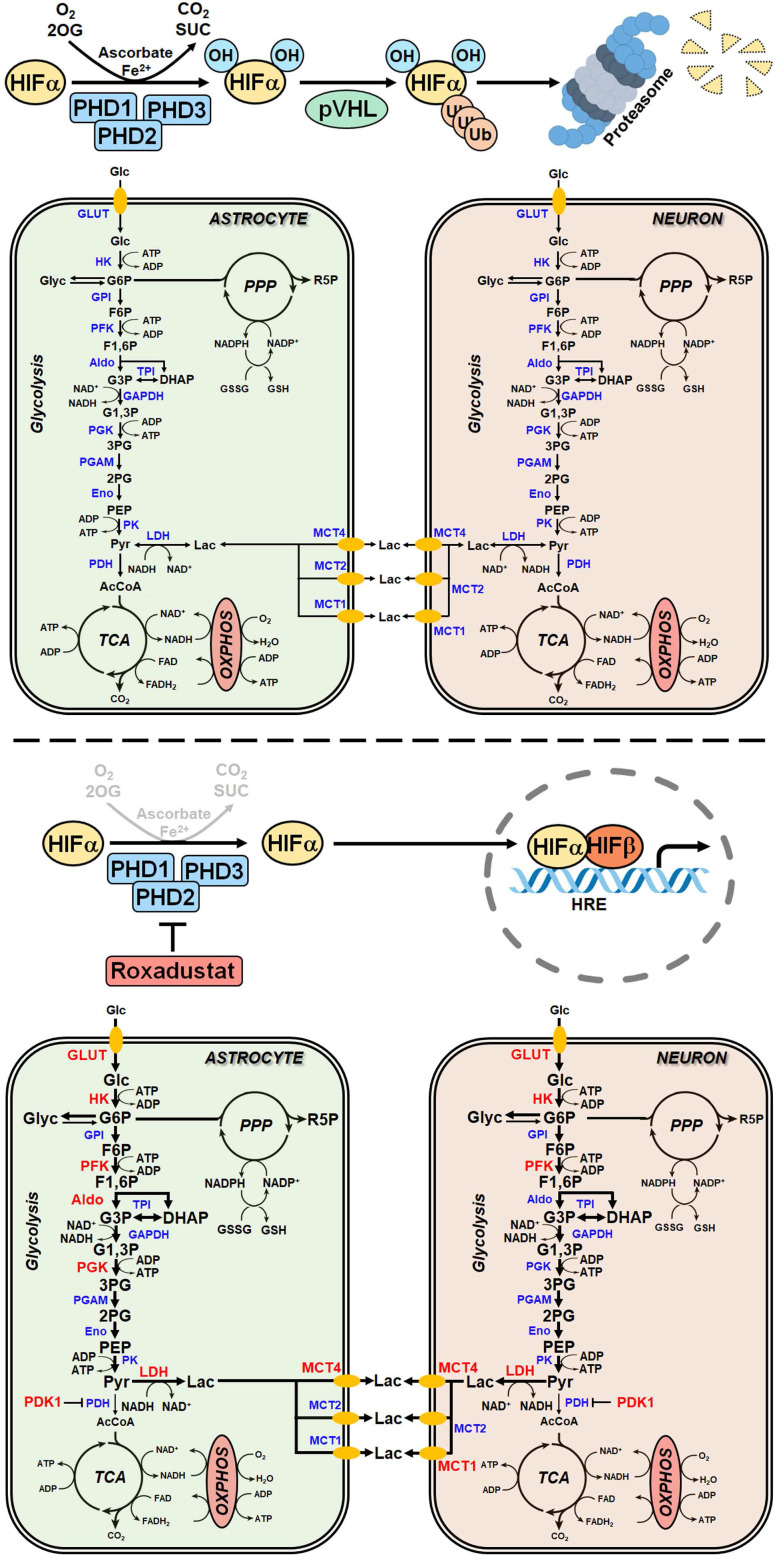
Figure 9.
Pharmacological activation of the HIF pathway improves the ischemic tolerance of brain-resident cells by reprogramming of glucose metabolism. Preventing the destabilization and degradation of HIF-1α in neurons and astrocytes by pharmacological inhibition of PHDs using roxadustat increases their rate of glucose uptake, glycogenesis, glycolysis and the release of lactate into the extracellular space through HIF-1-dependent upregulation of GLUT1, key enzyme in glycogen synthesis, glycolytic enzymes and MCTs, respectively. Along this line, elevating cellular glucose stores concomitant with increasing the capacity for O2-independent glycolytic ATP production may represents an efficient metabolic adaptation of brain-resident cells to survive glucose and oxygen depletion during ischemic stroke. 2OG: 2-oxoglutarate; 2PG: 2-phosphoglycerate; 3PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; AcCoA: acetyl-coenzyme A; Aldo: fructose-bisphosphate aldolase; CO2: carbon dioxide; DHAP: dihydroxyacetonephosphate; Eno: enolase; F1,6P: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; F6P: fructose-6-phosphate; G1,3P: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; G3P: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; G6P: glucose-6-phosphate; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Glc: glucose; GLUT: glucose transporter; Glyc: glycogen; GPI: glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; GSH: glutathione; HK: hexokinase; HIF: hypoxia-inducible factor; HRE: hypoxia response element; Lac: lactate; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; MCT: monocarboxylate transporter; MS: mass spectrometry; NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADP: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; O2: oxygen; OXPHOS: oxidative phosphorylation; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDK1: pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PFK: phosphofructokinase; PGAM: phosphoglycerate mutase; PGK: phosphoglycerate kinase; PHD: prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain; PK: pyruvate kinase; PPP: pentose-phosphate pathway; Pyr: pyruvate; R5P: ribose-5-phosphate; SUC: succinate; TCA: tricarboxylic acid; TPI: triose-phosphate isomerase.