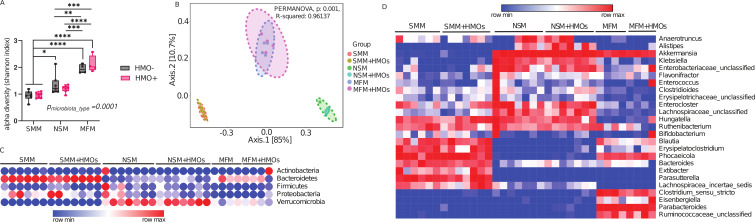
Fig 1.
Maternal secretor status shapes infant microbiota differently from non-secretor or infant formula feeding. (A) Alpha diversity as represented by Shannon index, (B) beta diversity shown as Bray-Curtis Dissimilarity, and (C) Phylum and (D) Genus level microbiota composition of mice colonized with microbiota from infants whose mothers were secretor or non-secretor or those consuming dairy-based formula. Group differences, the effect of microbiota, HMOs, and interaction were determined using the two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison tests in GraphPad Prism Version 10.0. 2 (www.graphpad.com), and adjusted P < 0.05 was considered significant in 1A. Group differences in Beta diversity were determined using a permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) test. SMM = mice transplanted with fecal material from infants consuming milk from secretor mothers, NSM = mice transplanted with fecal material from infants consuming milk from non-secretor mothers, MFM = mice transplanted with fecal material from infants consuming dairy-based milk formula, HMO − = without human milk oligosaccharides supplementation, HMO+ = with human milk oligosaccharides.