecular simulations. ELife. 2022;11:e81432. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Dal Peraro M, van der Goot FG. Pore-forming toxins: ancient, but never really out of fashion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;14:77–92. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Wade KR, et al. An intermolecular electrostatic interaction controls the prepore-to-pore transition in a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:2204–2209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423754112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Yamashita D, et al. Molecular basis of transmembrane beta-barrel formation of staphylococcal pore-forming toxins. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4897. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.van Pee K, et al. CryoEM structures of membrane pore and prepore complex reveal cytolytic mechanism of Pneumolysin. ELife. 2017;6:e23644. doi: 10.7554/eLife.23644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Vögele M, et al. Membrane perforation by the pore-forming toxin pneumolysin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:13352–13357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904304116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Degiacomi MT, et al. Molecular assembly of the aerolysin pore reveals a swirling membrane-insertion mechanism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013;9:623–629. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Vasudevan SO, Behl B, Rathinam VA. Pyroptosis-induced inflammation and tissue damage. Semin. Immunol. 2023;69:101781. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Kayagaki N, Dixit VM. Rescue from a fiery death: a therapeutic endeavor. Science. 2019;366:688–689. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Kayagaki N, et al. NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. Nature. 2021;591:131–136. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Borges JP, et al. Glycine inhibits NINJ1 membrane clustering to suppress plasma membrane rupture in cell death. ELife. 2022;11:e78609. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Dondelinger Y, et al. NINJ1 is activated by cell swelling to regulate plasma membrane permeabilization during regulated necrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14:755. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06284-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Wang Y, Shao F. NINJ1, rupturing swollen membranes for cataclysmic cell lysis. Mol. Cell. 2021;81:1370–1371. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.DiPeso L, Ji DX, Vance RE, Price JV. Cell death and cell lysis are separable events during pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2017;3:17070. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2017.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Fink SL, Cookson BT. Caspase-1-dependent pore formation during pyroptosis leads to osmotic lysis of infected host macrophages. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:1812–1825. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Rühl S, et al. ESCRT-dependent membrane repair negatively regulates pyroptosis downstream of GSDMD activation. Science. 2018;362:956–960. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Nozaki K, et al. Caspase-7 activates ASM to repair gasdermin and perforin pores. Nature. 2022;606:960–967. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04825-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Fan W, et al. Flotillin-mediated endocytosis and ALIX-syntenin-1-mediated exocytosis protect the cell membrane from damage caused by necroptosis. Sci. Signal. 2019;12:eaaw3423. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw3423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Bock FJ, Tait SWG. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:85–100. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Kondolf HC, D’Orlando DA, Dubyak GR, Abbott DW. Protein engineering reveals that gasdermin A preferentially targets mitochondrial membranes over the plasma membrane during pyroptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2023;299:102908. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Miao N, et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA induces gasdermin D oligomerization in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:872. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36522-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Dang EV, McDonald JG, Russell DW, Cyster JG. Oxysterol restraint of cholesterol synthesis prevents AIM2 inflammasome activation. Cell. 2017;171:1057–1071. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Próchnicki T, et al. Mitochondrial damage activates the NLRP10 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2023;24:595–603. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01451-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Zhivaki D, Kagan JC. Innate immune detection of lipid oxidation as a threat assessment strategy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022;22:322–330. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00618-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Kanneganti A, et al. GSDMD is critical for autoinflammatory pathology in a mouse model of familial Mediterranean fever. J. Exp. Med. 2018;215:1519–1529. doi: 10.1084/jem.20172060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Rashidi M, et al. The pyroptotic cell death effector gasdermin D is activated by gout-associated uric acid crystals but is dispensable for cell death and IL-1β release. J. Immunol. 2019;203:736–748. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Liew PX, Kubes P. The neutrophil’s role during health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2019;99:1223–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00012.2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Yow SJ, Yeap HW, Chen KW. Inflammasome and gasdermin signaling in neutrophils. Mol. Microbiol. 2022;117:961–972. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Tyrkalska SD, Candel S, Mulero V. The neutrophil inflammasome. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021;115:103874. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Chen KW, et al. The neutrophil NLRC4 inflammasome selectively promotes IL-1β maturation without pyroptosis during acute Salmonella challenge. Cell Rep. 2014;8:570–582. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Karmakar M, et al. Neutrophil IL-1β processing induced by pneumolysin is mediated by the NLRP3/ASC inflammasome and caspase-1 activation and is dependent on K+ efflux. J. Immunol. 2015;194:1763–1775. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Mankan AK, Dau T, Jenne D, Hornung V. The NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 axis regulates IL-1β processing in neutrophils. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012;42:710–715. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Netea MG, van de Veerdonk FL, van der Meer JW, Dinarello CA, Joosten LA. Inflammasome-independent regulation of IL-1-family cytokines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015;33:49–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Monteleone M, et al. Interleukin-1β maturation triggers its relocation to the plasma membrane for gasdermin-D-dependent and -independent secretion. Cell Rep. 2018;24:1425–1433. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Qu Y, et al. P2X7 receptor-stimulated secretion of MHC class II-containing exosomes requires the ASC/NLRP3 inflammasome but is independent of caspase-1. J. Immunol. 2009;182:5052–5062. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Qu Y, Franchi L, Nunez G, Dubyak GR. Nonclassical IL-1 beta secretion stimulated by P2X7 receptors is dependent on inflammasome activation and correlated with exosome release in murine macrophages. J. Immunol. 2007;179:1913–1925. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Kimura T, et al. Dedicated SNAREs and specialized TRIM cargo receptors mediate secretory autophagy. EMBO J. 2017;36:42–60. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Bulek K, et al. Epithelial-derived gasdermin D mediates nonlytic IL-1β release during experimental colitis. J. Clin. Invest. 2020;130:4218–4234. doi: 10.1172/JCI138103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Ratitong B, Marshall M, Pearlman E. β-Glucan-stimulated neutrophil secretion of IL-1α is independent of GSDMD and mediated through extracellular vesicles. Cell Rep. 2021;35:109139. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Chao YY, et al. Human T(H)17 cells engage gasdermin E pores to release IL-1α on NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2023;24:295–308. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01386-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Tan G, Huang C, Chen J, Zhi F. HMGB1 released from GSDME-mediated pyroptotic epithelial cells participates in the tumorigenesis of colitis-associated colorectal cancer through the ERK1/2 pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020;13:149. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00985-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.de Torre-Minguela C, Barberà-Cremades M, Gómez AI, Martín-Sánchez F, Pelegrín P. Macrophage activation and polarization modify P2X7 receptor secretome influencing the inflammatory process. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:22586. doi: 10.1038/srep22586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Brinkmann V, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1532–1535. doi: 10.1126/science.1092385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Papayannopoulos V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018;18:134–147. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Thiam HR, Wong SL, Wagner DD, Waterman CM. Cellular mechanisms of NETosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020;36:191–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-020520-111016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Poli V, Zanoni I. Neutrophil intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of NETosis in health and disease. Trends Microbiol. 2023;31:280–293. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Nauseef WM, Kubes P. Pondering neutrophil extracellular traps with healthy skepticism. Cell Microbiol. 2016;18:1349–1357. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Desai J, Mulay SR, Nakazawa D, Anders HJ. Matters of life and death. How neutrophils die or survive along NET release and is “NETosis” = necroptosis? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016;73:2211–2219. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2195-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Chauhan D, et al. GSDMD drives canonical inflammasome-induced neutrophil pyroptosis and is dispensable for NETosis. EMBO Rep. 2022;23:e54277. doi: 10.15252/embr.202154277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Amara N, et al. Selective activation of PFKL suppresses the phagocytic oxidative burst. Cell. 2021;184:4480–4494. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Stojkov D, et al. NET formation is independent of gasdermin D and pyroptotic cell death. Sci. Signal. 2023;16:eabm0517. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abm0517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Li M, et al. Gasdermin D maintains bone mass by rewiring the endo-lysosomal pathway of osteoclastic bone resorption. Dev. Cell. 2022;57:2365–2380. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Zhang Q, et al. GSDMD enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting the phosphorylation of eIF2α and activating the ER-stress response. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:114. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00915-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Benaoudia S, et al. A genome-wide screen identifies IRF2 as a key regulator of caspase-4 in human cells. EMBO Rep. 2019;20:e4823. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.Liu Z, et al. Melatonin alleviates inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through inhibiting NF-κB/GSDMD signal in mice adipose tissue. J. Pineal Res. 2017;63:jpi.12414. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Zhu CL, et al. PD-L1 promotes GSDMD-mediated NET release by maintaining the transcriptional activity of Stat3 in sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023;19:1413–1429. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.79913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Li Y, et al. Type I IFN operates pyroptosis and necroptosis during multidrug-resistant A. baumannii infection. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:1304–1318. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0041-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Deng L, Meng T, Chen L, Wei W, Wang P. The role of ubiquitination in tumorigenesis and targeted drug discovery. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020;5:11. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0107-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Popovic D, Vucic D, Dikic I. Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med. 2014;20:1242–1253. doi: 10.1038/nm.3739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 293.Hu H, Sun SC. Ubiquitin signaling in immune responses. Cell Res. 2016;26:457–483. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 294.Cruz Walma DA, Chen Z, Bullock AN, Yamada KM. Ubiquitin ligases: guardians of mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022;23:350–367. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 295.Buetow L, Huang DT. Structural insights into the catalysis and regulation of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016;17:626–642. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 296.Jiang Q, Zhu Z, Mao X. Ubiquitination is a major modulator for the activation of inflammasomes and pyroptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2023;1866:194955. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 297.Tang J, et al. Sequential ubiquitination of NLRP3 by RNF125 and Cbl-b limits inflammasome activation and endotoxemia. J. Exp. Med. 2020;217:e20182091. doi: 10.1084/jem.20182091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 298.Song H, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31 attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting proteasomal degradation of NLRP3. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:13727. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 299.Humphries F, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Pellino2 mediates priming of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1560. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03669-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 300.Suzuki S, et al. Shigella IpaH7.8 E3 ubiquitin ligase targets glomulin and activates inflammasomes to demolish macrophages. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E4254–E4263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324021111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 301.Zhang L, et al. Peli1 facilitates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by mediating ASC ubiquitination. Cell Rep. 2021;37:109904. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 302.Liu Q, Zhang S, Sun Z, Guo X, Zhou H. E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4 is a key negative regulator for non-canonical inflammasome activation. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:2386–2399. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0308-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 303.Shi Y, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1 is a key positive regulator for GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:106. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04553-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 304.He H, et al. USP24-GSDMB complex promotes bladder cancer proliferation via activation of the STAT3 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021;17:2417–2429. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.54442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 305.Wu F, et al. Inhibition of CDC20 potentiates anti-tumor immunity through facilitating GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in prostate cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023;12:67. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00428-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 306.Di M, et al. OTUD4-mediated GSDME deubiquitination enhances radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inducing pyroptosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022;41:328. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02533-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 307.Ren Y, et al. USP48 stabilizes gasdermin E to promote pyroptosis in cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:1074–1093. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-1812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 308.Hunter T. Why nature chose phosphate to modify proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012;367:2513–2516. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 309.Kamerlin SC, Sharma PK, Prasad RB, Warshel A. Why nature really chose phosphate. Q Rev. Biophys. 2013;46:1–132. doi: 10.1017/S0033583512000157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 310.Hornbeck PV, et al. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D512–D520. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 311.Ai YL, et al. Mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through AMPK activated by metabolite GlcNAc-6P. Cell Res. 2023;33:904–922. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00848-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 312.Santamaria A, et al. The Plk1-dependent phosphoproteome of the early mitotic spindle. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011;10:M110.004457. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.004457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 313.Evavold CL, et al. Control of gasdermin D oligomerization and pyroptosis by the Ragulator-Rag-mTORC1 pathway. Cell. 2021;184:4495–4511. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 314.Li Y, Pu D, Huang J, Zhang Y, Yin H. Protein phosphatase 1 regulates phosphorylation of gasdermin D and pyroptosis. Chem. Commun. 2022;58:11965–11968. doi: 10.1039/D2CC03590A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 315.Basak C, et al. NF-kappaB- and C/EBPbeta-driven interleukin-1beta gene expression and PAK1-mediated caspase-1 activation play essential roles in interleukin-1beta release from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:4279–4288. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412820200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 316.Jia SH, Parodo J, Kapus A, Rotstein OD, Marshall JC. Dynamic regulation of neutrophil survival through tyrosine phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of caspase-8. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:5402–5413. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706462200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 317.Voss OH, Kim S, Wewers MD, Doseff AI. Regulation of monocyte apoptosis by the protein kinase Cdelta-dependent phosphorylation of caspase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:17371–17379. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412449200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 318.Alvarado-Kristensson M, et al. p38-MAPK signals survival by phosphorylation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 in human neutrophils. J. Exp. Med. 2004;199:449–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 319.Li X, et al. Phosphorylation of caspase-7 by p21-activated protein kinase (PAK) 2 inhibits chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis of breast cancer cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:22291–22299. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.236596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 320.Bambouskova M, et al. Itaconate confers tolerance to late NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Rep. 2021;34:108756. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 321.Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2011;469:221–225. doi: 10.1038/nature09663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 322.Misawa T, et al. Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2013;14:454–460. doi: 10.1038/ni.2550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 323.Wang Y, et al. Mitochondrial ROS promote macrophage pyroptosis by inducing GSDMD oxidation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019;11:1069–1082. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 324.Balasubramanian, A. et al. Palmitoylation of gasdermin D directs its membrane translocation and pore formation in pyroptosis. Preprint at bioRxiv 2023.02.21.529402 (2023). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 325.Du, G. et al. ROS-dependent palmitoylation is an obligate licensing modification for GSDMD pore formation. Preprint at bioRxiv 2023.03.07.531538 (2023).
- 326.Hu L, et al. Chemotherapy-induced pyroptosis is mediated by BAK/BAX-caspase-3-GSDME pathway and inhibited by 2-bromopalmitate. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:281. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2476-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 327.Aicart-Ramos C, Valero RA, Rodriguez-Crespo I. Protein palmitoylation and subcellular trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1808:2981–2994. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 328.Linder ME, Deschenes RJ. Palmitoylation: policing protein stability and traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:74–84. doi: 10.1038/nrm2084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 329.Tanaka S, Mizushina Y, Kato Y, Tamura M, Shiroishi T. Functional conservation of Gsdma cluster genes specifically duplicated in the mouse genome. G3. 2013;3:1843–1850. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.007393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 330.Galluzzi L, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 331.Singer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 332.Napolitano LM. Sepsis 2018: definitions and guideline changes. Surg. Infect. 2018;19:117–125. doi: 10.1089/sur.2017.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 333.Dellinger RP, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit. Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 334.Dellinger RP, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Crit. Care Med. 2013;39:165–228. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 335.Rhodes A, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:304–377. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 336.van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, Netea MG. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017;17:407–420. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 337.Hamers L, Kox M, Pickkers P. Sepsis-induced immunoparalysis: mechanisms, markers, and treatment options. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015;81:426–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 338.Huang M, Cai S, Su J. The pathogenesis of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:5376. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 339.Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Osuchowski MF, Valentine C, Kurosawa S, Remick DG. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011;6:19–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 340.Steinhagen F, et al. Immunotherapy in sepsis - brake or accelerate? Pharm. Ther. 2020;208:107476. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 341.Zhang W, et al. The pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets in sepsis. MedComm. 2023;4:e418. doi: 10.1002/mco2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 342.Wu J, Cai J, Tang Y, Lu B. The noncanonical inflammasome-induced pyroptosis and septic shock. Semin. Immunol. 2023;70:101844. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 343.Chen R, et al. cAMP metabolism controls caspase-11 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in sepsis. Sci. Adv. 2019;5:eaav5562. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 344.Kang R, et al. Lipid peroxidation drives gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis in lethal polymicrobial sepsis. Cell Host Microbe. 2018;24:97–108. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 345.Dai S, et al. GSDMD mediates LPS-induced septic myocardial dysfunction by regulating ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021;9:779432. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.779432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 346.Swanson KV, Deng M, Ting JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019;19:477–489. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0165-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 347.Ge Y, Huang M, Yao YM. Recent advances in the biology of IL-1 family cytokines and their potential roles in development of sepsis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;45:24–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 348.Palomo J, Dietrich D, Martin P, Palmer G, Gabay C. The interleukin (IL)-1 cytokine family-Balance between agonists and antagonists in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2015;76:25–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 349.Opal SM, et al. Confirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist sepsis investigator group. Crit. Care Med. 1997;25:1115–1124. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199707000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 350.Fisher CJ, et al. Recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of patients with sepsis syndrome. Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phase III rhIL-1ra Sepsis Syndrome Study Group. JAMA. 1994;271:1836–1843. doi: 10.1001/jama.1994.03510470040032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 351.Van’t Wout JW, Van der Meer JW, Barza M, Dinarello CA. Protection of neutropenic mice from lethal Candida albicans infection by recombinant interleukin 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988;18:1143–1146. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 352.Ding X, et al. Inflammasome-mediated GSDMD activation facilitates escape of Candida albicans from macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:6699. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27034-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 353.Ganesan S, et al. Caspase-8 modulates dectin-1 and complement receptor 3-driven IL-1β production in response to β-glucans and the fungal pathogen, Candida albicans. J. Immunol. 2014;193:2519–2530. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 354.McDonald B, et al. Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice. Blood. 2017;129:1357–1367. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-741298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 355.Lelubre C, Vincent JL. Mechanisms and treatment of organ failure in sepsis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018;14:417–427. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 356.Levi M, van der Poll T. Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2017;149:38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2016.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 357.Yang X, et al. Bacterial endotoxin activates the coagulation cascade through gasdermin D-dependent phosphatidylserine exposure. Immunity. 2019;51:983–996. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 358.Vora SM, Lieberman J, Wu H. Inflammasome activation at the crux of severe COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021;21:694–703. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00588-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 359.Peng Y, et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles induce disseminated intravascular coagulation through the caspase-11-gasdermin D pathway. Thromb. Res. 2020;196:159–166. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 360.Zhang H, et al. TMEM173 drives lethal coagulation in sepsis. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27:556–570. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 361.Mackman N. Role of tissue factor in hemostasis, thrombosis, and vascular development. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004;24:1015–1022. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000130465.23430.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 362.Gando S, Levi M, Toh CH. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016;2:16037. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 363.Su M, et al. Gasdermin D-dependent platelet pyroptosis exacerbates NET formation and inflammation in severe sepsis. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022;1:732–747. doi: 10.1038/s44161-022-00108-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 364.Liu L, Sun B. Neutrophil pyroptosis: new perspectives on sepsis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019;76:2031–2042. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03060-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 365.Silvestre-Roig C, Fridlender ZG, Glogauer M, Scapini P. Neutrophil diversity in health and disease. Trends Immunol. 2019;40:565–583. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 366.Margraf A, Ley K, Zarbock A. Neutrophil recruitment: from model systems to tissue-specific patterns. Trends Immunol. 2019;40:613–634. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 367.Denning NL, Aziz M, Gurien SD, Wang P. DAMPs and NETs in sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2019;10:2536. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 368.Tan C, Aziz M, Wang P. The vitals of NETs. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021;110:797–808. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3RU0620-375R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 369.Pruenster M, et al. E-selectin-mediated rapid NLRP3 inflammasome activation regulates S100A8/S100A9 release from neutrophils via transient gasdermin D pore formation. Nat. Immunol. 2023;24:2021–2031. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01656-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 370.Eichholz K, et al. Immune-complexed adenovirus induce AIM2-mediated pyroptosis in human dendritic cells. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005871. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 371.Chen N, et al. HuNoV non-structural protein P22 induces maturation of IL-1β and IL-18 and N-GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis through activating NLRP3 inflammasome. Vaccines. 2023;11:993. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11050993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 372.Zhu S, et al. Nlrp9b inflammasome restricts rotavirus infection in intestinal epithelial cells. Nature. 2017;546:667–670. doi: 10.1038/nature22967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 373.Doitsh G, et al. Cell death by pyroptosis drives CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 2014;505:509–514. doi: 10.1038/nature12940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 374.Zhang C, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome induces CD4+ T cell loss in chronically HIV-1-infected patients. J. Clin. Invest. 2021;131:e138861. doi: 10.1172/JCI138861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 375.Doitsh G, Greene WC. Dissecting how CD4 T cells are lost during HIV infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;19:280–291. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 376.Xia P, et al. Activation-induced pyroptosis contributes to the loss of MAIT cells in chronic HIV-1 infected patients. Mil. Med. Res. 2022;9:24. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00384-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 377.Chan JF, et al. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020;9:221–236. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 378.Stein SR, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy. Nature. 2022;612:758–763. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05542-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 379.Yang H, Rao Z. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021;19:685–700. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 380.Mehta P, et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395:1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 381.Li Q, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: what is next? Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:1107–1122. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01015-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 382.Junqueira C, et al. FcγR-mediated SARS-CoV-2 infection of monocytes activates inflammation. Nature. 2022;606:576–584. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04702-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 383.Silva CMS, et al. Gasdermin-D activation by SARS-CoV-2 triggers NET and mediate COVID-19 immunopathology. Crit. Care. 2022;26:206. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04062-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 384.Xie J, et al. GSDMD-mediated NETosis promotes the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023;53:e2250011. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 385.Ma J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid suppresses host pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D cleavage. EMBO J. 2021;40:e108249. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 386.Zhao L, et al. Gasdermin D inhibits coronavirus infection by promoting the noncanonical secretion of beta interferon. mBio. 2021;13:e0360021. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03600-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 387.Shi F, et al. Coronaviruses Nsp5 antagonizes porcine gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis by cleaving pore-forming p30 fragment. mBio. 2022;13:e0273921. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02739-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 388.Zhao G, et al. African swine fever virus cysteine protease pS273R inhibits pyroptosis by noncanonically cleaving gasdermin D. J. Biol. Chem. 2022;298:101480. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 389.Lei X, et al. Enterovirus 71 inhibits pyroptosis through cleavage of gasdermin D. J. Virol. 2017;91:e01069–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01069-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 390.Hutchinson EC. Influenza virus. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26:809–810. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 391.Rosli S, et al. Gasdermin D promotes hyperinflammation and immunopathology during severe influenza A virus infection. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14:727. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06258-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 392.Speaks, S. et al. Gasdermin D promotes influenza virus-induced mortality through neutrophil amplification of inflammation.Preprint at bioRxiv 2023.03.08.531787 (2023). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 393.Wan X, et al. H7N9 virus infection triggers lethal cytokine storm by activating gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis of lung alveolar epithelial cells. Natl Sci. Rev. 2022;9:nwab137. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 394.Zhao Z, et al. Zika virus causes placental pyroptosis and associated adverse fetal outcomes by activating GSDME. ELife. 2022;11:e73792. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 395.Ren X, et al. Foot-and-mouth disease virus induces porcine gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis through the protease activity of 3C(pro) J. Virol. 2023;97:e0068623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00686-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 396.Lin J, et al. Oncolytic parapoxvirus induces Gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis and activates antitumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:224. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35917-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 397.Yuan R, et al. Cucurbitacin B inhibits non-small cell lung cancer in vivo and in vitro by triggering TLR4/NLRP3/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis. Pharm. Res. 2021;170:105748. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 398.Teng JF, et al. Polyphyllin VI induces caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis via the induction of ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD signal axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers. 2020;12:193. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 399.Yan H, et al. Cisplatin induces pyroptosis via activation of MEG3/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021;17:2606–2621. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.60292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 400.Wang X, et al. Citric acid of ovarian cancer metabolite induces pyroptosis via the caspase-4/TXNIP-NLRP3-GSDMD pathway in ovarian cancer. FASEB J. 2022;36:e22362. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101993RR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 401.Feng WQ, et al. IL-17A-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction induces pyroptosis in colorectal cancer cells and promotes CD8 + T-cell tumour infiltration. J. Transl. Med. 2023;21:335. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04187-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 402.Sala R, et al. GSDMD-dependent pyroptotic induction by a multivalent CXCR4-targeted nanotoxin blocks colorectal cancer metastases. Drug Deliv. 2022;29:1384–1397. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2069302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 403.Mu M, et al. A pan-cancer analysis of molecular characteristics and oncogenic role of gasdermins. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22:80. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02483-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 404.Ning H, et al. Enhancer decommissioning by MLL4 ablation elicits dsRNA-interferon signaling and GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis to potentiate anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:6578. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34253-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 405.Wang WJ, et al. Downregulation of gasdermin D promotes gastric cancer proliferation by regulating cell cycle-related proteins. J. Dig. Dis. 2018;19:74–83. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 406.Xi G, et al. GSDMD is required for effector CD8(+) T cell responses to lung cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105713. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 407.Peng X, et al. Nuclear translocation of Gasdermin D sensitizes colorectal cancer to chemotherapy in a pyroptosis-independent manner. Oncogene. 2022;41:5092–5106. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 408.Gao J, et al. Downregulation of GSDMD attenuates tumor proliferation via the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and inhibition of EGFR/Akt signaling and predicts a good prognosis in non‑small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018;40:1971–1984. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 409.Lv T, et al. Targeting of GSDMD sensitizes HCC to anti-PD-1 by activating cGAS pathway and downregulating PD-L1 expression. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2022;10:e004763. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 410.Jiang Y, et al. Gasdermin D restricts anti-tumor immunity during PD-L1 checkpoint blockade. Cell Rep. 2022;41:111553. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 411.Yao L, Li J, Xu Z, Yan Y, Hu K. GSDMs are potential therapeutic targets and prognostic biomarkers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging. 2022;14:2758–2774. doi: 10.18632/aging.203973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 412.Hu K, et al. Integrated analysis of expression, prognostic value and immune infiltration of GSDMs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging. 2021;13:24117–24135. doi: 10.18632/aging.203669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 413.Yu P, et al. Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase regulates the cross-talk between autophagy and pyroptosis in doxorubicin-treated human melanoma cells in vitro. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2019;40:1237–1244. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0222-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 414.Cai J, et al. Natural product triptolide induces GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in head and neck cancer through suppressing mitochondrial hexokinase-ΙΙ. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021;40:190. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01995-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 415.Wittwer NL, et al. An anti-mesothelin targeting antibody drug conjugate induces pyroptosis and ignites antitumor immunity in mouse models of cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2023;11:e006274. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 416.Liu Z, et al. Apoptin induces pyroptosis of colorectal cancer cells via the GSDME-dependent pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022;18:717–730. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.64350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 417.Wang S, et al. GSDME is related to prognosis and response to chemotherapy in oral cancer. J. Dent. Res. 2022;101:848–858. doi: 10.1177/00220345211073072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 418.Yu J, et al. Cleavage of GSDME by caspase-3 determines lobaplatin-induced pyroptosis in colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:193. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1441-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 419.An H, et al. Tetraarsenic hexoxide enhances generation of mitochondrial ROS to promote pyroptosis by inducing the activation of caspase-3/GSDME in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:159. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03454-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 420.Hu Y, et al. Alantolactone induces concurrent apoptosis and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis of anaplastic thyroid cancer through ROS mitochondria-dependent caspase pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023;108:154528. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 421.Tan G, et al. Radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer and radiation-induced gut damages are regulated by gasdermin E. Cancer Lett. 2022;529:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 422.Lv J, et al. Gasdermin E mediates resistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma to enzymatic digestion through a YBX1-mucin pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022;24:364–372. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00857-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 423.Wang, H., Wang, H., Chen, J., Liu, P. & Xiao, X. Overexpressed FAM111B degrades GSDMA to promote esophageal cancer tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance. Cell Oncol. 47, 343–359 (2023). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 424.Gámez-Chiachio M, et al. Gasdermin B over-expression modulates HER2-targeted therapy resistance by inducing protective autophagy through Rab7 activation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022;41:285. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02497-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 425.Molina-Crespo Á, et al. Intracellular delivery of an antibody targeting gasdermin-B reduces HER2 breast cancer aggressiveness. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:4846–4858. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 426.Wei J, et al. Overexpression of GSDMC is a prognostic factor for predicting a poor outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020;21:360–370. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 427.Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883–899. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 428.Elinav E, et al. Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2013;13:759–771. doi: 10.1038/nrc3611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 429.Zhaolin Z, Guohua L, Shiyuan W, Zuo W. Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12563. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 430.Pavillard LE, Marín-Aguilar F, Bullon P, Cordero MD. Cardiovascular diseases, NLRP3 inflammasome, and western dietary patterns. Pharm. Res. 2018;131:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 431.Taleb S. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016;109:708–715. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2016.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 432.Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592:524–533. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 433.Ridker PM, et al. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:1119–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 434.Opoku E, et al. Gasdermin D mediates inflammation-induced defects in reverse cholesterol transport and promotes atherosclerosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021;9:715211. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.715211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 435.Xu S, et al. Circ-USP9X interacts with EIF4A3 to promote endothelial cell pyroptosis by regulating GSDMD stability in atherosclerosis. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023;45:2186319. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2023.2186319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 436.Fan X, et al. Non-canonical NF-κB contributes to endothelial pyroptosis and atherogenesis dependent on IRF-1. Transl. Res. 2023;255:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 437.Sakalihasan N, Limet R, Defawe OD. Abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 2005;365:1577–1589. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 438.Golledge J, Thanigaimani S, Powell JT, Tsao PS. Pathogenesis and management of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur. Heart J. 2023;44:2682–2697. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 439.Gao J, et al. Gasdermin D deficiency in vascular smooth muscle cells ameliorates abdominal aortic aneurysm through reducing putrescine synthesis. Adv. Sci. 2023;10:e2204038. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 440.Sun K, Li YY, Jin J. A double-edged sword of immuno-microenvironment in cardiac homeostasis and injury repair. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021;6:79. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00455-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 441.Sahoo S, Losordo DW. Exosomes and cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2014;114:333–344. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.300639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 442.Shi H, et al. GSDMD-mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis promotes myocardial I/R injury. Circ. Res. 2021;129:383–396. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 443.Kawaguchi M, et al. Inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts is essential for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2011;123:594–604. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.982777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 444.Jiang K, et al. Gasdermin D inhibition confers antineutrophil-mediated cardioprotection in acute myocardial infarction. J. Clin. Invest. 2022;132:e151268. doi: 10.1172/JCI151268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 445.Zhong L, et al. Novel GSDMD inhibitor GI-Y1 protects heart against pyroptosis and ischemia/reperfusion injury by blocking pyroptotic pore formation. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2023;118:40. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 446.Ye B, et al. Gasdermin D mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis and cardiotoxicity via directly binding to doxorubicin and changes in mitochondrial damage. Transl. Res. 2022;248:36–50. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 447.Qu Y, et al. Gasdermin D mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress via FAM134B to regulate cardiomyocyte autophagy and apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:901. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05333-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 448.Hou Y, et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019;15:565–581. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 449.Temple S. Advancing cell therapy for neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30:512–529. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 450.Voet S, Srinivasan S, Lamkanfi M, van Loo G. Inflammasomes in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019;11:e10248. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201810248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 451.Van Opdenbosch N, Lamkanfi M. Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and disease. Immunity. 2019;50:1352–1364. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.05.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 452.Feng YS, Tan ZX, Wu LY, Dong F, Zhang F. The involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020;64:101192. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 453.Flores J, et al. Caspase-1 inhibition alleviates cognitive impairment and neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:3916. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06449-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 454.Rui W, et al. Systemic inflammasome activation and pyroptosis associate with the progression of amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:280. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02329-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 455.Shen H, et al. Pyroptosis executive protein GSDMD as a biomarker for diagnosis and identification of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav. 2021;11:e02063. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 456.Moonen S, et al. Pyroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: cell type-specific activation in microglia, astrocytes and neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2023;145:175–195. doi: 10.1007/s00401-022-02528-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 457.Wang S, Yuan YH, Chen NH, Wang HB. The mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis activation and their role in Parkinson’s disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019;67:458–464. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 458.Ma X, et al. Prussian blue nanozyme as a pyroptosis inhibitor alleviates neurodegeneration. Adv. Mater. 2022;34:e2106723. doi: 10.1002/adma.202106723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 459.Wang B, et al. GSDMD in peripheral myeloid cells regulates microglial immune training and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2023;13:2663–2679. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 460.Byrne CD, Targher G. NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015;62:S47–S64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 461.Canfora EE, Meex RCR, Venema K, Blaak EE. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019;15:261–273. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0156-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 462.Tilg H, Moschen AR, Roden M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;14:32–42. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 463.Mridha AR, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J. Hepatol. 2017;66:1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.01.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 464.Henao-Mejia J, et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature. 2012;482:179–185. doi: 10.1038/nature10809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 465.Wan X, et al. Uric acid regulates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance through the NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent mechanism. J. Hepatol. 2016;64:925–932. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 466.Xu B, et al. Gasdermin D plays a key role as a pyroptosis executor of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in humans and mice. J. Hepatol. 2018;68:773–782. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 467.Ouyang X, Ghani A, Mehal WZ. Inflammasome biology in fibrogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013;1832:979–988. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 468.Gaul S, et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2021;74:156–167. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 469.Petrasek J, et al. IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:3476–3489. doi: 10.1172/JCI60777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 470.Alicic RZ, Rooney MT, Tuttle KR. Diabetic kidney disease: challenges, progress, and possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017;12:2032–2045. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11491116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 471.Lin J, et al. New insights into the mechanisms of pyroptosis and implications for diabetic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:7057. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 472.Zuo Y, et al. GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis: a critical mechanism of diabetic nephropathy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2021;23:e23. doi: 10.1017/erm.2021.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 473.Cao Z, et al. Pyroptosis in diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2022;531:188–196. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2022.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 474.Al Mamun A, et al. Pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2021;523:131–143. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 475.Wang Y, et al. TLR4/NF-κB signaling induces GSDMD-related pyroptosis in tubular cells in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2019;10:603. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 476.Yuan S, et al. Gasdermin D is involved in switching from apoptosis to pyroptosis in TLR4-mediated renal tubular epithelial cells injury in diabetic kidney disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022;727:109347. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 477.Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T, Susztak K. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2014;124:2333–2340. doi: 10.1172/JCI72271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 478.Cheng Q, et al. Caspase-11/4 and gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis contributes to podocyte injury in mouse diabetic nephropathy. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2021;42:954–963. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00525-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 479.Han J, et al. Hirudin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting Gsdmd-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2023;39:573–589. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09622-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 480.Shao Y, et al. Molecular mechanism of GSDMD mediated glomerular endothelial cells pyroptosis: an implying in the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023;122:110632. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 481.Chang JT. Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:2652–2664. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2002697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 482.Khor B, Gardet A, Xavier RJ. Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011;474:307–317. doi: 10.1038/nature10209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 483.Gao H, et al. Dysregulated microbiota-driven gasdermin D activation promotes colitis development by mediating IL-18 release. Front. Immunol. 2021;12:750841. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.750841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 484.Schwarzer R, Jiao H, Wachsmuth L, Tresch A, Pasparakis M. FADD and caspase-8 regulate gut homeostasis and inflammation by controlling MLKL- and GSDMD-mediated death of intestinal epithelial cells. Immunity. 2020;52:978–993. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 485.Xiao J, Sun K, Wang C, Abu-Amer Y, Mbalaviele G. Compound loss of GSDMD and GSDME function is necessary to achieve maximal therapeutic effect in colitis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2022;5:100162. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2022.100162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 486.Chen H, et al. Dysregulation of CD177(+) neutrophils on intraepithelial lymphocytes exacerbates gut inflammation via decreasing microbiota-derived DMF. Gut Microbes. 2023;15:2172668. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2172668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 487.Ma C, et al. Gasdermin D in macrophages restrains colitis by controlling cGAS-mediated inflammation. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eaaz6717. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz6717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 488.Schaller MD. Cellular functions of FAK kinases: insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J. Cell Sci. 2010;123:1007–1013. doi: 10.1242/jcs.045112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 489.Antoniades I, et al. FAK displacement from focal adhesions: a promising strategy to target processes implicated in cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021;19:3. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00671-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 490.Hu YL, et al. FAK and paxillin dynamics at focal adhesions in the protrusions of migrating cells. Sci. Rep. 2014;4:6024. doi: 10.1038/srep06024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 491.Singh J, Sharma K, Frost EE, Pillai PP. Role of PDGF-A-activated ERK signaling mediated FAK-Paxillin interaction in oligodendrocyte progenitor cell migration. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019;67:564–573. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-1260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 492.Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–2038. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 493.Smolen, J. S. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers4, 18002 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 494.Zhang X, et al. Pyroptosis by NLRP3/caspase-1/gasdermin-D pathway in synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023;27:2448–2456. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 495.Wu XY, et al. Complement C1q synergizes with PTX3 in promoting NLRP3 inflammasome over-activation and pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020;106:102336. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 496.Gao J, Zhang H, Yang Y, Tao J. Therapeutic potential of targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. 2023;46:835–852. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01795-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 497.Correale J, Gaitán MI, Ysrraelit MC, Fiol MP. Progressive multiple sclerosis: from pathogenic mechanisms to treatment. Brain. 2017;140:527–546. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 498.Oh J, Vidal-Jordana A, Montalban X. Multiple sclerosis: clinical aspects. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018;31:752–759. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 499.Dobson R, Giovannoni G. Multiple sclerosis - a review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019;26:27–40. doi: 10.1111/ene.13819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 500.McKenzie BA, et al. Caspase-1 inhibition prevents glial inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in models of multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:E6065–e6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722041115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 501.Song S, et al. Liraglutide attenuate central nervous inflammation and demyelination through AMPK and pyroptosis-related NLRP3 pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022;28:422–434. doi: 10.1111/cns.13791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 502.Li S, et al. Gasdermin D in peripheral myeloid cells drives neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 2019;216:2562–2581. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 503.Cao R, et al. Identification of a small molecule with strong anti-inflammatory activity in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and sepsis through blocking gasdermin D activation. J. Immunol. 2022;209:820–828. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 504.Kiriakidou M, Ching CL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Intern Med. 2020;172:Itc81–itc96. doi: 10.7326/AITC202006020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 505.Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:2110–2121. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1100359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 506.Zhuang L, et al. Disulfiram alleviates pristane-induced lupus via inhibiting GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:379. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01167-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 507.Wang X, et al. Effects of gasdermin D in modulating murine lupus and its associated organ damage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:2118–2129. doi: 10.1002/art.41444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 508.Sun L, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell. 2012;148:213–227. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 509.Han C, et al. New mechanism of nerve injury in Alzheimer’s disease: β-amyloid-induced neuronal pyroptosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020;24:8078–8090. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 510.Boersma B, et al. Inhibition of IL-1β release from macrophages targeted with necrosulfonamide-loaded porous nanoparticles. J. Control Release. 2022;351:989–1002. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 511.Wu YL, et al. Inhibitor necrosulfonamide alleviates lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure in mice. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022;10:1148–1154. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 512.Zhang J, Wei K. Necrosulfonamide reverses pyroptosis-induced inhibition of proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2021;405:112648. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 513.Wen-Yuan W, et al. mTORC1-dependent and GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis in developmental sevoflurane neurotoxicity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023;60:116–132. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 514.Ou AT, et al. Disulfiram-loaded lactoferrin nanoparticles for treating inflammatory diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2021;42:1913–1920. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00770-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 515.Zhou W, et al. Disulfiram with Cu(2+) alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Theranostics. 2023;13:2879–2895. doi: 10.7150/thno.81571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 516.Yao F, et al. HDAC11 promotes both NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD and caspase-3/GSDME pathways causing pyroptosis via ERG in vascular endothelial cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:112. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00906-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 517.Bernier M, et al. Disulfiram treatment normalizes body weight in obese mice. Cell Metab. 2020;32:203–214.e204. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 518.Jia Y, Xu H, Yu Q, Tan L, Xiong Z. Identification and verification of vascular cell adhesion protein 1 as an immune-related hub gene associated with the tubulointerstitial injury in diabetic kidney disease. Bioengineered. 2021;12:6655–6673. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1976540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 519.Lei Y, et al. Disulfiram ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:6862. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34671-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 520.Fillmore N, et al. Disulfiram use is associated with lower risk of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0259061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 521.Bai Y, et al. Disulfiram blocks inflammatory TLR4 signaling by targeting MD-2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2023;120:e2306399120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2306399120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 522.Liu M, et al. Caffeic acid, but not ferulic acid, inhibits macrophage pyroptosis by directly blocking gasdermin D activation. MedComm. 2023;4:e255. doi: 10.1002/mco2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 523.Hooftman A, et al. The immunomodulatory metabolite itaconate modifies NLRP3 and inhibits inflammasome activation. Cell Metab. 2020;32:468–478.e46. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 524.Huang LS, et al. mtDNA activates cGAS signaling and suppresses the YAP-mediated endothelial cell proliferation program to promote inflammatory injury. Immunity. 2020;52:475–486.e475. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 525.Zhou B, Abbott DW. Gasdermin E permits interleukin-1 beta release in distinct sublytic and pyroptotic phases. Cell Rep. 2021;35:108998. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 526.Zheng M, Kanneganti TD. The regulation of the ZBP1-NLRP3 inflammasome and its implications in pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis) Immunol. Rev. 2020;297:26–38. doi: 10.1111/imr.12909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 527.Wang Q, et al. A bioorthogonal system reveals antitumour immune function of pyroptosis. Nature. 2020;579:421–426. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 528.Zhong H, et al. Nanodrug augmenting antitumor immunity for enhanced TNBC therapy via pyroptosis and cGAS-STING activation. Nano Lett. 2023;23:5083–5091. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c01008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 529.Kusumaningrum N, Lee DH, Yoon HS, Park CH, Chung JH. Ultraviolet light-induced gasdermin C expression is mediated via TRPV1/calcium/calcineurin/NFATc1 signaling. Int J. Mol. Med. 2018;42:2859–2866. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 530.Wang C, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation triggers gasdermin D-independent inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2021;6:eabj3859. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abj3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 531.Yang, W. et al. Immune response gene-1 [IRG1]/itaconate protect against multi-organ injury via inhibiting gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis and inflammatory response. Inflammopharmacology32, 419–432 (2023). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 532.Yang W, et al. Protective effects of IRG1/itaconate on acute colitis through the inhibition of gasdermins-mediated pyroptosis and inflammation response. Genes Dis. 2023;10:1552–1563. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.05.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 533.Wu YT, et al. 4-octyl itaconate ameliorates alveolar macrophage pyroptosis against ARDS via rescuing mitochondrial dysfunction and suppressing the cGAS/STING pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;118:110104. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]