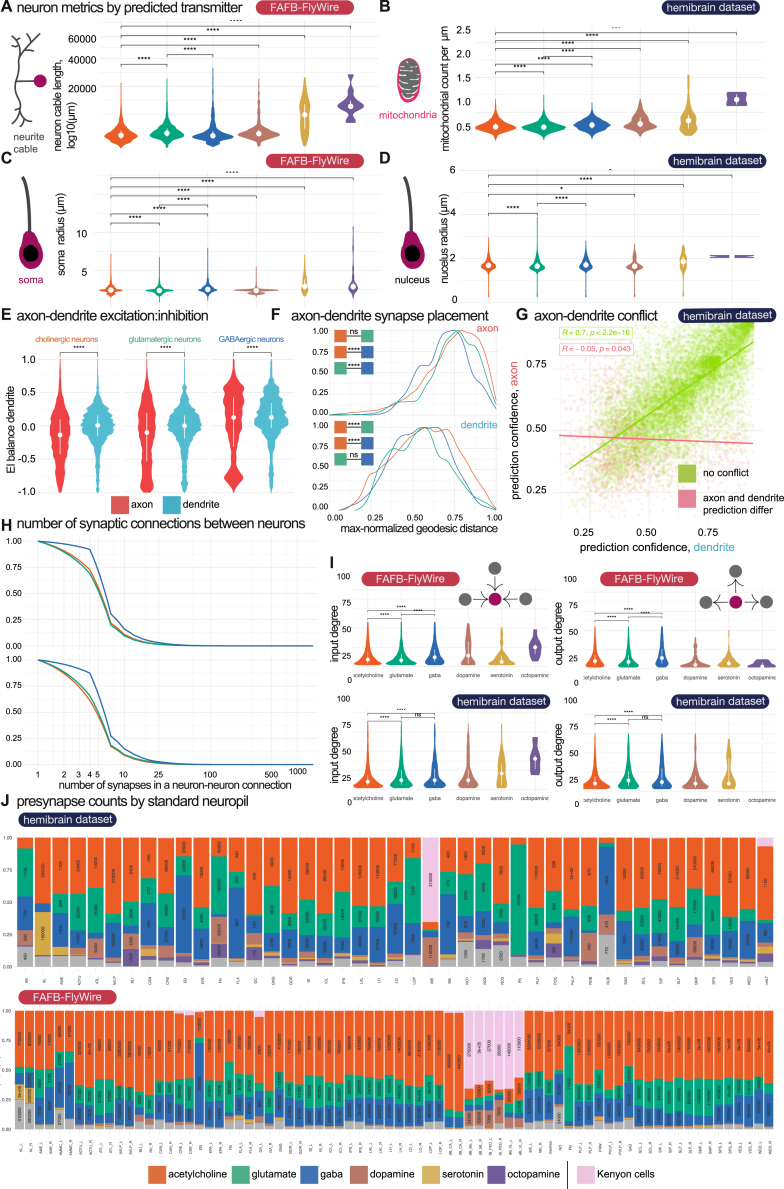
Figure S3.
Comparing neuron features across transmitter classes, related to Figure 5
(A) Cable length by neuron-level transmitter prediction.
(B) Mitochondria density by neuron-level transmitter predictions. Violin plots show the number of automatically detected mitochondia135 per micron cubed. Volume measures per neuron originate from the HemiBrain’s automatically reconstructed 3D neuron volumes.51 A mitochondria detection is currently only available in the HemiBrain dataset. The mean number of mitochondria per neuron is 245, s.d. 275.
(C) Soma, i.e., neuronal cell body, and (D) nucleus size by neuron-level transmitter predictions. The HemiBrain dataset provides a soma segmentation (left), and the FAFB-FlyWire dataset provides a nucleus segmentation (right)17,135.
(E) Violin plots of excitation:inhibition balance by neuron-level transmitter prediction and compartment.
(F) Correlation between compartment-level transmitter prediction score for axons and dendrites. Each point is a separate neuron in the HemiBrain dataset, n = 10,122. 11.0% disagree on the compartment-level transmitter prediction (red). The scatterplot displays Pearson’s product-moment correlation, giving R, the coefficient and the associated p-value.
(G) Scaled density plot showing the density of input connections onto all FAFB-FlyWire and HemiBrain neurons (facets) at different synaptic weights (X axis, log2).
(H) Scaled density plots showing the max-normalised geodesic distance (the distance along a neuron’s arbour) from input synapses (colored by the source neuron’s neuron-level transmitter prediction) to the target neurons’ cell body.
(I) Differences in the number of outgoing and incoming connections by neuron-level transmitter prediction. The input and output degree for a neuron is the number of unitary connections it has incoming and outgoing, respectively (the number of synaptic pairs, regardless of synaptic weight). All source-target connections with a synaptic count 10 included. Left, boxplots show the distribution of input degrees by the target neurons’ neuron-level transmitter prediction. Right, output degrees by the source neurons’ neuron-level transmitter prediction. A subset of total central brain neurons that were skeletonized (see STAR Methods) were used for this analysis (FAFB-FlyWire: 88,115, HemiBrain: 11,277).
(J) Breakdown of neuron-level transmitter predictions by brain region in HemiBrain. Plot shows the proportion of synapses in each HemiBrain neuropil that belong to a neuron of a given neuron-level transmitter prediction (colors). A total of 4,000,000 were assigned a neuropil and neuron-level transmitter prediction, which helps buffer erroneous synapse-level transmitter predictions. Number labels give the total number of synapses in each group. Not all the standard neuropils54 are shown because the HemiBrain only comprises 1/3 of the central brain. Total number of neuronal reconstructions (see STAR Methods) by dataset: FAFB-FlyWire: 136,927, HemiBrain: 24,666. (J) Breakdown of neuron-level transmitter predictions by brain region in FAFB-FlyWire. Neuropils54: AB, asymmetric body, AL, antennal lobe, AME, accessory medulla, AOTU, anterior optic tubercle, ATL, antler, AVLP, anterior ventrolaterla protocerebrum (incomplete in in HemiBrain), BU, bulb, CAN, cantle, CRE, crepine, EB, ellipsoid body, EPA, epaulette, FB, fan-shaped body, FLA, flange, GC, great commissure (incomplete in HemiBrain), GNG, gnathal ganglion (incomplete in HemiBrain), GOR, gorget, IB, inframedial bridge, ICL, inferior clamp, IPS, inferior posterior slope, LAL, lateral accessory lobe, LH, lateral horn, LO, lobula (incomplete in HemiBrain), LOP, lobula plate (incomplete in HemiBrain), ME, medulla (incomplete in HemiBrain), NO1, nodulus compartment 1, NO2, nodulus compartment 2, NO3, nodulus compartment 3, PB, protocerebral bridge, PLP, posterior lateral protocerebrum, POC, posterior optic commissure, PVLP, posterior ventrolateral protocerebrum (incomplete), ROB, round body, RUB, rubus, SAD, saddle, SCL, superior clamp, SIP, superior intermediate protocerebrum, SLP, superior lateral protocerebrum, SMP, superior medial protocerebrum, SPS, superior posterior slope, VES, vest, WED, wedge. Violin plots show the median value (dot) and the inter-quartile range (line, 25th to 75th percentiles). Significance values: ns: p > 0.05; ∗: p ≤0.05; ∗∗: p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗: p ≤0.001; ∗∗∗∗: p ≤ 0.0001.