Figure 11. DOAC Laboratory Monitoring.
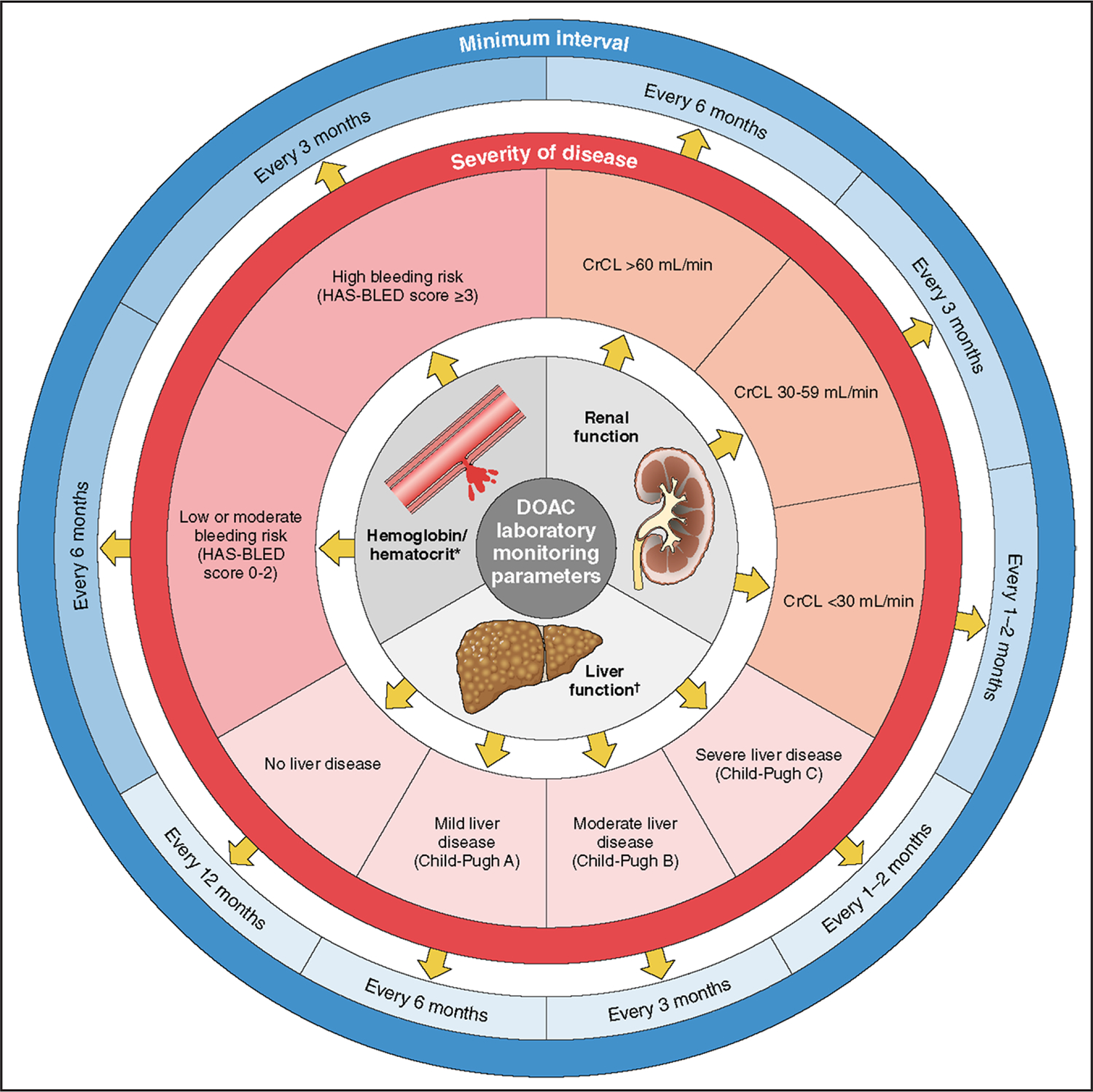
*HAS-BLED scoring (low risk=score 0, moderate risk=score 1–2, high risk=score ≥3): uncontrolled hypertension (systolic blood pressure >160 mm Hg)=1 point; abnormal renal (serum creatinine >2.26 mg/dL, dialysis, or kidney transplant) or hepatic function (bilirubin >2 times upper limit normal, alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase/alkaline phosphatase >3 times upper limit normal, or cirrhosis)=1 or 2 points; stroke (hemorrhagic or ischemic)=1 point; bleeding history or predisposition=1 point; labile INR (time in therapeutic range <60%)=1 point; elderly age ≥65 years=1 point; drugs (antiplatelet agents or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or excessive alcohol intake (8 units/week)=1 or 2 points. †Child-Pugh scoring: the severity of liver disease, primarily cirrhosis in patients with documented liver disease. Child-Pugh A (mild): 5 to 6 points; Child-Pugh B (moderate): 7 to 9 points; Child-Pugh C (severe): 10 to 15 points. The score is based on the 5 variables: encephalopathy (none=1 point, grade 1 and 2=2 points, grade 3 and 4=3 points); ascites (none=1 point, slight=2 points, moderate=3 points); total bilirubin (<2 mg/mL=1 point, 2–3 mg/mL=2 points, >3 mg/mL=3 points); albumin (>3.5 mg/mL=1 point, 2.8–3.5 mg/mL=2 points, <2.8 mg/mL=3 points); INR (<1.7=1 point, 1.7–2.2=2 points, >2.2=3 points). Original figure created by the 2023 Atrial Fibrillation Guideline Writing Committee. CrCL indicates creatinine clearance based on actual body weight; DOAC, direct oral anticoagulant; and INR, international normalized ratio.
