Abstract

Provided herein are novel exatecan-derived topoisomerase-1 inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions, use of such compounds in treating cancer, and processes for preparing such compounds.
Important Compound Classes
Title
Exatecan-Derived Topoisomerase-1 Inhibitors Pharmaceutical Compositions, and Uses thereof
Patent Publication Number
WO 2024/049931 A1
Publication Date
March 7, 2024
Priority Applications
US 63/403,515, US 63/421,844, and US 63/488,007
Priority Dates
September 2, 2022, November 2, 2022, and March 2, 2023
Inventors
Bacauanu, V.; Charati, M. B.; Johnson, R. E.; Lang, S. B.; Quiroz, R. V.; Seganish, W. M.; Yang, S.; Zepeda, N. S.
Assignee Company
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, USA
Disease Area
Cancer
Biological Target
Topoisomerase-1
Summary
The topoisomerase-1 inhibitors derived from the exatecan scaffold, which can be used for oncologic therapies, are cytotoxic chemotherapeutic derivatives with a camptothecin core. The use of the camptothecin derivative exatecan is disclosed. Specifically, the compounds are described as alcohol- and amine-containing exatecan amides and analogs. The compounds are cytotoxic and can be applied as chemotherapeutic drugs in oncologic settings, for example as antitumor agents. The compounds are potent, novel in structure, and active across multiple cancer cell lines.
The present application describes a series of novel exatecan-derived topoisomerase-1 inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, and pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
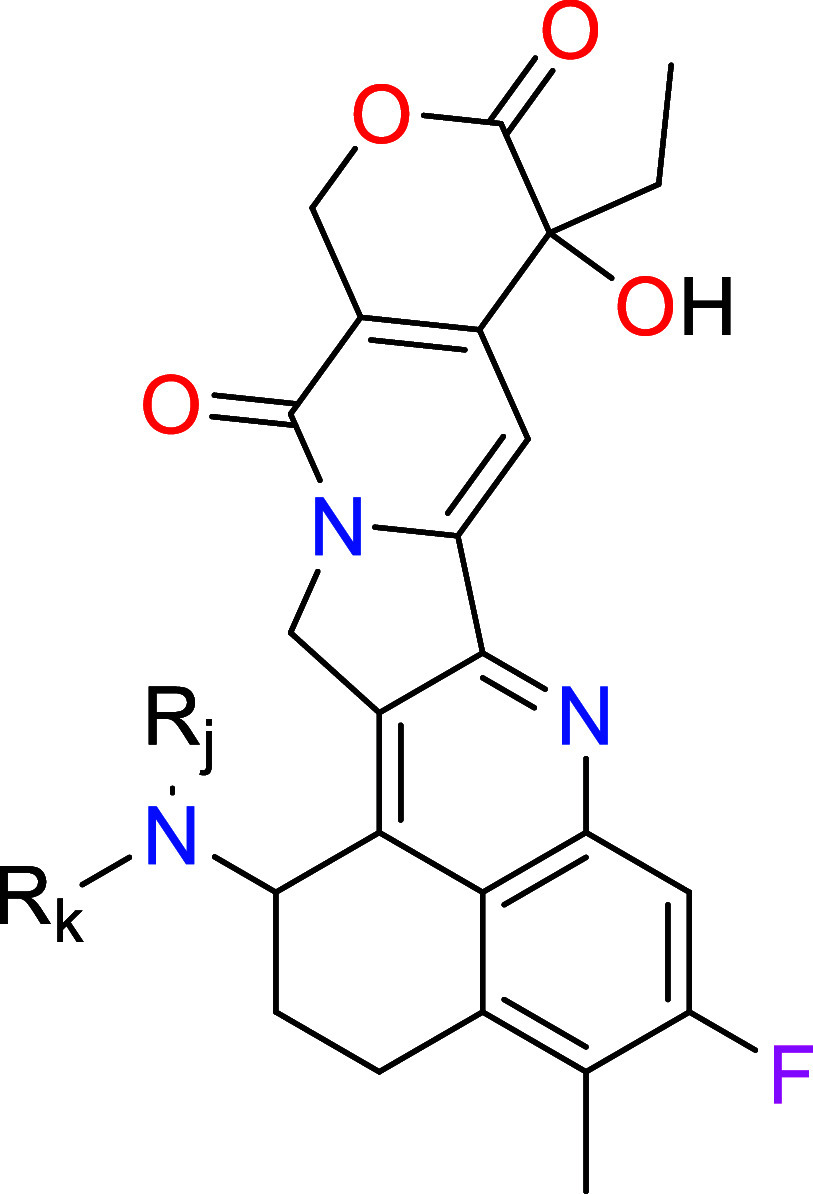
Rk = H, C1–6 alkyl, (CH2)nC(O)NHC1–6 alkyl,
(CH2)nC6–10 aryl,  , said alkyl and
aryl optionally substituted with 1 to 3 groups
of OH, and C1–6 alkylOH, said alkyl further optionally
substituted with 1 to 10 halogens;
, said alkyl and
aryl optionally substituted with 1 to 3 groups
of OH, and C1–6 alkylOH, said alkyl further optionally
substituted with 1 to 10 halogens;
Rj = H or C1–6 alkyl, said alkyl optionally substituted with 1 to 10 halogens; and n = 0, 1, 2 or 3.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The CellTiter Glo 2.0 cytotoxicity assay using Jeko-1 cells was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit topoisomerase 1. The topoisomerase-1 EC50 values (nM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below
shows representative
compounds that were tested for topoisomerase-1 inhibition and the
biological data obtained from testing representative examples.
Claims
Total claims: 22
Compound claims: 18
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 2
Use of compound claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Angulo-Elizari E.; Henriquez-Figuereo A.; Moran-Serradilla C.; Plano D.; Sanmartin C. Unlocking the potential of 1,4-naphthoquinones: A comprehensive review of their anticancer properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 268, 116249 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolak M.; Holota S.; Deyak Y.; Dziduch K.; Dudchak R.; Wujec M.; Bielawski K.; Lesyk R.; Bielawska A. Tubulin inhibitors. Selected scaffolds and main trends in the design of novel anticancer and antiparasitic agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 143, 107076 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.107076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagelli S.; Westermarck J. CIP2A coordinates phosphosignaling, mitosis, and the DNA damage response. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 52–64. 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakkala P. A.; Penumallu N. R.; Shafi S.; Kamal A. Prospects of Topoisomerase Inhibitors as Promising Anti-Cancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1456. 10.3390/ph16101456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedan H. K.; Kassab A. E.; Gedawy E. M.; Elmeligie S. E. Topoisomerase II inhibitors design: Early studies and new perspectives. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 136, 106548 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu C.; Chaurasiya A.; Chawla P. A. Nitrogen-containing heterocycles as topoisomerase II inhibitors for targeting cancer: Recent updates. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2023, 60, 899–928. 10.1002/jhet.4588. [DOI] [Google Scholar]



