Abstract
In this study, 21 species of Hybos Meigen, 1803 are reviewed in Huaping National Nature Reserve, China. Among these, three species, i.e., Hybosdenticulatussp. nov., Hybosforcipatasp. nov. and H.paraterminalissp. nov., are described as new to science. In addition, nine known species of this genus are reported for the first time in Guangxi. All the known species were enumerated, and an identification key to the species of Hybos from Huaping National Nature Reserve based on morphological characteristics is provided.
Key words: Checklist, hybotid flies, key, new species, newly recorded species, South China region, taxonomy
Introduction
Hybos Meigen, 1803 is a species-rich genus of Empidoidea occurring worldwide. To date, 242 species of Hybos have been recorded worldwide, of which 28 species are distributed in the Palaearctic Realm and 191 species are distributed in the Oriental Realm (Yang and Yang 2004; Yang et al. 2007; Plant 2013; Shamshev et al. 2013; Shamshev et al. 2015; Li et al. 2017; Cao et al. 2018; Kanavalová et al. 2021; Li et al. 2022; Li and Yang 2023).
Huaping National Nature Reserve, the oldest national-level nature reserve established in Guangxi, has rich and diverse animal and plant resources and is an important gene bank of biological species in China. The climate here is humid, with relative humidity ranging from 85% to 90% during the rainy season from April to August, and a forest coverage rate of 98.2%, providing a relatively suitable environment for the survival of Hybos. During the collection investigation of Huaping National Nature Reserve in June 1982, five new Hybos species were discovered and reported (H.ensatus Yang & Yang, 1986, H.flaviscutellum Yang & Yang, 1986, H.longshengensis Yang & Yang, 1986, H.orientalis Yang & Yang, 1986, H.truncatus Yang & Yang, 1986), showcasing its rich biodiversity (Yang and Yang, 2004).
We surveyed the insect diversity in the national nature reserve twice in 2023 to update the faunal information of the South China region. In this study, three new species, H.denticulatus sp. nov., H.forcipata sp. nov. and H.paraterminalis sp. nov., are reported and described. While, nine species, H.bawanglingensis Yang, 2008, H.fujianensis Li & Yang, 2023, H.guizhouensis Yang & Yang, 1988, H.jianyangensis Yang & Yang, 2004, H.leucopogus Li & Yang, 2023, H.obtusatus Yang & Grootaert, 2005, H.particularis Yang, Yang & Hu, 2002, H.pingbianensis Yang & Yang, 2004 and H.xiaohuangshanensis Yang, Gaimari & Grootaert, 2005 are newly recorded in Guangxi.
Diagnosis and figures are provided for all 21 species, including related known ones (H.anae Yang & Yang, 2004, H.chinensis Yang & Yang, 2004, H.ensatus Yang & Yang, 1986, H.flaviscutellum Yang & Yang, 1986, H.longshengensis Yang & Yang, 1986, H.orientalis Yang & Yang, 1986 and H.truncatus Yang & Yang, 1986). Further, the male genitalia of H.bawanglingensis and H.nasutus Yang & Yang, 1986 are re-illustrated, and 13 known species are photographed (H.bawanglingensis, H.ensatus, H.fujianensis, H.guizhouensis, H.jianyangensis, H.longshengensis, H.nasutus, H.obtusatus, H.orientalis, H.particularis, H.pingbianensis, H.truncatus and H.xiaohuangshanensis). A checklist and key of Hybos from Huaping National Nature Reserve are also provided.
Material and methods
Material for this study were collected by sweeping in Huaping National Nature Reserve, Guangxi in May and August 2023. All the studied specimens are preserved in 80% ethanol and deposited in the Entomological Museum of China Agricultural University (CAU), Beijing.
Specimens were examined using a ZEISS Stemi 2000c. Images were made by connecting the microscope with a Canon EOS 5D Mark IV camera. Image plates were post-processed with Adobe Photoshop CS6 Extended. Representative specimens were dissected. Male external genitalia were drawn after macerating the apical portion of the abdomen with cold 20% hydroxide (NAOH) for 4–8 h. Species of Hybos from China have been thoroughly reviewed and keyed (Yang and Yang 2004), providing us with a useful tool to identify the species in this study.
Abbreviations and morphological terms used in the text: acr–acrostichal bristle(s), ad–anterodorsal bristle(s), av–anteroventral bristle(s), dc–dorsocentral bristle(s), ppn–postpronotal humeral bristle(s), npl–notopleural bristle(s), oc–ocellar bristle(s), pd–posterodorsal bristle(s), prsc–prescutellar bristle(s), psa–postalar bristle(s), pv–posteroventral bristle(s), sc–scutellar bristle(s).
Taxonomy
Family. Hybotidae
Meigen, 1820
0D8BCA01-AA89-5BCF-928E-4DEBDAC10C30
Hybotinae Meigen, 1820: x. Type genus Hybos Meigen, 1803.
Hybotidae Macquart, 1827: 136.
Genus. Hybos
Meigen, 1803.
42E5402E-91E6-5513-896E-CDD40BCB390C
Hybos Meigen, 1803: 269. Type species: Hybosfunebris Meigen, 1804.
Neoza Meigen, 1800: 27. Type species: Muscagrossipes Linnaeus, 1767.
Pseudosyneches Frey, 1953: 66. Type species: Hybos (Pseudosyneches) palawanus Frey, 1953.
Diagnosis.
Hybos is distinguished from all other Empidoidea genera by the following combination of characters: (1) vein Rs short arising distal to the middle of cell bm; (2) cell cup usually distinctly longer than bm; (3) eyes narrowly but distinctly separated on face, not virtually contiguous; (4) proboscis narrow, long spine-like, as long as head or longer, lacking pseudotracheae; (5) hind femur usually strongly thickened with strong ventral bristles; and (6) hind tibia linear (apart from basal geniculation) or slightly thickened apically.
Key to species of Hybos from Huaping National Nature Reserve
This key is used for identifying Hybos in Huaping National Nature Reserve. Users are urged to confirm all decisions by referring to detailed descriptions. There are likely to be other undiscovered new species in Huaping National Nature Reserve. Therefore, it needs to be used with caution.
| 1 | All legs uniformly dark brown to black excluding hind knee | 2 |
| – | Legs at least partly yellow to yellow-brown excluding hind knee | 9 |
| 2 | All legs uniformly black-brown to black including hind knee | 3 |
| – | Legs dark brown to blackish, but only hind knee dark yellow | H.fujianensis Li & Yang, 2023 |
| 3 | Hind tibia apically without one pd and one av | 4 |
| – | Hind tibia apically with one pd and one av | H.paraterminalis sp. nov. |
| 4 | Hind tibia without distinct bristles | 5 |
| – | Hind tibia with one dorsal bristle near apex | 7 |
| 5 | Mid tibia with one or two dorsal bristles | 6 |
| – | Mid tibia with four dorsal bristles | H.jianyangensis Yang & Yang, 2004 |
| 6 | R4+5 and M1 nearly parallel apically; mid tibia with two long dorsal bristles on basal ½ | H.anae Yang & Yang, 2004 |
| – | R4+5 and M1 weakly convergent apically; mid tibia with one very long dorsal bristle at middle | H.leucopogus Li & Yang, 2023 |
| 7 | Mid femur with ad and pv | 8 |
| – | Mid femur only with pv | H.obtusatus Yang & Grootaert, 2005 |
| 8 | Hypandrium with row of long bristles near apical margin | H.denticulatus sp. nov. |
| – | Hypandrium without long bristles near apical margin | H.forcipata sp. nov. |
| 9 | Fore and mid femora brownish to black | 10 |
| – | Fore and mid femora uniformly or mostly yellow | 15 |
| 10 | Mid tibia black-brown to black | 11 |
| – | Mid tibia yellow to brownish | 12 |
| 11 | Hind knee black-brown and fore tibia only with one dorsal bristle at middle | H.ensatus Yang & Yang, 1986 |
| – | Hind knee yellow and fore tibia with four to five dorsal bristles | H.xiaohuangshanensis Yang, Gaimari & Grootaert, 2005 |
| 12 | Legs uniformly brownish | H.truncatus Yang & Yang, 1986 |
| – | Legs partly brownish | 13 |
| 13 | Fore tarsomeres 1–2 yellow | H.guizhouensis Yang & Yang, 1988 |
| – | Fore tarsomeres 1–2 black-brown to black | 14 |
| 14 | Left surstylus with two processes | H.longshengensis Yang & Yang, 1986 |
| – | Left surstylus with three processes | H.particularis Yang, Yang & Hu, 2002 |
| 15 | Fore and mid femora uniformly yellow including dorsally | 16 |
| – | Fore and mid femora mostly yellow except dark yellow-brown dorsally | H.serratus Yang & Yang, 1992 |
| 16 | Hind femur black-brown to black | 17 |
| – | Hind femur mostly yellow | 18 |
| 17 | Fore coxa black-brown | H.chinensis Yang & Yang, 2004 |
| – | Fore coxa yellow | H.pingbianensis Yang & Yang, 2004 |
| 18 | Hind tibia with one dorsal bristle at middle | 19 |
| – | Hind tibia without dorsal bristles at middle | H.flaviscutellum Yang & Yang, 1986 |
| 19 | Arista with short pubescence | 20 |
| – | Arista bare | H.nasutus Yang & Yang, 1986 |
| 20 | Right surstylus furcated, with three processes | H.bawanglingensis Yang, 2008 |
| – | Right surstylus triangular, without processes | H.orientalis Yang & Yang, 1986 |
Checklist of Hybos in Huaping National Nature Reserve of China
New records in Guangxi in bold
Hybosanae Yang & Yang, 2004 (Fujian, Guangxi)
Hybosbawanglingensis Yang, 2008 (Guangxi, Hainan)
Hyboschinensis Yang & Yang, 2004 (Fujian, Guangxi, Guizhou, Zhejiang)
Hybosdenticulatus sp. nov. (Guangxi)
Hybosensatus Yang & Yang, 1986 (Guangxi, Guizhou, Henan, Sichuan)
Hybosflaviscutellum Yang & Yang, 1986 (Guangxi, Zhejiang)
Hybosforcipata sp. nov. (Guangxi)
Hybosfujianensis Li & Yang, 2023 (Fujian, Guangxi)
Hybosguizhouensis Yang & Yang, 1988 (Guangxi, Guizhou)
Hybosjianyangensis Yang & Yang, 2004 (Fujian, Guangxi, Guizhou, Zhejiang)
Hybosleucopogus Li & Yang, 2023 (Fujian, Guangxi)
Hyboslongshengensis Yang & Yang, 1986 (Fujian, Guangxi)
Hybosnasutus Yang & Yang, 1986 (Guangxi)
Hybosobtusatus Yang & Grootaert, 2005 (Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou)
Hybosorientalis Yang & Yang, 1986 (Fujian, Guangxi, Henan)
Hybosparaterminalis sp. nov. (Guangxi)
Hybosparticularis Yang, Yang & Hu, 2002 (Guangxi, Hainan)
Hybospingbianensis Yang & Yang, 2004 (Guangxi, Yunnan)
Hybosserratus Yang & Yang, 1992 (Fujian, Guangxi, Gzuihou, Henan, Sichuan, Yunnan, Zhejiang; Thailand)
Hybostruncatus Yang & Yang, 1986 (Guangxi)
Hybosxiaohuangshanensis Yang, Gaimari & Grootaert, 2005 (Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi)
. Hybos anae
Yang & Yang, 2004
31AC1F96-B2CC-542F-8137-F8A9270BEB7C
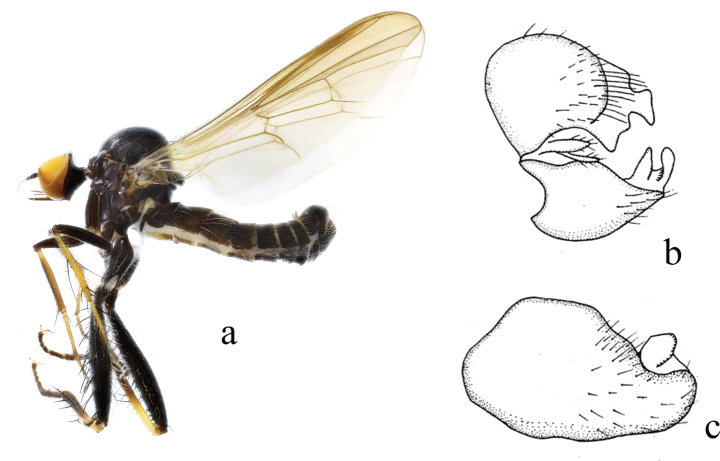
Figure 1.
Hybosanaea male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (after Li and Yang 2023). Abbreviations: lepn = left epandrial lamella; lsur = left surstylus; repn = right epandrial lamella; rsur = right surstylus.
Hybos anae Yang & Yang, 2004: 124.
Type locality.
China: Guangxi, Longsheng.
Diagnosis.
Legs entirely black-brown. R4+5 and M1 nearly parallel apically. Hypandrium shallowly incised apically, with one long thick finger-like right process, bifurcated apically, and small subtriangular left process.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi).
. Hybos bawanglingensis
Yang, 2008
1C0CB951-1038-5645-9FAD-11CD1BE1DACB
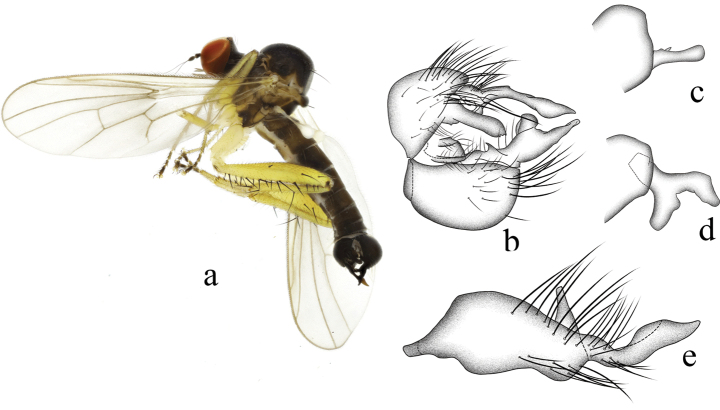
Figure 2.
Hybosbawanglingensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view
Hybos bawanglingensis Yang, 2008: 618.
Type locality.
China: Hainan, Bawangling.
Material examined.
China • 2♂ 1♀, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Tianpingshan; 770 m, 1 June 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU. China • 1♂ 3♀, Guangxi, Laibin, Dayaoshan, Shengtangshan; 1434 m, 14 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs yellow except hind knee dark brown, tarsomeres 3–5 black. Hind tibia with one ad at middle. Hypandrium with a narrow cleft apically.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi, Hainan).
. Hybos chinensis
Yang & Yang, 2004
D2EB1B77-DB26-5662-97B2-A3516D405ED8
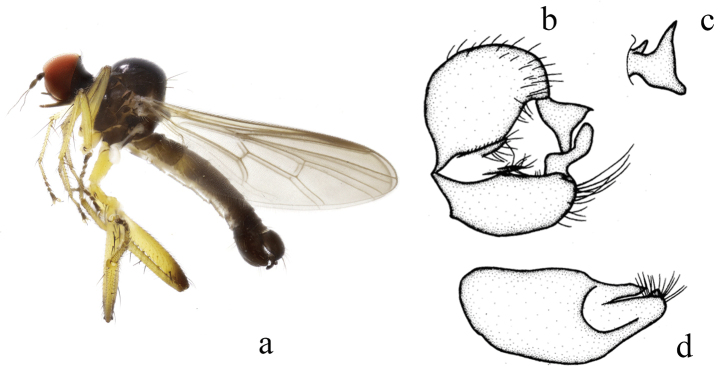
Figure 3.
Hyboschinensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos chinensis Frey, 1953: 64; Yang and Yang 2004: 143.
Type locality.
China: Fujian.
Material examined.
China • 6♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1340 m, 26 May 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs black-brown, except fore and mid knees, femora, tarsomeres 1–2 and all tibiae yellow; fore and mid tarsomeres 3–5 yellow-brown, hind tarsus yellow-brown. Hypandrium with small process on left corner.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi, Guizhou, Zhejiang).
. Hybos denticulatus sp. nov.
CB50AEEA-D648-53BB-92D3-F0B485C30F0F
https://zoobank.org/416CDB05-FFAF-415A-BA07-45606E7C65F1
Figure 4.
Hybosdenticulatus sp. nov. a male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view
Type material examined.
Holotype: China •♂; Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; (25°33'44.2"N, 109°56'42.4"E, 1340 m), 28 May 2023, Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs entirely black. Hind tibia with one ad near apex. R2+3 curved, R4+5 and M1 slightly convergent apically. Hypandrium with row of long bristles near apical margin.
Description.
Male. Body length 4.7 mm. Wing length 4.3 mm.
Head black with gray pollen. Eyes contiguous on frons, black-brown with slightly enlarged dorsal facets yellow-brown. Hairs and bristles on head black except posteroventral surface with partly dark brown hairs; ocellar tubercle distinct with two long oc and two short posterior hairs. Antenna black; scape without hairs, pedicel with circlet of blackish subapical hairs; first flagellomere blackish, not elongated, nearly as long as scape and pedicel combined, without dorsal hairs; arista blackish, short pubescent except apical ¼ or so thin and bare. Proboscis shorter than head, black. Palpus blackish, with one blackish apical hair.
Thorax black with gray pollen. Hairs on thorax blackish, bristles black; hairs on mesonotum slightly long, ppn absent, two npl (anterior npl rather short), uniserial hair–like dc nearly as long as irregularly quadriserial acr, two prsc, one psa; scutellum with eight marginal hairs and two sc. Legs entirely black. Hairs on legs mostly dark brown to blackish, bristles black-brown to black, but those on coxae partly brownish. Fore femur 1.3× and hind femur 1.9× as wide as mid femur. Fore femur with row of pv distinctly longer than femur thickness. Mid femur with 3–4 ad on basal ⅓ and row of pv distinctly longer than femur thickness; apically with one weak ad. Hind femur with row of ad on apical 2/3, ~ three rows of spine-like ventral bristles on tubercles and some dorsal hairs on basal 1/5. Fore tibia with row of short or slightly long ad and some long thin pv hairs; apically with 4 bristles including one thick ad. Mid tibia with row of thin or slightly thick ad; apically with one long av. Hind tibia with one ad near apex. Fore tarsomere 1 with some long ad and pv hairs. Mid tarsomere 1 with one ad near middle; apically with one slightly long ad. Hind tarsomere 1 with short dense spine-like ventral bristles. Wing hyaline, stigma dark brown; veins brown to black-brown, R2+3 curved, R4+5 and M1 slightly convergent apically. Squama dark yellow with dark yellow hairs. Halter dark yellow with dark brown stem and pale-yellow knob.
Abdomen short thick, black with pale gray pollen, hypopygium slightly thicker than pregenital segments. Hairs and bristles on abdomen yellow-brown to brown except those on hypopygium black.
Male genitalia. Left epandrial lamella distinctly wider than right epandrial lamella (Fig. 4b); left surstylus with wide finger-like process, right lateral margin with one process, left lateral margin with some middle denticles (Fig. 4d). Right epandrial lamella with concave inner margin; right surstylus with long wide subtriangular process, lateral margin with one thin finger-like process apically (Fig. 4c). Hypandrium ~ 1.5× longer than wide, narrow basally and wide apically, apical margin with two wide processes, with row of long bristles near apical margin (Fig. 4e).
Female. Unknown.
Etymology.
This specific name refers to the left surstylus with some middle denticles on the lateral margin.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi).
Remarks.
The new species is similar to H.brevis Yang & Yang from Zhejiang, 1995, but may be separated by the arista and the left surstylus. In the new species, the arista is short pubescent, and the left surstylus has some middle denticles on the lateral margin. In H.brevis, the arista is bare, and the left surstylus lacks denticles (Yang and Yang 2004).
. Hybos ensatus
Yang & Yang, 1986
85C61305-4B5A-570A-B283-73863EE08CF7
Figure 5.
Hybosensatusa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d hypandrium, ventral view. (b–d: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos ensatus Yang & Yang, 1986: 83; Yang and Yang 2004: 155.
Type locality:
China: Guangxi, Longsheng.
Diagnosis.
Legs black-brown, except mid tarsi yellow-brown. Mid tibia with 2 long bristles on basal half. Male genitalia: left epandrial lobe with process at inner margin near middle; right surstylus sword-shaped.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi, Guizhou, Henan, Sichuan).
. Hybos flaviscutellum
Yang & Yang, 1986
1ABA61C2-2FB5-568E-809F-854EB4F13515
Figure 6.
Hybosflaviscutelluma hypandrium, ventral view b genitalia, dorsal view (after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos flaviscutellum Yang & Yang, 1986: 81; Yang and Yang 2004: 158.
Type locality.
China: Guangxi, Longsheng.
Diagnosis.
Scutellum yellow. Legs yellow to yellow-brown, except tarsomeres 3–5 dark yellow. Male genitalia: left epandrial lobe rather wide; left surstylus knife-shaped.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi, Zhejiang).
. Hybos forcipata sp. nov.
241670C2-4457-58B1-9E20-1BD8971EF1B1
https://zoobank.org/4CC29607-1E47-49BA-8153-8C19966E2407
Figure 7.
Hybosforcipata sp. nov. a male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view
Type material examined.
Holotype: China •♂; Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; (25°33'42.0"N, 109°56'37.2"E, 1413 m), 7 August 2023, Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs entirely black. Mid tarsomere 1 with one ad near apex and some short or long hairs. R4+5 and M1 slightly convergent apically. Left surstylus claw-shaped in lateral view.
Description.
Male. Body length 3.3 mm. Wing length 2.8 mm.
Head black with gray pollen. Eyes contiguous on frons, black-brown with slightly enlarged dorsal facets yellow-brown. Hairs and bristles on head black except posteroventral surface with partly dark brown hairs; ocellar tubercle distinct with two very short hairs. Antenna blackish; scape without hairs, pedicel with circlet of black-brown subapical hairs; first flagellomere black-brown, slightly elongated, longer than scape and pedicel combined, without dorsal hairs; arista black-brown, short pubescent. Proboscis distinctly shorter than head, black-brown. Palpus blackish, with one black-brown apical hair.
Thorax black with gray pollen. Hairs on thorax blackish, bristles black; hairs on mesonotum short, ppn absent, two npl (anterior npl rather short), uniserial hair–like dc nearly as long as irregularly quadriserial acr, two prsc, one psa; scutellum with eight marginal hairs and two sc. Legs entirely black. Hairs on legs mostly black-brown to black, bristles blackish to black, but those on coxae partly brown. Fore femur 1.5× and hind femur 2.4× as wide as mid femur. Fore femur with row of pv distinctly longer than femur thickness. Mid femur with row of ad on apical ⅓ and row of long thin pv distinctly longer than femur thickness. Hind femur with two ad on apical ½ and ~ three rows of long spine-like ventral bristles on tubercles. Fore tibia with some short or long ad and pv hairs. Mid tibia with two ad on basal ½ and some long hairs; apically with one very long av. Hind tibia with one ad near apex. Fore tarsomere 1 with some short or long ad and pv hairs. Mid tarsomere 1 with one ad near apex and some short or long hairs. Hind tarsomere 1 with row of short dense spine-like ventral bristles. Wing hyaline, stigma brownish; veins brownish to dark brown, R4+5 and M1 slightly convergent apically. Squama dark yellow with dark yellow hairs. Halter dark yellow with brown stem and pale-yellow knob.
Abdomen black with pale gray pollen. Hairs and bristles on abdomen brown except those on hypopygium blackish. Hypopygium distinctly thicker than pregenital segments.
Male genitalia. Left epandrial lamella slightly narrower than right epandrial lamella, with inner margin obliquely subtruncate (Fig. 7b); left surstylus claw-shaped in lateral view; with one curved apical lateral process and one long process, furcated apically (Fig. 7d). Right epandrial lamella with weakly convex inner margin near middle; right surstylus furcated into one small triangular process and one finger-like process (Fig. 7c). Hypandrium ~ 2.2× longer than wide, narrow apically, right lateral margin with one trapezoid process and one triangle-like process (Fig. 7e).
Female. Unknown.
Etymology.
This specific name refers to the claw-shaped left surstylus, in lateral view.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi).
Remarks.
The new species is similar to H.curvatus Yang & Grootaert, 2005 from Guangdong, but may be separated by the form of the fore tibia and hypandrium. In the new species, the fore tibia bears some ad and pv hairs, and the hypandrium has two processes at lateral margin. In H.curvatus, the fore tibia has one av and one pv apically, and the hypandrium lacks processes on the lateral margin (Yang and Grootaert 2005).
. Hybos fujianensis
Li & Yang, 2023
60A5250C-3922-511C-B6B0-D3C34454F608
Figure 8.
Hybosfujianensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (b–e: after Li and Yang 2023)
Hybos fujianensis Li & Yang, 2023: 313–351
Type locality.
China: Fujian, Wuyishan.
Material examined.
China • 1♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1413 m, 7 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
First flagellomere with two blackish dorsal hairs; arista bare. Legs mostly dark brown to black-brown. Hind tibia apically with long thin pd.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi).
. Hybos guizhouensis
Yang & Yang, 1988
9C1BB19A-966E-5F71-8D34-13347A7A8B13
Figure 9.
Hybosguizhouensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c hypandrium, ventral view (b, c: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos guizhouensis Yang & Yang, 1988: 136; Yang and Yang 2004: 168.
Type locality.
China: Guizhou, Fanjingshan.
Material examined.
China • 1♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Hongtan; 849 m, 30 May 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs brownish, except base of mid and hind tibia, fore and mid tarsomeres 1–2 yellow. Hypandrium with irregular process on apical margin.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi, Guizhou).
. Hybos jianyangensis
Yang & Yang, 2004
DB8D7430-10B0-5E6B-85ED-855D9CFF2166
Figure 10.
Hybosjianyangensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (b–e: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos jianyangensis Yang & Yang, 2004: 178.
Type locality.
China: Fujian, Jianyang.
Material examined.
China • 2♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Hongtan; 849 m, 30 May 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs entirely black. Mid tibia with 4 dorsal bristles and 2 ventral bristles. Male genitalia: left surstylus rather wide with short finger-like inner lateral process.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi, Guizhou, Zhejiang).
. Hybos leucopogus
Li & Yang, 2023
F8DBEC06-6CE9-5427-BDC8-974CCA6DBFEF
Figure 11.
Hybosleucopogusa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (after Li and Yang 2023)
Hybos fujianensis Li & Yang, 2023: 313–351
Type locality.
China: Fujian, Wuyishan.
Material examined.
China • 1♂ 1♀, Guangxi, Laibin, Dayaoshan, Yinshangongyuan; 1150 m, 15 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs entirely black. Hind femur distinctly thickened. Hind tibia with one row of ad hairs and four pd hairs on basal ½. R2+3 weakly curved, R4+5 and M1 weakly convergent apically. Hypandrium narrow basally, bifurcated apically.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi).
. Hybos longshengensis
Yang & Yang, 1986
C89F3B4F-C50A-57C2-A1D3-C7C08D0F852B
Figure 12.
Hyboslongshengensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c hypandrium, ventral view (b, c: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos longshengensis Yang & Yang, 1986: 78; Yang and Yang 2004: 187.
Type locality.
China: Guangxi, Longsheng.
Diagnosis.
Arista bare. Legs black-brown, except mid tibia and tarsomeres 1–2 yellow, tips of hind femur, base and tips of tibia and all tarsi yellow. Hypandrium with right apical corner elongated outwards into one process.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi).
. Hybos nasutus
Yang & Yang, 1986
45483903-0F4B-5C71-B77F-C2260A3024CF
Figure 13.
Hyboslongshengensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view
Hybos nasutus Yang & Yang, 1986: 79; Yang and Yang 2004: 197.
Type locality.
China: Guangxi, Jinxiu.
Material examined.
China • 4♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1413 m, 7 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU. China • 3♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1413 m, 7 August 2023, Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Arista bare. Legs yellow, except tarsomeres 3–5 dark yellow. Hind tibia with one dorsal bristle at middle; apically with one dorsal bristle and one ventral bristle.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi).
. Hybos obtusatus
Yang & Grootaert, 2005
61AA9DD7-A86E-5698-8A13-D8DB7368C62A
Figure 14.
Hybosobtusatusa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (b–e: after Yang and Grootaert 2005)
Hybos obtusatus Yang & Grootaert, 2005: 410.
Type locality.
China: Guangdong.
Material examined.
China • 1♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1340 m, 26 May 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Palpus blackish with two long bristles at tip. Legs entirely black. R4+5 and M1 parallel apically.
Distribution.
China (Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou).
. Hybos orientalis
Yang & Yang, 1986
CEF19C21-4F9E-5CB9-9D93-70AE7920CDB4
Figure 15.
Hybosorientalisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d hypandrium, ventral view (b–d: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos orientalis Yang & Yang, 1986: 82; Yang and Yang 2004: 201.
Type locality.
China: Guangxi, Longsheng; Fujian, Jianyang.
Material examined.
China • 5♂5♀, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1494 m, 7 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU. China • 5♂15♀, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1514 m, 7 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs yellow, except tarsomeres 3–5 dark yellow and extreme tip of hind femur black. Hypandrium wide basally and small and obtuse apically.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi, Henan).
. Hybos paraterminalis sp. nov.
FFA91AFC-D152-5B67-A161-E684A276821C
https://zoobank.org/2AB98B64-7EC8-4962-94E3-2F4DCFEAE076
Figure 16.
Hybosparaterminalis sp. nov. a male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view.
Type material examined.
Holotype: China •♂; Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; (25°33'39.8"N, 109°56'41.9"E, 1340 m), 26 May 2023, Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs mostly black-brown to black except extreme base of hind femur and all tarsi brown to dark brown. Mid tarsomere 1 with two pv on basal ½. R4+5 and M1 divergent apically.
Description.
Male. Body length 4.2 mm. Wing length 4.3 mm.
Head black with gray pollen. Eyes contiguous on frons, black-brown with distinctly enlarged dorsal facets yellow-brown. Hairs and bristles on head black except posteroventral surface with partly dark yellow hairs; ocellar tubercle indistinct. Antenna dark brown; scape without hairs, pedicel with circlet of brown subapical hairs; first flagellomere and arista absent. Proboscis slightly shorter than head, dark brown. Palpus dark brown, with one brown apical hair.
Thorax black with gray pollen. Hairs on thorax blackish, bristles black; hairs on mesonotum short, ppn absent, two npl (anterior npl rather short), uniserial hair–like dc nearly as long as irregularly quadriserial acr, two long prsc, one psa; scutellum with 6 marginal hairs and two very long sc. Legs mostly black-brown to black except extreme base of hind femur and all tarsi brown to dark brown. Hairs on legs mostly brownish to dark brown, bristles black-brown to black, but those on coxae partly dark yellow, fore and mid femora with brownish bristles and hind femur with partly dark yellow hairs and bristles. Fore femur 1.2× and hind femur 1.6× as wide as mid femur. Fore femur with row of weak pv shorter than femur thickness. Mid femur with row of weak pv; apically with one ad. Hind femur with 4 ad on apical ½, ~ two rows of long spine-like ventral bristles on tubercles and row of long thin outer pv on apical ½. Fore tibia with one short ad near middle; apically with one ad. Mid tibia with one very long ad at apical ⅓, one very long av near middle; apically with 5 bristles including one rather long av. Hind tibia with two ad near middle; apically with one pd and one short av. Fore tarsomere 1 with one pv at extreme base. Mid tarsomere 1 with two pv on basal ½; apically with circle of bristles including one pv. Hind tarsomere 1 with row of short spine-like ventral bristles. Wing hyaline, stigma dark brown; veins brown to black-brown, R4+5 and M1 divergent apically. Squama dark yellow with dark yellow hairs. Halter dark yellow with brownish stem and pale-yellow knob.
Abdomen black with pale gray pollen. Hairs and bristles on abdomen dark yellow to brownish except those on hypopygium blackish. Hypopygium distinctly thicker than pregenital segments.
Male genitalia. Left epandrial lamella as wide as right epandrial lamella, with inner margin slightly convex medially (Fig. 16b); left surstylus with apical margin very wide, truncate, apico–lateral portion with one small subtriangular process (Fig. 16d). Right epandrial lamella with concave inner margin near apex; right surstylus slightly wider at middle, long narrow apical portion (Fig. 16c). Hypandrium ~ 2.0× longer than wide, bilobate apically (left process wide and irregular in shape; right process wide finger-like, straight) (Fig. 16e).
Female. Unknown.
Etymology.
This specific name refers to the left surstylus with the very wide and truncate apical margin.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi).
Remarks.
The new species is similar to H.guizhouensis Yang & Yang, 1988 from Guizhou, but may be separated by having all tarsi brown to dark brown and the right surstylus slightly wider in the middle and a long narrow tip. In H.guizhouensis, the fore and mid tarsomeres 1–2 are yellow; and the right surstylus is narrow in the middle and slightly wider at the tip (Yang and Yang 2004).
. Hybos particularis
Yang, Yang & Hu, 2002
02A7BFEB-5BFD-5E47-B3B0-F7DA2E608AE2
Figure 17.
Hybosparticularisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (b–e: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos particularis Yang, Yang & Hu, 2002: 734; Yang and Yang 2004: 205.
Type locality.
China: Hainan, Jianfengling.
Material examined.
China • 1♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Tianpingshan; 542 m, 4 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs black, except tips of mid femur brownish, mid tibia and tarsomeres 1–2 yellow. Hypandrium long narrow, apically with deep incision.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi, Hainan); Thailand.
. Hybos pingbianensis
Yang & Yang, 2004
20CE3E70-3997-5E4D-8898-05B25E4A0F74
Figure 18.
Hybospingbianensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (b–e: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos pingbianensis Yang & Yang, 2004: 207
Type locality:
China: Yunnan, Pingbian, Daweishan.
Material examined.
China • 1♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1413 m, 7 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs yellow; hind coxae black; hind trochanter and femur black, hind tibia (except basal portion) blackish; tarsi dark brown, except fore and mid tarsomeres 1–2 and hind tarsomere 1 yellow. Right and left surstyli with three processes.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi, Yunnan).
. Hybos serratus
Yang & Yang, 1992
FC53598E-2CA8-5207-A9AE-590E211D9CC1
Figure 19.
Hybosserratusa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c hypandrium, ventral view (b, c: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos serratus Yang & Yang, 1992: 1089; Yang and Yang 2004: 210.
Type locality.
China: Sichuan, Xichang.
Material examined.
China • 2♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1413 m, 7 August 2023; Wenqiang Cao; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Legs yellow, except coxae yellow-brown, femora dark yellow, tarsomeres 2–5 dark yellow. Hypandrium large and wide with apical margin weakly incised medially
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangxi, Gzuihou, Henan, Sichuan, Yunnan, Zhejiang); Thailand
. Hybos truncatus
Yang & Yang, 1986
D50EF11D-0578-5332-B48D-75854D1737A9
Figure 20.
Hybostruncatusa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view c hypandrium, ventral view (b, c: after Yang and Yang 2004)
Hybos truncatus Yang & Yang, 1986: 80; Yang and Yang 2004: 220.
Type locality.
China: Guangxi, Longsheng.
Diagnosis.
Legs brownish. Mid tibia with one dorsal bristle at base, two long thin dorssal bristles at middle; apically with one long thin ventral bristle. Hypandrium large and wide, apical margin obliquely subtruncate with row of long bristles.
Distribution.
China (Guangxi).
. Hybos xiaohuangshanensis
Yang, Gaimari & Grootaert, 2005
EC97882A-CCDF-5BF3-ABFA-62EE9FF57D27
Figure 21.
Hybosxiaohuangshanensisa male habitus, lateral view b genitalia, dorsal view; c right surstylus d left surstylus e hypandrium, ventral view (b–e: after Yang, Gaimari and Grootaert 2005)
Hybos xiaohuangshanensis Yang, Gaimari & Grootaert, 2005: 5.
Type locality.
China: Guangdong, Nanling.
Material examined.
China • 3♂2♀, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Anjiangping; 1340 m, 28 May 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU. China • 1♂, Guangxi, Guilin, Huaping, Hongtan; 849 m, 30 May 2023; Wei Zeng; CAU.
Diagnosis.
Arista bare. Legs black except hind knee (distal femur and proximal tibia) and mid and hind tarsi yellow-brown. Hypandrium obliquely incised apically, with long marginal bristles.
Distribution.
China (Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi).
Discussion
The main interspecific diagnostic characteristics in this genus include the short pubescent or bare arista, the color of the legs, the position of bristles on the legs, the relationship between R4+5 and M1 apically, and the shape of the hypandrium. Sexual dimorphism frequently occurs in Hybos, particularly in groups with yellow legs. The diverse female genitalia have also been identified as important specific characteristics (Plant 2013; Li and Yang 2023). Unfortunately, the females of the new species mentioned in the article have not been collected yet. They will be collected more extensively in the future for further study and supplementation.
Huaping National Nature Reserve is part of the Nanling Mountain range. Nanling Mountain Area is the largest mountain system and an important geographical boundary in southern China. It is also the largest oasis around 25 degrees north latitude and has a high diversity of flora and fauna. Two studies on local species richness in the family Argentidae (Hymenoptera) and butterflies (Lepidoptera) revealed that the insect fauna was predominantly composed of Oriental elements (You 2009; Zhou et al. 2016). This is consistent with the research findings of the article, where all nine new record species are from the Oriental region.
Huaping National Nature Reserve is a typical subtropical monsoon climate, with vegetation belonging to the category of evergreen broad-leaved forests. During the period we investigated from May to August, it was the rainy season, and the weather was mostly very humid. In the collected specimens, Hybosparticularis is widely distributed in Thailand but is often found in seasonal dry forest biotopes. This provides an interesting example for further exploration of the habitat of Hybos. This genus is species-rich and widely distributed in various ecoregions in China. Further research on Hybos biology, phenology, distribution patterns, and endemicity would be valuable and meaningful.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Ms Wei Zeng and Mr Wenqiang Cao (Beijing) for collecting specimens. We thank Dr Scott Williams and Dr Yan Yan (Boston) for checking this manuscript.
Citation
Li M, Wang J, Yang D (2024) New species and records of Hybos Meigen (Diptera, Empidoidea) from Huaping National Nature Reserve, China. ZooKeys 1200: 41–63. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.1200.120258
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Ethical statement
No ethical statement was reported.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31970444)
Author contributions
All authors have contributed equally.
Author ORCIDs
Meilin Li https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2473-110X
Jingyu Wang https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0396-8547
Ding Yang https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7685-3478
Data availability
All of the data that support the findings of this study are available in the main text.
References
- Cao YK, Yu H, Wang N, Yang D. (2018) Hybos Meigen (Diptera: Empididae) from Wangdongyang Nature Reserve, Zhejiang with descriptions of three new species. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 144(1): 197–218. 10.3157/061.144.0110 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Frey R. (1953) Studien über ostasiatische Dipteren. II. Hybotinae, Ocydromiinae, Hormopeza Zett. Notulae Entomologicae 33: 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kanavalová L, Grootaert P, Kubík S, Barták M. (2021) Four new West Palaearctic species and new distributional records of Hybotidae (Diptera). ZooKeys 1019: 141–162. 10.3897/zookeys.1019.61496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li ML, Yang D. (2023) New species and records of the genus Hybos Meigen (Diptera, Empidoidea, Hybotinae) from Wuyishan National Park, China. ZooKeys 1172: 313–351. 10.3897/zookeys.1172.105952 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li XL, Wang N, Yang D. (2017) Hybos Meigen (Diptera: Empididae) from Wanglang National Nature Reserve, Sichuan. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 143(2): 435–452. 10.3157/061.143.0212 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li ML, Fatima N, Lin C, Yang D. (2022) Four new species of Hybos (Diptera: Empididae) from Gaoligongshan, China. Entomotaxonomia 44(02): 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Macquart J. (1827) Insectes diptères du nord de la France. Platypézines, dolichopodes, empides, hybotides. Lille, 159 pp. 10.5962/bhl.title.148911 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Meigen JW. (1800) Nouvelle classification des mouches à deux ailes (Dipter L.) d ‘après un plan tout nouveau. Paris, 40 pp. 10.5962/bhl.title.119764 [DOI]
- Meigen JW. (1803) Versuch einer neuen Gattungseintheilung der europäischen zweiflügelingen Insekten. Magazin fur Insektenkunde 2: 259–281. [Google Scholar]
- Meigen JW. (1820) Systematische Beschreibung der bekannten Europäischen zweiflügligen Insekten. Zweiter Theil. Forstmann, Aachen, 363 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Plant AR. (2013) The genus Hybos Meigen (Diptera: Empidoidea: Hybotidae) in Thailand. Zootaxa 3690(1): 1–98. 10.11646/zootaxa.3690.1.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamshev IV, Grootaert P, Yang D. (2013) New data on the genus Hybos (Diptera: Hybotidae) from the Russian Far East, with description of a new species. Russian Entomological Journal 22(2): 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shamshev IV, Grootaert P, Kustov S. (2015) New data on the genus Hybos Meigen (Diptera: Hybotidae) from the Palaearctic Region. Zootaxa 3936(4): 451–484. 10.11646/zootaxa.3936.4.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D, Grootaert P. (2005) Two new species of Hybos from Guangdong (Diptera: Empidoidea: Hybotinae). Annales Zoologici 55(3): 409–411. [Google Scholar]
- Yang D, Yang CK. (2004) Diptera, Empididae, Hemerodromiinae and Hybotinae. Fauna Sinica Insecta Vol. 34. Science Press, Beijing, 329 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Yang D, Gaimari SD, Grootaert P. (2005) New species of Hybos Meigen from Guangdong Province, South China (Diptera: Empididae). Zootaxa 912(1): 1–7. 10.11646/zootaxa.912.1.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D, Zhang KY, Yao G, Zhang JH. (2007) World Catalog of Empididae (Insecta: Diptera). China Agricultural Press, Beijing, 599 pp. [Google Scholar]
- You Q. (2009) Species and fauna of Argidae (Hymenoptera) in Nanling Mountains, China. Caoye Xuebao 18: 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou GY, Gu MB, Gong YN, Wang SK, Wu ZM, Xie GG. (2016) Diversity and fauna of butterflies in Nanling National Nature Reserve. Environmental Entomology 38: 971–978. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All of the data that support the findings of this study are available in the main text.