Summary
Dysregulated innate immune signaling is linked to preleukemic conditions and myeloid malignancies. However, it is unknown whether sustained innate immune signaling contributes to malignant transformation. Here we show that cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling driven by miR-146a deletion (miR-146aKO), a commonly deleted gene in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), cooperates with mutant RUNX1 (RUNX1mut) to initially induce marrow failure and features of MDS. However, miR-146aKO hematopoietic stem and/or progenitor cells (HSPCs) expressing RUNX1mut eventually progress to a fatal AML. miR-146aKO HSPCs exhaust during serial transplantation, while expression of RUNX1mut restored their hematopoietic cell function. Thus, HSPCs exhibiting dysregulated innate immune signaling require a second hit to develop AML. Inhibiting the dysregulated innate immune pathways with a TRAF6-UBE2N inhibitor suppressed leukemic miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs, highlighting the necessity of TRAF6-dependent cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling in initiating and maintaining AML. These findings underscore the critical role of dysregulated cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling in driving preleukemic cells toward AML progression.
Subject areas: Disease, Pathophysiology, Immune response
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Deletion of miR-146a and the presence of RUNX1mut lead to MDS/BMF
-
•
HSPCs lacking miR-146a but with RUNX1mut progress to AML
-
•
RUNX1mut alters immune-inflammatory signaling and expands miR-146aKO HSPCs
-
•
miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut AML relies on immune-inflammatory signaling
Disease; Pathophysiology; Immune response
Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive myeloid malignancy that arises in hematopoietic stem and/or progenitor cells (HSPCs). In some cases, AML can be preceded by preleukemic states, such as myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).1 The transition from MDS to AML typically involves the acquisition of mutations in genes like RUNX1, NRAS/KRAS, or FLT3.2 However, the preleukemic molecular and cellular states that are amenable to transformation to overt AML are not entirely understood. In preleukemic conditions, there is a notable presence of cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling within mutant HSPCs. Additionally, dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory signaling can provide a competitive fitness advantage to mutant HSPCs, especially in the context of systemic inflammation, potentially leading to bone marrow failure (BMF) or MDS-like phenotypes.3,4,5,6
Although the dysregulation of cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling and chronic inflammation may contribute to the development of leukemia, it has not been definitively established whether they directly lead to AML or result in overt disease in mouse models. Nonetheless, mouse models featuring dysregulated cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling emphasize the significance of these pathways in hematologic malignancies.3 For example, miR-146a, a commonly deleted gene in MDS and AML, negatively regulates the expression of several genes of the innate immune signaling, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1).7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 HSPCs from mice lacking miR-146a display constitutive activation of NF-κB via TRAF6 and IRAK1, contributing to ineffective hematopoiesis and BMF, although not resulting in AML.18,19 Therefore, acquired mutations in HSPCs with dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory signaling are seemingly required for transformation into AML.
RUNX1 is one of the most frequently mutated genes in AML pathogenesis, undergoing various chromosomal translocations, loss-of-function mutations, and copy number gains.20,21 Furthermore, RUNX1 mutations are linked to altered innate immune and inflammatory signaling and often act as secondary hits in the progression from MDS to AML.22,23,24 Therefore, our study aimed to investigate whether RUNX1 mutations could lead to the development of overt AML in preleukemic cells displaying cell-intrinsic innate immune activation.
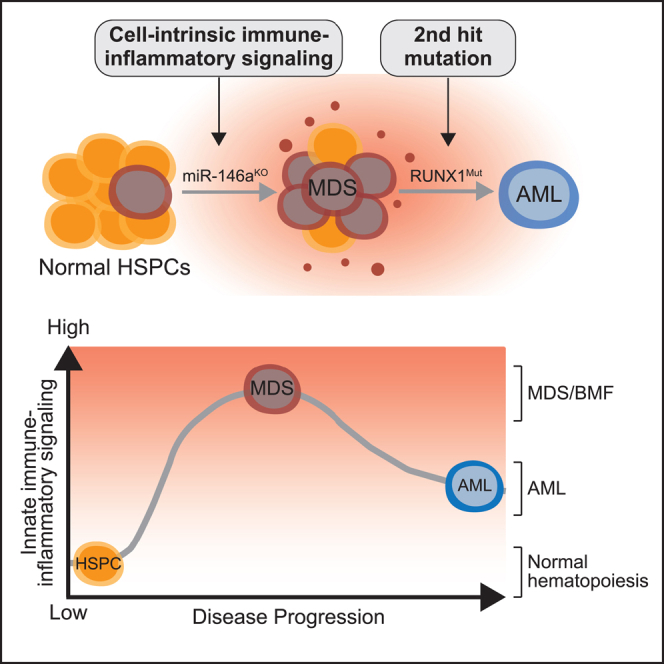
Here we show that cell-intrinsic innate immune and inflammatory signaling driven by deletion of the microRNA miR146a cooperates with a RUNX1 mutant to initially induce features of marrow failure. However, over time miR-146a-deficient (miR-146aKO) HSPCs expressing mutant RUNX1 (RUNX1mut) developed AML, which was not observed in mice engrafted with either miR-146aKO or RUNX1mut HSPCs. Moreover, expression of RUNX1mut rescued the hematopoietic repopulation deficiency of miR-146aKO HSPCs. Thus, HSPCs exhibiting dysregulated cell-intrinsic innate immune and inflammatory signaling require a second hit to develop AML. Gene expression analyses confirmed that deletion of miR-146a results in broad dysregulation of innate immune and inflammatory pathways; however, we observed that expression of RUNX1mut in miR-146aKO HSPCs unexpectedly restricted the expression of these pathways to discrete innate immune and inflammatory genes at the AML stage. Lastly, we show that inhibition of innate immune signaling with a TRAF6-UBE2N inhibitor was sufficient to suppress the leukemic miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs, indicating that TRAF6-dependent cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling is not only required for initiating AML but is also necessary for sustaining the leukemic phenotype. Taken together, our findings revealed that dysregulation of cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling is required for propagating preleukemic cells and contributes to the progression of AML.
Results
Loss of miR-146a and expression of RUNX1 mutant cooperate to induce an MDS/BMF-like disease
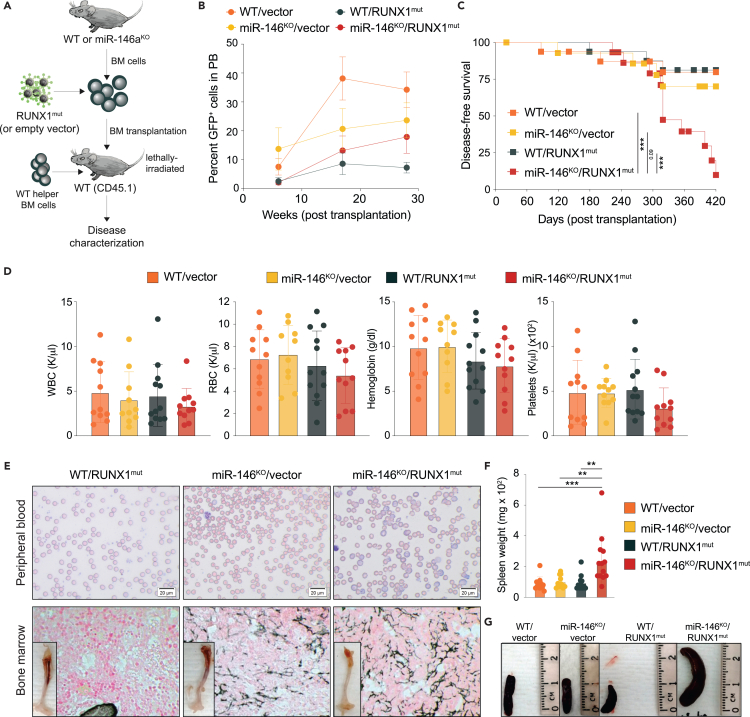
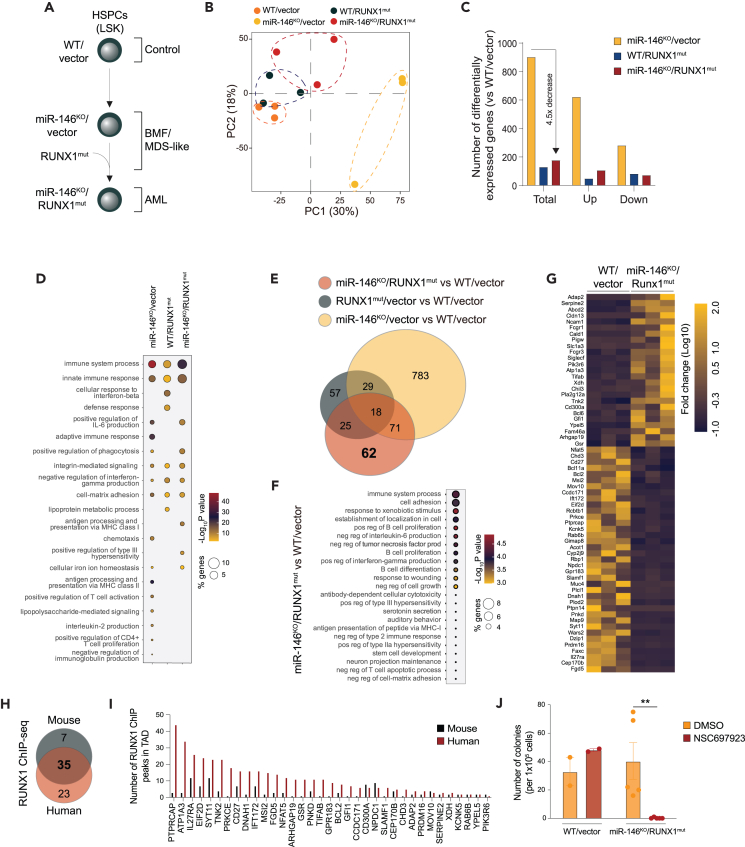
Since dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory signaling is observed in preleukemic states, it is viewed as an early alteration, while second-hit mutations, such as in RUNX1, RAS, or FLT3, are associated with malignant transformation.2 Therefore, to model the progression from preleukemic states to overt AML, we introduced a dominant-negative RUNX1 frameshift mutant (S291fsX300, herein RUNX1mut) into miR-146a knockout (KO) HSPCs.25 This mutation results in the C-terminal truncation of the wild-type RUNX1 protein, which still retains DNA binding activity, but it is unable to recruit co-activators/repressors due to the lack of the transactivation domain.26,27 Retroviral vectors (MSCV-IRES-GFP) encoding RUNX1mut or an empty control were retrovirally transduced into CD45.2 wild-type C57BL/6J (WT) or miR-146aKO bone marrow (BM) cells (Figure 1A). Expression of the transduced human RUNX1mut and of miR-146a in BM cells was confirmed by quantitative PCR analysis (Figure S1A). The transduced GFP-expressing cells successfully engrafted and established chimerism in peripheral blood (PB) (Figure 1B). The majority of recipient mice transplanted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut BM cells (n = 10/15) succumbed to a hematologic malignancy within 14 months post-transplantation. Within the same period, 3 out of 16 RUNX1mut mice developed an MDS-like phenotype. Occasionally mice transplanted with miR-146aKO (n = 4/15) BM cells developed a hematologic malignancy during this period. miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice had shorter median survival as compared to RUNX1mut mice (319 versus 453 days, p = 0.01). (Figure 1C). At the time of death, miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice showed thrombocytopenia, normal levels of white blood cells (WBCs) and reduced red blood cells (RBCs) compared to the other groups, with low hemoglobin and increased mean corpuscular volume (MCV), consistent with macrocytic anemia. (Figures 1D and S1B). While we observed mild signs of ineffective erythropoiesis in the miR-146aKO and RUNX1mut mice, it was more pronounced in the miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice (Figure S1C). Primary transplanted miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice showed anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, teardrop-shaped RBCs, nucleated RBCs, and variable degrees of polychromasia (Figures 1E and S1C). We also observed several hypersegmented neutrophils in miR-146aKO and miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice, but not in control or RUNX1mut mice. Mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut BM cells developed splenomegaly (Figures 1F, 1G, and S1D), osteopetrosis, and moderate reticulin fibrosis in BM (Figures 1E and S1D). Reticulin fibrosis was also present in BM of miR-146aKO mice, indicating that the loss of miR146a drives this phenotype. At the time of death, miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice had increased levels of the macrophage marker F4/80 and the megakaryocyte marker CD61, and reduced levels of thymocytes compared to control mice suggestive of megakaryocytic and monocytic proliferation (Figure S1E). RUNX1mut mice showed elevated Ter119+ cells and lowered CD3+NK1.1 cells in PB compared to control mice (Figure S1E). Based on the Bethesda proposals for the classification of nonlymphoid hematopoietic neoplasms, the miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice developed a BMF with myelofibrosis,28 resembling human MDS with fibrosis.29
Figure 1.
Loss of miR-146a and RUNX1 mutant cooperate to induce an MDS-like disease
(A) Schematic of experimental design for primary BM transplants.
(B) Percentage of GFP-positive cells in PB post-transplantation measured by flow cytometry.
(C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve for primary BM transplanted mice.
(D) PB counts from primary transplanted mice at time of death. WBC, white blood cell; RBC, red blood cell.
(E) Representative images of Giemsa staining of PB smears (upper panel) or reticulin staining of BM (lower panel) from primary transplanted mice at time of death. A representative femur is shown in the lower panel. Magnification 40×.
(F) Spleen weight of primary transplanted mice at time of death.
(G) Representative pictures of the spleen. WT, wild type; KO, knockout; mut, mutant. Error bars represent the standard error of mean. ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001.
Persistence of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs results in overt AML
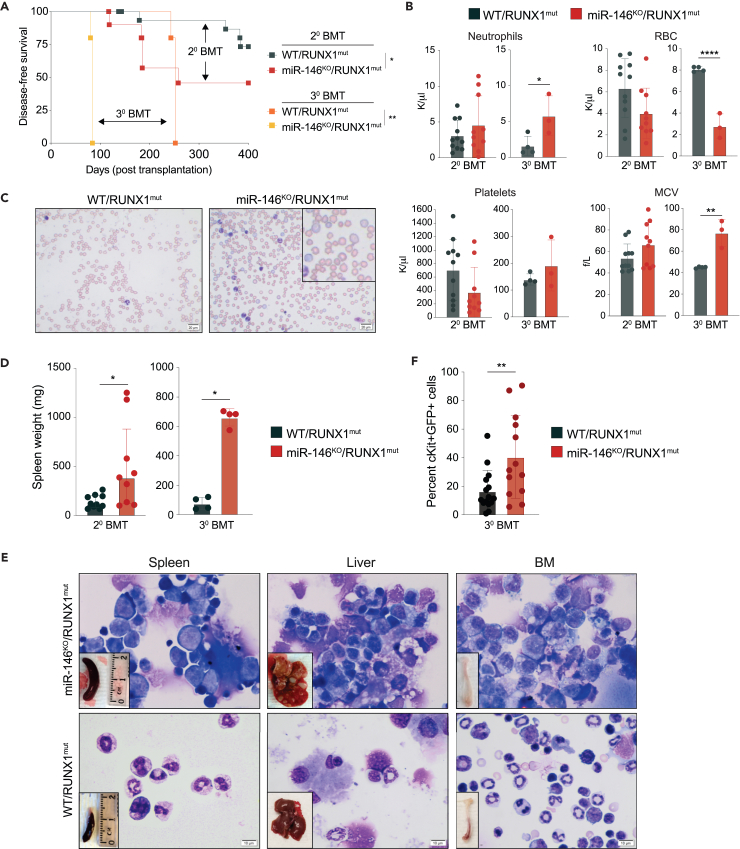
To evaluate disease progression, we next performed secondary and tertiary transplantations into lethally irradiated WT mice using the RUNX1mut or miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut BM cells isolated from the primary recipient mice. The overall survival of mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut BM cells was shorter than mice engrafted with RUNX1mut cells following the secondary (median survival of 258 days versus 489 days, respectively) and tertiary transplants (median survival of 84 days versus 252 days, respectively) (Figure 2A). In secondary transplants, miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut exhibited anemia and erythroid dysplasia (Figures 2B and 2C). Flow cytometric and histologic examination at the time of death showed an expansion of myeloid blasts in the BM and spleen, and blast infiltration into the liver (Figures 2D, 2E, S2A, and S2B). The number of WBCs was also elevated in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice (Figure S2C), and the percentage of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut GFP/c-kit double-positive cells in PB was significantly increased as compared to RUNX1mut cells (Figure 2F). The percentage of GFP/c-kit double-positive cells in the BM was comparable between the groups (Figure S2D). To confirm that the myeloid blasts were derived from miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut cells, GFP+ and GFP− BM cells were isolated and examined morphologically. The miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut (GFP+) cells showed evidence of myeloid blasts, while the GFP negative (GFP−) cells were primarily neutrophil bands, mature myeloid cells, and transit-amplifying cells (Figure S2E). To examine erythroid maturation in secondary transplanted miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice, we analyzed cell surface markers CD71 and Ter119. At the time of death, we observed the increased proportions of the immature S1 population (CD71high/Ter119-; 30.9% versus 10.8% in controls) and reduced proportions of the S4 population (CD71+/Ter119high; 1.8% versus 9.6% in controls), indicating a block in erythroid maturation of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut cells (Figures S2F and S2G).
Figure 2.
Preleukemic miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs progress to overt AML
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve for secondary (20, n = 7/group) and tertiary (30, n = 5/group) BM transplanted mice (BMT). Arrows indicate the mice group comparisons.
(B) PB counts from serially transplanted mice at the time of death.
(C) Representative Wright-Giemsa staining of PB smears from secondary transplanted mice at the time of death. 40× magnification.
(D) Spleen weights of secondary and tertiary BM transplanted mice.
(E) Representative Wright-Giemsa staining of spleen, BM, and liver cytospins from secondary transplanted mice at the time of death. Magnification 100×. A representative spleen, liver, and femur are shown in the lower left corner.
(F) Percentage of double cKit- and GFP-positive cells in PB post-transplantation measured by flow cytometry. WT, wild type; KO, knockout; mut, mutant. Error bars represent the standard error of mean. ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗, p < 0.0001.
When miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut BM cells were transplanted into tertiary recipients, the disease was fatal with a median survival of 8 weeks (Figure 2A). The miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice were diagnosed with either AML or MDS with excess blasts (MDS-EB). Although RUNX1mut cells repopulated mice following secondary and tertiary transplantations, mice engrafted with RUNX1mut cells did not progress to overt myeloid leukemia (Figure 2A). Several mice engrafted with RUNX1mut cells became anemic and developed solid tumors (in the liver or abdominal cavity), presenting with enlarged thymus or splenomegaly (data not shown).
RUNX1mut is necessary for the expansion of preleukemic miR-146aKO HSPCs
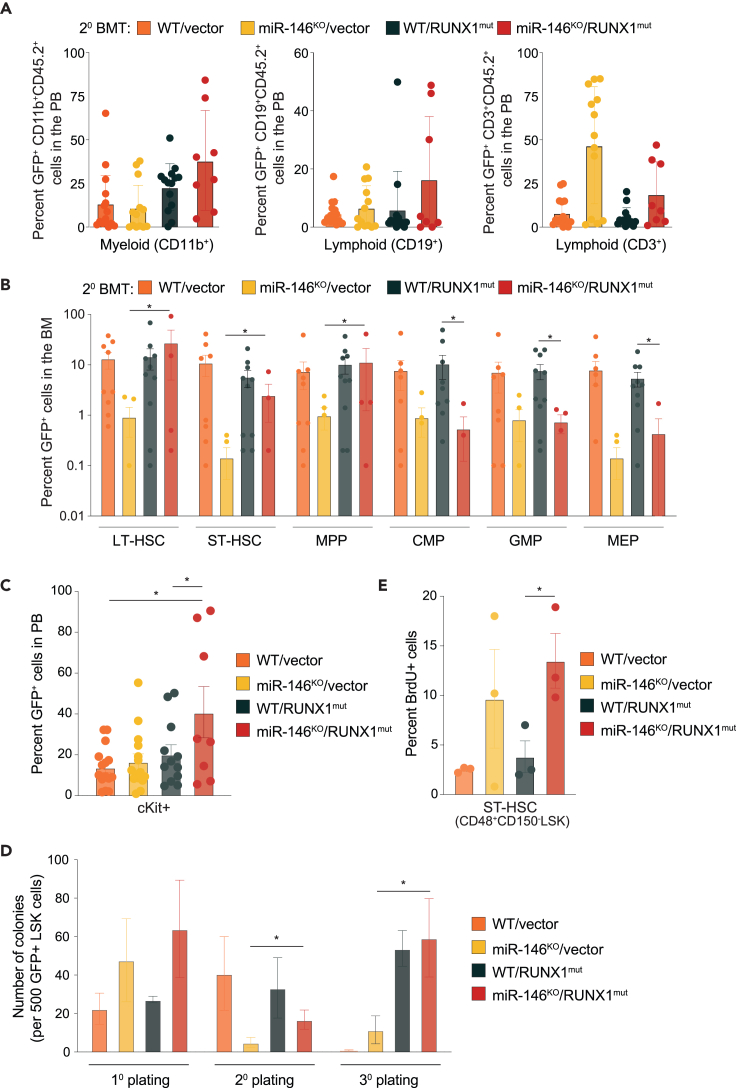
To determine the cellular basis for the accelerated disease progression and AML development in mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut BM cells, we examined hematopoietic cell populations. We first evaluated the chimerism of CD45.2+GFP+ cells in myeloid and lymphoid populations in PB postsecondary transplantation. Transgene-expressing (GFP+) mature lymphoid (CD19+ and CD3+) and myeloid (CD11b+) cells were produced, to varying degrees by miR-146aKO/vector, WT/RUNX1mut, and miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice related to control mice at 22 weeks (Figure 3A). Although miR-146aKO/vector mice produced myeloid and lymphoid cells, we detected low proportions of long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSCs), short-term hematopoietic cells (ST-HSCs), and multipotent progenitor cells (MPPs) derived from the miR-146aKO/vector (GFP+) cells at time of death (Figure 3B). As expected, the proportions of RUNX1mut expressing cells were not significantly different from WT cells (Figure 3B). In contrast, miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LT-HSCs, ST-HSCs, and MPPs were significantly expanded as compared to the miR-146aKO/vector cohort (Figure 3B). The differences among the HSPC populations were not attributed to differences in BM cellularity (Figure S3A). These findings suggest that expression of RUNX1mut restores the attrition of miR-146aKO HSPCs, which are primed for leukemic transformation. Moreover, immature cKit+ cells were expanded in the PB of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice as compared to either miR-146KO or RUNX1mut cohorts following secondary transplantations (Figure 3C). This expansion was restricted to the miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut cells as non-transgene expressing cells (GFP−) did not exhibit expansion of cKit+ cells (Figure S3B).
Figure 3.
RUNX1mut is necessary for the expansion of preleukemic miR-146aKO HSPCs
(A) Percentage of GFP+ myeloid and lymphoid cells in PB of secondary transplanted mice at time of death determined by flow cytometry.
(B) Percentage of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells expressing GFP in BM of secondary transplanted mice. ∗, p < 0.01.
(C) Donor-derived (GFP+) c-Kit+ cells in PB of secondary transplanted mice determined by flow cytometry.
(D) Colony assay of LSK cells from secondary transplanted mice at time of death.
(E) Proliferation of short-term hematopoietic cells (ST-HSC) from transplanted mice measured by bromouridine incorporation. Error bars represent the standard error of mean (A, B, C, and E) and standard deviation (D). ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗, p < 0.0001.
To examine the function of isolated miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs, the progenitor frequency was determined by serial replating in methylcellulose assays of sorted GFP+ LSK cells. Consistent with a decline of miR-146aKO/vector HSPCs in secondary transplanted mice, miR-146aKO/vector LSK cells (GFP+) isolated from primary transplanted mice exhausted after two rounds of replating (Figure 3D). In contrast, miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSKs resulted in serial replating (Figure 3D). These findings suggest that chronic innate immune activation, such as via loss of miR-146a, results in attrition of HSPCs; however, a second hit mutation, such as RUNX1, rescue the fitness advantage of these defective HSPCs in vivo.
To further explore the cellular basis for expansion of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs, we examined cell proliferation in vivo by administering BrdU into primary recipient mice. We observed increased proportion of BrdU incorporation into miR-146aKO and miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut (GFP+) ST-HSCs as compared with control or RUNX1mut cells (Figure 3E). There were no observed differences in apoptosis in BM and spleen cells (Figure S3C). These results reveal that the RUNX1mut rescues the hematopoietic repopulation deficiency of miR-146aKO HSPCs and suggest that RUNX1mut is necessary for the clonal expansion of preleukemic miR-146aKO HSPCs.
Increased systemic inflammation is widely observed in MDS and AML and is associated with worse outcomes.30,31 To investigate the inflammatory state of diseased mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut cells, we examined cytokines levels in the PB plasma of primary and secondary recipient mice (from Figure 2). The levels of IL6, TNFα, and MCP1 were trending higher in mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut cells as compared to miR-146aKO, RUNX1mut, or WT mice (Figure S4). Therefore, RUNX1mut maintains or can exacerbate the inflammatory phenotype of miR-146aKO HSPCs in diseased mice.
Cooperating proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes do not contribute to the transformation of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs
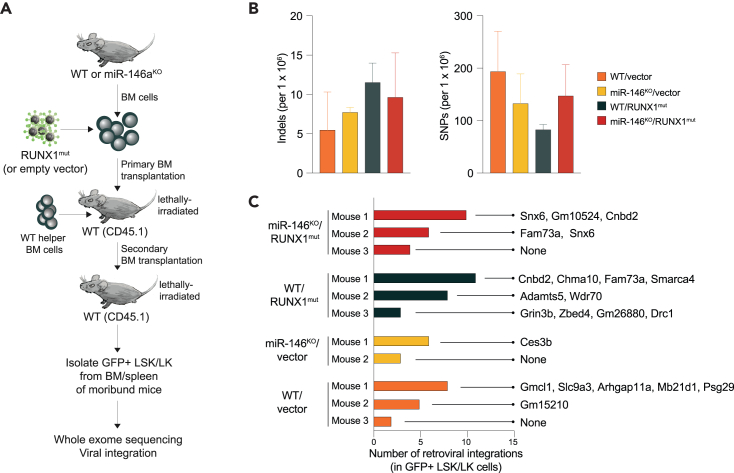
Previous studies implicated chronic inflammation as a contributing factor to DNA damage leading to the accumulation of mutations and various epigenetic changes in cells.32,33 To investigate whether deletion of miR-146a results in DNA damage in the leukemic cells, we performed whole exome sequencing of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs (GFP+) isolated from independent moribund mice (n = 3) along with control mice (WT/vector, WT/RUNX1mut, and miR-146aKO/vector) (Figure 4A). The frequency of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and insertions or deletions (INDEL) was not significantly elevated in leukemic miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice (Figure 4B). RUNX1 mutations can cause AML in murine retroviral transduction and BMT models, typically after retroviral vector insertion mutagenesis at Evi1 or Mn1 loci.25 Therefore, we next determined whether the prolonged latency of AML in mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut cells is due to retroviral integration adjacent to known cooperating genes. Through analysis of the provirus sequences in the exome sequencing analysis, we confirmed proviral integrations from 1 to 10 per mouse (Figure 4C; Table S1). Examination of the proviral integrations also revealed potentially impacted neighboring host genes. In some cases, such as for miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mouse #3, no neighboring genes were identified. Importantly, none of the proviral integrations occurred in genes with known roles in leukemia development (Figure 4C; Table S1). Collectively, the AML phenotypes observed in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut mice are not due to genomic instability or from opportunistic activation of proto-oncogenes or inactivation of tumor suppressor genes from retroviral integration.
Figure 4.
Whole exome sequencing and pro-viral integration analysis of miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs
(A) Schematic of experimental design for the exome sequencing analysis of LK and LSK cells from secondary transplanted mice.
(B) Number of insertions-deletions (indels) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) determined by whole exome sequencing detected in sorted GFP+ LSK/LK cells from secondary transplanted mice at time of death.
(C) Number of retroviral integrations detected in GFP+ LSK/LK of secondary transplanted mice. Genes with retroviral integrations are indicated. A comprehensive list of genes is in Table S2. Error bars are the standard deviation.
RUNX1mut rewires the transcriptome of preleukemic miR-146aKO HSPCs
To identify the molecular basis of how miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs gain a fitness advantage and progress to AML, we performed RNA sequencing on LSK (GFP+) isolated from secondary recipient mice engrafted with miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut, miR-146aKO, RUNX1mut, or WT HSPCs (Figure 5A). Principal component analysis (PCA) showed that miR-146aKO LSK have a gene expression pattern distinct from miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut, RUNX1mut, or WT LSKs (Figure 5B). Among the groups, miR-146aKO LSK had the greatest number of dysregulated genes (n = >800, fold change > |1.5|, p < 0.05) compared to WT controls (Figure 5C). As previously reported, we observed broad dysregulation of innate and adaptive immune signaling in miR-146aKO versus WT (empty vector) LSK cells9,16,17,18,34 (Figure 5D; Tables S2 and S3). In contrast, RUNX1mut LSK cells had the fewest gene expression changes (n = 129) as compared to WT LSK (48 upregulated and 81 downregulated, fold change >|1.5|, p < 0.05) (Figure 5C; Tables S4 and S5). Interestingly, miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK cells had fewer dysregulated genes (n = 176) as compared to miR-146aKO LSK (Figure 5C), suggesting that RUNX1mut is altering the transcriptome in miR-146aKO HSPCs. Among the downregulated genes are those involved in interferon (IFN) regulation (Cd27 and Il27ra), cell differentiation (Prdm16, Nkx2-3, Dzip1, and Bex1), genes that regulate B and T cell function (Slamf1, Tnfsf4, Il27ra, Bcl11a, Bcl2, and Nfat5), while upregulated genes belonged to the innate immune response (Tlr1, Tlr7, Tlr13, C4b, Cfp, and ifi204), inflammation (Chil3, CD163, Csf1r, and Spic), cell adhesion (Cd36, Itga9, Itgb2, Itgb5, and Siglec1), osteoclast differentiation (Fcgr1, Fcgr3, Fcgr4, and Ncf2), and master regulators of normal and malignant hematopoiesis (Msi2, Gfi1, and Bcl6) (Figure 5D; Table S4). Although the number of dysregulated genes in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK was significantly fewer than in miR-146aKO LSK, the miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSKs exhibited a greater enrichment of genes related to innate immune responses as compared to miR-146aKO LSK (Figure 5D; Tables S6 and S7). These findings suggest that deletion of miR-146a results in broad gene dysregulation and that a second hit RUNX1 mutation consolidates the transcriptional responses to ones primarily related to immune signaling and malignant hematopoiesis.
Figure 5.
RUNX1mut rewires the transcriptome of preleukemic miR-146aKO HSPCs
(A) Schematic of experimental design for the RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis of GFP+ LSK cells from secondary transplanted mice. Phenotypes of each of the mouse models are indicated.
(B) Principal component analysis of RNA-seq samples for each of the mouse model groups. Each dot represents a sample. A dotted line was manually added to aid in the visualization of sample grouping.
(C) Bar graph indicating the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in each of the mouse models compared to wild-type/vector mice. Total DEGs, unregulated (up), and downregulated (down) genes are indicated.
(D) Balloon plot showing the gene set enrichment analysis for the DEGs including GO terms biological processes. The size of the circles corresponds with the percent of enriched genes in each category. The color indicates the statistical significance, with red mapping to the most significant value.
(E) Venn diagram intersecting the DEGs in LSK cells in each of the mouse models. DEGs unique to miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK cells are indicated in bold.
(F) Balloon plot for gene set enrichment for the DEGs in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK cells. The size of the circles corresponds with the percent of enriched genes in each category. The color indicates the statistical significance, with red mapping to the most significant value.
(G) Heatmap of the 62 DEGs unique to miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK cells. Upregulated genes appear in yellow and downregulated genes in blue. The scale on the right represents the row Z score.
(H) Venn diagram intersecting the genes with RUNX1 ChIP peaks in mouse and human hematopoietic cells. Only the DEGs in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK cells are considered in this analysis.
(I) Bar graph showing the number of RUNX1 ChIP-seq peaks found near the DEGs in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK cells in mouse and human public samples.
(J) Colony formation assay of WT/vector and miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut GFP+LSK cells treated with NSC697923 (2 μM). Error bars are the standard error of mean. ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗, p < 0.0001.
To identify the transcriptional changes that might be contributing to the leukemic phenotype in the miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs, we intersected the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut, miR-146aKO, and RUNX1mut LSKs (Figure 5E). miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs exhibited 62 unique DEG (Figure 5E). The genes unique to miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs are involved in regulation of innate immunity (FCGR1, BCL6, CD300A, PRKCE, GPR183, and SLAMF1), malignant hematopoiesis (MSI2, GFI1, BCL6, PRDM16, BCL11A, and BCL2), and cell adhesion (PRKCE, CLDN13, NCAM1, MUC4, SIGLECF, and SLAMF1)35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42 (Figures 5F and 5G; Table S8).
To determine whether RUNX1 directly regulates the expression of the genes unique to miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSCPs, we evaluated RUNX1 genome wide occupancy in murine and human hematopoietic cells. We first compiled all RUNX1 chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) analyses (21 mouse and 31 human ChIP-seq GEO datasets) performed in healthy and leukemic hematopoietic cells and then identified genomic locations bound by RUNX1 (Table S9). To determine whether these RUNX1 bound regions are associated with the transcriptional changes in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK, we assigned RUNX1 ChIP peaks to the 62 unique DEGs miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSKs by proximity within the context of the topologically associated domain. RUNX1 bound regions were nominated if they were present in >50% of the datasets. Twenty-three and 7 of the DEGs were identified exclusively in human or mouse ChiP-seq datasets so these were excluded from further analysis (Figure 5H). We observed human and mouse RUNX1 peaks adjacent to 35 of the 62 DEGs (Figure 5H; Table S10). The RUNX1 bound genes that are differentially expressed in miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSKs include regulators of HSC expansion (i.e., BCL2, MSI2, and GFI1) and differentiation (i.e., PRDM16, TIFAB, and CDH3), innate and adaptive immune signaling (i.e., SLAMF1, CD27, GPR183, IL27RA, and NFAT5), and cytokine production (i.e., SYT11, SLAMF1, and IL27RA) (Figure 5I). These observations suggest that RUNX1mut rewires the transcriptome of preleukemic miR-146aKO HSPCs resulting in sustained expression of innate immune and stem cell genes.
Given that dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory signaling pathways are sustained by miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut AML cells, we wanted to investigate whether these pathways remain critical for the leukemic cells. We evaluated an inhibitor (NSC697923) that targets TRAF6, a key target of miR-146a in MDS/AML, via inhibition of its co-factor UBE2N.43,44 Treatment with NSC697923 abolished colony formation by miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut AML cells while not impacting WT/vector hematopoietic cells (Figures 5J and S5). These findings suggest that cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling is not only required for initiating AML but is also required for sustaining the leukemic phenotype. Collectively, we provide evidence that dysregulation of innate immune and inflammatory signaling contributes to the progression and maintenance of AML.
Discussion
Cell-intrinsic dysregulation of innate immune and inflammatory-related pathways as well as systemic inflammation are implicated in hematopoietic defects associated with myeloid malignancies. Various genetic and molecular changes affect innate immune- and inflammatory-related pathways. There is also substantive evidence of microenvironment changes within the MDS and AML BM niche. More recent findings have supported the premise that dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory pathways in leukemic cells do not result in increased pathway activation, but rather alter their response to the microenvironment in a way that favors the competitive advantage of leukemic clones.3 Muto et al. found that preleukemic HSPCs are protected from chronic inflammation compared to normal HSPCs.45 In response to inflammation, preleukemic HSPCs switch from canonical to noncanonical NF-κB signaling, which is dependent on TLR-TRAF6-mediated activation of A20.45 ASXL1 mutations also promote clonal dominance by altering their response to inflammation by expressing negative regulators of inflammatory signaling.46 TET2-deficient myeloid cells and HSPCs acquire resistance to IL6-mediated inflammatory stress by increasing expression of the anti-apoptotic lncRNA Morrbid.47 In separate studies, TET2-deficient HSPCs that have impaired TLR-TRAF6 signaling can malignantly transform to AML.44 IFNγ signaling during chronic infection can drive DNMT3A-loss-of-function clonal hematopoiesis and mimic clonal hematopoiesis by becoming unresponsive to IFNy-induced stress.48 Collectively, these studies reveal how preleukemic and leukemic clones disrupt the stoichiometry of key innate-immune relating signaling hubs in a way that alters their circuitry and adaptations that allow for their outgrowth.
In certain cases, response to inflammatory stress can result in maladaptive changes to leukemic HSPCs. In a model of del(5q)-like MDS, inflammation impaired del(5q)-like HSPCs, leading to reduced numbers, premature attrition, and increased p53 expression.49 The functional defect of the del(5q)-like MDS was restored by p53 deletion. The findings suggest that inflammation provides a competitive advantage to functionally defective del(5q) HSPCs upon p53 loss, potentially influencing the selective pressure for genetic inactivation of p53 or expansion of a pre-existing TP53-mutant clone in del(5q) AML following an MDS diagnosis. Herein, we propose a distinct mechanism by which a second hit mutation directly alters cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling, a step necessary for malignant transformation. Expression of RUNX1mut rescued the hematopoietic repopulation deficiency of miR-146aKO HSPCs. Although deletion of miR-146a results in broad dysregulation of innate immune and inflammatory pathways, expression of RUNX1mut in miR-146aKO HSPCs restricted the expression of these pathways to a subset of innate immune and inflammatory genes at the AML stage. These findings represent evidence that dysregulation of innate immune and inflammatory signaling is required for propagating preleukemic cells and contributes to the progression of AML. While we describe cooperation between RUNX1 mutations and the dysregulation of cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling (resulting from the loss of miR-146a), the exact mechanistic basis remains unknown and necessitates further investigation.
RUNX1 or AML1 encodes a transcription factor with location on chromosome 21q22 and is the most frequent target for chromosomal translocation in leukemia.50,51 RUNX1 mutations can cause MDS/AML in murine retroviral transduction mediated overexpression and BMT models; however, the latency is long and retroviral vector insertion mutagenesis at Evi1 or Mn1 loci seems critical for MDS/AML development in these models.25 Germline mutations in the RUNX1 gene, typically at R188Q, are also implicated in causing familial platelet disorder (FPD), which have an associated risk of MDS/AML.20 Runx1R188Q HSPCs exhibited defective DNA-damage response, reduced differentiation of long-term repopulating HSCs, and enhanced competitive capacity, but do not develop MDS/AML.52 Thus, RUNX1 mutations require a cooperating mutation to induce overt disease. Furthermore, RUNX1 mutations are linked to altered innate immune and inflammatory signaling. RUNX1 is crucial for epigenetically repressing two inflammatory signaling pathways: TLR4 and type I IFN signaling.23,24 Loss of RUNX1 in granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs) increases neutrophils’ inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharides (LPS), partly through elevated CD14 expression.24 RUNX1 binds CD14 and other genes in the TLR4 and IFN pathways, leading to increased chromatin accessibility when RUNX1 is absent. Consistent with these observations, Runx1R188Q mutation in mice lead to increased HSPCs, in part due to systemic inflammation.52 In human HSPCs, RUNX1 loss also reduces proliferative capacity and stem cell function by selectively upregulating the IL-3 receptor.53 Exposure to IL-3 rescues proliferative and competitive defects in RUNX1-deficient cells. These studies highlight the complex interplay between RUNX1 function and inflammatory signaling in hematopoietic cells and support our findings that chronic activation of innate immune signaling cooperates with mutant RUNX1 to drive the progression from preleukemia to AML.
There has been growing interest in targeting innate immune pathways in preleukemic and leukemic conditions.54,55,56,57 We showed that inhibition of innate immune signaling with an UBE2N inhibitor was sufficient to suppress the leukemic miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut HSPCs. These findings suggest that dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory signaling contribute to the pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies but also that these pathways remain necessary for maintaining the leukemic cells. Additional genetic studies are needed to precisely define which innate immune and inflammatory effectors are critical for sustaining the leukemic phenotypes in the miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut model. In prior studies, we found that UBE2N is required for leukemic cell function in vitro and in vivo by maintaining oncogenic immune signaling states.58 UBE2N (Ubc13) is a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme implicated in the regulation of TRAF6, an E3 ubiquitin ligase and effector of the TLR/IL1R signaling pathway.59 Using small-molecule inhibitors identified in in silico structure-based and cellular-based screens, we revealed the therapeutic efficacy of interfering with UBE2N function by blocking of ubiquitination of innate immune- and inflammatory-related substrates in human AML cells.58 Inhibition of UBE2N function disrupted oncogenic immune signaling by promoting cell death of leukemic HSPCs while sparing normal HSPCs in vitro.58 In a clonal evolution model of AML using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), Wang et al. found that the earliest persistent signaling alterations involve genes related to inflammation and innate immunity.60 Targeting inflammatory signaling with UBE2N or IRAK1/4 inhibitors in the iPSC progression model exerted inhibitory effects at all disease stages, suggesting that modulation of inflammatory signaling as a therapeutic avenue for early-stage intervention in MDS and AML.60 Importantly, our data herein provide further evidence of the importance of dysregulated innate immune and inflammatory signaling for propagating preleukemic cells and its contribution to the progression and maintenance of AML.
Limitations of the study
The study has several limitations that warrant consideration. Firstly, the use of a retroviral approach to express RUNX1mut may introduce variability and non-physiological gene expression, potentially affecting the development of the observed phenotypes. Additionally, serial BM transplantations induce additional layers of hematopoietic stress, which may influence disease development. Furthermore, while miR-146a is a key gene within the del(5q) segment in MDS and AML, we acknowledge that other genes within the deleted region may also play a role in disease progression in cooperation with RUNX1mut. Moreover, while our in vitro studies demonstrate the importance of TRAF6-UBE2N signaling in AML cell function, future research should explore the development of AML in vivo to fully understand its implications. Lastly, the exact cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the cooperation between RUNX1 mutations and dysregulation of cell-intrinsic innate immune signaling via miR-146a loss remain unclear, suggesting the need for further investigation.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| CD11b-PE-cy7 | eBiosciences | 25-0112-81 |
| Gr1-eFluor450 | eBiosciences | 48-5931-82 |
| CD3-PE | eBiosciences | 12-0031-83 |
| B220-APC | eBiosciences | 17-0452-82 |
| CD45.1 | BioLegend | 110741 |
| CD45.2 | eBiosciences | 47-0454-82 |
| lineage biotin panel | eBiosciences | 88-7774-75 |
| streptavidin | eBiosciences | 47-4317-82 |
| Sca-1-PE | eBiosciences | 12-5981-82 |
| c-Kit-APC | eBiosciences | 17-1171-81 |
| CD48-FITC | Affymetrix | 11-0481-85 |
| CD150-PE-cy7 | BioLegend | 115914 |
| CD48-APC | Biolegend | 103412 Clone HM48-1 |
| CD150 Percp | Biolegend | 115922 Clone TC15-12F12.2 |
| cKit-APC-Cy7 | eBiosciences | 135135, clone ACK2 |
| sAv-eFluor 450 | eBiosciences | 48-4317-82 |
| CD34-AF700 | eBioscience | 56-0341-82, clone RAM34 |
| CD16/CD32-BV510 | Biolegend | 101333, clone 93 |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| BrdU | Sigma-Aldrich | B5002 |
| BrdU Flow Kit | BD Biosciences | 559619 |
| Methylcellulose | Stemcell Technologies | 3434 |
| RNeasy Plus Micro Kit | Qiagen | 74034 |
| NSC697923 | Selleckchem | S7142 |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| 32-plex mouse cytokine panel | Millipore Sigma | MCYTOMAG-70K |
| SureSelectXT Mouse All Exon | Agilent Technologies | 5190-4641 |
| SPRIworks HT Reagent Kit | Beckman Coulter | B06938 |
| Deposited data | ||
| RUNX1 ChIP seq (multiple data sets) | Sources in Tables S9 and S10 | Identifiers in Tables S9 and S10 |
| miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut LSK RNA-seq | This paper | GSE264051, GSE26053 |
| miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut WES | This paper | GSE264052 |
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
| miR-146a-/- C57BL/6 | JAX | 016239 |
| C57BL/6 | JAX | 000664 |
| B6.SJL-Ptprca Pepcb/BoyJ | JAX | 002014 |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| Human Runx1 probes | Taqman | Hs04186042_m1 |
| Murine miR-146a probes | Taqman | hsa-miR-146a |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| RUNX1 S291fsX300 (pMYs-IRES-GFP) | Gang Huang | Watanabe-Okochi et al. (ref.25) |
| pMYs-IRES-GFP | Addgene | 163361 |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| Prism | Graphpad | v10 |
| GSEA | Subramanian et al. (ref.61) | |
| Genome Analysis Toolkit | https://www.broadinstitute.org/gatk/ | v3.4-46 |
| Burrows Wheeler Aligner | http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net | BWA v0.7.17 |
| Picard | https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/ | v1.114 |
| Variant Effect Predictor | https://useast.ensembl.org/info/docs/tools/vep/ | VEP, v96 |
| Ggplot2 | Wickham et al. (ref.62) | |
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for reagents can be directed and fulfilled by the lead contact, Daniel Starczynowski (Daniel.Starczynowski@cchmc.org).
Materials availability
This study did not generate new unique reagents.
Cell lines and mouse models used in these studies are publicly available through commercial sources or may be made available from the authors upon written request and material transfer agreement approval. The authors are also glad to share guidance regarding protocols and assays used in these studies upon written request.
Data and code availability
-
•
Bulk RNA-seq and whole exome sequencing data have been deposited at GEO: GSE264053, GSE264051, GSE264052.
-
•
No original code was developed for this study.
-
•
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported is available from the lead contact upon request.
Method details
Mouse models
miR-146a-/- C57BL/6 mice were obtained from Dr. David Baltimore as previously described.9 All mouse experiments were performed in accordance with the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care-accredited animal facility of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
Retroviral vectors, packaging cell lines, and bone marrow transplantation
The RUNX1 S291fsX300 construct inserted between EcoRI/NotI sites in the pMYs-IRES-GFP retroviral vector was obtained from Dr Gang Huang’s lab at CCHMC. For retroviral production, 293T cells were co-transfected with the packaging plasmids pCMV-Gag-Pol, pCMV-Eco, and either pMYs-IRES-GFP or pMYs-RUNX1-S291fsX300-IRES-GFP using Fugene6 reagent-based transfection protocol (E2691, Promega). Transfections for retrovirus production were performed in 6 well tissue culture dishes when 293T cells reached at least 80-90% of confluency. 48-hours post-transfection, 293T cell supernatants were collected and filtrated with 0.45um filter. For retroviral transduction, we injected 5-Fluoroacil (80-100 ug/g) into miR146aKO or C57 mice 4 days prior to sacrifice. We harvested the BM cells by flushing the bones and isolated mononuclear cells with histopaque at room temperature. The target cells were resuspended in IMDM containing SCF, TPO and G-CSF (final concentration 100 ng/ml), and seeded in 10cm NTC dishes and culture overnight. Target cells were subjected to two rounds of transduction with retrovirus in two consecutive days. Briefly, transduction was performed in 6-well plates coated with retronectin (20ug/ml) and blocked with 2ml PBS+2%FBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. 2 ml viral supernatant were added to each well and the plate was spun down for 120min at 32C, 800xg. The virus supernatant was removed, and the target cells were added immediately to the plate and incubated overnight. The following day the cells were transduced with a second viral supernatant and polybrene (4 mg/mL; Sigma), and spin-infected with the respective retroviral supernatant for 90min at 32C, 800xg. 24 hours post-transduction, 8 x104 transduced BM mononuclear cells together with 250,000 wild type whole BM cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated Boy J mice by tail vein injection. For secondary transplants, 1x104 BM and 1x106 spleen cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated Boy J recipients along with 2 x105 wild-type whole BM by tail vein injection. For serial BM transplantation, 1x106 donor-derived BM or spleen cells were isolated from the previous recipients at time of death and transplanted into new lethally irradiated recipients along with fresh 250,000 wild-type whole BM. This process was repeated for two successive rounds. Transplant recipients were periodically bled and analyzed for the presence of GFP positive donor-derived lineage contribution in peripheral blood by flow cytometry.
Cell cycle analysis
BrdU (Sigma-Aldrich) was administered continuously to mice via drinking water (0.5 mg/ml). After 1 week, BrdU incorporation was analyzed using a BrdU Flow Kit (559619, BD Biosciences) according to the manufacture’s recommendation.
Colony forming assay
GFP+ LSK CD34-sorted cells (n = 3000 from primary or secondary transplanted mice were plated in 6 well plates with methylcellulose (3434; Stemcell Technologies). Plates were scored with automatic counting on the Stem Cell technologies counter after 7 days in culture. For serial replatings, 5000/ml GFP+ LSK CD34- cells were plated in methyl cellulose for a total of 5 replatings (7, 14, 21, 28, and 35 days).
Hematological analysis
Blood counts were measured with a hemacytometer (HEMAVET).
Flow cytometry
For immunophenotypic analysis of lineage positive cells, PB samples were processed with 1 x RBC lysis buffer, and then incubated with CD11b-PE-cy7 (25-0112-81, eBiosciences), Gr1-eFluor450 (48-5931-82, eBiosciences), CD3-PE (12-0031-83, eBiosciences), and B220-APC (17-0452-82, eBiosciences). To distinguish donor from recipient hematopoietic cells, PB were stained with CD45.1-Brilliant Violet 510 (110741, BioLegend), and CD45.2-APC-eFluor780 (47-0454-82, eBiosciences) or CD45.2- eFluor450 (48-0454-82, eBiosciences). For HSC analysis, BM cells were washed and incubated for 30 minutes with biotin conjugated lineage markers (CD11b, Gr1, Ter119, CD3, B220, mouse hematopoietic lineage biotin panel, [88-7774-75 eBiosciences]), followed by staining with streptavidin eFluor780 (47-4317-82, eBiosciences), Sca-1-PE (12-5981-82, eBiosciences), c-Kit-APC (17-1171-81, eBiosciences), CD48-FITC (11-0481-85, Affymetrix), CD150-PE-cy7 (115914, BioLegend). SLAM-HSC were identified based on expression of Lin-Sca-1+c-Kit+CD150+CD48; multipotent progenitor cells (MPP) were identified based on expression of Lin-cKit+Sca1+CD48+CD150-; short-term hematopoietic stem cells (ST-HSC) were identified based on expression of Lin-cKit+Sca1+CD48-CD150-; long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSC) were identified based on expression of Lin-cKit+Sca1+CD48-CD150+). CD48-APC (103412 Clone HM48-1, Biolegend), CD150 Percp. Cy5.5 (115922 Clone TC15-12F12.2, Biolegend), cKit-APC-Cy7 (135135, clone ACK2), sAv-eFluor 450 (Streptavidin APC-eFluor® 450, 48-4317-82, eBioscience), CD34-AF700 (56-0341-82, clone RAM34, eBioscience), CD16/CD32-BV510 (101333, clone 93, Biolegend). The identification and analysis of erythroid progenitors was performed as previously described using the CD71/TER119 flow-cytometric assay.63
RNA sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from sorted GFP+/lin-/ckit+/Sca+cells using RNeasy Plus Micro Kit (Qiagen). The initial amplification step for all samples was done with the NuGEN Ovation RNA-Seq System v2. The assay was used to amplify RNA samples to create double stranded cDNA. The concentrations were measured using the Qubit dsDNA BR assay. Libraries were then created for all samples using the Illumina protocol (Nextera XT DNA Sample Preparation Kit). The concentrations were measured using the Qubit dsDNA HS assay. The size of the libraries for each sample was measured using the Agilent HS DNA chip. The concentration of the pool was optimized to acquire at least 15-20 million reads per sample. The analysis of RNA sequencing was performed with iGeak.61 Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed as previously described.62
Quantitative PCR
cDNA (10-25 ng) extracted from BM aspirates from primary transplanted mice were used to detect the expression of human Runx1 (Taqman probe Hs04186042_m1), and murine miR-146a (hsa-miR-146a Taqman probe) with the 2X Taqman GEA Master mix in a Step One Plus instrument. A GAPDH or U18 taqman probe was utilized for normalization of gene expression.
Cytokine analysis
Peripheral blood was obtained from each mouse in K3 EDTA-coated tubes on ice, then samples were centrifuged for 10 minutes at 2,000 g within 30 minutes at 4°C. After centrifugation, supernatant was immediately transferred to ice cold eppendorf tubes and frozen at -70°C until further use. Samples were thawed on ice, vortexed thoroughly prior to being diluted 1:1 in assay buffer using the mouse cytokines/chemokines magnetic bead panel kit to quantify 32-plex mouse panel (Cat no. MCYTOMAG-70K; Millipore Sigma) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of BM
Mouse femurs and tibia were dissected and fixed with 10% formalin at room temperature, sectioned and stained with hematoxylin and eosin by the CCHMC pathology core. Imaging performed on the Motic Type 102M Microscope and image capture, and processing was accomplished using Olympus LC Micro Imaging (Olympus) Software and Adobe Photoshop (Adobe).
Peripheral blood, spleen and bone marrow histology
Mouse femurs and tibia were dissected and fixed with 10% formalin at room temperature, sectioned and stained with hematoxylin and eosin or reticulin or anti-cleaved caspase 3 antibody by the CCHMC pathology core. Peripheral blood smears and bone marrow and spleen or liver cytospins were stained with the Hematek 3000 using Hematek Wright-Giemsa (Siemens). Imaging performed on the Motic Type 102M Microscope and image capture, and processing was accomplished using Olympus LC Micro Imaging (Olympus) Software and Adobe Photoshop (Adobe).
Whole exome sequencing
Pooled genomic DNA isolated from FACS sorted BM GFP+/lin-/ckit+/Sca+ cells from WT/vector (n = 3), WT/RUNX1mut (n = 3), miR-146aKO/vector (n = 3), and miR-146aKO/RUNX1mut (n = 3) secondary transplanted mice were submitted to Otogenetics Corporation (Atlanta, GA, USA) for mouse exome capture and sequencing. Briefly, gDNA was subjected to agarose gel and OD ratio tests via Nanodrop to confirm the purity and concentration prior to Bioruptor (Diagenode Inc.) fragmentation. Fragmented gDNAs were tested for size distribution and concentration using an Agilent Tapestation 2200. Illumina libraries were made from qualified fragmented gDNA using SPRIworks HT Reagent Kit (B06938, Beckman Coulter) and the resulting libraries were subjected to exome enrichment using SureSelectXT Mouse All Exon (5190-4641, Agilent Technologies) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Enriched libraries were tested for enrichment by qPCR and for size distribution and concentration by an Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100. The samples were then sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq2000/2500 which generated paired-end reads of 100-125 nucleotides with designated average coverage of 30X.
The standard Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) pipeline (v3.4-46, https://www.broadinstitute.org/gatk/) was used, with modifications in the “Best Practices” document on their website. Briefly, after applying Illumina’s Chastity filter, raw sequenced reads were aligned using the Burrows Wheeler Aligner (BWA v0.7.17, http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net) against reference mouse genome (GRCm38). For each sample, reads appearing to be PCR artifacts were flagged, reads that overlap known or putative insertions/deletions (INDELs) realigned, then all base quality scores were recalibrated to the empirical error rate from non-polymorphic sites. The GATK HaplotypeCaller module was used to create a gVCF file for each patient sample containing confidence values for every position in the exome (variant and/or reference). A set of variant calls with the GenotypeGVCFs module was generated using every compatible sample sequenced by the sequencing facility to date. The Variant Quality Score Recalibration (VQSR) method was applied to filter variant calls. Finally, variant calls specific to the samples were extracted. Variants marked “PASS” were considered for further analysis. For INDELs, samples were individually preprocessed by realigning reads around putative INDELs using GATK’s IndelRealigner tool, marking putative polymerase chain reaction duplicate reads with Picard (v1.114, https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/) MarkDuplicates tool and by recalibrating base quality scores and calculating Base Alignment Quality scores with GATK’s CountCovariates and TableRecalibration tools. After preprocessing, samples were jointly processed with HaplotypeCaller to generate initial variant calls. Variants were then filtered using GATK Variant Quality Score Recalibration. Finally, variants were annotated using Variant Effect Predictor (VEP, v96, https://useast.ensembl.org/info/docs/tools/vep/).
ChiP-sequencing analysis
Collection of public ChIP-seq data from NCBI's GEO database
The objective of this section was to collect and process ChIP-seq experiments targeting the Runx1 protein, performed on stem cells, publicly available in NCBI's Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The set was curated by following these steps: 1) Programmatic search of public ChIP-seq experiments targeting the Runx1 protein, 2) Programmatic filtering of cell types using the following keywords: "aml|acute|myeloid|lsk|lk|marrow|hematopoietic|leuk", 3) Manual curation to keep experiments that used only stem cells. The final curated sets contained 35 human and 27 mouse ChIP-seq samples targeting the wild type RUNX1 protein in stem cells.
Processing of ChIP-seq data
ChIP-seq reads were downloaded from NCBI's Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database in FASTQ format. The following steps were taken to process the FASTQ data: 1) Quality control of raw reads using FastQC v0.11.9[1], 2) Trimming of adapter sequences or bad quality segments using Trim Galore! v0.6.7[2] and cutadapt v3.5[3], 3) Alignment of trimmed reads to their corresponding reference (human version GRCh38/hg38 and mouse version GRCm39/mm39) with the program HISAT2 version 2.2.1[4], 4) Aligned reads were stripped of duplicate reads with the program sambamba v0.8.2[5], 5) Peaks were called with the program MACS version 2.2.7.1[6], using the narrow peaks mode, 6) Common called peaks from human and mouse, separately, were defined by those present in at least 75% of the samples (20 and 26, respectively) and overlapping by at least 50% of their length (i.e. a ChIP-seq peak is common if it is at least present in 20 out of 27 samples); this was necessary to buffer the uncertainty in observed peaks due to the variable nature of the public samples, with varying laboratory conditions, 7) Common peaks, in BED format, were converted to a Gene Transfer Format (GTF) to enable fast counting of reads under the peaks with the program featureCounts v2.0.6[7] (Subread package).
The programs Samtools v1.13[8] and Bedtools v2.30.0[9] were used to manipulate BAM and BED file formats, respectively.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Differences among multiple groups were assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison posttest for all possible combinations. Comparison of two group was performed using the Mann-Whitney test or the Student’s t test (unpaired, two tailed) when sample size allowed. Unless otherwise specified, results are depicted as the mean ± standard deviation or standard error of the mean. A normal distribution of data was assessed for data sets >30. D’Agostino and Pearson and Shapiro-Wilk tests were performed to assess data distributions. For Kaplan-Meier analysis, Mantel-Cox test was used. All graphs and analysis were generated using GraphPad Prism software or using the package ggplot2 from R.64
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (U54DK126108, R35HL166430, R01CA271455, and R01CA275007), Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Research Foundation, CancerFree KIDS, and Blood Cancer Discoveries Grant program through The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, The Mark Foundation For Cancer Research and The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group to D.T.S. This work was supported by NIDDK U54 DK126108 at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and their Flow Cytometry and Comprehensive Mouse Cores. L.B. was supported by CancerFree KIDS.
Author contributions
L.B. and A.M.S. performed experiments, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote the manuscript. K.H., S.C., V.R., M.W., and K.G. performed experiments and analyzed and interpreted data. K.C. and M.P. performed bioinformatics analyses. D.W. evaluated the pathology of the models. G.H. provided input and reagents and interpreted data. D.T.S. conceived and directed the study, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote and/or edited the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Declaration of interests
D.T.S. serves on the scientific advisory board at Kurome Therapeutics and is a consultant for and/or received funding from Kurome Therapeutics, Captor Therapeutics, Treeline Biosciences, and Tolero Therapeutics. D.T.S. has equity in Kurome Therapeutics. L.B. is a current employee of Johnson and Johnson Innovative Medicine and an equity holder in a publicly traded company.
Published: April 24, 2024
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.109809.
Supplemental information
References
- 1.Menssen A.J., Walter M.J. Genetics of progression from MDS to secondary leukemia. Blood. 2020;136:50–60. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bănescu C., Tripon F., Muntean C. The Genetic Landscape of Myelodysplastic Neoplasm Progression to Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24 doi: 10.3390/ijms24065734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Trowbridge J.J., Starczynowski D.T. Innate immune pathways and inflammation in hematopoietic aging, clonal hematopoiesis, and MDS. J. Exp. Med. 2021;218 doi: 10.1084/jem.20201544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barreyro L., Chlon T.M., Starczynowski D.T. Chronic immune response dysregulation in MDS pathogenesis. Blood. 2018;132:1553–1560. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-03-784116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sallman D.A., List A. The central role of inflammatory signaling in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2019;133:1039–1048. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-10-844654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Varney M.E., Melgar K., Niederkorn M., Smith M., Barreyro L., Starczynowski D.T. Deconstructing innate immune signaling in myelodysplastic syndromes. Exp. Hematol. 2015;43:587–598. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stickel N., Prinz G., Pfeifer D., Hasselblatt P., Schmitt-Graeff A., Follo M., Thimme R., Finke J., Duyster J., Salzer U., Zeiser R. MiR-146a regulates the TRAF6/TNF-axis in donor T cells during GVHD. Blood. 2014;124:2586–2595. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-569046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Taganov K.D., Boldin M.P., Chang K.J., Baltimore D. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:12481–12486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605298103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boldin M.P., Taganov K.D., Rao D.S., Yang L., Zhao J.L., Kalwani M., Garcia-Flores Y., Luong M., Devrekanli A., Xu J., et al. miR-146a is a significant brake on autoimmunity, myeloproliferation, and cancer in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2011;208:1189–1201. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pauley K.M., Satoh M., Chan A.L., Bubb M.R., Reeves W.H., Chan E.K. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008;10 doi: 10.1186/ar2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tang Y., Luo X., Cui H., Ni X., Yuan M., Guo Y., Huang X., Zhou H., de Vries N., Tak P.P., et al. MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1065–1075. doi: 10.1002/art.24436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nahid M.A., Pauley K.M., Satoh M., Chan E.K.L. miR-146a is critical for endotoxin-induced tolerance: IMPLICATION IN INNATE IMMUNITY. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:34590–34599. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perry M.M., Moschos S.A., Williams A.E., Shepherd N.J., Larner-Svensson H.M., Lindsay M.A. Rapid changes in microRNA-146a expression negatively regulate the IL-1beta-induced inflammatory response in human lung alveolar epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2008;180:5689–5698. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.8.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Starczynowski D.T., Kuchenbauer F., Argiropoulos B., Sung S., Morin R., Muranyi A., Hirst M., Hogge D., Marra M., Wells R.A., et al. Identification of miR-145 and miR-146a as mediators of the 5q- syndrome phenotype. Nat. Med. 2010;16:49–58. doi: 10.1038/nm.2054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rhyasen G.W., Bolanos L., Fang J., Jerez A., Wunderlich M., Rigolino C., Mathews L., Ferrer M., Southall N., Guha R., et al. Targeting IRAK1 as a therapeutic approach for myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:90–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fang J., Barker B., Bolanos L., Liu X., Jerez A., Makishima H., Christie S., Chen X., Rao D.S., Grimes H.L., et al. Myeloid malignancies with chromosome 5q deletions acquire a dependency on an intrachromosomal NF-kappaB gene network. Cell Rep. 2014;8:1328–1338. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grants J.M., Wegrzyn J., Hui T., O'Neill K., Shadbolt M., Knapp D.J.H.F., Parker J., Deng Y., Gopal A., Docking T.R., et al. Altered microRNA expression links IL6 and TNF-induced inflammaging with myeloid malignancy in humans and mice. Blood. 2020;135:2235–2251. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhao J.L., Rao D.S., Boldin M.P., Taganov K.D., O'Connell R.M., Baltimore D. NF-kappaB dysregulation in microRNA-146a-deficient mice drives the development of myeloid malignancies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:9184–9189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105398108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Varney M.E., Choi K., Bolanos L., Christie S., Fang J., Grimes H.L., Maciejewski J.P., Inoue J.I., Starczynowski D.T. Epistasis between TIFAB and miR-146a: neighboring genes in del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2017;31:491–495. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bellissimo D.C., Speck N.A. RUNX1 Mutations in Inherited and Sporadic Leukemia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017;5:111. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sood R., Kamikubo Y., Liu P. Role of RUNX1 in hematological malignancies. Blood. 2017;129:2070–2082. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-687830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Olofsen P.A., Touw I.P. RUNX1 Mutations in the Leukemic Progression of Severe Congenital Neutropenia. Mol. Cell. 2020;43:139–144. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2020.0010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bellissimo D.C., Chen C.H., Zhu Q., Bagga S., Lee C.T., He B., Wertheim G.B., Jordan M., Tan K., Worthen G.S., et al. Runx1 negatively regulates inflammatory cytokine production by neutrophils in response to Toll-like receptor signaling. Blood Adv. 2020;4:1145–1158. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zezulin A.U., Yen D., Ye D., Howell E.D., Bresciani E., Diemer J., Ren J.G., Ahmad M.H., Castilla L.H., Touw I.P., et al. RUNX1 is required in granulocyte-monocyte progenitors to attenuate inflammatory cytokine production by neutrophils. Genes Dev. 2023;37:605–620. doi: 10.1101/gad.350418.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Watanabe-Okochi N., Kitaura J., Ono R., Harada H., Harada Y., Komeno Y., Nakajima H., Nosaka T., Inaba T., Kitamura T. AML1 mutations induced MDS and MDS/AML in a mouse BMT model. Blood. 2008;111:4297–4308. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-068346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Harada H., Harada Y., Tanaka H., Kimura A., Inaba T. Implications of somatic mutations in the AML1 gene in radiation-associated and therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:673–680. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Harada H., Harada Y., Kimura A. Implications of somatic mutations in the AML1/RUNX1 gene in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS): future molecular therapeutic directions for MDS. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6:553–565. doi: 10.2174/156800906778194595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kogan S.C., Ward J.M., Anver M.R., Berman J.J., Brayton C., Cardiff R.D., Carter J.S., de Coronado S., Downing J.R., Fredrickson T.N., et al. Bethesda proposals for classification of nonlymphoid hematopoietic neoplasms in mice. Blood. 2002;100:238–245. doi: 10.1182/blood.v100.1.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jain A.G., Zhang L., Bennett J.M., Komrokji R. Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Bone Marrow Fibrosis: An Update. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022;42:299–305. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liang Q., Zhao J., Zhang L., Gao Z., Pan H., Fang L., Shi J. Association of systemic inflammatory and autoimmune manifestations with myelodysplastic syndromes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltim.) 2022;101 doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Camacho V., Kuznetsova V., Welner R.S. Inflammatory Cytokines Shape an Altered Immune Response During Myeloid Malignancies. Front. Immunol. 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.772408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Canli Ö., Nicolas A.M., Gupta J., Finkelmeier F., Goncharova O., Pesic M., Neumann T., Horst D., Löwer M., Sahin U., Greten F.R. Myeloid Cell-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Induce Epithelial Mutagenesis. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:869–883.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Greten F.R., Grivennikov S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity. 2019;51:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhao J.L., Rao D.S., O'Connell R.M., Garcia-Flores Y., Baltimore D. MicroRNA-146a acts as a guardian of the quality and longevity of hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Elife. 2013;2 doi: 10.7554/eLife.00537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kharas M.G., Lengner C.J., Al-Shahrour F., Bullinger L., Ball B., Zaidi S., Morgan K., Tam W., Paktinat M., Okabe R., et al. Musashi-2 regulates normal hematopoiesis and promotes aggressive myeloid leukemia. Nat. Med. 2010;16:903–908. doi: 10.1038/nm.2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Park S.M., Gönen M., Vu L., Minuesa G., Tivnan P., Barlowe T.S., Taggart J., Lu Y., Deering R.P., Hacohen N., et al. Musashi2 sustains the mixed-lineage leukemia-driven stem cell regulatory program. J. Clin. Invest. 2015;125:1286–1298. doi: 10.1172/JCI78440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Marneth A.E., Botezatu L., Hönes J.M., Israël J.C.L., Schütte J., Vassen L., Lams R.F., Bergevoet S.M., Groothuis L., Mandoli A., et al. GFI1 is required for RUNX1/ETO positive acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2018;103:e395–e399. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.180844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kawabata K.C., Zong H., Meydan C., Wyman S., Wouters B.J., Sugita M., Goswami S., Albert M., Yip W., Roboz G.J., et al. BCL6 maintains survival and self-renewal of primary human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 2021;137:812–825. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hu T., Morita K., Hill M.C., Jiang Y., Kitano A., Saito Y., Wang F., Mao X., Hoegenauer K.A., Morishita K., et al. PRDM16s transforms megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors into myeloid leukemia-initiating cells. Blood. 2019;134:614–625. doi: 10.1182/blood.2018888255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Corrigan D.J., Luchsinger L.L., Justino de Almeida M., Williams L.J., Strikoudis A., Snoeck H.W. PRDM16 isoforms differentially regulate normal and leukemic hematopoiesis and inflammatory gene signature. J. Clin. Invest. 2018;128:3250–3264. doi: 10.1172/JCI99862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sunami Y., Yokoyama T., Yoshino S., Takahara T., Yamazaki Y., Harada H., Nakamura T. BCL11A promotes myeloid leukemogenesis by repressing PU.1 target genes. Blood Adv. 2022;6:1827–1843. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Marcucci G., Byrd J.C., Dai G., Klisovic M.I., Kourlas P.J., Young D.C., Cataland S.R., Fisher D.B., Lucas D., Chan K.K., et al. Phase 1 and pharmacodynamic studies of G3139, a Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide, in combination with chemotherapy in refractory or relapsed acute leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:425–432. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pulvino M., Liang Y., Oleksyn D., DeRan M., Van Pelt E., Shapiro J., Sanz I., Chen L., Zhao J. Inhibition of proliferation and survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by a small-molecule inhibitor of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13-Uev1A. Blood. 2012;120:1668–1677. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-406074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Muto T., Guillamot M., Yeung J., Fang J., Bennett J., Nadorp B., Lasry A., Redondo L.Z., Choi K., Gong Y., et al. TRAF6 functions as a tumor suppressor in myeloid malignancies by directly targeting MYC oncogenic activity. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29:298–314.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Muto T., Walker C.S., Choi K., Hueneman K., Smith M.A., Gul Z., Garcia-Manero G., Ma A., Zheng Y., Starczynowski D.T. Adaptive response to inflammation contributes to sustained myelopoiesis and confers a competitive advantage in myelodysplastic syndrome HSCs. Nat. Immunol. 2020;21:535–545. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0663-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Avagyan S., Henninger J.E., Mannherz W.P., Mistry M., Yoon J., Yang S., Weber M.C., Moore J.L., Zon L.I. Resistance to inflammation underlies enhanced fitness in clonal hematopoiesis. Science. 2021;374:768–772. doi: 10.1126/science.aba9304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cai Z., Kotzin J.J., Ramdas B., Chen S., Nelanuthala S., Palam L.R., Pandey R., Mali R.S., Liu Y., Kelley M.R., et al. Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling in Tet2 Mutant Preleukemic Cells Mitigates Stress-Induced Abnormalities and Clonal Hematopoiesis. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23:833–849.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hormaechea-Agulla D., Matatall K.A., Le D.T., Kain B., Long X., Kus P., Jaksik R., Challen G.A., Kimmel M., King K.Y. Chronic infection drives Dnmt3a-loss-of-function clonal hematopoiesis via IFNgamma signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:1428–1442.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Muto T., Walker C.S., Agarwal P., Vick E., Sampson A., Choi K., Niederkorn M., Ishikawa C., Hueneman K., Varney M., Starczynowski D.T. Inactivation of p53 provides a competitive advantage to del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome hematopoietic stem cells during inflammation. Haematologica. 2023;108:2715–2729. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.282349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lam K., Zhang D.E. RUNX1 and RUNX1-ETO: roles in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2012;17:1120–1139. doi: 10.2741/3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yokota A., Huo L., Lan F., Wu J., Huang G. The Clinical, Molecular, and Mechanistic Basis of RUNX1 Mutations Identified in Hematological Malignancies. Mol. Cell. 2020;43:145–152. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2019.0252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ahmad M.H., Hegde M., Wong W.J., Mohammadhosseini M., Garrett L., Carrascoso A., Issac N., Ebert B., Silva J.C., Pihan G., et al. Runx1-R188Q germline mutation induces inflammation and predisposition to hematologic malignancies in mice. Blood Adv. 2023;7:7304–7318. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fan A.C., Nakauchi Y., Bai L., Azizi A., Nuno K.A., Zhao F., Köhnke T., Karigane D., Cruz-Hernandez D., Reinisch A., et al. RUNX1 loss renders hematopoietic and leukemic cells dependent on IL-3 and sensitive to JAK inhibition. J. Clin. Invest. 2023;133 doi: 10.1172/JCI167053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bennett J., Starczynowski D.T. IRAK1 and IRAK4 as emerging therapeutic targets in hematologic malignancies. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2022;29:8–19. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hemmati S., Haque T., Gritsman K. Inflammatory Signaling Pathways in Preleukemic and Leukemic Stem Cells. Front. Oncol. 2017;7:265. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Balandrán J.C., Lasry A., Aifantis I. The Role of Inflammation in the Initiation and Progression of Myeloid Neoplasms. Blood Cancer Discov. 2023;4:254–266. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-22-0176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bennett J., Ishikawa C., Agarwal P., Yeung J., Sampson A., Uible E., Vick E., Bolanos L.C., Hueneman K., Wunderlich M., et al. Paralog-specific signaling by IRAK1/4 maintains MyD88-independent functions in MDS/AML. Blood. 2023;142:989–1007. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022018718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Barreyro L., Sampson A.M., Ishikawa C., Hueneman K.M., Choi K., Pujato M.A., Chutipongtanate S., Wyder M., Haffey W.D., O'Brien E., et al. Blocking UBE2N abrogates oncogenic immune signaling in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022;14 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb7695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hodge C.D., Spyracopoulos L., Glover J.N.M. Ubc13: the Lys63 ubiquitin chain building machine. Oncotarget. 2016;7:64471–64504. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wang T., Pine A.R., Kotini A.G., Yuan H., Zamparo L., Starczynowski D.T., Leslie C., Papapetrou E.P. Sequential CRISPR gene editing in human iPSCs charts the clonal evolution of myeloid leukemia and identifies early disease targets. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:1074–1089.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.01.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Choi K., Ratner N. iGEAK: an interactive gene expression analysis kit for seamless workflow using the R/shiny platform. BMC Genom. 2019;20:177. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5548-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K., Mukherjee S., Ebert B.L., Gillette M.A., Paulovich A., Pomeroy S.L., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Koulnis M., Pop R., Porpiglia E., Shearstone J.R., Hidalgo D., Socolovsky M. Identification and analysis of mouse erythroid progenitors using the CD71/TER119 flow-cytometric assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011 doi: 10.3791/2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wickham H. 2009. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
-
•
Bulk RNA-seq and whole exome sequencing data have been deposited at GEO: GSE264053, GSE264051, GSE264052.
-
•
No original code was developed for this study.
-
•
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported is available from the lead contact upon request.