Abstract
Zebrafish is an important model to study developmental biology and human diseases. However, an effective approach to achieve spatial and temporal gene knockout in zebrafish has not been well established. In this study, we have developed a new approach, namely bacterial artificial chromosome-rescue-based knockout (BACK), to achieve conditional gene knockout in zebrafish using the Cre/loxP system. We have successfully deleted the DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (dgcr8) in zebrafish germ line and demonstrated that the maternal-zygotic dgcr8 (MZdgcr8) embryos exhibit MZdicer-like phenotypes with morphological defects which could be rescued by miR-430, indicating that canonical microRNAs play critical role in early development. Our findings establish that Cre/loxP-mediated tissue-specific gene knockout could be achieved using this BACK strategy and that canonical microRNAs play important roles in early embryonic development in zebrafish.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2471-7) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Crispr-cas9, Maternal-zygotic transition, Germ layer specification, Small regulatory RNAs
Introduction
Zebrafish is an important model to study developmental biology and human diseases. Engineered nucleases, including zinc-finger nucleases, transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and the RNA-guided Cas9 system have been applied to achieve gene knockout in zebrafish [1–3]. However, these global gene knockout strategies were unable to investigate the functional roles of genes in a spatial and temporal manner. Conditional gene knockout can overcome these limitations [4–6]. Conditional gene knockout is usually achieved by employing the Cre/loxP system in which the loxP flanked sequence can be deleted in a Cre-dependent manner [7]. Using TALENs or the RNA-guided Cas9 system, single loxP sites have been inserted into the zebrafish genome as reported in some recent studies [8–10]. More recently, two loxP sites have been introduced into the zebrafish genome and Cre-mediated excision of the loxP flanked genomic fragment has been reported [11]. However, recombination of exogenous DNA into the zebrafish genome is still difficult, probably due to the low efficiency in the repair of the double DNA breakage by homologous recombination. Therefore, an alternative approach to achieve conditional knockout zebrafish is highly warranted.
MicroRNAs are 22-nt noncoding small RNAs that negatively regulate the stability and translation of mRNA transcripts [12]. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II as primary miRNA transcripts and process to 70-nt precursors by Dgcr8 and RNase III enzyme Drosha [13]. Pre-miRNAs are exported from the nucleus and further processed into 21-nt mature microRNA by Dicer [13]. Non-canonical pathway has been identified that some microRNAs can bypass Dgcr8 cleavage while others can bypass Dicer processing [14]. Moreover, other small RNAs, such as endo-siRNA and endo-shRNAs, are required to be processed by Dicer [14]. The functional roles of microRNA during early development have been investigated. In mice, dicer mutant is embryonic lethal due to defects in gastrulation and definitive endoderm formation, whereas the maternal-zygotic Dgcr8 mutant (MZdgcr8) exhibits post-implantation embryonic development defects [15]. In zebrafish, Dicer is maternally provided and zygotic dicer mutant shows no phenotypes [16], whereas maternal-zygotic dicer (MZdicer) mutant exhibits cell movement defects at the onset of gastrulation [17]. The developmental defects in MZdicer mutant can be partially rescued by miR-430, suggesting that miR-430 play important roles in early development [17]. Given that the biogenesis of the other small endogenous RNAs was also disrupted in the MZdicer mutant, the functional roles of microRNAs in early development remain to be established.
In this study, we describe a new approach, namely bacterial artificial chromosome-rescue-based knockout (BACK), to achieve conditional gene knockout in zebrafish using the Cre/loxP system. We have established the dgcr8 germline-specific mutation line using this BACK approach and found that the MZdgcr8 mutant exhibits severe morphological defects in embryonic development. Our findings demonstrate that tissue-specific gene knockout could be achieved using this BACK approach and that canonical microRNAs play essential roles during early embryonic development.
Materials and methods
Zebrafish husbandry
AB zebrafish were maintained at 28 °C in the zebrafish facility of Sun Yat-Sen University and the Chinese University of Hong Kong. All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines and approval of the respective Animal Research and Ethics Committees of Sun Yat-Sen University and the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Generation of dgcr8 mutant line
The TALENs for each target gene were assembled using the golden gate method as described previously [18–20]. The TALEN expression plasmids (pCS2-TALEN-ELD and pCS2-TALEN-KKR) were linearized by NotI restriction enzyme digestion. TALEN mRNAs were transcribed using the mMESSAGE mMACHINE SP6 kit (Ambion) and purified using the RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN).
To generate zebrafish mutant lines, TALEN mRNAs (500 pg/embryo) were microinjected into one-cell stage zebrafish embryos. Two days after injection, genomic DNA was isolated from 8 to 10 pooled larvae. The target genomic regions were amplified by PCR and subcloned into the pTZ57R/T vector (Fermentas). Single colonies were genotyped by sequencing. To obtain germline mutations, the TALEN injected embryos were raised to adulthood and outcrossed with wild-type (WT) fish. The F1 progeny were genotyped by sequencing. To obtain homozygous mutants, heterozygous mutants of the same mutation were obtained and self-crossed. The primers used in this study are listed in Supplemental Table S1.
Whole mount in situ hybridization
Whole mount in situ hybridization was performed as described [21]. A cDNA fragment of zebrafish dgcr8 was amplified by RT-PCR with specific primers, followed by in vitro transcription with either T7 or Sp6 RNA polymerase to generate the antisense probe using the DIG RNA Labeling Kit (Roche, USA).
BAC recombineering
The recombineering reagents including engineering bacterial strains (SW102, SW105, SW106) and plasmids (PL451, PL452) were obtained from the US National Cancer Institute (NCI) at Frederick. The piTol2 plasmids (piTol2-amp, piTol2-kan and piTol2-galk) were provided by Dr. Koichi Kawakami and Dr. Maximiliano L Suster. The BAC clone CH211-267E2 containing zebrafish dgcr8 was purchased from the BACPAC Resources Center of Children’s Hospital Oakland Research Institute.
BAC recombineering was carried out as previously reported [22]. The BAC DNA was electroporated into the engineering bacterial strain SW106. The first loxP cassette was amplified using primers with 45-bp homolog arms to the second intron of the dgcr8 gene (Table S1). After induction of recombinase expression, the SW106 was transformed with the first loxP cassette PCR product and positive recombinants on kanamycin plates were screened by PCR. For excision of the Neomycin cassette, 10% L (+)-arabinose (Sigma) was added when the bacterial culture OD600 reached about 0.5 and the targeting clones were screened by PCR and verified. Next, the first loxP positive BAC was transformed into SW105 strain by electroporation. The second loxP cassette was amplified using primers with 45-bp homolog arms to the third intron of the dgcr8 gene. After recombineering and excision, the positive clones were screened by PCR and verified. The iTol2 cassette was amplified using primers with 45-bp homolog arms to the BAC backbone to destroy the self-contained loxP site. After induction of recombinase, the iTol2 PCR product was transformed into the BAC-containing strain SW105 and the iTol2-amp cassette positive colonies were identified by PCR and verified.
BAC transgenesis
The Tol2-mediated BAC transgenesis was performed as described [22]. The purified BAC (200 pg/embryo) (MN BAC purification kit) and pCS2FA transposase mRNA (100 pg/embryo) were co-injected into one-cell stage embryos. The injected embryos were raised to adulthood and outcrossed with WT fish. The founders were further crossed with dgcr8 +/− fish to generate the dgcr8 +/−;Tg: dgcr8 fish.
Q-PCR analysis of pri-miRNAs and mature miRNA
To quantify the pri-miRNA and mature miRNA level, RNA was isolated from shield stage embryos using the miRNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN). Mature miRNA expression was analyzed using the miRCURY LNA™ Universal RT microRNA PCR system (EXIQON). Real-time PCR was performed on an ABI PRISM 7900 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems) using the SYBR Green I Kit (Applied Biosystem). The pri-miRNA transcript levels were normalized against ef1ɑ transcript level and mature miRNA levels were normalized against the U6 transcript level.
Q-PCR analysis of mRNA expression
Total RNA was isolated from zebrafish embryos at various developmental stages (shield, 75%-epiboly, prim-6, prim-16) with RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was synthesized using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (TAKARA). Real-time Q-PCR was performed on an ABI PRISM 7900 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems) using the SYBR Green I Kit (Applied Biosystem). The mRNA transcript levels were normalized against ef1ɑ transcript level.
Reporter assays
The dsRED sequence was cloned into pCS2-3XIPT-miR-430 plasmid by BamHI and Xhol [17]. The zsYellow was amplified from ZsYellow1-N1 which was a gift from Michael Davidson (Addgene plasmid # 54701) and cloned into the pCS2 vector bone. Two nl of a mixture (100 ng/μl dsRED-3XIPT miR-430 mRNA and 150 ng/μl zsYellow mRNA) were injected into the MZdgcr8 and WT embryos at one-cell stage. The embryos were photographed and analyzed at 24 hpf on an Olympus FV1000 Confocal System.
Rescue experiments
To perform rescue experiments, we amplified the full-length dgcr8 transcript from WT embryos using primer with T7 sequence. To obtain dgcr8 mRNA, in vitro transcription was performed using the mMESSAGE mMACHINE T7 kit (Ambion) and polyadenylation was performed using the Poly (A) Tailing Kit (Invitrogen). The purified dgcr8 mRNAs (100 pg/embryo) were microinjected into one-cell stage MZdgcr8 embryos and GFP mRNA (100 pg/embryo) was injected as control.
The miR-430 mimics were synthesized by Shanghai GenePharma Co.,Ltd as described in a previous study [17]. For rescue, miR-430 mimics (10 pg/embryo) were injected into one-cell stage MZdgcr8 embryos and the phenotypic changes were recorded on a stereomicroscope.
Results
Global dgcr8 KO by a dual TALEN approach in zebrafish
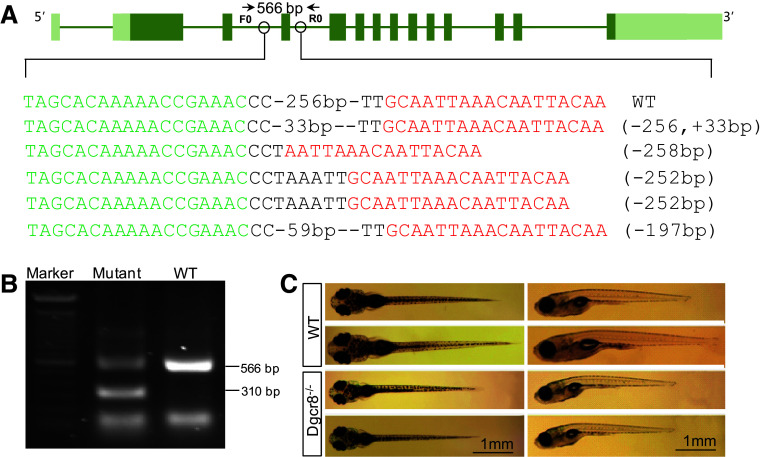
To disrupt dgcr8 in zebrafish, we assembled two pairs of TALENs to delete exon 4 of dgcr8 using our optimized TALEN platform (Fig. 1a) [19, 23]. The assembled TALENs were injected into 1-cell stage embryos and successful deletion of exon 4 was confirmed by sequencing (Fig. 1a). The injected embryos were raised to adulthood for founder screening. Of the eight fish screened, four have successfully transmitted the fragment deletions through the germline (Fig. 1b). We have further raised the F1 heterozygotes and obtained dgcr8 homozygote mutant with a 256-bp deletion in F2 embryos (Fig. S1). These homozygotes developed normally in the first 5 days post fertilization (dpf) during which organogenesis is completed. At 10 dpf, the dgcr8 homozygotes were smaller than the wild-type (Fig. 1c). No dgcr8 homozygote survived to adulthood (0 of 48 genotyped in F2), indicating that canonical microRNAs function are essential for later life stages.
Fig. 1.
Targeted deletion of dgcr8. a Schematic representation of the zebrafish dgcr8 and the TALEN binding sites. Target sites for two TALEN pairs were chosen at intron 4 and intron 5 to delete exon 4 of dgcr8 in zebrafish. Successful deletion of exon 4 in P0 generation was confirmed by sequencing. b Germline transmission of the deletion to F1. A PCR band of about 310-bp could be amplified after exon 4 deletion in F1 generation. The primer positions for genomic PCR were shown in a. c Representative pictures of wild-type and dgcr8 −/− mutant zebrafish larvae at 10 dpf. The mutant larvae were smaller than the wild-type ones
Similar to the zygotic dicer mutant [16], the lack of phenotype during early embryonic development is probably due to the presence of the maternally provided dgcr8 transcripts. Therefore, we examined whether dgcr8 transcripts are present in the early embryos using transcriptome data [24]. Dgcr8 is abundantly expressed in the 128-cell and oblong-sphere stage embryos but the expression is very low at the shield stage embryos (Fig. S2a). Whole mount in situ hybridization analysis further confirmed that the dgcr8 transcripts were maternally provided (Fig. S2b).
Germline-specific dgcr8 deletion using BACK approach
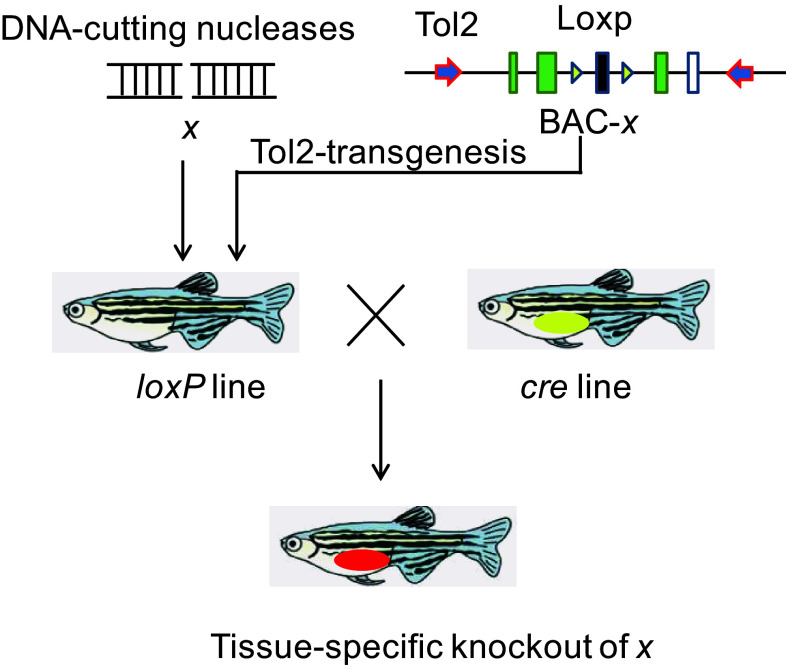
To eliminate the maternal dgcr8 transcripts, we then generated the conditional allele of dgcr8 using our BACK approach. The rationale of this BACK approach is that introduction of a loxP-modified gene x into an x-null background could rescue the x-null phenotype, and that conditional gene knockout can be achieved when the rescued line is crossed with a given Cre line (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram illustrating the BACK conditional gene knockout strategy. To achieve conditional knockout of gene x, the first step is to generate mutations of x using engineered nucleases. Then the BAC-containing gene x is modified to contain a Tol2 arm and two loxP sites. The modified BAC will be introduced to the x mutant background and crossed with a conditioned Cre line to delete the loxP flanking genomic sequence
We first obtained the bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) containing zebrafish dgcr8 and electroporated the BAC into the engineering bacterial strain SW106. We next introduced two loxP cassettes flanking exon 3 of dgcr8 via in vitro BAC recombineering (Fig. S3) [25–27]. We further engineered the BAC with the iTol2 element to facilitate transposon-mediated transgenesis [22]. Successful BAC engineering was confirmed by sequencing (Fig. S4). The loxP-modified dgcr8 DNA and the transposase mRNA were co-injected into zebrafish embryos with a dgcr8 +/− background. Two founders of the ten fish screened were identified to contain the BAC (dgcr8 +/−; Tg:dgcr8). To achieve germline-specific expression of Cre, we used the Tg(kop:cre) fish line in which Cre expression is restricted to the primordial germ cells [28]. We crossed the Tg(kop:cre) fish with dgcr8 +/− fish to obtain the dgcr8 +/−;Tg(kop:cre) fish. We then crossed the dgcr8 +/−; Tg:dgcr8 male with the dgcr8 +/−;Tg(kop:cre) female fish (because the kop promoter is maternally active). Of the 16 offspring screened at adulthood, four fish were found to be of the dgcr8 −/−; Tg:dgcr8 genotype (Fig. 3a, b). These fish possess no abnormal phenotype. Both male and female fish were fertile. The presence of dgcr8 −/− genotype at adulthood indicates that the loxP-modified dgcr8 transgene has successfully rescued the dgcr8 −/− lethal phenotype.
Fig. 3.
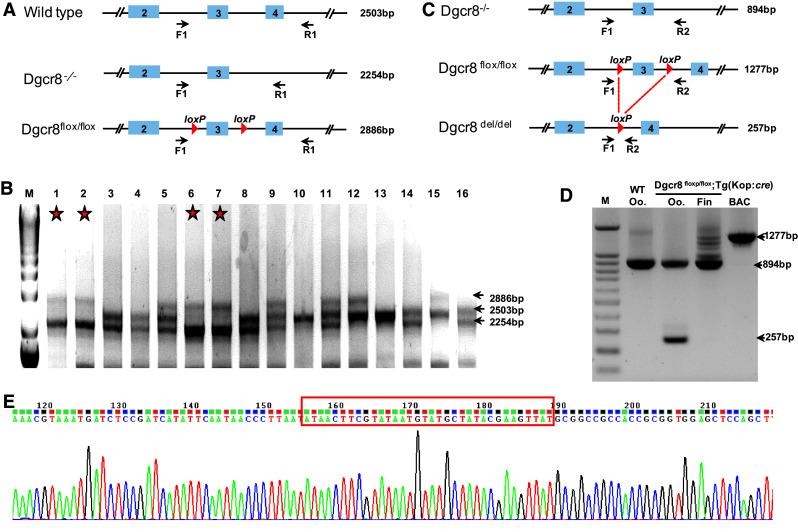
Germline-specific dgcr8 exon 3 deletion. a Primer positions and sizes of the target band for each genotype for genotyping of progenies from the dgcr8 +/−; Tg:dgcr8 and dgcr8 +/−; Tg(kop:cre) cross. b Gel picture of genomic PCR of fish fin from the dgcr8 +/−; Tg:dgcr8 and dgcr8 +/−; Tg(kop:cre) cross. The stars represent the dgcr8 −/−; Tg:dgcr8 genotype with two bands of 2254 bp and 2886 bp. c Primer positions and size of the target bands after Cre-mediated loxP excision. d Deletion of exon 3 was detected in the oocytes (Oo) but not in the fin by genomic PCR. e Sequencing result confirmed successful deletion of the loxP flanked genomic region
To examine whether exon 3 was specifically deleted in the germline, we collected genomic DNA of the tail fins and oocytes from the dgcr8 −/−; Tg:dgcr8 line. Genomic PCR indicated that exon 3 of dgcr8 was deleted in the oocytes but not in the tail fin (Fig. 3c, d). Sequencing of the genomic PCR product confirmed that the loxP flanked genomic sequence has been successfully deleted (Fig. 3e). These data indicate that we have successfully generated germline-specific deletion of dgcr8 using our BACK approach.
Germline-specific dgcr8 deletion disrupts microRNA processing
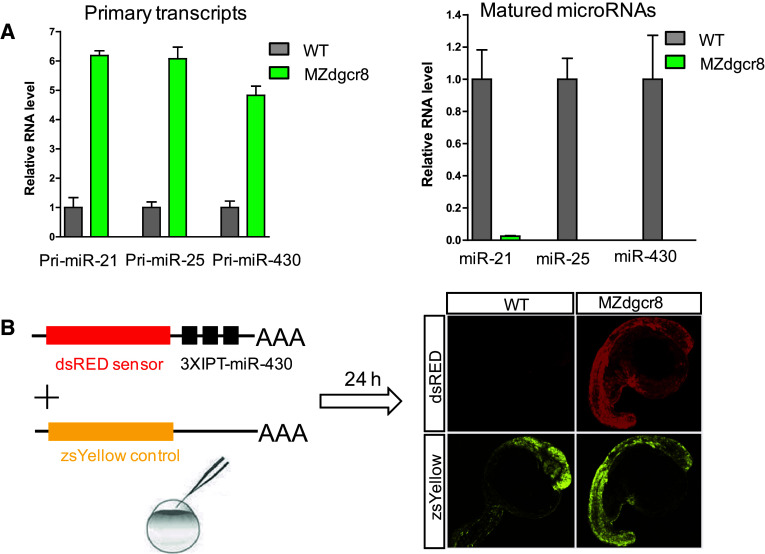
We subsequently crossed the dgcr8 −/−; Tg:dgcr8 fish and obtained the MZdgcr8 embryos. Q-PCR analysis showed that the primary microRNA transcripts (pri-miR-21, pri-miR-25 and pri-miR-430) were increased but their mature microRNAs were depleted in the MZdgcr8 embryos (Fig. 4a), suggesting that microRNA biogenesis was disrupted in the MZdgcr8 mutant. Functional reporter assays showed that miR-430 failed to suppress reporter expression in the MZdgcr8 embryos but not in the WT embryos (Fig. 4b), indicating that miRNA mediated target suppression was abolished in the MZdgcr8 embryos. Moreover, the expression of the known miR-430 target mRNAs (gstm and cd82b) was significantly increased in the MZdgcr8 mutant and the increased mRNA level was suppressed by injection of miR-430 mimics [29] (Fig. S5). These results indicated that germline deletion of dgcr8 disrupts canonical microRNA processing and function.
Fig. 4.
Germline deletion of dgcr8 disrupts canonical microRNA function. a Q-PCR analysis of pri-miRNA and mature miRNA expression in embryos from the wild-type and MZdgcr8 mutant line at 6 hpf. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 4). b miR-430 efficiently suppresses a dsRED reporter containing three imperfect targets (IPT) in the wild-type embryos but not in the MZdgcr8 mutant at 24 hpf
Germline-specific dgcr8 deletion disrupts early embryonic development
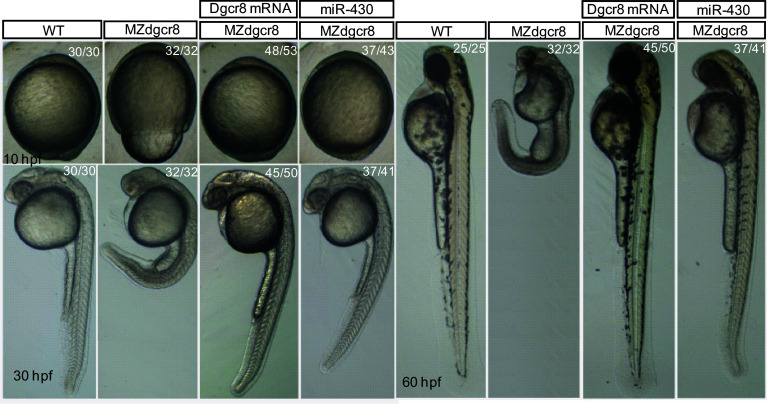
The MZdgcr8 embryos exhibited developmental delay from shield stage (6 h post fertilization, hpf) and developed slower than the WT for about 3–4 h at 24 hpf. The epiboly movements were disrupted with a longer animal–vegetal axis but a shorter dorsal–ventral axis (Fig. 5). The brain was smaller with no obvious brain boundaries (Fig. 5). No heart beat or circulation can be observed in the MZdgcr8 mutant at 30 hpf. To demonstrate that the observed phenotypes were due to the loss of function of dgcr8, we next performed rescue experiments. Injection of dgcr8 mRNA into MZdgcr8 embryos efficiently rescued the mutant phenotypes (Fig. 5). In contrast to the MZdgcr8 mutant embryos which died within 5 dpf, the rescued embryos survived up to 12 dpf. Interestingly, the MZdgcr8 mutant phenotype was also well rescued by injection of miR-430 (Fig. 5), the most abundantly expressed microRNA in early embryonic development [17], suggesting that the early developmental defect observed in the MZdgcr8 was due to the loss of function of miR-430.
Fig. 5.
Germline deletion of dgcr8 causes severe developmental defects. Representative morphologies of embryos for each genotype exhibited at the indicated times during early development. The ratios of embryos with the presented phenotypes are indicated
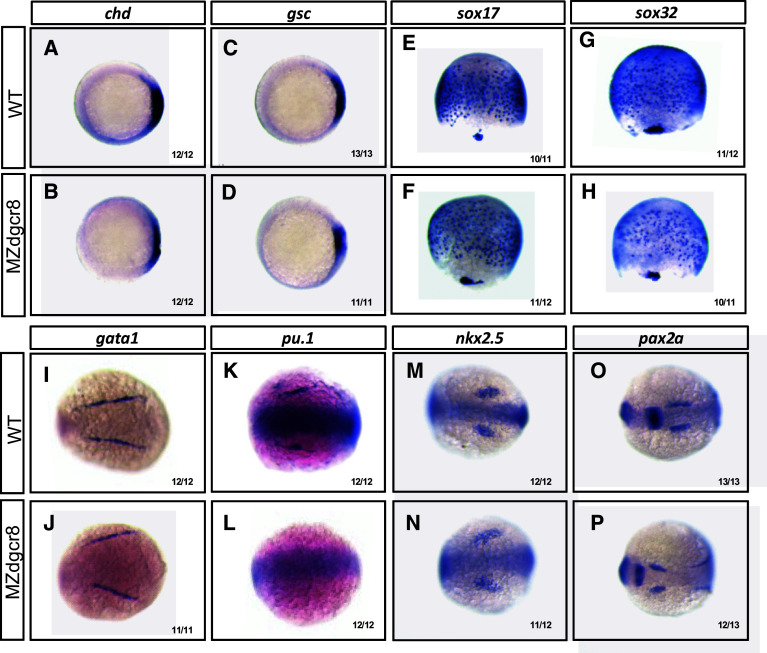
We then analyzed the MZdgcr8 phenotypes using whole mount in situ hybridization and qPCR analysis of marker gene expression (Fig. 6, Fig. S6). In the MZdgcr8 embryos, the expression of dorsal mesoderm markers (chd and gsc) and the endoderm markers (sox17 and sox32) was reduced (Fig. 6a–g). The erythroid progenitor (marked by gata1) was specified but the myeloid progenitor (marked by pu.1) was absent at the 6-somite stage (Fig. 6h–k). The cardiac progenitor (marked by nkx2.5) was specified at the 6-somite stage but failed to migrate to the middle line at 32 hpf in the MZdgcr8 mutant (Fig. 6m, n, Fig. S7). In the brain, the mid-hind boundary domain was reduced and the optic placode was expanded (Fig. 6o, p). The embryonic body was expanded mediolaterally and the anterior-posterior axis was reduced (Fig. 6i, j, m–p), suggesting that the convergence and extension movements was disrupted in the MZdgcr8 embryos. Collectively, this data indicating that canonical microRNA function are required for germ layer specification, organ progenitor formation and cell movements.
Fig. 6.
Maker gene expression analysis of the MZdgcr8 mutant. The expression of the indicated marker genes in the control and MZdgcr8 mutant embryos at shield stage (a–d), 75% epiboly stage (e–h) and 6-somite stage (i–p). The ratios of the affected embryos are indicated
Discussions
The development of engineered artificial nucleases enables targeted genome editing across species [30]. To achieve genome editing, the engineered nucleases were applied to introduce targeted DNA double strand breakages in the genome [31, 32]. The DNA repair pathway will be activated and targeted mutagenesis could be achieved by error-prone repair pathway while DNA replacement could be achieved by homologous recombination pathway [33]. In human cell lines and mouse, gene replacement is relatively well established [34, 35]. However, a high frequency of targeted mutagenesis could be easily achieved but targeted knock-in of an exogenous DNA is difficult to achieve in zebrafish. Indeed, efforts have been made to knock-in a loxP site into targeted locus in several studies [8, 9], but thus far only one study reported successful Cre-loxP-mediated conditional knockout in zebrafish [11]. Therefore, other approaches for conditional knockout are in high demand in zebrafish as well as in other species in which knock-in is difficult to perform.
In this study, we have described a BACK approach. Compared to the established conditional knockout approach, our BACK approach has several advantages. First, this BACK approach is not dependent on the efficiency of the precise repair pathway. Second, the replacement of DNA to a specific genomic site is limited by whether the specific locus is targetable by engineered nucleases, but there is no such limitation in our BACK approach. Moreover, this BACK approach also provides an opportunity to rescue the knockout phenotype to confirm the target specificity of the engineered nucleases.
Using the BACK approach, we have successfully generated germline-specific knockout of dgcr8. We found that the processing of microRNAs and early embryonic development were disrupted in the MZdgcr8 mutant. The MZdgcr8 embryos resemble MZdicer phenotypes in several aspects [17]: the exhibition of marked developmental delay, the disruption of brain development, and the shorter body axis and the lack of circulation. These data suggested that the canonical microRNAs but not other small RNAs processed by Dicer play important roles in early development. Furthermore, the MZdgcr8 phenotype could be well rescued by miR-430, indicating that miR-430 is the key microRNA in the early embryonic stage. Deletion of the miR-430 cluster could produce MZdgcr8-like phenotypes (our unpublished data), providing further support that miR-430 is the major functional microRNA in early development. Therefore, most of the observed MZdgcr8 phenotypes in the early embryonic stages could be due to disruption of miR-430 function. An important function of miR-430 is to remove the maternal transcripts after zygotic genome activation [28, 36, 37]. Several hundreds of maternal transcripts were not efficiently removed in the MZdicer mutant [29], and this may lead to development delay. The observed development delay in the MZdgcr8 mutant may also due to the delayed clearance of maternal transcripts by miR-430. Moreover, miR-430 plays important roles in promoting nodal signaling [38–40]. Both agonist and antagonist of the nodal pathway were directly regulated by miR-430 [38]. In the MZdicer mutant, nodal signaling activity was decreased and mesoendoderm development was disrupted [38]. Similar mesoendoderm development was observed in the MZdgcr8 mutant, probably due to decreased nodal signaling upon loss of function of miR-430. Cell movement defects were observed in both MZdicer and MZdgcr8 mutant. Further investigations are highly warranted to understand how this process is regulated.
In summary, we have demonstrated that the Cre/loxP-mediated tissue-specific gene knockout strategy could be achieved in zebrafish using our BACK approach. This approach could conceivably be applied to other genes in zebrafish and possibly in other species as well. Moreover, the dgcr8 line produced in this study could be crossed with other Cre line to investigate the functional roles of canonical microRNAs in other biological processes.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are given to Dr. Koichi Kawakami (National Institute of Genetics, Japan) and Dr. Maximiliano L Suster (Uni Research AS, Norway) for the piTol2 plasmids. We thank Dr. Daiguan Yu (Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, China) for suggestions on the design of BAC recombineering, and Dr. Didier Stainier (Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Germany) for critical comments on the manuscript. We thank Ms. Kathy W.Y. Sham for technical assistance and the Core Laboratories in the School of Biomedical Sciences for the provision of equipment and technical support.
This work was supported by the Research Grant Council of Hong Kong (Grant No. 14119715) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 151gzs102 and 151gzs121).
Footnotes
Y. Liu and Z. Zhu contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Doyon Y, McCammon JM, Miller JC, Faraji F, Ngo C, Katibah GE, Amora R, Hocking TD, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD, Amacher SL. Heritable targeted gene disruption in zebrafish using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:702–708. doi: 10.1038/nbt1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Huang P, Xiao A, Zhou M, Zhu Z, Lin S, Zhang B. Heritable gene targeting in zebrafish using customized TALENs. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:699–700. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hwang WY, Fu Y, Reyon D, Maeder ML, Tsai SQ, Sander JD, Peterson RT, Yeh JR, Joung JK. Efficient genome editing in zebrafish using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:227–229. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Auer TO, Del BF. CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN-mediated knock-in approaches in zebrafish. Methods. 2014;69:142–150. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ni TT, Lu J, Zhu M, Maddison LA, Boyd KL, Huskey L, Ju B, Hesselson D, Zhong TP, Page-McCaw PS, Stainier DY, Chen W. Conditional control of gene function by an invertible gene trap in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:15389–15394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206131109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ablain J, Durand EM, Yang S, Zhou Y, Zon LI. A CRISPR/Cas9 vector system for tissue-specific gene disruption in zebrafish. Dev Cell. 2015;32:756–764. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.01.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nagy A. Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis. 2000;26:99–109. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1526-968X(200002)26:2<99::AID-GENE1>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bedell VM, Wang Y, Campbell JM, Poshusta TL, Starker CG, Krug RN, Tan W, Penheiter SG, Ma AC, Leung AY, Fahrenkrug SC, Carlson DF, Voytas DF, Clark KJ, Essner JJ, Ekker SC. In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature. 2012;491:114–118. doi: 10.1038/nature11537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chang N, Sun C, Gao L, Zhu D, Xu X, Zhu X, Xiong JW, Xi JJ. Genome editing with RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease in zebrafish embryos. Cell Res. 2013;23:465–472. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hwang WY, Fu Y, Reyon D, Maeder ML, Kaini P, Sander JD, Joung JK, Peterson RT, Yeh JR. Heritable and precise zebrafish genome editing using a CRISPR-Cas system. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hoshijima K, Jurynec MJ, Grunwald DJ. Precise editing of the zebrafish genome made simple and efficient. Dev Cell. 2016;36:654–667. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:126–139. doi: 10.1038/nrm2632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yang JS, Lai EC. Alternative miRNA biogenesis pathways and the interpretation of core miRNA pathway mutants. Mol Cell. 2011;43:892–903. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.07.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Spruce T, Pernaute B, Di-Gregorio A, Cobb BS, Merkenschlager M, Manzanares M, Rodriguez TA. An early developmental role for miRNAs in the maintenance of extraembryonic stem cells in the mouse embryo. Dev Cell. 2010;19:207–219. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wienholds E, Koudijs MJ, van Eeden FJ, Cuppen E, Plasterk RH. The microRNA-producing enzyme Dicer1 is essential for zebrafish development. Nat Genet. 2003;35:217–218. doi: 10.1038/ng1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Giraldez AJ, Cinalli RM, Glasner ME, Enright AJ, Thomson JM, Baskerville S, Hammond SM, Bartel DP, Schier AF. MicroRNAs regulate brain morphogenesis in zebrafish. Science. 2005;308:833–838. doi: 10.1126/science.1109020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lei Y, Guo X, Liu Y, Cao Y, Deng Y, Chen X, Cheng CH, Dawid IB, Chen Y, Zhao H. Efficient targeted gene disruption in Xenopus embryos using engineered transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:17484–17489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215421109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liu Y, Luo D, Lei Y, Hu W, Zhao H, Cheng CH. A highly effective TALEN-mediated approach for targeted gene disruption in Xenopus tropicalis and zebrafish. Methods. 2014;69:58–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu Y, Luo D, Zhao H, Zhu Z, Hu W, Cheng CH. Inheritable and precise large genomic deletions of non-coding RNA genes in zebrafish using TALENs. PLoS One. 2013;8:e76387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li J, Wu P, Liu Y, Wang D, Cheng CH. Temporal and spatial expression of the four Igf ligands and two Igf type 1 receptors in zebrafish during early embryonic development. Gene Expr Patterns. 2014;15:104–111. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2014.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Suster ML, Abe G, Schouw A, Kawakami K. Transposon-mediated BAC transgenesis in zebrafish. Nat Protoc. 2011;6:1998–2021. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu Y, Zhao H, Cheng CH. Mutagenesis in Xenopus and Zebrafish using TALENs. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1338:207–227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2932-0_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang H, Zhou Y, Gu J, Xie S, Xu Y, Zhu G, Wang L, Huang J, Ma H, Yao J. Deep mRNA sequencing analysis to capture the transcriptome landscape of zebrafish embryos and larvae. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Warming S, Costantino N, Court DL, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG. Simple and highly efficient BAC recombineering using galK selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:e36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yu D, Ellis HM, Lee EC, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Court DL. An efficient recombination system for chromosome engineering in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:5978–5983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.100127597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu P, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG. A highly efficient recombineering-based method for generating conditional knockout mutations. Genome Res. 2003;13:476–484. doi: 10.1101/gr.749203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xiong F, Wei ZQ, Zhu ZY, Sun YH. Targeted expression in zebrafish primordial germ cells by Cre/loxP and Gal4/UAS systems. Mar Biotechnol. 2013;15:526–539. doi: 10.1007/s10126-013-9505-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Giraldez AJ, Mishima Y, Rihel J, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen S, Inoue K, Enright AJ, Schier AF. Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science. 2006;312:75–79. doi: 10.1126/science.1122689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim H, Kim JS. A guide to genome engineering with programmable nucleases. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:321–534. doi: 10.1038/nrg3686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bibikova M, Golic M, Golic KG, Carroll D. Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics. 2002;161:1169–1175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/161.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hsu PD, Lander ES, Zhang F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell. 2014;157:1262–1278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Holmes MC, Zhang HS, Gregory PD. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:636–646. doi: 10.1038/nrg2842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chen F, Pruett-Miller SM, Huang Y, Gjoka M, Duda K, Taunton J, Collingwood TN, Frodin M, Davis GD. High-frequency genome editing using ssDNA oligonucleotides with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Methods. 2011;8:753–755. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Platt RJ, Chen S, Zhou Y, Yim MJ, Swiech L, Kempton HR, Dahlman JE, Parnas O, Eisenhaure TM, Jovanovic M, Graham DB, Jhunjhunwala S, Heidenreich M, Xavier RJ, Langer R, Anderson DG, Hacohen N, Regev A, Feng G, Sharp PA, Zhang F. CRISPR-Cas9 knockin mice for genome editing and cancer modeling. Cell. 2014;159:440–455. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.36.Lee MT, Bonneau AR, Takacs CM, Bazzini AA, DiVito KR, Fleming ES, Giraldez AJ (2013) Nanog, Pou5f1 and SoxB1 activate zygotic gene expression during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Nature 503:360–364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Lund E, Liu M, Hartley RS, Sheets MD, Dahlberg JE. Deadenylation of maternal mRNAs mediated by miR-427 in Xenopus laevis embryos. RNA. 2009;15:2351–2363. doi: 10.1261/rna.1882009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Choi WY, Giraldez AJ, Schier AF. Target protectors reveal dampening and balancing of Nodal agonist and antagonist by miR-430. Science. 2007;318:271–274. doi: 10.1126/science.1147535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rosa A, Spagnoli FM, Brivanlou AH. The miR-430/427/302 family controls mesendodermal fate specification via species-specific target selection. Dev Cell. 2009;16:517–527. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.van Boxtel AL, Chesebro JE, Heliot C, Ramel MC, Stone RK, Hill CS. A temporal window for signal activation dictates the dimensions of a nodal signaling domain. Dev Cell. 2015;35:175–185. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.