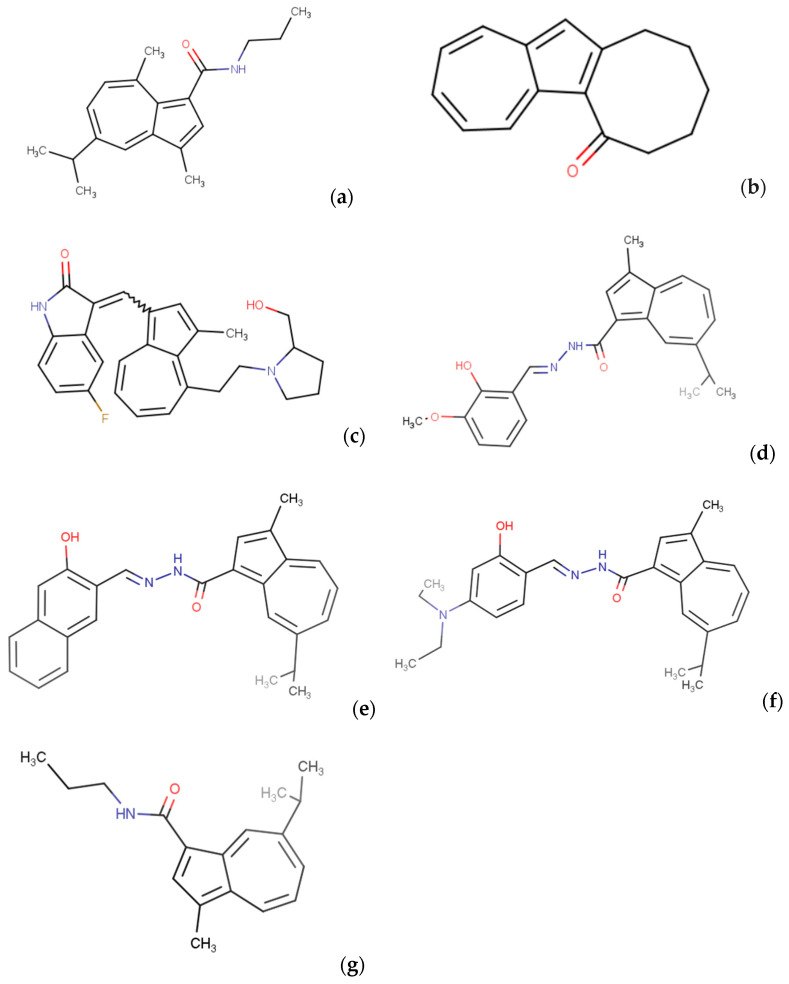
Figure 5.
Structural formula of 3,8-dimethyl-5-(propan-2-yl)-N-propylazulene-1-carboxamide (a); 6H,7H,8H,9H,10H,11H-cycloocta[a]azulen-6-one (b); 5-fluoro-3-[(4-{2-[2-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]ethyl}-3-methylazulen-1-yl)methylidene]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-one (c); N′-[(E)-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methylidene]-3-methyl-7-(propan-2-yl)azulene-1-carbohydrazide (d); N′-[(E)-(3-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)methylidene]-3-methyl-7-(propan-2-yl)azulene-1-carbohydrazide (e); N′-[(E)-[4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxyphenyl]methylidene]-3-methyl-7-(propan-2-yl)azulene-1-carbohydrazide (f); and 3-methyl-7-(propan-2-yl)-N-propylazulene-1-carboxamide (g), which are azulene derivatives with potential anticancer activity.