Abstract
In mammals, the development of male or female gonads from fetal bipotential gonads depends on intricate genetic networks. Changes in dosage or temporal expression of sex-determining genes can lead to differences of gonadal development. Two rare conditions are associated with disruptions in ovarian determination, including 46,XX testicular differences in sex development (DSD), in which the 46,XX gonads differentiate into testes, and 46,XX ovotesticular DSD, characterized by the coexistence of ovarian and testicular tissue in the same individual. Several mechanisms have been identified that may contribute to the development of testicular tissue in XX gonads. This includes translocation of SRY to the X chromosome or an autosome. In the absence of SRY, other genes associated with testis development may be overexpressed or there may be a reduction in the activity of pro-ovarian/antitesticular factors. However, it is important to note that a significant number of patients with these DSD conditions have not yet recognized a genetic diagnosis. This finding suggests that there are additional genetic pathways or epigenetic mechanisms that have yet to be identified. The text will provide an overview of the current understanding of the genetic factors contributing to 46,XX DSD, specifically focusing on testicular and ovotesticular DSD conditions. It will summarize the existing knowledge regarding the genetic causes of these differences. Furthermore, it will explore the potential involvement of other factors, such as epigenetic mechanisms, in developing these conditions.
Keywords: differences of sex development (DSD), 46, XX testicular DSD, 46, XX ovotesticular DSD, gonadal development, ovary
Introduction
Gonadal development is a fundamental step in forming the reproductive system, and several diseases are associated with atypical gonadal development. The determination and differentiation of gonads from the bipotential gonadal primordium can be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, making it a species-specific process among vertebrates (1).
In mammals, sex is determined by genetic heritage during fertilization. The differentiation of fetal bipotential gonads into testes or ovaries occurs through the action of specific genetic networks. These developmental pathways are typically distinct, mutually exclusive, and driven by a complex interchange of antagonistic genes (2). Changes in the dosage and/or spatiotemporal expression of sex-determining genes can lead to disruptions in the typical development of male or female gonads, causing differences in sex development (DSD). In rare conditions, testicular tissue can develop into an XX gonad, resulting in the condition called 46,XX ovotesticular or testicular DSD.
Clinical presentation
Testicular difference of sex development
Testicular DSD (T DSD) has an estimated frequency of 1:20,000 to 1:25,000 newborn boys. These conditions account for about 2% of cases of male infertility. In about 80% of affected individuals, the genital male phenotype appears typical at birth, but diagnosis usually occurs during or after puberty due to symptoms such as gynecomastia, hypogonadism, and infertility (3). However, in some cases, individuals may present with atypical external genitalia, which enables for earlier investigation and evaluation. The severity of the condition depends on the extent of testicular tissue development.
Ovotesticular difference of sex development
Ovotesticular DSD (OT DSD) is a rare form of DSD, with an estimated incidence of 1:100,000 births (4). This condition is characterized by the presence of both male gonadal tissues, with well-developed seminiferous tubules, and female gonadal tissue, with primordial follicles, within the same individual. In some patients, both types of gonadal tissues may be present in the same gonad, which is referred to as an ovotestis (5). The 46,XX karyotype is the most commonly identified chromosomal pattern in OT DSD, accounting for 65 to 90% of patients (6–8).
Most of the affected individuals present with atypical genitalia at birth. Individuals assigned as males at birth might experience breast development and/or cyclic hematuria. Similarly, individuals assigned as females may exhibit breast development and menstrual irregularities and/or signs of masculinization (9–11).
Although most cases of TDSD and OTDSD are sporadic, there are reports in the literature of individuals with both conditions occurring in the same family. This suggests that a common genetic origin may contribute to the development of these conditions (12–15).
Genetic regulation of gonad development
Gonad development initially follows a similar trajectory in both XX and XY fetuses, with a bipotential gonad being formed from the urogenital crest. After the formation of the bipotential gonad, the processes involved in sex determination guide the development of sex-specific gonadal structures. In male development, there is an interaction between a network of pro-testis genes that promote the differentiation of the bipotential XY gonads into testes. Conversely, in female development, a network of pro-ovarian genes interacts to differentiate the XX bipotential gonads into ovaries (16).
Bipotential gonad
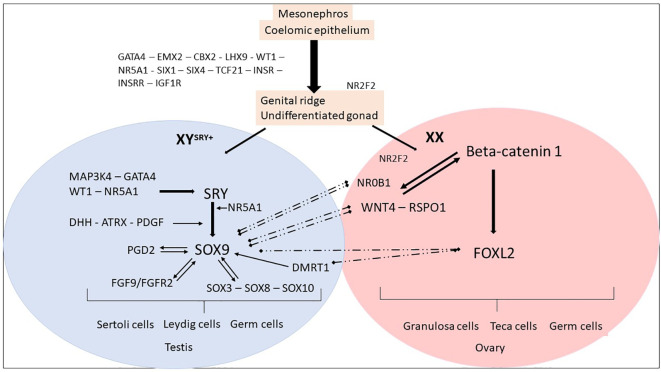
In humans, the genital ridge first emerges between the fourth and fifth weeks of pregnancy. During this period, coelomic epithelial cells undergo proliferation on the ventromedial surface of the mesonephros. This proliferation process is tightly regulated by numerous genes and involves coordinated activity, which leads to the formation of bipotential gonads (17–19) ( Figure 1 ).
Figure 1.
Genes and mechanisms of sex determination. The proliferation of cells from the mesonephros and coelomic epithelium leads to the formation of an undifferentiated and bipotential gonad. This process is regulated by several factors, including GATA4, EMX2, CBX2, LHX9, and WT1. These factors, in turn, regulate NR5A1, SIX1, SIX4, TCF21, and members of the IGF family, leading to the formation of an undifferentiated gonad. The process continues until the fate of the gonad is established, resulting in the formation of either an ovary or a testis. Ovarian differentiation. In the XX fetuses (absence of SRY), the expression of SOX9 remains low and other factors such as NR0B1, FOXL2, WNT4, and RSPO1 become dominant. The upregulation of WNT4 and RSPO1 leads to the activation of the canonical WNT signaling pathway, which in turn upregulates and stabilizes β-catenin. The activation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway plays a crucial role in the differentiation of the female gonad. NR2F2 has a role in maintaining a multipotent state in early supporting gonadal cells, which seems to be necessary for commitment to ovarian development. After birth, FOXL2 continues to suppress male-specific factors, including SOX9 and DMRT1. Testicular differentiation. In XY fetuses, the expression of SRY is triggered by MAP3K4, GATA4, WT1, and NR5A1. The presence of SRY and NR5A1 initiates the expression of SOX9, which leads to the differentiation of pre-Sertoli cells and subsequent Sertoli cells. Other members of the SOX family are also upregulated. SOX9 expression is maintained through positive feedback loops involving FGF9 and PGD2, as well as the regulation from WT1 and NR5A1. The increased expression of SOX9 prevails over NR0B1, FOXL2, WNT4, and RSPO1, promoting testicular differentiation. After birth, DMRT1 suppresses the female-specific factor FOXL2. These interactions between the male and female pathways remain essential throughout adulthood to maintain the gonadal identity.
In mice, null mutations in genes such as Emx2 (Empty Spiracles Homeobox 2), Cbx2 (Chromobox protein homolog 2), Gata4 (GATA Binding Protein 4), Lhx9 (LIM homeobox 9), Wt1 (Wilms tumor 1), and Nr5a1 (Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 5 Group A Member 1) result in regression and changes in the development of the gonadal ridge. Coelomic epithelial cells differentiate into two distinct somatic precursor lineages: supportive cell precursors and steroidogenic cell precursors (20, 21).
Concurrently, primordial germ cells migrate from the yolk sac along the hindgut and dorsal mesentery to colonize the gonad (22). The interaction between somatic and germ cells and signaling from somatic cells is essential for the proliferation and differentiation of primordial germ cells. Furthermore, the female germ cells play a role in maintaining the ovary (23). Subsequently, the bipotential gonad differentiates into testis and ovary, respectively, through a sex-related genes antagonistic network.
Genetic control of ovarian development
In bipotential gonadal tissue of XX individuals, the process of ovarian determination is initiated by a cooperative network of pro-ovarian genes, which includes WNT4 (Wingless Type MMTV integration site family, member 4), RSPO1 (R-Spondin1), and FOXL2 (Forkhead box L2) (24–26) ( Table 1 ). These factors not only activate genes required for ovarian development but also repress pro-testis gene expression (27). In XX individuals, WNT4 and RSPO1 initially direct ovarian determination by upregulating and stabilizing the beta-catenin signaling pathway. CTNNB1 (Catenin Beta 1) essentially promotes germ cell proliferation and granulosa cell differentiation (25, 28). RSPO1, through CTNNB1, prevents WNT4 degradation to maintain ovarian fate (25). FOXL2 expression is initiated in the supporting somatic cells of bipotential gonads, in conjunction with WNT4 and RSPO1 ( Figure 1 ).
Table 1.
Genes associated with testicular development in 46,XX DSD patients.
| Gene | Locus | Protein | Protein action | 46,XX DSD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Name | Phenotype | Condition | Proposed Mechanisms | |||
| DMRT1 | Double sex, Mab3, Related transcription factor 1 | 9p24.3 | DMRT1 | Transcriptional factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Overexpression | Gene implicated in early gonadal development. In adult testis is required to maintain Sertoli cell identity |
| FOXL2 | Forkhead transcriptional factor 2 | 3q23 | FOXL2 | Transcriptional factor | POI/BPES | Underexpression | Gene implicated in maintain granulosa cell transcriptional profiles. In adult ovaries is required to maintain granulosa cell identity |
| FGF9 | Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 | 13q12.11 | FGF9 | Signaling molecule | 46,XX male with hypospadias | Overexpression | Gene affecting later events. It is required for Leydig cell differentiation. |
| NR0B1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 0 group B member 1 | Xp21.3 | DAX1 | Nuclear receptor transcription factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Underexpression | Gene affecting later events. It represses SF1 action. |
| NR2F2 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group F Member 2 | 15q26.2 | COUP-TFII | Nuclear receptor transcription factor | Syndromic 46,XX T DSD | Underexpression | Gene regulates cell fate during gonad development |
| NR5A1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 1 | 9q33 | SF1 | Nuclear receptor transcription factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD POI |
Unknown | Gene implicated in early gonadal development in both sexes |
| RSPO1 | R-spondin homolog 1 | 1p34.3 | RSPO1 | Signaling molecule | Syndromic 46,XX T DSD | Underexpression | Gene required for ovarian development |
| SOX3 | SRY-related, HMG-box gene 3 | Xq27.1 | SOX3 | Transcriptional factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Overexpression | Gene affecting later events – reinforces testis differentiation |
| SOX9 | SRY-related, HMG-box gene 9 | 17q24.3 | SOX9 | Transcriptional factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Overexpression | Gene affecting later events – specification of Sertoli cell, promoting testicular differentiation |
| SOX10 | SRY-related, HMG-box gene 10 | 22q13.1 | SOX10 | Transcriptional factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Overexpression | Gene affecting later events – reinforces testis differentiation |
| SRY | Sex-determining Region-Y chromosome | Yp11.3 | SRY | Transcriptional factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Translocation | Gene affecting later events- required for testis development |
| WNT4 | Wingless-type mmtv integration site family, member 4 | 1p35 | WNT4 | Member of the WNT signaling pathway | MRKH syndrome Serkal syndrome |
Underexpression | Gene required for ovarian development |
| WT1 | Wilms’ Tumor 1 | 11p13 | WT1 | Transcriptional factor | 46,XX T DSD 46,XX OT DSD |
Unknown | Gene implicated in early gonadal development in both sexes |
T, testicular; OT, ovotesticular; POI, Premature ovarian insufficiency; GD, Gonadal dysgenesis, DDS, Dosage sensitive sex reversal, Adrenal hypoplasia; BPES, blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus-inverse syndrome; MRKH, Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome; WAGR, Wilms tumor, aniridia, genitourinary anomalies, mental retardation syndrome).
FOXL2 is required throughout ovarian development and into adulthood to maintain granulosa cell differentiation and support folliculogenesis (2, 29). Foxl2 performs these functions through several mechanisms, such as interacting with ovarian pathway genes, Fst (Follistatin) and Cyp19a1 (cytochrome P450 family 19 subfamily A member 1) (30) and binding to a Sox9 enhancer to reduce Sox9 expression (31). CTNNB1 also promotes the repression of SOX9 expression. The genes involved in ovarian determination tend to show their expression a little later in the process of bipotential gonadal differentiation than the genes of the testicular pathway (32).
Genetic control of testis development
In individuals with XY chromosomes, the SRY gene triggers the cascade of testicular differentiation (33), regulated by WT1 (34), NR5A1 (35), CBX (36), GATA4 (37) and its co-factor ZFPM2 (Zinc Finger Protein, FOG Family Member 2) (38), inducing the expression of the SOX9 gene (39) ( Figure 1 ). SOX9 expression is upregulated immediately after SRY expression in the supporting cells of the developing testis and marks their differentiation into Sertoli cells (40). Subsequently, SOX9 plays a central role in regulating the expression of various genes involved in male sexual differentiation, such as FGF9/FGF2R (Fibroblast Growth Factor/Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2) (41), PTGDS (Prostaglandin D2 Synthase) (42), and AMH (Anti-Mullerian Hormone). Like SRY, the activity of SOX9 is both necessary and sufficient to induce testis development in the genital ridges (43, 44) ( Figure 1 ). Indeed, SOX9 prevents the expression of genes inducing the ovarian differentiation, such as RSPO1 and FOXL2 (45, 46). Other genes, including MAP3K1 (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 1) (47, 48), WWOX (WW Domain Containing Oxidoreductase) (49), DMRT1 (Doublesex and Mab-3 Related Transcription factor 1) (50) and DHX37 (DEAH-Box Helicase 37) (51), have been added as participants in the testicular determination pathway after the identification of deleterious point mutations or copy number alterations associated with the phenotype of differences of testicular differentiation in humans and mice (45).
Molecular mechanisms involved with the development of testicular tissue in the 46,XX gonads
SRY-negative with insufficient expression of pro-ovarian genes
WNT4 gene
WNT4 (1p36.12) encodes a glycoprotein that plays multiple roles in ovarian differentiation and Müllerian duct formation (52) ( Table 1 ). It is modulated by RSPO1 and acts by decreasing the phosphorylation and degradation of β-catenin. Increased levels of β-catenin antagonize SOX9, leading to upregulation of DAX1, which in turn antagonizes SF1 (53) ( Figure 2 ). In mice with Wnt4 knockout, XX individuals exhibit virilization with the presence of Leydig-like cells in their gonad. While Wolffian ducts develop typically, Müllerian ducts are absent (54). In humans, heterozygous loss-of-function pathogenic variants in WNT4 have been found in virilized 46,XX women, who presented excess ovarian androgens and atypical Mullerian duct development (55–58). Additionally, a homozygous WNT4 pathogenic variant has been reported in a consanguineous family with a rare embryonic lethal syndrome known as SERKAL (SEx Reversion, Kidneys, Adrenal and Lung dysgenesis) syndrome ( Table 2 ). This syndrome is characterized by SRY-negative 46,XX testicular or ovotesticular DSD, as well as adrenal hypoplasia, renal agenesis, and severe defects in the lungs and cardiovascular structures (68).
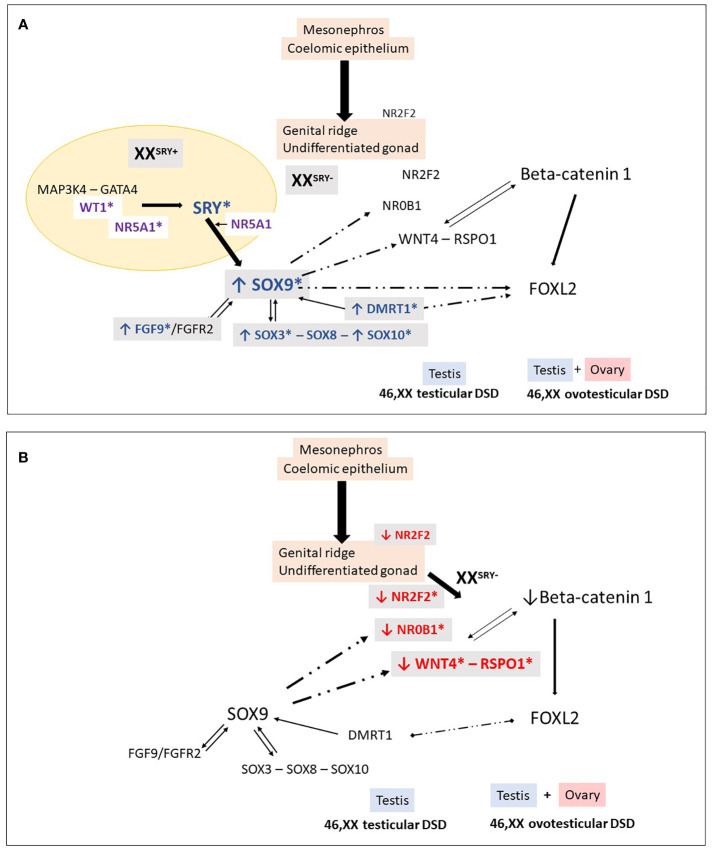
Figure 2.
46,XX Testicular and ovotesticular DSD. Loss of the antagonistic balance of the RSPO1/WNT4/β-catenin pathway and the SRY/SOX9/FGF9 pathway can lead to the development of an abnormal gonad. (A) In XX individuals with Yp translocations and the presence of SRY, testicular differentiation can occur. In 46,XX SRY-negative individuals, testicular development may result from different conditions: overexpression of “pro-testicular” factors such as SOX9, SOX3, SOX10, FGF9, DMRT1, and (B) reduced expression of “pro-ovarian” factors such as RSPO1, WNT4, NR2F2. These changes in gene expression can be caused by an increase in the number of gene copies or their regulatory sequences. Additionally, in particular conditions, factors like WT1 and NR5A1 can also promote testicular development in 46,XX individuals. *Indicates genes associated with 46,XX testicular and ovotesticular DSD in humans.
Table 2.
WNT4, RSPO1 and NR2F2: Genotype and clinical and gonadal characteristics of patients with SRY-negative 46,XX Testicular and Ovotesticular DSD reported in the literature.
| Gene | Pathogenic mechanisms | Molecular findings |
Diagnosis | External genitalia | Gonads | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WNT4 | Decreased Expression | c. 341C>T, (p.Ala114Val) | SERKAL syndrome | Atypical | Fe1: Dysgenetic testis Fe2: Ovotestis |
Mandel H, 2008 (59) |
| RSPO1 | Decreased Expression | c.108_109insG | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical, palmo-plantar keratosis | ND | Parma P, 2006 (60) Micali G, 2005 (61) |
| Deletion of 2752bp (exon 4) | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical, palmo-plantar keratosis | ND | Parma P, 2006 (60) Vernole P, 2000 (62) | ||
| Splice-donor site mutation (c.286 + 1G>A) |
46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical, palmo-plantar keratosis | Ovotestis | Tomaselli S, 2008 (62) | ||
| c.332G>A, (p.Cys111Tyr) | P1: 46,XX Testicular DSD P2: 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD |
P1: Atypical, palmo-plantar keratosis P2: Atypical, palmo-plantar keratosis |
P1: Dysgenetic testis P2: ND |
Naasse Y, 2017 (63) | ||
| c.43_43del A (p.Thr15Argfs*77) | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical, palmo-plantar keratosis | ND | Tallapaka K, 2018 (64) | ||
| NR2F2 | Decreased Expression | c.103_109delGGCGCCC (p.Gly35Argfs*75) | P1: 46,XX DSD | P1: Male genitalia, non-palpable gonads |
P1: ND | Bashamboo A, 2018 (65) |
| c.97_103delCCGCCCG (p.Pro33Alafs*77) | P2: 46,XX DSD | P2: Atypical | P2: ND | |||
| c.97_103delCCGCCCG (p.Pro33Alafs*77) | P3: 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P3: Atypical | P3: Ovotestis (Bilateral) |
|||
| 3-Mb 15q26.2 (95127653_ 98146649)x1 deletion, arr[GRCh37] |
46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis | Carvalheira G, 2019 (66) | ||
| c.23G>A, p.(Trp8*) | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testis | Ganapathi M, 2023 (67) |
SERKAL syndrome, SEx Reversion, Kidneys, Adrenal and Lung dysgenesis syndrome; ND, not described; P, Patient; Fe- Fetus.
RSPO1 gene
RSPO1 gene (1p34.3) encodes a secreted agonist protein of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, that is widely expressed during fetal development ( Table 1 ). RSPO1 plays a key role in gonad differentiation toward the ovary by synergizing the WNT4 to stabilize β-catenin in XX gonads (52, 59). In XX mice, the gonadal phenotype of the Rspo1 and the Wnt4 knockouts are strikingly similar: it ranges from small testes to ovotestes (26). RSPO1 is also expressed in fibroblasts and regulates the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes (69).
Homozygous deleterious RSOP1 variants have been identified in SRY-negative 46,XX DSD patients with atypical genitalia and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and increased susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (60, 62, 69, 70) ( Table 2 ). These variants are typically located in the cysteine-rich furin domains of RSPO1, which are important for stabilizing cytosolic β-catenin. Dysregulation of β-catenin might result in the inhibition of Sox9 degradation and contribute to testis development ( Figure 2 ).
Histological examination of gonads of two affected individuals reveals testicular structures with Leydig cell hyperplasia and ovotestes with small residual ovarian tissue, respectively (63, 70). The absence of RSPO1 also affects the skin microenvironment and epidermal integrity, contributing to an elevated risk of squamous cell carcinoma in palmoplantar regions exposed to frictional stresses (71). Some patients may also present with congenital microphthalmia, cataracts, coloboma of the iris and choroid, onychodystrophy, laryngeal carcinoma, and hearing impairment (60–62, 70, 72).
NR2F2 gene
The NR2F2 (Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group F Member 2) gene (15q26.2) encodes the chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor 2 (COUP-TF2), which is an orphan nuclear receptor ( Table 1 ). COUP-TFII plays important roles during embryogenesis, particularly in cell fate determination, organogenesis, angiogenesis, and metabolism (64, 73). It also plays a role in cell regeneration or dedifferentiation. High expression of COUP-TFII is observed in the mesenchymal component of various organs, including the heart, brain, kidney, adrenal cortex, genital tubercle, otocyst, periocular mesenchyme, optic stalk, and olfactory placode, during development and organogenesis (74). Knockout and heterozygous mice lacking COUP-TFII exhibit multiple vascular abnormalities, especially in the heart and brain. These abnormalities can lead to premature death, with embryonic mortality observed in COUP-TFII knockout mice and death occurring within the first few days of life in heterozygous mice (74).
In the gonadal ridges, COUP-TF2 acts as a “pro-ovary” and “anti-testis” factor (75). Previous studies suggest that the Nr2f2 repression is necessary for fetal Leydig cell differentiation (76).
Ferreira et al. demonstrated that the human NR2F2 is highly upregulated during bipotential gonad development, being detected in early somatic cells that precede the steroidogenic cell emergence in the undifferentiated gonad. The authors propose that COUP-TFII regulates cell fate during gonad development by modulating the WNT signaling pathway, Runx2 (RUNX family transcription factor 2) activity, and the expression of Pparg (Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma) and Sox9. Impairment of its function might disrupt the transcriptional plasticity of early supporting gonadal cells. This disruption during early gonad development may cause early supporting gonadal cells to commit to the testicular pathway (77).
Less than 40 individuals with heterozygous pathogenic variants in NR2F2 have been reported (78). Congenital heart defects are the most well-known phenotypes associated with its pathogenic variants, according to the expression pattern of COUP-TF2 (67, 73). However, the clinical features associated with NR2F2 variants are variable. These features include intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), congenital heart disease (CHD), congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH), blepharophimosis ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES), developmental delays, hypotonia, feeding difficulties, failure to thrive, congenital and acquired microcephaly, dysmorphic facial features (such as up-slanted or short palpebral fissures, micrognathia or retrognathia, low-set or dysplastic ears, hypertelorism, and full cheeks), renal failure, hearing loss, strabismus, asplenia, and vascular malformations. Genital anomalies and DSD have also been described (78).
The molecular mechanisms leading to testis development in some 46,XX patients with COUP-TFII loss-of-function have yet to be defined (77, 79). NR2F2 pathogenic variants/deletion were found to be associated with five patients who had a syndromic form of SRY-negative 46,XX T/OT DSD ( Table 2 ) (65, 66, 78, 79).
These patients presented with atypical genitalia (4/5), congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) (3/5), blepharophimosis ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES) (3/5), and congenital heart disease (CHD) (2/5). Three of the patients had frameshift variants affecting the N-terminal region of the protein, specifically, p.Gly35Argfs*75 and p.Pro33Alafs*77 and the fourth patient had a de novo nonsense variant, p.Trp8* (78, 79).
( Table 2 ). In the fifth patient, a CGH array assay identified a 3-Mb 15q26.2 [arr(GRCh37) 95127653_98146649] x1 deletion that encompassed the entire NR2F2 gene (65, 66).
Genotype-phenotype correlations cannot be identified, as individuals carrying identical NR2F2 variants may present with variable phenotypic manifestations. In the case of 46,XX patients, a single-copy genomic deletion that encompasses the entire NR2F2 gene may result in testicular tissue and atypical external genitalia in some cases, but in others, there may be no evidence of genital anomalies or DSD, despite the presence of other syndromic features (65, 66, 78, 80). These findings suggest that the phenotypic expression of NR2F2-related differences may be likely influenced by additional modifiers.
Presence of SRY gene in the pro-ovarian genes pathway
SRY initiates the formation of male gonadal tissue from bipotential gonadal primordia by stimulating a cascade of related genes, the SRY-related HMG box-containing genes (SOX) ( Table 1 ). These genes play an essential role in the differentiation of Sertoli cells and the development of the testes (81).
The main cause of 46,XX T DSD patients is related to a chromosomal rearrangement during paternal meiosis that leads to the translocation of the SRY from the paternal Y chromosome to the X chromosome or an autosome. In such cases, patients typically exhibit external and internal male genitalia (82).
In such cases, the genetic etiological diagnosis of 46,XX T DSD can be established using the fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) technique, which identifies a fluorescent signal indicating the sequence of the SRY translocated onto the X chromosome or autosome. Alternatively, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to identify the presence of the SRY in the individual’s DNA being evaluated. Microarray analysis is also used to detect the presence of SRY.
It is worth noting that the formation of the testis can occur in 46,XX individuals, even in the absence of SRY, particularly among those who have dosage variations in HMG-box transcription factors ( Table 1 ).
SRY-negative with overexpression of pro-testicular genes
The increased expression of genes associated with male gonadal determination is a well-established etiological cause of 46,XX T/OT DSD patients. Among these genes, members of the SOX family play a significant role in this process.
SOX family
The SOX (SRY-related HMG box) family of proteins is a group of transcriptional regulators that contain a highly conserved high-mobility group domain (83, 84). The high-mobility group domain was first identified in the SRY gene, and several genes from the SOX family have been linked to the etiology of differences of gonadal developmental in mammals.
SOX9 gene
SOX9 (17q24.3) is a transcription factor that plays a significant role in various tissues, including chondrocytes and testes (84) ( Table 1 ). Studies investigating the relationship between phenotype and genotype in humans and mice have demonstrated that SOX9 expression is a critical step in testis development, occurring downstream of SRY. SOX9 is responsible for the specification of Sertoli cells, which in turn initiates testicular differentiation and triggers the production of AMH (85, 86).
Overexpression of SOX9, often caused by gene duplications or copy number variations in the upstream promoter region, has been linked to testis determination in the absence of SRY (84, 87, 88) ( Figure 2 ). In many cases of 46,XX T/OT DSD, SOX9 duplications have been identified as the most commonly observed genetic cause, second only to SRY translocation ( Table 3 ).
Table 3.
SOX9: Genotype and clinical and gonadal characteristics of patients with SRY-negative 46,XX Testicular and Ovotesticular DSD reported in the literature.
| Gene | Pathogenic mechanisms | Molecular findings | Diagnosis | External Genitalia | Gonads | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOX9 | Increased expression | Duplication of SOX9 | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | ND | Huang B, 1999 (85) |
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | Testis | Lee GM, 2014 (89) | |||
| Duplication/Triplication of SOX9 regulatory sequences |
46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testis | Refai O, 2010 (90) | ||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | Testis | Cox JJ, 2011 (91) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | Testis | Vetro A, 2011 (92) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD |
P1: Atypical P2: Atypical P3: Atypical |
P1: ND P2: Testis/ovary P3: Ovotestis/dysgenetic gonad |
Benko S, 2011 (93) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Hypospadias | ND | Xiao B, 2013 (94) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD |
P1: Male P2: Atypical P3: Male |
P1: ND P2: Ovotestis (bilateral) P3: ND |
Vetro A, 2015 (95) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis/Testis | Kim GJ, 2015 (88) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD |
P1: Male P2: Male P3: Male |
P1: Dysgenetic testis P2: Dysgenetic testis P3: ND |
Hyon C, 2015 (96) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Male | Ovotestis | Ohnesorg T, 2017 (97) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Male | ND/ovotestis | Shankara N, 2017 (98) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovary e ovotestis | López-Hernández B, 2018 (99) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD |
P1: ND P2: ND |
P1: Testis P2: Ovotestis |
Croft B, 2018 (100) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Testis/ovary | Mengen E, 2020 (101) | |||
| Promoter-specific gain-of-function variant in the SOX9 | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis/Ovary | Ushijima K, 2021 (102) |
ND, not described; P, Patient; F, Family.
Many of these duplications involve a noncoding region spanning at least 24 kb, known as the RevSex region, located approximately 0.5-0.6 Mb upstream of the SOX9 gene (89–100) ( Table 3 ). This region is predicted to contain a human testis-specific enhancer, and the duplication of this enhancer drives the atypical expression of SOX9, leading to the activation of testicular differentiation (87, 92).
Ushijima et al. escribed an SRY-negative 46,XX OT DSD patient with a novel SOX9 missense variant (p.Glu50Lys) with promoter-specific gain-of-function (GoF) activity in in vitro studies. The authors demonstrated that E50K-SOX9 had (GoF) activity in the mTESCO-luciferase reporter, suggesting that it was due to change(s) in its bioactivity. GoF activity was observed in mTESCO-luc but not in mAmh-luc, thereby indicating that the acquisition of GoF activity was promoter-specific. To associate the promotor SOX9 variant with atypical expression of SOX9, and the beginning of testicular differentiation in the 46,XX OT DSD patient, mice carrying the Sox9 p.E50K were also generated and characterized. These mice, nevertheless, did not develop ovotestis (101). Such discordance of expressivity/phenotype among humans and mice are not limited to sox9/SOX9 (102) but are also described in other genes associated with DSD, including Nr5a1/NR5A1 (103) and Wt1/WT1 (104). The molecular mechanism of the promoter -specific GoF activity of E50K-SOX9 remains to be elucidated.
SOX3 gene
SOX3 (Xq27.1) is another member of the SOX gene family that is involved in gonadal development. It encodes a protein that is highly SRY-like, with an amino acid sequence similarity of 67% for the protein and 90% for the HMG DNA-binding domain (105) ( Table 1 ). Studies in transgenic mice have shown that increased ectopic expression of Sox3 in undifferentiated gonads can lead to sex reversal in XX mice, with complete virilization of external genitalia observed in 77% of animals (106). These findings suggest that Sox3 hyperexpression acts as a counterpart of Sry, leading to increased expression of Sox9. Together with Nr5a1, Sox3 binds to the enhancer region of Sox9 (106).
Like the findings in mice, when increased expression of SOX3 is observed in humans, this gene acts in conjunction with NR5A1 to promote overexpression of SOX9. This phenomenon directs the gonads toward male determination (105) ( Figure 2 ).
The duplication of the SOX3 in a patient with SRY-negative 46,XX OT DSD was initially identified by Sutton et al. (105). Several other 46,XX patients with testicular development (T and OT) and duplications of the SOX3 or in the regions located upstream of this gene have been reported (94, 107–114), supporting the importance of SOX3 in testis development ( Table 3 ).
A heterozygous deletion downstream of SOX3 was also reported in an SRY-negative 46,XX infertility male. The authors of the study speculated that this deletion may play a role in the regulation of the SOX3, potentially resulting in increased expression of SOX3 (115).
SOX10 gene
SOX10 (22q13.1) is another gene closely correlated with SOX9 in humans ( Table 1 ). Initially expressed in neural crest cells during the embryonic period, it plays a critical role in their development. SOX10 is also expressed in fetal gonads (116). In mice, the expression of Sox10 specifically in Sertoli cells strongly indicates its involvement in the testicular differentiation process and reinforces its role in the male pathway (117).
Studies in transgenic animal models have demonstrated that Sox10 overexpression causes sex reversal in XX mice (117). These studies demonstrated that the expression level of Sox10 is crucial in determining the gonadal phenotype. Complete testicular differentiation in all mice was observed in the lineage with higher levels of Sox10 expression, while the lineage expressing lower levels of the transgene showed only 30% of mice with complete sex reversal in the postnatal period. Interestingly, all fetuses from the second group (lower expression levels) were able to initiate Sertoli cell differentiation (presence of cells expressing Sox9 in XX transgenic gonads). In these gonads, cells committed to the female pathway, identified by the expression of Foxl2, were interspersed with Sox9-positive cells (117). This same pattern has been described in ovotestis in humans, as well as in mouse models of ovotestis development (118).
Similarly, gonadal, and reproductive system alterations have been reported in cases of partial duplication of chromosome 22q in 46,XX humans, a chromosomal region that contains SOX10 ( Table 4 ). Rare patients diagnosed with 46,XX T/OT DSD, both syndromic and non-syndromic, have also been described in the literature with chromosome 22 aneuploidies (116, 119–121) ( Table 4 ).
Table 4.
SOX3 and SOX10: Genotype and clinical and gonadal characteristics of the patients with SRY-negative 46,XX Testicular and Ovotesticular DSD reported in the literature.
| Gene | Pathogenic mechanisms | Molecular findings | Diagnosis | External Genitalia | Gonads | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOX3 | Increased expression | Duplication of SOX3 | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P1: Male P2: Male P3: Male |
P1: ND P2: ND P3: ND |
Sutton E, 2011 (103) |
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | ND | Moalem S, 2012 (105) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | ND | Vetro A, 2015 (95) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis | Grinspon RP, 2016 (82) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Hypospadias | ND | Tasic V, 2019 (108) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis | Zhuang J, 2021 (109) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis/Testis | Wei J, 2022 (110) | |||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male and cryptorchidism | ND | Oroz M, 2022 (111) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P1: Atypical | P1: Ovotestis | Oliveira FM, 2023 (112) | |||
| 46,XX DSD | P2: Atypical | P2: Ovary | ||||
| Rearrangement of SOX3 regulatory sequences |
46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testis | Mizuno K, 2014 (106) | ||
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | Dysgenetic testis | Vetro A, 2015 (95) | |||
| 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Testis/Ovary | Haines B, 2015 (107) | |||
| Deletion located downstream of the SOX3 | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | ND | Qin S et al, 2022 (113) | ||
| SOX10 | Increased expression | Duplication of SOX10 | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Testis/Ovary | Aleck KA, 1999 (119) |
| 46,XX Testicular DSD | Male | ND | Seeherunvong T, 2004 (114) | |||
| 46,XX DSD | Male | ND | Falah N, 2017 (117) | |||
| Chromosome 22 - Triplication |
46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Dysgenetic testis | Nicholl RM, 1994 (118) |
ND, not described; P, Patient; F, Family.
DMRT1 gene
The DMRT1 gene (9p24.3) encodes a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in sex determination and gonadal development in various species ( Table 1 ). It possesses a zinc-finger-like DNA binding domain known as the DM (doublesex/MAB-3) domain. This domain allows DMRT1 to bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate the expression of genes involved in sex differentiation (122). DMRT1 expression has been observed in the undifferentiated human XY gonadal primordium. During the early fetal period (gestational weeks 8-20), it is primarily expressed in Sertoli cells, which play a crucial role in testicular development. In the second gestational trimester, childhood, and post-puberty, DMRT1 expression becomes more abundant in spermatogonia (123) This dynamic pattern of expression suggests that DMRT1 plays a significant role in both the early and later stages of male gonadal development.
DMRT1 expression has indeed been detected in oogonia and oocytes during the early stages of ovarian development, up until gestational week 20. However, it is important to note that after the onset of meiotic germ cell division, DMRT1 expression becomes absent in these cells (123).
In contrast to DMRT1 homologs in other vertebrates, mammalian DMRT1 seems to not be involved in the initial sex determination but is instead required for maintaining male gonadal fate (124, 125). Studies in mice have demonstrated that the loss of expression of certain key genes in postnatal life can lead to the reprogramming of Sertoli cells into granulosa cells and vice versa. This suggests that there is a level of plasticity in gonadal fate even after the typical formation of a testis or ovary (31, 124).
Ectopic expression of DMRT1 has been shown to reprogram differentiated female granulosa cells into male Sertoli-like cells. DMRT1 functions in collaboration with other key male sex regulators like SOX9 to maintain and reprogram sexual cell fate. It acts as a singular transcription factor, by regulating gene expression and chromatin accessibility (126).
Bertini et al. reported a three-year-old boy who presented with a typical male phenotype and an SRY-negative 46,XX karyotype (127). The genetic study conducted showed a heterozygous de novo in tandem duplication of 50,221 bp on chromosome 9p. This duplication encompassed exons 2 and 3 of the DMRT1 and was detected using MPLA, CGH-array analysis, and Sanger sequencing. The breakpoints of the duplication were in the intronic regions, and it did not disrupt the coding frame of DMRT1. To investigate other potential genetic factors contributing to the phenotype, a custom NGS panel and whole genome sequencing were performed, but no additional pathogenic or uncertain variants were found in genes known to be involved in pro-testis/anti-ovary gene cascades.
The identified duplication might have allowed DMRT1 to escape the usual transcriptional repression that occurs in 46,XX fetal gonads, leading to the activation of the testicular determination cascade. Notably, no previous cases of SRY-negative 46,XX DSD associated with alterations in DMRT1 have been reported thus far.
FGF9 gene
The FGF9 gene (13q12.1) is a signaling peptide involved in the development of various organs, including limbs, lungs, the adenohypophysis, and the gonadal ridges ( Table 1 ). FGFs are typically considered paracrine factors and play important roles in tissue patterning and organogenesis during embryogenesis. The FGF9 subfamily, which signals from epithelium to mesenchyme, stimulates mesenchymal proliferation. In Fgf9 knockout XY mice, gonadal development is severely impaired during embryonic and fetal life, leading to reproductive phenotypes ranging from different range of undervirilization to complete feminization of external genitalia (128).
In a study by Chiang et al., an SRY-negative 46,XX male with hypospadias and azoospermia was identified (129). Array-CGH analysis revealed duplicated regions on chromosomes 13q12.11 (21.143874–21.174184 Mb) and 13q31.1 (79.807500–79.813700 Mb). These duplicated regions encompassed the entire FGF9 and SPRY2 genes, respectively. The genomic gain of FGF9 was hypothesized to result in FGF9 overexpression, which could explain testicular development instead of ovarian development. Additionally, SPRY2 was previously related to a potential role in male sex organogenesis by controlling FGF9 gene-induced mesonephric cell migration to the developing testis (130). The higher amount of FGF9 would interfere with the expression of WNT4 in the embryo, thereby impeding ovarian development in SRY-negative 46,XX males.
SRY-negative with pathogenic mechanisms not completely comprehended
WT1 gene (11p13) is a transcription factor that encodes a zinc-finger protein ( Table 1 ). It is widely expressed in the condensing mesenchyme, genital ridge, fetal gonads, renal vesicle, developing podocytes of the fetal kidney, and mesothelium (131). The Wt1 and Lhx9 (Lim homeobox 9) genes act as direct activators of the Nr5a1 and play a critical role in the development of the undifferentiated gonad (132).
More than 30 protein isoforms originating from WT1 alternative splicing, alternative translation start sites, and different RNA editing are known. The alternative splice site in intron 9 allows WT1 isoforms with omission or inclusion of three amino acids [lysine-threonine-serine (KTS)] between the third and fourth zinc fingers. These isoforms regulate specific urogenital differentiation processes (133, 134).
Pathogenic WT1 variants are associated with several phenotypes, including 46,XY and 46,XX DSD (135).
WT1 also plays a crucial role in the differentiation and maintenance of Sertoli cells, and this function is positively related to the testicular abnormalities observed in XY patients with pathogenic WT1 variants (37).
The role of WT1 in ovarian development is not yet completely understood. In mice, Wt1 is essential for the maintenance of granulosa cells, and its inactivation leads to atypical ovary development, characterized by reduced ovary size and a fewer number of developing follicles (136, 137).
In SRY-negative 46,XX individuals with testicular and ovotesticular DSD, seven pathogenic variants of WT1 have been identified ( Table 5 ) (147–150). These variants affect the fourth zinc finger, which is a highly conserved region of the WT1 protein. Testicular development in this condition may be influenced by the inappropriate interaction between the mutated WT1 protein and the main ovarian determinant, beta-catenin 1. Additionally, studies have shown that pathogenic variants in exon 10 increase the expression of genes such as SOX9, NR5A1, and DMRT1, which are involved in the development of Sertoli cells. It has been suggested that these alterations could promote the sequestration of beta-catenin 1, leading to the upregulation of pro-testicular pathways (148, 149).
Table 5.
NR5A1, NR0B1 and WT1: Genotype and clinical and gonadal characteristics of the patients with SRY-negative 46,XX Testicular and Ovotesticular DSD reported in the literature.
| Gene | Molecular findings | Diagnosis | External genitalia | Gonadal histology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR5A1 | c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testes (Bilateral) | Domenice S, 2016 (138) |
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD |
F1(n=2): Atypical F2(n=1): Male, micropenis F3(n=1): Male, micropenis F4(n=1): Male, hypospadias |
F1(n=2): Ovotestis (Bilateral) F2(n=1): ND F3(n=1): ND F4(n=1): Dysgenetic testis (Bilateral) |
Bashamboo A, 2016 (139) | |
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD 46,XX DSD Testicular | P1: Atypical P2: Male |
P1: Testis/ovotestis P2: Testis (Bilateral) |
Igarashi M, 2016 (140) | |
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Testicular DSD 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD 46,XX Testicular DSD |
P1: Female, clitoromegaly P2: Atypical P3: Male |
P1: Testis/streak P2: Ovotestis bilateral P3: Testis (Bilateral) |
Baetens D, 2016 (141) | |
| c.275G>A, p.Arg92Gln | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | P1: Ovotestis (Bilateral) | Swartz JM, 2016 (142) | |
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX DSD | Atypical | ND | Takasawa K, 2017 (143) | |
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P1: Male, non-palpable gonads | P1: ND | Knarston IM, 2019 (144) | |
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P2: Atypical | P2: Ovotestis (Bilateral) | ||
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P3: Atypical | P3: ND | ||
| c.779C>T, p.Ala260Val | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P4: Atypical | P4: Ovotestis/ovary | ||
| c.274C>T, p.Arg92Trp | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testes (Bilateral) | Askari M, 2020 (145) | |
| NR0B1 | 80 kb microdeletion removing the regulatory and the NR0B1 sequences | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | Atypical | Ovotestis (Bilateral) | Dangle P, 2017 (146) |
| WT1 | c.1453_1456del, p.Arg485Glyfs*14 | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testis (bilateral) | Gomes NL, 2019 (136) |
| p. Arg495Gly | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P1: Atypical | P1: Dysgenetic testis (bilateral) | Eozenou C, 2020 (137) | |
| p.Pro481Leufs*15 | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P2: Atypical | P2: Dysgenetic testis (bilateral) | ||
| p.Arg495Gln | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P3: Atypical | P3: Dysgenetic testis (bilateral) | ||
| p.Arg495Gln | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P4: Atypical | P4: Ovotestis (bilateral) | ||
| p.Arg495Gln | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P5: Atypical | P5: Ovotestis (bilateral) | ||
| p.Ser478Thrfs*17 | 46,XX Ovotesticular DSD | P6: Atypical | P6: ND | ||
| p.Lys491Glu | 46,XX Testicular DSD | P7: Male | P7: Testis (bilateral) | ||
| c.1437 A>G | 46,XX DSD | Atypical | ND | Sirokha D, 2021 (147) | |
| p.Arg495Gln | 46,XX Testicular DSD | Atypical | Testis (bilateral) | Kirino S, 2023 (148) |
ND, not described; P, Patient; F, Family.
NR5A1 gene
NR5A1 (9q33.3) encodes the steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1), which is expressed in the developing urogenital ridge, hypothalamus, anterior pituitary gland, and steroidogenic tissues ( Table 1 ). SF-1 plays a crucial role in controlling several steps of adrenal and gonadal development (138, 151). NR5A1 variants are associated with a wide phenotypic spectrum of 46,XX, and 46,XY DSD (139, 140).
A single and recurrent variant in the NR5A1 (c.C274T, p.Arg92Trp), present in a heterozygous state, was identified in several 46,XX OT/T DSD patients ( Table 5 ) (140) (141–143, 145, 152). In the study by Askari et al. (152), the p.Arg92Trp variant was identified in a pair of siblings with 46,XX DSD (ovotesticular and testicular DSD patients), as well as in their father who had oligospermia. This further supports the notion that the NR5A1 variant can play a role in the development of different gonadal phenotypes (145). Another variant was identified in the Arg92 codon, just by changing the amino acid to Glutamine (c.G275A, p.Arg92Gln) in a 46,XX OT DSD patient (153). The arginine 92 residue is in a highly conserved region of NR5A1, which is crucial for its interaction with DNA. A third variant (c.C779T, p.Ala260Val) in the NR5A1 was identified in a single 46,XX OT DSD patient (144).
To date, 13 families consisting of 15 patients with 46,XX DSD, and deleterious NR5A1 variants have been reported ( Table 5 ). These patients exhibit a variable range of virilization in the external genitalia, including isolated clitoromegaly, hypospadias, male genitalia with micropenis and cryptorchidism, or male genitalia and cryptorchidism. Likewise, the gonadal tissues also exhibit a diverse range, from streak/dysgenetic gonads to ovotestis or testis, depending on the specific case.
The mechanism which these three variants activate the testicular development in 46,XX OT/T DSD carriers remain elusive. It is suggested that they reduce the inhibition of the expression of male pathway genes, such as SOX9 and AMH (141, 143), by disrupting specific ovarian development signals, mainly in the WNT/β-catenin pathway (144, 153).
NR0B1 gene
NR0B1 (Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 0 Group B Member 1) gene is located in the dosage-sensitive sex reversal (DSS) region at Xp21.2 ( Table 1 ). It encodes an unusual orphan nuclear receptor that lacks the classic DNA-binding domain (154, 155). NR0B1/DAX1 is expressed in various tissues including the developing urogenital ridge, hypothalamus, anterior pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and gonads. It is known to have a role in both ovarian and testicular development, especially in spermatogenesis (156, 157) In mice, a coordinated expression of Nr0b1, Sry, and potentially other factors is necessary to upregulate Sox9 expression in precursor somatic cells. This coordinated expression is crucial for the development of Sertoli cells in the testes (158). These findings confirm an essential role for NR0B1 in both Sertoli and Leydig cell function (157, 159). However, the phenotype of male mice lacking Nr0b1 can vary depending on the strain due to the background-specific abundance of male-determining Sry gene transcripts. This means that the presence of different genetic backgrounds can lead to variability in the phenotypes of XY mice lacking Dax1 (Nr0b1) (160). Additionally, Nr0b1 can be upregulated by Wnt4 through the activation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway (161). Loss of function of NR0B1 causes X-linked primary adrenal insufficiency and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (162, 163).
If normal levels of NR0B1 are crucial for testicular development and spermatogenesis, an excessive dosage of NR0B1 has been suggested to act as an anti-testicular factor (164) Xp21.1 duplications, which include NR0B1 and testis-specific MAGEB genes, have been identified in some XY patients with gonadal dysgenesis. These duplications contribute to abnormalities in gonadal development and function (146, 155, 165–168).
Dangle et al. (169) identified a copy number rearrangement in an SRY-negative 46,XX OT DSD patient using microarray analysis ( Table 5 ). This rearrangement involved an 80 kb microdeletion and disrupted the Xp21.2 DSS critical region. The condition not only resulted in the removal of the regulatory sequences and the NR0B1 gene, but it also impacted the normal genomic organization. This disturbance led to modified gene expression patterns through a position effect (169).
Epigenetics control of gonadal development
Studies have indeed shown that epigenetic profiles undergo dynamic changes during mammalian development, serving as a critical mechanism in determining cell fate decisions and facilitating cellular differentiation (170). Although knowledge about the involvement of epigenetic regulators in human gonadal development remains limited, their role is unquestionable (171, 172).
Regarding the expression of miRNAs in fetal gonads, it is widely recognized that they play a role in the regulation of proteins that are critically involved in gonad development (173, 174). Moreover, it is observed that several miRNAs exhibit a sexually dimorphic expression pattern in fetal gonads, indicating their potential involvement in directing cell fate decisions and maintaining cellular states (174).
In the ovary, the role of miRNAs in follicle assembly, growth, differentiation, and ovulation has been identified (175). Real et al. (176) described miR-124 as a promising candidate gene for mice ovarian development. They found that miR-124 potentially targets several genes involved in sex determination, including Sox9, in their 3’-UTR regions. The authors also demonstrated that inhibiting miR-124 in XX gonadal cells resulted in the ectopic expression of Sox9, suggesting that this miRNA may down-regulate Sox9 in female gonads during the critical period of sex determination. Furthermore, miR-124 exhibited differential up-regulation in XX mice gonads during early stages of differentiation, but not in XY mice gonads (176). In humans, no report of miRNA abnormalities was related to 46,XX DSD etiology.
Various studies have also presented evidence suggesting the involvement of methylation patterns in the process of gonadal determination (171). However, there is currently no direct confirmation of a link between abnormal methylation patterns and the etiology of 46,XX DSD. It is known that DNA methylation and histone modifications are actively involved in the spatiotemporal expression of Sry by making the enhancers and the promoter accessible for the binding of multiple transcription factors (16, 171, 177). Furthermore, methylation of the promoter/regulatory region directly impacts the expression of the Sox9 gene in the testis and ovary of mammals. The adult testis exhibits strong Sox9 expression, while site-specific methylation in the adult ovary could play a crucial role in reducing Sox9 gene expression (178).
Certainly, innovative studies will play a crucial role in establishing the involvement of epigenetic mechanisms in the etiology of 46,XX DSD. These studies will contribute to expanding our understanding of gonads determination.
Conclusion
While our understanding of ovarian determination has significantly advanced, the process of testicular tissue development in an SRY-negative 46,XX gonad remains intriguing. It is worth noting that the majority of individuals with SRY-negative 46,XX testicular and ovotesticular DSD have not received a confirmed genetic diagnosis. This highlights the possibility of unknown genetic pathways or epigenetic mechanisms involved in these conditions. Further research and expansion of patient cohorts are needed to identify these other new members of the gonadal determination cascade.
Author contributions
MF: Writing – review & editing. ES: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BM:Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SD: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding Statement
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) Grants No. 312543/2021-2 (to SD) and 307571/2021-1 (to BM), and by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) Grants No. 2019/26780-9 (to BM), and by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) (to MF).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1. Nagahama Y, Chakraborty T, Paul-Prasanth B, Ohta K, Nakamura M. Sex determination, gonadal sex differentiation, and plasticity in vertebrate species. Physiol Rev. (2021) 101:1237–308. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00044.2019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Arboleda VA, Sandberg DE, Vilain E. DSDs: genetics, underlying pathologies and psychosexual differentiation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2014) 10:603–15. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Wu QY, Li N, Li WW, Li TF, Zhang C, Cui YX, et al. Clinical, molecular and cytogenetic analysis of 46, XX testicular disorder of sex development with SRY-positive. BMC Urol. (2014) 14:70. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-14-70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Blackless M, Charuvastra A, Derryck A, Fausto-Sterling A, Lauzanne K, Lee E. How sexually dimorphic are we? Review and synthesis. Am J Hum Biol. (2000) 12:151–66. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1520-6300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Osorio Acosta VA, Alonso Domínguez FJ. [True hermaphroditism]. Arch Esp Urol. (2004) 57:856–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wiersma R. The clinical spectrum and treatment of ovotesticular disorder of sexual development. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2011) 707:101–3. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-8002-1_21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Mao Y, Chen S, Wang R, Wang X, Qin D, Tang Y. Evaluation and treatment for ovotesticular disorder of sex development (OT-DSD) - experience based on a Chinese series. BMC Urol. (2017) 17:21. doi: 10.1186/s12894-017-0212-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Sircili MH, Denes FT, Costa EM, MaChado MG, Inacio M, Silva RB, et al. Long-term followup of a large cohort of patients with ovotesticular disorder of sex development. J Urol. (2014) 191:1532–6. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.10.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ouhilal S, Turco J, Nangia A, Stotland M, Manganiello PD. True hermaphroditism presenting as bilateral gynecomastia in an adolescent phenotypic male. Fertil Steril. (2005) 83:1041. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2004.09.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Matsui F, Shimada K, Matsumoto F, Itesako T, Nara K, Ida S, et al. Long-term outcome of ovotesticular disorder of sex development: a single center experience. Int J Urol. (2011) 18:231–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2010.02700.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hisamatsu E, Nakagawa Y, Sugita Y. Two cases of late-diagnosed ovotesticular disorder of sex development. APSP J Case Rep. (2013) 4:40.eCollection. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Maciel-Guerra AT, de Mello MP, Coeli FB, Ribeiro ML, Miranda ML, Marques-de-Faria AP, et al. XX Maleness and XX true hermaphroditism in SRY-negative monozygotic twins: additional evidence for a common origin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2008) 93:339–43. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Toublanc JE, Boucekkine C, Abbas N, Barama D, Vilain E, McElreavey K, et al. Hormonal and molecular genetic findings in 46,XX subjects with sexual ambiguity and testicular differentiation. Eur J Pediatr. (1993) 152 Suppl 2:S70–5. doi: 10.1007/BF02125443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Verkauskas G, Jaubert F, Lortat-Jacob S, Malan V, Thibaud E, Nihoul-Fékété C. The long-term followup of 33 cases of true hermaphroditism: a 40-year experience with conservative gonadal surgery. J Urol. (2007) 177:726–31. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.10.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Abbas NE, Toublanc JE, Boucekkine C, Toublanc M, Affara NA, Job JC, et al. A possible common origin of “Y-negative” human XX males and XX true hermaphrodites. Hum Genet. (1990) 84:356–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00196234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Stévant I, Nef S. Genetic control of gonadal sex determination and development. Trends Genet. (2019) 35:346–58. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.02.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. MacLaughlin DT, Donahoe PK. Sex determination and differentiation. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:367–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra022784 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Ostrer H, Huang HY, Masch RJ, Shapiro E. A cellular study of human testis development. Sex Dev. (2007) 1:286–92. doi: 10.1159/000108930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Nef S, Stévant I, Greenfield A. Characterizing the bipotential mammalian gonad. Curr Top Dev Biol. (2019) 134:167–94. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2019.01.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ross AJ, Capel B. Signaling at the crossroads of gonad development. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 16:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2004.11.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. McLaren A. Somatic and germ-cell sex in mammals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. (1988) 322:3–9. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Richardson BE, Lehmann R. Mechanisms guiding primordial germ cell migration: strategies from different organisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2010) 11:37–49. doi: 10.1038/nrm2815 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Xie Y, Wu C, Li Z, Wu Z, Hong L. Early gonadal development and sex determination in mammal. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(14):7500. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ottolenghi C, Omari S, Garcia-Ortiz JE, Uda M, Crisponi L, Forabosco A, et al. Foxl2 is required for commitment to ovary differentiation. Hum Mol Genet. (2005) 14:2053–62. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chassot AA, Gillot I, Chaboissier MC. R-spondin1, WNT4, and the CTNNB1 signaling pathway: strict control over ovarian differentiation. Reproduction. (2014) 148:R97–110. doi: 10.1530/REP-14-0177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Chassot AA, Ranc F, Gregoire EP, Roepers-Gajadien HL, Taketo MM, Camerino G, et al. Activation of beta-catenin signaling by Rspo1 controls differentiation of the mammalian ovary. Hum Mol Genet. (2008) 17:1264–77. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Bashamboo A, McElreavey K. Mechanism of sex determination in humans: insights from disorders of sex development. Sex Dev. (2016) 10:313–25. doi: 10.1159/000452637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ohnesorg T, Vilain E, Sinclair AH. The genetics of disorders of sex development in humans. Sex Dev. (2014) 8:262–72. doi: 10.1159/000357956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Pannetier M, Chassot AA, Chaboissier MC, Pailhoux E. Involvement of FOXL2 and RSPO1 in ovarian determination, development, and maintenance in mammals. Sex Dev. (2016) 10:167–84. doi: 10.1159/000448667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Pannetier M, Fabre S, Batista F, Kocer A, Renault L, Jolivet G, et al. FOXL2 activates P450 aromatase gene transcription: towards a better characterization of the early steps of mammalian ovarian development. J Mol Endocrinol. (2006) 36:399–413. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.01947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Uhlenhaut NH, Jakob S, Anlag K, Eisenberger T, Sekido R, Kress J, et al. Somatic sex reprogramming of adult ovaries to testes by FOXL2 ablation. Cell. (2009) 139:1130–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Lin YT, Capel B. Cell fate commitment during mammalian sex determination. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2015) 32:144–52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.03.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Hacker A, Capel B, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R. Expression of Sry, the mouse sex determining gene. Development. (1995) 121:1603–14. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.6.1603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Hossain A, Saunders GF. The human sex-determining gene SRY is a direct target of WT1. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:16817–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009056200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. de Santa Barbara P, Méjean C, Moniot B, Malclès MH, Berta P, Boizet-Bonhoure B. Steroidogenic factor-1 contributes to the cyclic-adenosine monophosphate down-regulation of human SRY gene expression. Biol Reprod. (2001) 64:775–83. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod64.3.775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Katoh-Fukui Y, Miyabayashi K, Komatsu T, Owaki A, Baba T, Shima Y, et al. Cbx2, a polycomb group gene, is required for Sry gene expression in mice. Endocrinology. (2012) 153:913–24. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Miyamoto Y, Taniguchi H, Hamel F, Silversides DW, Viger RS. A GATA4/WT1 cooperation regulates transcription of genes required for mammalian sex determination and differentiation. BMC Mol Biol. (2008) 9:44. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Tevosian SG, Albrecht KH, Crispino JD, Fujiwara Y, Eicher EM, Orkin SH. Gonadal differentiation, sex determination and normal Sry expression in mice require direct interaction between transcription partners GATA4 and FOG2. Development. (2002) 129:4627–34. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.19.4627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Hanley NA, Hagan DM, Clement-Jones M, Ball SG, Strachan T, Salas-Cortés L, et al. SRY, SOX9, and DAX1 expression patterns during human sex determination and gonadal development. Mech Dev. (2000) 91:403–7. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00307-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Sekido R, Lovell-Badge R. Sex determination involves synergistic action of SRY and SF1 on a specific Sox9 enhancer. Nature. (2008) 453:930–4. doi: 10.1038/nature06944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Jameson SA, Lin YT, Capel B. Testis development requires the repression of Wnt4 by Fgf signaling. Dev Biol. (2012) 370:24–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Moniot B, Declosmenil F, Barrionuevo F, Scherer G, Aritake K, Malki S, et al. The PGD2 pathway, independently of FGF9, amplifies SOX9 activity in Sertoli cells during male sexual differentiation. Development. (2009) 136:1813–21. doi: 10.1242/dev.032631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Barrionuevo F, Bagheri-Fam S, Klattig J, Kist R, Taketo MM, Englert C, et al. Homozygous inactivation of Sox9 causes complete XY sex reversal in mice. Biol Reprod. (2006) 74:195–201. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.105.045930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Chaboissier MC, Kobayashi A, Vidal VI, Lützkendorf S, van de Kant HJ, Wegner M, et al. Functional analysis of Sox8 and Sox9 during sex determination in the mouse. Development. (2004) 131:1891–901. doi: 10.1242/dev.01087 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Ono M, Harley VR. Disorders of sex development: new genes, new concepts. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2013) 9:79–91. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.235 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Eggers S, Ohnesorg T, Sinclair A. Genetic regulation of mammalian gonad development. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2014) 10:673–83. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Loke J, Pearlman A, Radi O, Zuffardi O, Giussani U, Pallotta R, et al. Mutations in MAP3K1 tilt the balance from SOX9/FGF9 to WNT/β-catenin signaling. Hum Mol Genet. (2014) 23:1073–83. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Pearlman A, Loke J, Le Caignec C, White S, Chin L, Friedman A, et al. Mutations in MAP3K1 cause 46,XY disorders of sex development and implicate a common signal transduction pathway in human testis determination. Am J Hum Genet. (2010) 87:898–904. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.11.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. White S, Hewitt J, Turbitt E, van der Zwan Y, Hersmus R, Drop S, et al. A multi-exon deletion within WWOX is associated with a 46,XY disorder of sex development. Eur J Hum Genet. (2012) 20:348–51. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Ledig S, Hiort O, Scherer G, Hoffmann M, Wolff G, Morlot S, et al. Array-CGH analysis in patients with syndromic and non-syndromic XY gonadal dysgenesis: evaluation of array CGH as diagnostic tool and search for new candidate loci. Hum Reprod. (2010) 25:2637–46. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deq167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. da Silva TE, Gomes NL, Lerario AM, Keegan CE, Nishi MY, Carvalho FM, et al. Genetic evidence of the association of DEAH-box helicase 37 defects with 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis spectrum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 104:5923–34. doi: 10.1210/jc.2019-00984 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Biason-Lauber A, Chaboissier MC. Ovarian development and disease: The known and the unexpected. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2015) 45:59–67. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.10.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Carré GA, Greenfield A. Characterising novel pathways in testis determination using mouse genetics. Sex Dev. (2014) 8:199–207. doi: 10.1159/000358402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Vainio S, Heikkilä M, Kispert A, Chin N, McMahon AP. Female development in mammals is regulated by Wnt-4 signalling. Nature. (1999) 397:405–9. doi: 10.1038/17068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Jordan BK, Mohammed M, Ching ST, Délot E, Chen XN, Dewing P, et al. Up-regulation of WNT-4 signaling and dosage-sensitive sex reversal in humans. Am J Hum Genet. (2001) 68:1102–9. doi: 10.1086/320125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Biason-Lauber A, Konrad D, Navratil F, Schoenle EJ. A WNT4 mutation associated with Müllerian-duct regression and virilization in a 46,XX woman. N Engl J Med. (2004) 351:792–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Biason-Lauber A, De Filippo G, Konrad D, Scarano G, Nazzaro A, Schoenle EJ. WNT4 deficiency–a clinical phenotype distinct from the classic Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome: a case report. Hum Reprod. (2007) 22:224–9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Philibert P, Biason-Lauber A, Rouzier R, Pienkowski C, Paris F, Konrad D, et al. Identification and functional analysis of a new WNT4 gene mutation among 28 adolescent girls with primary amenorrhea and müllerian duct abnormalities: a French collaborative study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2008) 93:895–900. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Tomizuka K, Horikoshi K, Kitada R, Sugawara Y, Iba Y, Kojima A, et al. R-spondin1 plays an essential role in ovarian development through positively regulating Wnt-4 signaling. Hum Mol Genet. (2008) 17:1278–91. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Radi O, Parma P, Imbeaud S, Nasca MR, Uccellatore F, Maraschio P, et al. XX sex reversal, palmoplantar keratoderma, and predisposition to squamous cell carcinoma: genetic analysis in one family. Am J Med Genet A. (2005) 138a:241–6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30935 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Micali G, Nasca MR, Innocenzi D, Frasin LA, Radi O, Parma P, et al. Association of palmoplantar keratoderma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, dental anomalies, and hypogenitalism in four siblings with 46,XX karyotype: a new syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2005) 53:S234–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.02.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Vernole P, Terrinoni A, Didona B, De Laurenzi V, Rossi P, Melino G, et al. An SRY-negative XX male with Huriez syndrome. Clin Genet. (2000) 57:61–6. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.2000.570109.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Naasse Y, Bakhchane A, Charoute H, Jennane F, Bignon-Topalovic J, Malki A, et al. A novel homozygous missense mutation in the FU-CRD2 domain of the R-spondin1 gene associated with familial 46,XX DSD. Sex Dev. (2017) 11:269–74. doi: 10.1159/000485393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Lin FJ, Qin J, Tang K, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ. Coup d’Etat: an orphan takes control. Endocr Rev. (2011) 32:404–21. doi: 10.1210/er.2010-0021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Carvalheira G, Malinverni AM, Moysés-Oliveira M, Ueta R, Cardili L, Monteagudo P, et al. The natural history of a man with ovotesticular 46,XX DSD caused by a novel 3-Mb 15q26.2 deletion containing NR2F2 gene. J Endocr Soc. (2019) 3:2107–13. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Carvalheira G, Malinverni AM, Moysés-Oliveira M, Ueta R, Cardili L, Monteagudo P, et al. CORRIGENDUM FOR “The natural history of a man with ovotesticular 46,XX DSD due to a Novel 3-Mb 15q26.2 deletion containing NR2F2 gene”. J Endocr Soc. (2020) 4:bvaa022. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Al Turki S, Manickaraj AK, Mercer CL, Gerety SS, Hitz MP, Lindsay S, et al. Rare variants in NR2F2 cause congenital heart defects in humans. Am J Hum Genet. (2014) 94:574–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.03.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Mandel H, Shemer R, Borochowitz ZU, Okopnik M, Knopf C, Indelman M, et al. SERKAL syndrome: an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by a loss-of-function mutation in WNT4. Am J Hum Genet. (2008) 82:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.08.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Parma P, Radi O, Vidal V, Chaboissier MC, Dellambra E, Valentini S, et al. R-spondin1 is essential in sex determination, skin differentiation and Malignancy. Nat Genet. (2006) 38:1304–9. doi: 10.1038/ng1907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Tomaselli S, Megiorni F, De Bernardo C, Felici A, Marrocco G, Maggiulli G, et al. Syndromic true hermaphroditism due to an R-spondin1 (RSPO1) homozygous mutation. Hum Mutat. (2008) 29:220–6. doi: 10.1002/humu.v29:2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Dellambra E, Cordisco S, Delle Monache F, Bondanza S, Teson M, Nicodemi EM, et al. RSPO1-mutated keratinocytes from palmoplantar keratoderma display impaired differentiation, alteration of cell-cell adhesion, EMT-like phenotype and invasiveness properties: implications for squamous cell carcinoma susceptibility in patients with 46XX disorder of sexual development. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2022) 17:275. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02434-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Tallapaka K, Venugopal V, Dalal A, Aggarwal S. Novel RSPO1 mutation causing 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development with palmoplantar keratoderma: A review of literature and expansion of clinical phenotype. Am J Med Genet A. (2018) 176:1006–10. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Polvani S, Pepe S, Milani S, Galli A. COUP-TFII in health and disease. Cells. (2019) 9(1):101. doi: 10.3390/cells9010101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Pereira FA, Qiu Y, Zhou G, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY. The orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII is required for angiogenesis and heart development. Genes Dev. (1999) 13:1037–49. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.8.1037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Gomes NL, Chetty T, Jorgensen A, Mitchell RT. Disorders of sex development-novel regulators, impacts on fertility, and options for fertility preservation. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(7):2282. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. van den Driesche S, Walker M, McKinnell C, Scott HM, Eddie SL, Mitchell RT, et al. Proposed role for COUP-TFII in regulating fetal Leydig cell steroidogenesis, perturbation of which leads to masculinization disorders in rodents. PloS One. (2012) 7:e37064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Ferreira LGA, Kizys MML, Gama GAC, Pachernegg S, Robevska G, Sinclair AH, et al. COUP-TFII regulates early bipotential gonad signaling and commitment to ovarian progenitors. Cell Biosci. (2024) 14:3. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01182-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Ganapathi M, Matsuoka LS, March M, Li D, Brokamp E, Benito-Sanz S, et al. Heterozygous rare variants in NR2F2 cause a recognizable multiple congenital anomaly syndrome with developmental delays. Eur J Hum Genet. (2023) 31:1117–24. doi: 10.1038/s41431-023-01434-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Bashamboo A, Eozenou C, Jorgensen A, Bignon-Topalovic J, Siffroi JP, Hyon C, et al. Loss of function of the nuclear receptor NR2F2, encoding COUP-TF2, causes testis development and cardiac defects in 46,XX children. Am J Hum Genet. (2018) 102:487–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.01.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Brady PD, DeKoninck P, Fryns JP, Devriendt K, Deprest JA, Vermeesch JR. Identification of dosage-sensitive genes in fetuses referred with severe isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Prenat Diagn. (2013) 33:1283–92. doi: 10.1002/pd.4244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Grinspon RP, Rey RA. Disorders of sex development with testicular differentiation in SRY-negative 46,XX individuals: clinical and genetic aspects. Sex Dev. (2016) 10:6089. doi: 10.1159/000445088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Grinspon RP, Rey RA. Molecular characterization of XX maleness. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Kamachi Y, Kondoh H. Sox proteins: regulators of cell fate specification and differentiation. Development. (2013) 140:4129–44. doi: 10.1242/dev.091793 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Huang B, Wang S, Ning Y, Lamb AN, Bartley J. Autosomal XX sex reversal caused by duplication of SOX9. Am J Med Genet. (1999) 87:349–53. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Lefebvre V, Dumitriu B, Penzo-Méndez A, Han Y, Pallavi B. Control of cell fate and differentiation by Sry-related high-mobility-group box (Sox) transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2007) 39:2195–214. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.05.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. De Santa Barbara P, Bonneaud N, Boizet B, Desclozeaux M, Moniot B, Sudbeck P, et al. Direct interaction of SRY-related protein SOX9 and steroidogenic factor 1 regulates transcription of the human anti-Müllerian hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol. (1998) 18:6653–65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.11.6653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Kim GJ, Sock E, Buchberger A, Just W, Denzer F, Hoepffner W, et al. Copy number variation of two separate regulatory regions upstream of SOX9 causes isolated 46,XY or 46,XX disorder of sex development. J Med Genet. (2015) 52:240–7. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Lee GM, Ko JM, Shin CH, Yang SW. A Korean boy with 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development caused by SOX9 duplication. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2014) 19:108–12. doi: 10.6065/apem.2014.19.2.108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Refai O, Friedman A, Terry L, Jewett T, Pearlman A, Perle MA, et al. De novo 12;17 translocation upstream of SOX9 resulting in 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development. Am J Med Genet A. (2010) 152a:422–6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Cox JJ, Willatt L, Homfray T, Woods CG. A SOX9 duplication and familial 46,XX developmental testicular disorder. N Engl J Med. (2011) 364:91–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1010311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Vetro A, Ciccone R, Giorda R, Patricelli MG, Della Mina E, Forlino A, et al. XX males SRY negative: a confirmed cause of infertility. J Med Genet. (2011) 48:710–2. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Ohnesorg T, van den Bergen JA, Belluoccio D, Shankara-Narayana N, Kean AM, Vasilaras A, et al. A duplication in a patient with 46,XX ovo-testicular disorder of sex development refines the SOX9 testis-specific regulatory region to 24 kb. Clin Genet. (2017) 92:347–9. doi: 10.1111/cge.12976 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Xiao B, Ji X, Xing Y, Chen YW, Tao J. A rare case of 46, XX SRY-negative male with approximately 74-kb duplication in a region upstream of SOX9. Eur J Med Genet. (2013) 56:695–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2013.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Vetro A, Dehghani MR, Kraoua L, Giorda R, Beri S, Cardarelli L, et al. Testis development in the absence of SRY: chromosomal rearrangements at SOX9 and SOX3. Eur J Hum Genet. (2015) 23:1025–32. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Hyon C, Chantot-Bastaraud S, Harbuz R, Bhouri R, Perrot N, Peycelon M, et al. Refining the regulatory region upstream of SOX9 associated with 46,XX testicular disorders of Sex Development (DSD). Am J Med Genet A. (2015) 167a:1851–8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Shankara Narayana N, Kean AM, Ewans L, Ohnesorg T, Ayers KL, Watson G, et al. Painful ovulation in a 46,XX SRY -ve adult male with SOX9 duplication. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. (2017) 2017:17–0045. doi: 10.1530/EDM-17-0045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Benko S, Gordon CT, Mallet D, Sreenivasan R, Thauvin-Robinet C, Brendehaug A, et al. Disruption of a long distance regulatory region upstream of SOX9 in isolated disorders of sex development. J Med Genet. (2011) 48:825–30. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. López-Hernández B, Méndez JP, Coral-Vázquez RM, Benítez-Granados J, Zenteno JC, Villegas-Ruiz V, et al. Duplication of SOX9 associated with 46,XX ovotesticular disorder of sex development. Reprod BioMed Online. (2018) 37:107–12. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.03.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Croft B, Ohnesorg T, Hewitt J, Bowles J, Quinn A, Tan J, et al. Human sex reversal is caused by duplication or deletion of core enhancers upstream of SOX9. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:5319. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07784-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Mengen E, Kayhan G, Kocaay P, Uçaktürk SA. A duplication upstream of SOX9 associated with SRY negative 46,XX ovotesticular disorder of sex development: A case report. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. (2020) 12:308–14. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Ushijima K, Ogawa Y, Terao M, Asakura Y, Muroya K, Hayashi M, et al. Identification of the first promoter-specific gain-of-function SOX9 missense variant (p.E50K) in a patient with 46,XX ovotesticular disorder of sex development. Am J Med Genet A. (2021) 185:1067–75. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Bi W, Huang W, Whitworth DJ, Deng JM, Zhang Z, Behringer RR, et al. Haploinsufficiency of Sox9 results in defective cartilage primordia and premature skeletal mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2001) 98:6698–703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111092198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Miyado M, Inui M, Igarashi M, Katoh-Fukui Y, Takasawa K, Hakoda A, et al. The p.R92W variant of NR5A1/Nr5a1 induces testicular development of 46,XX gonads in humans, but not in mice: phenotypic comparison of human patients and mutation-induced mice. Biol Sex Differ. (2016) 7:56. doi: 10.1186/s13293-016-0114-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Kreidberg JA, Sariola H, Loring JM, Maeda M, Pelletier J, Housman D, et al. WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell. (1993) 74:679–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90515-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Sutton E, Hughes J, White S, Sekido R, Tan J, Arboleda V, et al. Identification of SOX3 as an XX male sex reversal gene in mice and humans. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:328–41. doi: 10.1172/JCI42580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Del Valle I, Buonocore F, Duncan AJ, Lin L, Barenco M, Parnaik R, et al. A genomic atlas of human adrenal and gonad development. Wellcome Open Res. (2017) 2:25. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Moalem S, Babul-Hirji R, Stavropolous DJ, Wherrett D, Bägli DJ, Thomas P, et al. XX male sex reversal with genital abnormalities associated with a de novo SOX3 gene duplication. Am J Med Genet A. (2012) 158a:1759–64. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35390 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Mizuno K, Kojima Y, Kamisawa H, Moritoki Y, Nishio H, Nakane A, et al. Elucidation of distinctive genomic DNA structures in patients with 46,XX testicular disorders of sex development using genome wide analyses. J Urol. (2014) 192:535–41. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.02.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Haines B, Hughes J, Corbett M, Shaw M, Innes J, Patel L, et al. Interchromosomal insertional translocation at Xq26.3 alters SOX3 expression in an individual with XX male sex reversal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 100:E815–20. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Tasic V, Mitrotti A, Riepe FG, Kulle AE, Laban N, Polenakovic M, et al. Duplication of the SOX3 gene in an sry-negative 46,XX male with associated congenital anomalies of kidneys and the urinary tract: case report and review of the literature. Balkan J Med Genet. (2019) 22:81–8. doi: 10.2478/bjmg-2019-0006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Zhuang J, Chen C, Li J, Jiang Y, Wang J, Wang Y, et al. The 46, XX ovotesticular disorder of sex development with xq27.1q27.2 duplication involving the SOX3 gene: A rare case report and literature review. Front Pediatr. (2021) 9:682846. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.682846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Wei J, Liu C, Zhang M, Liu S, Fu J, Lin P. Duplication of SOX3 in an SRY-negative 46,XX male with prostatic utricle: case report and literature review. BMC Med Genomics. (2022) 15:188. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01347-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Oroz M, Vičić A, Požgaj Šepec M, Karnaš H, Stipančić G, Stipoljev F. The smallest dislocated microduplication of Xq27.1 harboring SOX3 gene associated with XX male phenotype. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 36:86–90. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2022-0324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. de Oliveira FM, Barros BA, Dos Santos AP, Campos NLV, Mazzola TN, Filho PL, et al. SOX3 duplication in a boy with 46,XX ovotesticular disorder of sex development and his 46,XX sister with atypical genitalia: Probable germline mosaicism. Am J Med Genet A. (2023) 191:592–8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.63051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Qin S, Wang X, Wang J. Identification of an SRY-negative 46,XX infertility male with a heterozygous deletion downstream of SOX3 gene. Mol Cytogenet. (2022) 15:2. doi: 10.1186/s13039-022-00580-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Seeherunvong T, Perera EM, Bao Y, Benke PJ, Benigno A, Donahue RP, et al. 46,XX sex reversal with partial duplication of chromosome arm 22q. Am J Med Genet A. (2004) 127a:149–51. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.20630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Polanco JC, Wilhelm D, Davidson TL, Knight D, Koopman P. Sox10 gain-of-function causes XX sex reversal in mice: implications for human 22q-linked disorders of sex development. Hum Mol Genet. (2010) 19:506–16. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Wilhelm D, Washburn LL, Truong V, Fellous M, Eicher EM, Koopman P. Antagonism of the testis- and ovary-determining pathways during ovotestis development in mice. Mech Dev. (2009) 126:324–36. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2009.02.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Falah N, Posey JE, Thorson W, Benke P, Tekin M, Tarshish B, et al. 22q11.2q13 duplication including SOX10 causes sex-reversal and peripheral demyelinating neuropathy, central dysmyelinating leukodystrophy, Waardenburg syndrome, and Hirschsprung disease. Am J Med Genet A. (2017) 173:1066–70. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Nicholl RM, Grimsley L, Butler L, Palmer RW, Rees HC, Savage MO, et al. Trisomy 22 and intersex. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. (1994) 71:F57–8. doi: 10.1136/fn.71.1.F57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Aleck KA, Argueso L, Stone J, Hackel JG, Erickson RP. True hermaphroditism with partial duplication of chromosome 22 and without SRY. Am J Med Genet. (1999) 85:2–4. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Raymond CS, Shamu CE, Shen MM, Seifert KJ, Hirsch B, Hodgkin J, et al. Evidence for evolutionary conservation of sex-determining genes. Nature. (1998) 391:691–5. doi: 10.1038/35618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Jørgensen A, Nielsen JE, Blomberg Jensen M, Græm N, Rajpert-De Meyts E. Analysis of meiosis regulators in human gonads: a sexually dimorphic spatio-temporal expression pattern suggests involvement of DMRT1 in meiotic entry. Mol Hum Reprod. (2012) 18:523–34. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gas030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Matson CK, Murphy MW, Sarver AL, Griswold MD, Bardwell VJ, Zarkower D. DMRT1 prevents female reprogramming in the postnatal mammalian testis. Nature. (2011) 476:101–4. doi: 10.1038/nature10239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Matson CK, Zarkower D. Sex and the singular DM domain: insights into sexual regulation, evolution and plasticity. Nat Rev Genet. (2012) 13:163–74. doi: 10.1038/nrg3161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Zarkower D, Murphy MW. DMRT1: an ancient sexual regulator required for human gonadogenesis. Sex Dev. (2022) 16:112–25. doi: 10.1159/000518272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Bertini V, Baldinotti F, Parma P, Tyutyusheva N, Sepich M, Bertolucci G, et al. In tandem intragenic duplication of doublesex and mab-3-related transcription factor 1 (DMRT1) in an SRY-negative boy with a 46,XX disorder of sex development. Genes (Basel). (2023) 14:2067. doi: 10.3390/genes14112067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Colvin JS, Green RP, Schmahl J, Capel B, Ornitz DM. Male-to-female sex reversal in mice lacking fibroblast growth factor 9. Cell. (2001) 104:875–89. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00284-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Chiang HS, Wu YN, Wu CC, Hwang JL. Cytogenic and molecular analyses of 46,XX male syndrome with clinical comparison to other groups with testicular azoospermia of genetic origin. J Formos Med Assoc. (2013) 112:72–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2012.02.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Chi L, Itäranta P, Zhang S, Vainio S. Sprouty2 is involved in male sex organogenesis by controlling fibroblast growth factor 9-induced mesonephric cell migration to the developing testis. Endocrinology. (2006) 147:3777–88. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Ambu R, Vinci L, Gerosa C, Fanni D, Obinu E, Faa A, et al. WT1 expression in the human fetus during development. Eur J Histochem. (2015) 59:2499. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2499 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Wilhelm D, Englert C. The Wilms tumor suppressor WT1 regulates early gonad development by activation of Sf1. Genes Dev. (2002) 16:1839–51. doi: 10.1101/gad.220102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Haber DA, Sohn RL, Buckler AJ, Pelletier J, Call KM, Housman DE. Alternative splicing and genomic structure of the Wilms tumor gene WT1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1991) 88:9618–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Hammes A, Guo JK, Lutsch G, Leheste JR, Landrock D, Ziegler U, et al. Two splice variants of the Wilms’ tumor 1 gene have distinct functions during sex determination and nephron formation. Cell. (2001) 106:319–29. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00453-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Ferrari MTM, Elias FM, Gomes NLRA, Batista RL, Faria JAD, Nishi MY, et al. WT1: A single gene associated with multiple and severe phenotypes. Endocrine Metab Science. (2023) 13:100143. doi: 10.1016/j.endmts.2023.100143 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Cen C, Chen M, Zhou J, Zhang L, Duo S, Jiang L, et al. Inactivation of Wt1 causes pre-granulosa cell to steroidogenic cell transformation and defect of ovary development†. Biol Reprod. (2020) 103:60–9. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaa042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Gao F, Zhang J, Wang X, Yang J, Chen D, Huff V, et al. Wt1 functions in ovarian follicle development by regulating granulosa cell differentiation. Hum Mol Genet. (2014) 23:333–41. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Morohashi KI, Inoue M, Baba T. Coordination of multiple cellular processes by NR5A1/nr5a1. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). (2020) 35:756–64. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Lin L, Achermann JC. Steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, Ad4BP, NR5A1) and disorders of testis development. Sex Dev. (2008) 2:200–9. doi: 10.1159/000152036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Domenice S, MaChado AZ, Ferreira FM, Ferraz-de-Souza B, Lerario AM, Lin L, et al. Wide spectrum of NR5A1-related phenotypes in 46,XY and 46,XX individuals. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. (2016) 108:309–20. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Igarashi M, Takasawa K, Hakoda A, Kanno J, Takada S, Miyado M, et al. Identical NR5A1 missense mutations in two unrelated 46,XX individuals with testicular tissues. Hum Mutat. (2017) 38:39–42. doi: 10.1002/humu.23116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Baetens D, Stoop H, Peelman F, Todeschini AL, Rosseel T, Coppieters F, et al. NR5A1 is a novel disease gene for 46,XX testicular and ovotesticular disorders of sex development. Genet Med. (2017) 19:367–76. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Bashamboo A, Donohoue PA, Vilain E, Rojo S, Calvel P, Seneviratne SN, et al. A recurrent p.Arg92Trp variant in steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1) can act as a molecular switch in human sex development. Hum Mol Genet. (2016) 25:3446–53. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Knarston IM, Robevska G, van den Bergen JA, Eggers S, Croft B, Yates J, et al. NR5A1 gene variants repress the ovarian-specific WNT signaling pathway in 46,XX disorders of sex development patients. Hum Mutat. (2019) 40:207–16. doi: 10.1002/humu.23672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Takasawa K, Igarashi M, Ono M, Takemoto A, Takada S, Yamataka A, et al. Phenotypic variation in 46,XX disorders of sex development due to the NR5A1 p.R92W variant: a sibling case report and literature review. Sex Dev. (2017) 11:284–8. doi: 10.1159/000485868 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. García-Acero M, Molina M, Moreno O, Ramirez A, Forero C, Céspedes C, et al. Gene dosage of DAX-1, determining in sexual differentiation: duplication of DAX-1 in two sisters with gonadal dysgenesis. Mol Biol Rep. (2019) 46:2971–8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04758-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Gomes NL, de Paula LCP, Silva JM, Silva TE, Lerario AM, Nishi MY, et al. A 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development caused by a Wilms’ tumour Factor-1 (WT1) pathogenic variant. Clin Genet. (2019) 95:172–6. doi: 10.1111/cge.13459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Eozenou C, Gonen N, Touzon MS, Jorgensen A, Yatsenko SA, Fusee L, et al. Testis formation in XX individuals resulting from novel pathogenic variants in Wilms’ tumor 1 (WT1) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2020) 117:13680–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921676117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Sirokha D, Gorodna O, Vitrenko Y, Zelinska N, Ploski R, Nef S, et al. A novel WT1 mutation identified in a 46,XX testicular/ovotesticular DSD patient results in the retention of intron 9. Biol (Basel). 30(12):1248. doi: 10.3390/biology10121248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Kirino S, Yogi A, Adachi E, Nakatani H, Gau M, Iemura R, et al. Phenotypic variation in 46,XX disorders of sex development due to the 4th zinc finger domain variant of WT1: A familial case report. Sex Dev. (2023) 17(1):51–5. doi: 10.1159/000529720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Parker KL, Rice DA, Lala DS, Ikeda Y, Luo X, Wong M, et al. Steroidogenic factor 1: an essential mediator of endocrine development. Recent Prog Horm Res. (2002) 57:19–36. doi: 10.1210/rp.57.1.19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Askari M, Rastari M, Seresht-Ahmadi M, McElreavey K, Bashamboo A, Razzaghy-Azar M, et al. A missense mutation in NR5A1 causing female to male sex reversal: A case report. Andrologia. (2020) 52:e13585. doi: 10.1111/and.13585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153. Swartz JM, Ciarlo R, Guo MH, Abrha A, Weaver B, Diamond DA, et al. A 46,XX ovotesticular disorder of sex development likely caused by a steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1) variant. Horm Res Paediatr. (2017) 87:191–5. doi: 10.1159/000452888 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Zanaria E, Muscatelli F, Bardoni B, Strom TM, Guioli S, Guo W, et al. An unusual member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily responsible for X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita. Nature. (1994) 372:635–41. doi: 10.1038/372635a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Bardoni B, Zanaria E, Guioli S, Floridia G, Worley KC, Tonini G, et al. A dosage sensitive locus at chromosome Xp21 is involved in male to female sex reversal. Nat Genet. (1994) 7:497–501. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. Iyer AK, McCabe ER. Molecular mechanisms of DAX1 action. Mol Genet Metab. (2004) 83:60–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.07.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157. Meeks JJ, Weiss J, Jameson JL. Dax1 is required for testis determination. Nat Genet. (2003) 34:32–3. doi: 10.1038/ng1141 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158. Bouma GJ, Albrecht KH, Washburn LL, Recknagel AK, Churchill GA, Eicher EM. Gonadal sex reversal in mutant Dax1 XY mice: a failure to upregulate Sox9 in pre-Sertoli cells. Development. (2005) 132:3045–54. doi: 10.1242/dev.01890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159. Meeks JJ, Crawford SE, Russell TA, Morohashi K, Weiss J, Jameson JL. Dax1 regulates testis cord organization during gonadal differentiation. Development. (2003) 130:1029–36. doi: 10.1242/dev.00316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160. Fernandes-Freitas I, Milona A, Murphy KG, Dhillo WS, Owen BM. Live birth in sex-reversed XY mice lacking the nuclear receptor dax1. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:1703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58788-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161. Mizusaki H, Kawabe K, Mukai T, Ariyoshi E, Kasahara M, Yoshioka H, et al. Dax-1 (dosage-sensitive sex reversal-adrenal hypoplasia congenita critical region on the X chromosome, gene 1) gene transcription is regulated by wnt4 in the female developing gonad. Mol Endocrinol. (2003) 17:507–19. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162. Seminara SB, Achermann JC, Genel M, Jameson JL, Crowley WF, Jr. X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita: a mutation in DAX1 expands the phenotypic spectrum in males and females. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1999) 84:4501–9. doi: 10.1210/jc.84.12.4501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163. El-Khairi R, Martinez-Aguayo A, Ferraz-de-Souza B, Lin L, Achermann JC. Role of DAX-1 (NR0B1) and steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1) in human adrenal function. Endocr Dev. (2011) 20:38–46. doi: 10.1159/000321213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164. Goodfellow PN, Camerino G. DAX-1, an “antitestis” gene. Exs. (2001) 91):57–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165. Barbaro M, Oscarson M, Schoumans J, Staaf J, Ivarsson SA, Wedell A. Isolated 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis in two sisters caused by a Xp21.2 interstitial duplication containing the DAX1 gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2007) 92:3305–13. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166. Igarashi M, Dung VC, Suzuki E, Ida S, Nakacho M, Nakabayashi K, et al. Cryptic genomic rearrangements in three patients with 46,XY disorders of sex development. PloS One. (2013) 8:e68194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167. Norling A, Lindén Hirschberg A, Iwarsson E, Persson B, Wedell A, Barbaro M. Novel candidate genes for 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis identified by a customized 1 M array-CGH platform. Eur J Med Genet. (2013) 56:661–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2013.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168. Nishi MY, Faria Júnior JAD, Krepischi ACV, de Moraes DR, da Costa SS, Silva E, et al. A small supernumerary xp marker chromosome including genes NR0B1 and MAGEB causing partial gonadal dysgenesis and gonadoblastoma. Sex Dev. (2022) 16:55–63. doi: 10.1159/000517085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169. Dangle P, Touzon MS, Reyes-Múgica M, Witchel SF, Rajkovic A, Schneck FX, et al. Female-to-male sex reversal associated with unique Xp21.2 deletion disrupting genomic regulatory architecture of the dosage-sensitive sex reversal region. J Med Genet. (2017) 54:705–9. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-104128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170. Reik W. Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature. (2007) 447:425–32. doi: 10.1038/nature05918 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171. Tachibana M. Epigenetics of sex determination in mammals. Reprod Med Biol. (2016) 15:59–67. doi: 10.1007/s12522-015-0223-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172. Miyawaki S, Tachibana M. Role of epigenetic regulation in mammalian sex determination. Curr Top Dev Biol. (2019) 134:195–221. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2019.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173. Knarston I, Ayers K, Sinclair A. Molecular mechanisms associated with 46,XX disorders of sex development. Clin Sci (Lond). (2016) 130:421–32. doi: 10.1042/CS20150579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174. Gunes SO, Metin Mahmutoglu A, Agarwal A. Genetic and epigenetic effects in sex determination. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. (2016) 108:321–36. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175. Grossman H, Shalgi R. A role of microRNAs in cell differentiation during gonad development. Results Probl Cell Differ. (2016) 58:309–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-31973-5_12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176. Real FM, Sekido R, Lupiáñez DG, Lovell-Badge R, Jiménez R, Burgos M. A microRNA (mmu-miR-124) prevents Sox9 expression in developing mouse ovarian cells. Biol Reprod. (2013) 89:78. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.110957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177. Tanaka SS, Nishinakamura R. Regulation of male sex determination: genital ridge formation and Sry activation in mice. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2014) 71:4781–802. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1703-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178. Pamnani M, Sinha P, Singh A, Nara S, Sachan M. Methylation of the Sox9 and Oct4 promoters and its correlation with gene expression during testicular development in the laboratory mouse. Genet Mol Biol. (2016) 39:452–8. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2015-0172 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]