Abstract
Highly hazardous DNA double-strand breaks can be induced in eukaryotic cells by a number of agents including pathogenic bacterial strains. We have investigated the genotoxic potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an opportunistic pathogen causing devastating nosocomial infections in cystic fibrosis or immunocompromised patients. Our data revealed that infection of immune or epithelial cells by P. aeruginosa triggered DNA strand breaks and phosphorylation of histone H2AX (γH2AX), a marker of DNA double-strand breaks. Moreover, it induced formation of discrete nuclear repair foci similar to gamma-irradiation-induced foci, and containing γH2AX and 53BP1, an adaptor protein mediating the DNA-damage response pathway. Gene deletion, mutagenesis, and complementation in P. aeruginosa identified ExoS bacterial toxin as the major factor involved in γH2AX induction. Chemical inhibition of several kinases known to phosphorylate H2AX demonstrated that Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM) was the principal kinase in P. aeruginosa-induced H2AX phosphorylation. Finally, infection led to ATM kinase activation by an auto-phosphorylation mechanism. Together, these data show for the first time that infection by P. aeruginosa activates the DNA double-strand break repair machinery of the host cells. This novel information sheds new light on the consequences of P. aeruginosa infection in mammalian cells. As pathogenic Escherichia coli or carcinogenic Helicobacter pylori can alter genome integrity through DNA double-strand breaks, leading to chromosomal instability and eventually cancer, our findings highlight possible new routes for further investigations of P. aeruginosa in cancer biology and they identify ATM as a potential target molecule for drug design.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1392-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: DNA double-strand breaks, Infection, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ATM, H2AX
Introduction
In response to endogenous or environmental stress, cells have developed adaptative strategies to maintain their genome integrity. Damaged DNA can be repaired by a number of mechanisms depending primarily on the nature of the initial genotoxic stress and on the extent of DNA damage [1]. For example, ionizing radiation produces DNA double-strand breaks (DSB), which are highly hazardous lesions for the cells as they can lead to genome rearrangements [1]. One of the first molecules that acts as a sensor of DSB is Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), a kinase that phosphorylates the histone H2AX [2]. H2AX, a variant in the H2A histone family, has a unique C-terminal motif containing a serine residue at position 139 [3]. Upon genotoxic stress such as ionization radiation, H2AX is rapidly phosphorylated at serine 139 (γH2AX) and forms protein foci at the DSB sites [3, 4]. These so-called ionizing radiation-induced foci (IRIF) or DNA repair foci are initiated by the recruitment of Mre11 (Meiotic recombination 11)/Rad50/NBS1 (Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1) protein complex to DSB, followed by ATM activation and H2AX phosphorylation. The presence of γH2AX initiates the mobilization of MDC1 (mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1) which, in turn, enables RNF8 and RNF168 (ring finger protein 8 and 168) recruitment [2, 3]. These proteins facilitate histone ubiquitination that, through a poorly understood mechanism, enables the concentration of 53BP1 at DSB. The localized action of ATM and 53BP1 at DSB promotes the relaxation of heterochromatin allowing appropriate DNA repair through homologous recombination or non-homologous end joining [1]. Recently, γH2AX has been used in several clinical studies as a very sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair in cancer [4, 5].
Some bacteria exhibit genotoxic potential. For instance, Nougayrède and colleagues [6] have discovered that extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains of the phylogenetic group B2 possess a pks genomic island that produces a new type of cytotoxin called colibactin, which activates the DNA damage cascade response. The resulting H2AX phosphorylation correlates with DSB. In another study, this group showed that cells infected in vivo at a low dose with E. coli harboring a pks island exhibited an increase in gene mutation frequency and chromosomal instability [7]. Because DSB can give rise to genomic instability, bacteria containing the pks island may constitute a predisposing factor for the development of intestinal cancer [6, 7]. Another bacterial toxin, called CDT (cytolethal distending toxin), expressed in several pathogenic bacteria, including E. coli, Haemophilus ducreyi, Shigella dysenteriae, or Salmonella typhi, exhibits a DNase I type structure [8] and induces single- and double-strand breaks in cells and in vitro [8, 9]. CDT activity is associated with the formation of γH2AX foci in proliferating and non-proliferating cells, as well as DNA repair complex formation [8–10]. To date, very little is known about the potential genotoxic effect of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
This ubiquitous Gram-negative bacterium, frequently associated with nosocomial diseases, causes devastating infections in patients with cystic fibrosis or in immunocompromised patients, such as AIDS patients, those undergoing a surgical procedure, or those affected by severe burn wounds [11, 12]. Because of its resistance to a variety of antibiotics, P. aeruginosa infections remain a medical challenge and generates considerable direct and indirect economic costs [11, 12]. Although the late effects of P. aeruginosa infection are known and often lead to cell death, it is not clear whether and how this pathogen affects genome integrity at early time points of infection. Wu [13] and collaborators showed recently that synthesis of the DNA repair protein OGG1 (8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase) is induced upon infection with the P. aeruginosa PAO1 strain in lung epithelial cells and in mice. OGG1, a component of the base excision DNA repair pathway, is involved in the base excision of 8-oxoguanine, a potential mutagenic byproduct that results from exposure to reactive oxygen species [14]. A central component of the P. aeruginosa virulence repertoire [15] is a type III secretion system (T3SS) that is associated with acute toxicity [16, 17]. The T3SS is formed by a multicomponent protein complex that forms a needle-like structure that inserts through the host cell membrane, making a continuous channel between the bacterium and the host cytoplasm for the delivery of effector toxins [18 for review]. Four effectors can be present in P. aeruginosa: Exoenzyme (Exo) T, ExoY and either ExoS or ExoU. ExoS and ExoT are related enzymes that both possess a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and an ADP ribosyltransferase (ADP-RT) domain [19 and references therein]. The GAP activities of ExoS and ExoT appear to be identical and they target the Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 proteins. The ADP-RT domain of ExoS has multiple targets, and it elicits a cytotoxic phenotype that has features of apoptosis, necrosis, or even pyroptosis depending on the cell type infected [20, 21]. The ExoT ADP-RT domain has a restricted number of targets, namely the CrkI and CrkII (CT-10 regulator of kinase) proteins [18]. ExoT seems to be primarily involved in the alteration of the host actin cytoskeleton, leading to an arrest of phagocytosis and a disruption of epithelial barriers in order to facilitate bacterial dissemination. ExoY and ExoU have adenylate cyclase and lysophospholipase A activities, respectively [18 and references therein].
Given the importance of T3SS in the pathogenesis of P. aeruginosa infections, we investigated the consequences of this virulence mechanism in a macrophage model, a crucial component of the innate immune system involved in the host response to microorganisms. We further extended our study to carcinoma lung cells. For the first time, our study shows that DNA double-strand breaks, which are particularly severe lesions for the cells, occur upon P. aeruginosa infection.
Materials and methods
Reagents
Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate (PMA) was from LC Laboratories (Euromedex, Souffleweyersheim, France). Primary antibodies were as follows: c-Jun (H-79), GAPDH (FL-335) from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Heidelberg, Germany), monoclonal anti-MEF2D and mouse PARP1 (C2-10 clone) from BD Transduction Laboratories (Le-Pont-De-Claix, France), mouse anti-γH2AX, c-JunS63, ATM, and phosphoATM (ser1981) from Millipore Upstate (Saint-Quentin-En-Ynes, France), c-JunS73 from Cell Signaling Technology (Ozyme, Saint-Quentin Yvelines, France) and 53BP1 from Novus Biologicals (Cambridge, UK). Polyclonal anti-ExoS antibodies were raised in rabbit and directed against the recombinant GAP domain of ExoS. Kinase inhibitors were as follows: JNK (SP1600125), p38 (SB202190), Erk (FR180204), and ATM kinase (KU55933) inhibitors were purchased from Calbiochem (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) and dissolved in culture grade DMSO. Etoposide (Eto) was from Sigma (Saint Quentin Fallavier, France) (E1383).
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
The P. aeruginosa and E. coli strains, as well as the plasmids used in this study, are listed in supplemental Table 1. The sequences of the oligonucleotides designed for cloning or mutagenesis are given in supplemental Table 2. Plasmid and strain constructions are fully described in supplemental “Materials and methods”. P. aeruginosa was grown in liquid Luria Broth (LB) medium at 37 °C with agitation or on Pseudomonas isolation Agar plates (PIA, Difco, Beckton Dickinson, Le-Pont-De-Claix, France). Antibiotics were added at the following concentrations (in mg/l): 100 (ampicillin), 25 (kanamycin) and 10 (tetracycline) for E. coli, 500 (carbenicillin), 200 (gentamicin), and 200 (tetracycline) for P. aeruginosa. For in vitro induction of T3SS, P. aeruginosa overnight cultures were diluted to an optical density of 0.1 at 600 nm (A 600) in LB containing 5 mM EGTA and 20 mM MgCl2. Incubation was performed at 37 °C with agitation until the cultures reached an A 600 value of 1.0. The cultures were then centrifuged (12,000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C) and 20 μl of the supernatants were directly loaded on 12 % SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-ExoS antibodies.
Cell culture, differentiation, infection, and irradiation
Human pro-myeloid HL60 cells were grown exactly as described previously [22]. PMA (10 ng/ml) was added for 24 h for cells to differentiate into macrophages. H1299 lung epithelial cells (non-small cell lung carcinoma), obtained from Dr J. Baudier, were cultured in high-glucose DMEM containing GlutaMax (Gibco-BRL, Life Technologies, Saint Aubin, France), 10 % fetal calf serum and antibiotics. Exponential cultures of bacteria were grown to an A600 of 1. Unless otherwise stated, the multiplicity of infection (MOI) was 10 and cell extracts were prepared 2.5 h after infection. The mock plates received the same amount of LB medium as the infected plates and they were treated exactly like the infected plates. After infection, cells were harvested, pelleted and washed twice in cold PBS before being processed for protein extraction. As a positive control for γH2AX foci, cells were submitted to gamma irradiation (2 Gy) in the “Anémone/Bio” irradiator (60Co, 2 Gy/min) in the ARC-Nucléart facility at the CEA-Grenoble. After irradiation, cultures returned to the incubator for 30–60 min and they were processed for immunofluorescent staining as described below.
Cell extracts and Western blotting
Cells were lysed in RIPA as described [22]. Before Western-blot analysis, samples were pre-calibrated on 15 % Coomassie-stained SDS gels using core histone bands as reference (even nuclei number). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad, Marnes La Coquette, France) and incubated overnight with primary antibodies. After washes in TBS containing 0.1 % Tween 20, blots were incubated with secondary antibodies labeled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and these were detected by chemiluminescence (ECL Plus, GE Healthcare, Velizy Villacoublay, France). When indicated, blots were quantified with ImageJ software and protein expression levels were normalized to that of GAPDH. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The relative expression of protein was set to 1 (dark bar on histogram) usually for mock macrophages unless otherwise stated.
Dephosphorylation experiments
HL60 differentiation and infection were performed as described above. Two and half hours post-infection, cell were lysed in 10 mM Tris–HCl pH 8, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5 % Igepal, 0.2 % sodium deoxycholate, 1 mM PMSF. Twenty-five microliters of cell lysates were incubated with 2 μl of calf intestine phosphatase (CIP, NEBioLabs, Evry, France, 10 U/μl) in the presence of CIP buffer in a final volume of 50 μl for 30 min at 37 °C. When required, phosphatase inhibitors (2.5 mM sodium fluoride and 5 mM sodium orthovanadate) were added to the reactions. Reactions were then stopped by the addition of Laemmli sample buffer and analyzed by Western blot.
Apoptosis detection by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)
After infection, cells were gently flushed, washed to remove bacteria, and resuspended in annexin binding buffer (140 mM NaCl, 5 mM NaCl2, 10 mM HEPES pH 7.4 (NaOH)). Cells were then incubated with Annexin-AlexaFluor 488 (Molecular Probes, Life Technologies, Saint Aubin, France) for 15 min in the dark. Propidium iodide (PI) was added to the cell suspension just before flow cytometry. Controls were included for each time point in the study. Data acquisition and analysis were performed with a FacsCalibur flow cytometer equipped with CellQuest software (Beckton Dickinson, Le-Pont-De-Claix, France). Forty thousand cells were analyzed for each point.
Immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy
HL60 macrophages and H1299 cells were grown on gelatin-coated glass LabTek (Nunc, Thermo Scientific, Illkirch, France), infected or irradiated as indicated above, rinsed in PBS and fixed in 4 % paraformaldehyde solution and processed exactly as described before [22]. Detection was performed with goat anti-mouse-Cy3 and anti-rabbit DyLight 488 secondary antibodies (Jackson ImmunoResearch, Newmarket, UK). Nuclei were counterstained with To-Pro3 (Molecular Probes, Life Technologies, Saint Aubin, France). Images were collected on a Leica TSC-P2 confocal microscope, on a sequential mode for three-color acquisitions (laser excitation at 488, 543, and 633 nm). Images were imported in Adobe Photoshop for figure preparation.
Comet assays
Mock and infected cells were collected by gentle scrapping after 1 h of contact with bacteria. Cells were put on ice, washed in cold PBS, and resuspended in PBS at 2 × 106 cells/ml. Prior to assay, microscope slides were coated with regular 1 % agarose and allowed to dry. A total of 50 μl of cell suspension was mixed with 450 μl of 0.6 % low-melting-point agarose in PBS. A total of 100 μl of the mix (about 20,000 cells) was deposited on duplicate slides and allowed to solidify on ice for 10 min. As a positive control, duplicate mock slides were incubated with a 60 μM hydrogen peroxide solution in PBS for 5 min on ice. Slides were immersed in cold lysis solution (2.5 M NaCl, 10 mM Tris base pH 10, 1 % N-lauroylsarcosine, 10 % DMSO, 1 % Triton X-100) for 45 min at 4 °C and then neutralized three times for 5 min in 0.4 M Tris–HCl pH 7.4. DNA was then allowed to unwind for 30 min in alkaline electrophoresis solution (300 mM NaOH, 1 mM EDTA, pH > 13). Electrophoresis was performed in a field of 0.9 V/cm and current 300 mA for 40 min. Slides were neutralized as above, dehydrated and dried. After ethidium bromide staining, comets were analyzed under the 20× objective of a fluorescence Apotome microscope equipped with the AxioVision acquisition software (Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Individual comets were then quantified with CometScore software. The “% of DNA in tail” parameter was calculated from at least 60 comets obtained on duplicate slides.
Results
c-Jun hyperphosphorylation is a sensitive marker of P. aeruginosa infection in macrophages
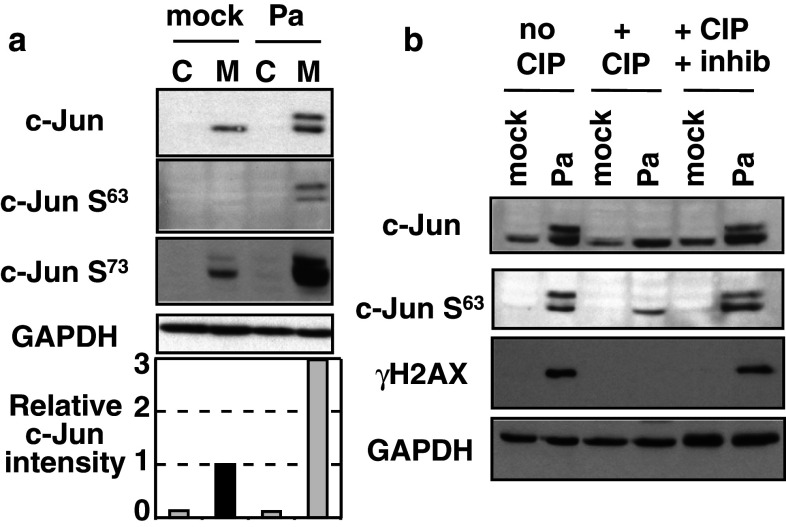
P. aeruginosa infections were performed in the human HL60 pro-myeloid cell line, which can efficiently differentiate, upon PMA treatment, into macrophages [22, 23]. We worked with the mucoid clinical P. aeruginosa strain named CHA, isolated from the lungs of a patient with cystic fibrosis and expressing the effector toxins ExoS, ExoT, and ExoY [24]. Because it is known that various reference strains of P. aeruginosa, such as PAK or PAO1, activate the c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) pathway [25] in HeLa [26] or in Chang epithelial cells [27], we used the transcription factor c-Jun, a target of JNK1, to monitor the host cell nucleus response to the infection. After contact with P. aeruginosa, a threefold increase in the level of c-Jun, associated with a doublet of the protein, appeared specifically in infected macrophages (Fig. 1a, compare Pa vs. mock). Undifferentiated cells had very low amounts of c-Jun protein and incubation with P. aeruginosa did not alter this pattern, consistent with the finding that undifferentiated HL60 were resistant to P. aeruginosa [28, 29]. Several phosphorylation sites are present in c-Jun, two of them being located in the N-terminal part of the protein on serine residues 63 and 73 and involved in an increased transcriptional activity of the protein [30]. Analysis with antibodies against phospho-c-Jun indicated that P. aeruginosa led to the phosphorylation of at least serines 63 and 73 on c-Jun in HL60 macrophages (Fig. 1a). To determine whether other modifications were involved, we performed an in vitro dephosphorylation reaction on cell lysates obtained from macrophages infected (or not) by P. aeruginosa. We observed the disappearance of the upper migrating band of c-Jun in the presence of alkaline phosphatase (CIP), but not when CIP was added together with phosphatase inhibitors (Fig. 1b). The remaining signal recognized by the anti c-JunS63 antibody could result from an incomplete dephosphorylation, although the phosphorylation on serine 139 of histone H2AX (γH2AX, see below) was completely lost under these conditions. Thus, these data indicated that c-Jun hyperphosphorylation is a very sensitive marker with which to follow macrophage infection by P. aeruginosa. We next evaluated the effects of infection downstream of c-Jun to determine whether the toxins injected by T3SS could be toxic to the host genome.
Fig. 1.
Hyperphosphorylation of c-Jun in HL60 macrophages in response to P. aeruginosa. a Undifferentiated control HL60 cells (C) or HL60 macrophages (M) were infected (or not, mock) with P. aeruginosa CHA strain (Pa) at a MOI of 10. Two and half hours post-infection, cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. Blots were quantified with ImageJ and c-Jun relative intensity normalized to GAPDH level was set to 1 (dark bar) in mock macrophages. b Cell extracts from HL60 macrophages infected as above (Pa) or not infected (mock) were incubated with CIP or with CIP in the presence of phosphatase inhibitors (CIP + Inhib) and then analyzed by Western blot
P. aeruginosa induces early H2AX phosphorylation
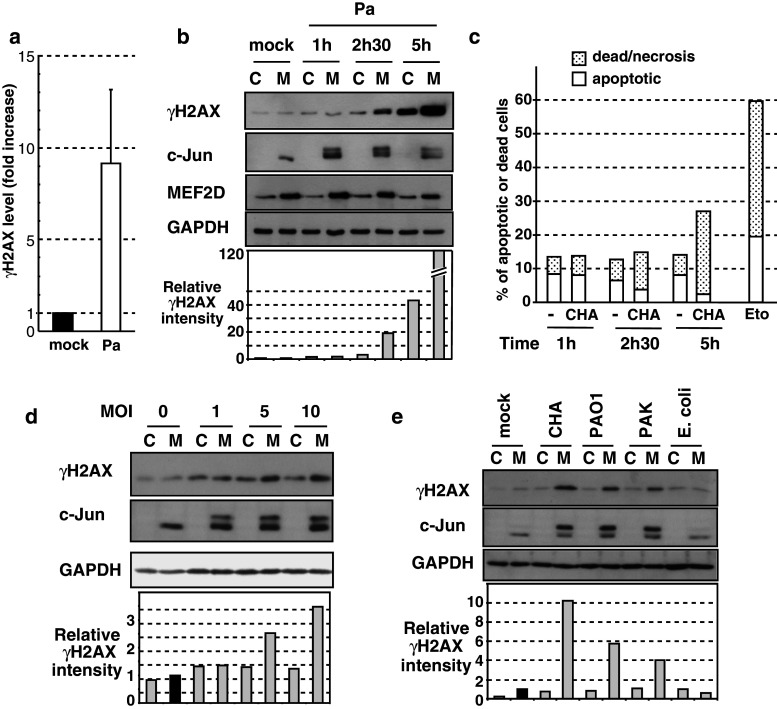
A typical marker to examine DNA damage upon genotoxic stress is the phosphorylation of the histone H2AX, namely γH2AX [3, 5]. Using a monoclonal antibody specific for γH2AX, we found a strong and very early H2AX phosphorylation by Western blot at 2.5 h post-infection in macrophages incubated with P. aeruginosa (Fig. 2a, b). The mean induction of γH2AX in infected macrophages (MOI = 10, 2.5 h post-infection) was 9.2 fold ± 4.0 in comparison to mock macrophages (range 3.5–19.2 fold), with data calculated from seven independent experiments (Fig. 2a).
Fig. 2.
P. aeruginosa induces H2AX phosphorylation. a HL60 macrophages were infected (Pa) or not (mock) with P. aeruginosa CHA strain at a MOI of 10 for 2.5 h. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot with γH2AX-specific antibody (as shown in Fig. 2b) and quantified. γH2AX relative intensity normalized to GAPDH level was set to 1 (dark bar) in mock macrophages for panel a, b, d, and e. Data were expressed as fold over mock macrophages. The results represented the mean ± SD of seven independent experiments. b Undifferentiated HL60 cells (C) or HL60 macrophages (M) were infected with P. aeruginosa CHA strain (Pa) at a MOI of 10. Cell extracts were prepared at the indicated times post-infection and analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. γH2AX relative intensity was determined as above. c Measurement of cell death and cell apoptosis by flow cytometry (40,000 cells analyzed for each point) after infection by P. aeruginosa CHA. Apoptotic cells are annexin-positive and propidium iodide-negative; dead or necrotic cells are both positive for annexin and propidium iodide. Etoposide (Eto, 10 μM for 18 h), an antitumor drug that causes DNA damage, was used as a positive control. d Undifferentiated HL60 control cells (C) or HL60 macrophages (M) were infected at MOI of 1, 5, and 10 or mock treated. Analysis by Western blot of cell extracts prepared 2.5 h after the infection. e Cells were infected as above with various strains of P. aeruginosa (CHA, PAO1, and PAK) or with an E. coli laboratory strain derived from K12, all at a MOI of 10. Extracts were analyzed by Western blot
Although one does not see fragmented nuclei, it has been reported that P. aeruginosa infection could induce apoptosis, usually after 4 or 5 h of infection [26, 27], necrosis, or oncosis [31]. Thus, we assessed cell apoptosis and cell death during the process of infection by an annexin V-Alexa 488/PI labeling and FACS. We analyzed 40,000 cells for each point. In most cases, cell viability ranged from 84 to 88 %, except at 5 h post-infection, where it dropped to 73 % (Fig. 2b). Treatment of parallel cultures with etoposide (Eto, 10 μM for 18 h), an anticancer drug acting as an inhibitor of topoisomerase II and inducing DSB, led to a high mortality, with 20 % of apoptotic cells (annexin-positive, PI-negative) and 40 % of dead or necrotic cells (annexin-positive, PI-positive). At 5 h post-infection, apoptotic cells were 2.3 % while the dead or necrotic cells represented 25 % of the total cells. In the meantime, the global number of dead/apoptotic cells was nearly identical at 1 and 2.5 h in mock or CHA-infected cells. Nevertheless, a slight increase could be seen at 2.5 h in CHA-infected cells (15 % of non-viable cells vs. 13.5 % in mock cells). This modest difference, however, is unlikely to contribute to the modification observed in γH2AX expression.
The γH2AX appearance was much stronger at 5 h in infected macrophages (Fig. 2b) and it could be in part associated with a cell death process (Fig. 2c). Hyperphosphorylated c-Jun, our infection marker, was specifically detected in macrophages as soon as 1 h after contact with bacteria; its highest level was reached 2.5 h post-infection and it remained well visible at 5 h (Fig. 2b). In the same experiment, we analyzed MEF2D, a transcription factor of the Myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) family that is implicated in c-Jun expression and is induced during macrophage differentiation [22]. Unlike c-Jun, MEF2D expression remained unaffected by the infection (Fig. 2b). Interestingly, in the late stages of infection, we consistently observed a significant γH2AX level in undifferentiated cells infected by P. aeruginosa that was not associated with any c-Jun expression or hyperphosphorylation. This late response probably involves several virulence systems of P. aeruginosa that contributed to H2AX phosphorylation after extended bacterial contact. Then after, we only worked at early time point of infection (1.5–2.5 h post-infection) to avoid the long-term toxic effects of the bacteria and to limit their proliferation in rich culture medium devoid of antibiotics. In these conditions, γH2AX induction was dependent on the MOI tested (Fig. 2d). H2AX phosphorylation was induced in macrophages when cells were infected at a moderate MOI (5–10 bacteria per host cell), whereas c-Jun activation was detected with as little as one bacterium per cell (Fig. 2d; supplemental Fig. S1).
Finally, we compared the macrophage response after infection by several strains of P. aeruginosa. Besides the mucoid CHA strain, which constitutively produces the exopolysaccharide alginate, we used the non-mucoid PAK and PAO1 strains, the three strains secreting ExoS, ExoT, and ExoY toxins. PAO1 and PAK could both activate c-Jun and γH2AX (Fig. 2e), even if they were somewhat less efficient than the CHA strain in the conditions tested. We could not obtain any data with a P. aeruginosa strain secreting ExoU toxin instead of ExoS, as the macrophages were all dead within 2.5 h of contact with the bacteria (not shown). On the contrary, an E. coli K12-derived laboratory strain, a Gram-negative non-pathogenic bacterium devoid of T3SS, was unable to activate c-Jun or γH2AX at a MOI of 10 in macrophages. These data showed that at least three strains of P. aeruginosa, namely CHA, PAK, and PAO1, activate the c-Jun pathway and led to potential DNA damages as monitored by γH2AX expression.
Detection of γH2AX/53BP1 foci and DNA strand breaks upon infection
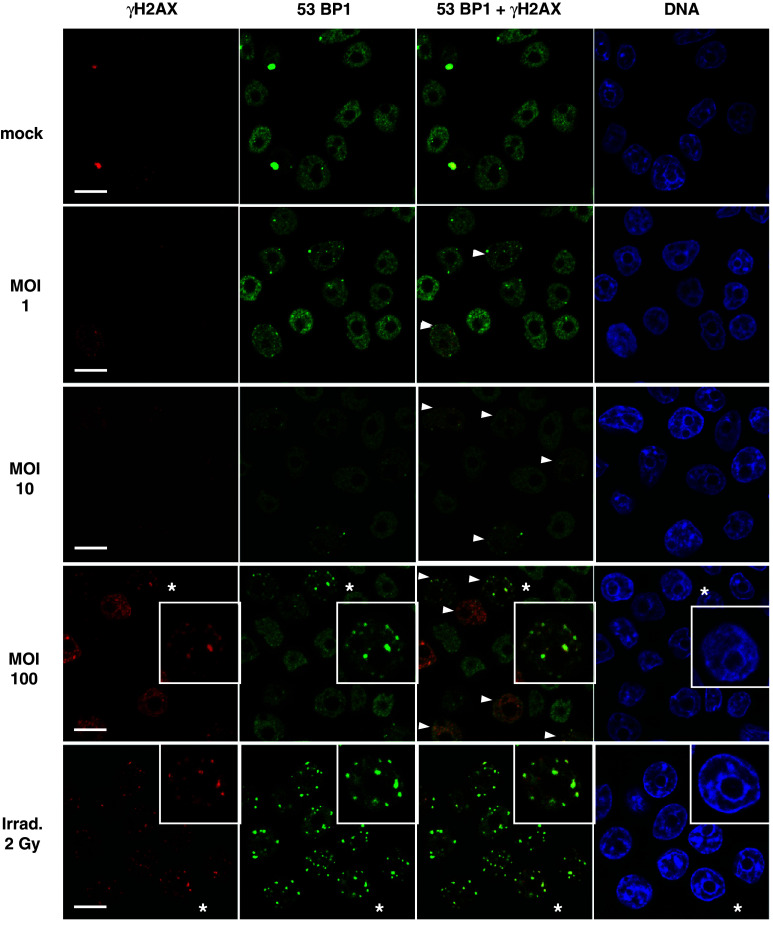
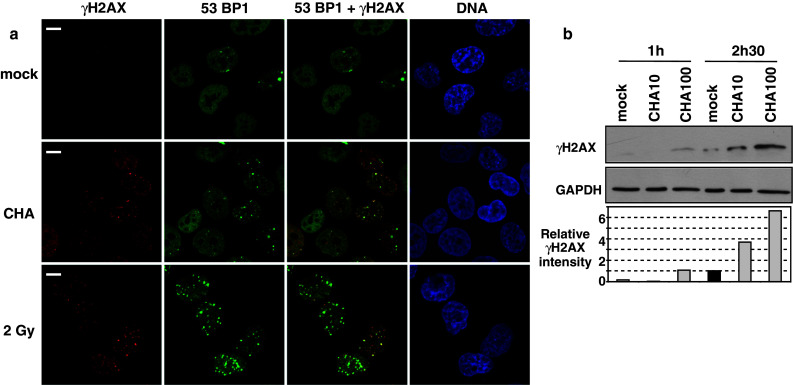
To analyze the cellular distribution of γH2AX after infection, we performed an immunofluorescent study using confocal microscopy. HL60 macrophages were infected at various MOI ranging from 1 to 100 and analyzed 1.5 h after infection. This study confirmed the presence of discrete γH2AX protein foci in macrophages infected by P. aeruginosa at 1.5 h post-infection, in a dose-dependent fashion, without any visible alteration of the nuclear structure or the presence of apoptotic bodies (Fig. 3). The foci are particularly well visible at the MOI of 100. Importantly, the 53BP1 mediator/adaptor, a protein activated later than γH2AX in the DNA-damage response pathway, re-localized from a homogenous nuclear distribution to γH2AX foci, underlining the formation of DNA repair foci (Fig. 3 arrowheads and enlargement denoted by * and supplemental Fig. S2). We could also see cells with a more intense staining, almost uniform through the cells, except a few foci that were more intense and well defined. Other cells had no γH2AX staining at all and, in this case, 53BP1 staining remained homogenous in the cell nucleus. Although we have not measured the size of the individual foci obtained upon infection, they looked overall similar to those obtained upon irradiation, with the same magnification for MOI of 100 and 2 Gy (Fig. 3). One major difference between the two stresses was that, upon irradiation, almost all the cells showed foci formation, with a foci number rather homogenous (mean 11.6 foci/cell ± 3.2), whereas upon infection, only a subset of the population displayed this picture. This could be explained by the fact that γ-irradiation hits virtually any cells in the culture chamber, whereas bacteria do not necessary attack all the cells, even at a high MOI, within the time frame of the experiment.
Fig. 3.
Induction of γH2AX/53BP1 foci formation upon P. aeruginosa infection. Analysis by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. HL60 macrophages grown on gelatin-coated LabTek were infected for 1.5 h with CHA bacteria at a MOI ranging from 1 to 100 as indicated and processed for immunofluorescent staining for γH2AX (red), 53BP1 (green), and DNA (blue). The lower panel shows the same cells submitted to γ-irradiation (2 Gy) as a positive control for γH2AX foci formation. Arrowheads point to examples of positive cells. The asterisk denotes the cells shown at a higher magnification. Scale bars 10 μm
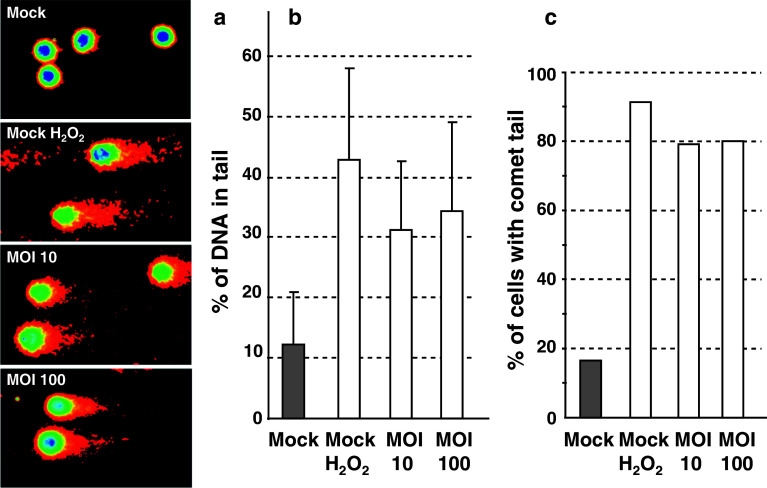
To directly visualize DNA damage potentially associated with γH2AX/53BP1 foci, alkaline DNA comet assays were performed on HL60 macrophages infected or not with P. aeruginosa. Mock non-infected cells displayed no or small comet tails in this assay (Fig. 4a, b) whereas treatment of the same cells with hydrogen peroxide generated DNA breaks as seen by the increased amount of DNA in comet tails (3.5-fold vs. mock). Upon infection, DNA strand breaks were clearly detected as soon as 1 h after infection in HL60 macrophages, at an MOI of 10 and 100, with a 2.5- and 2.8-fold increase as compared to mock cells, respectively. These results matched well with the number of cells displaying a comet tail (Fig. 4c). Although γH2AX variations were observed at MOI 10 vs. MOI 100 by immunofluorescence or Western blotting, DNA damage, as measured by the comet assay, was almost identical at an MOI 10 and MOI 100 1 h after infection. This discrepancy could be explained by the difference in sensitivity of the different techniques, or by DNA damage detected by the comet assay but not relevant to H2AX phosphorylation.
Fig. 4.
P. aeruginosa triggers DNA strand breaks in infected cells. HL60 macrophages were infected at a MOI of 10 or 100 and analyzed using single-cell comet assay. Some mock slides were treated with hydrogen peroxide as a control of DNA breaks. a Typical representation of cells and comets with CometScore software. Comet tails are in red. b, c Quantification of comets. The percentage of DNA present in the comet tail is indicated and expressed as the mean ± SD of at least 60 comets (b). The percentage of cells with a comet tail is shown in c
Taken together, these experiments showed that, early in the infection process, P. aeruginosa induced DNA damage in the host cells as visualized by comet tail formation and by the presence of γH2AX/53BP1 repair foci.
H2AX phosphorylation is T3SS-dependent and ExoS-dependent
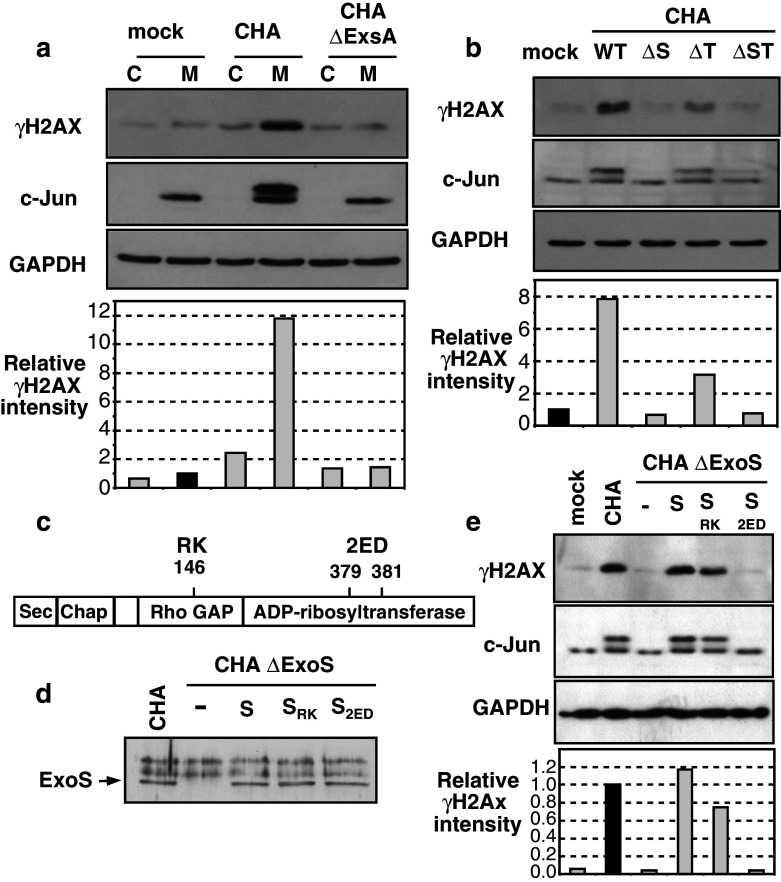
The T3SS of P. aeruginosa allows the delivery of toxins directly into the cytoplasm of the host cell. We tested its potential role in H2AX phosphorylation by using a CHA mutant devoid of T3SS activity (CHAΔExsA) due to the deletion of the exsA gene encoding the key transcription factor required for toxin expression [32]. Compared to the wild-type strain, infection with the isogenic mutant devoid of T3SS activity impaired both the induction of γH2AX and c-Jun hyperphosphorylation in macrophages (Fig. 5a). These data strongly supported the idea that the T3SS of P. aeruginosa was involved in H2AX phosphorylation.
Fig. 5.
Essential roles of T3SS and ExoS ADP-ribosyltransferase activity in γH2AX induction. a Undifferentiated HL60 cells (C) or HL60 macrophages (M) were infected with wild-type P. aeruginosa CHA strain (CHA) or a mutant strain with a deleted exsA gene and devoid of T3SS activity (CHAΔExsA), both at a MOI of 10. Cells extracts were analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. γH2AX relative intensity normalized to GAPDH level was set to 1 in mock macrophages (dark bar) for panel a and b. b HL60 macrophages were infected with a wild-type CHA strain (WT), or with isogenic strains with deletions of exoS (ΔS), exoT (ΔT) or both exoS and exoT (ΔST) genes. Western-blot analysis of cell extracts prepared 2.5 h post-infection. c Representation of the ExoS domains. Sec: secretion signal, Chap: zone of interaction with chaperone protein, RhoGAP and ADP-RT domains. RK indicates an inactivating mutation by replacement of an arginine with a lysine at position 146, 2ED indicates an inactivating mutation of the ADP-RT function by replacement of two glutamic acids with aspartic acids at positions 379 and 381. d Analysis by Western blot of ExoS secretion by CHA, CHAΔExoS, or CHAΔExoS complemented with wild-type ExoS (S), mutant ExoSRK (SRK), or mutant ExoS2ED (S2ED). The doublet above ExoS is non-specific. e HL60 macrophages were infected with CHA or the CHAΔExoS complemented strains described in (d), all at a MOI of 10. Cell extracts were prepared 2.5 h post-infection and analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. γH2AX relative intensity was set to 1 for macrophages infected with CHA (dark bar)
The main toxins secreted by T3SS of the CHA strain are ExoS and ExoT. These are related proteins containing ADP-RT activity at their C-terminus and Rho-GAP activity toward their N-terminus [16, 17]. To further identify the toxins leading to H2AX phosphorylation, we used mutants with the exoS and exoT genes deleted, individually or in combination. Deletion of exoS led to the disappearance of both the c-Jun doublet and γH2AX (Fig. 5b). Conversely, deletion of exoT mildly affected the ability of P. aeruginosa to activate c-Jun and γH2AX production. Deletion of both genes essentially led to the ΔExoS phenotype.
To evaluate the effect of ExoS, we inserted into the chromosome of the CHAΔExoS strain a wild-type exoS gene or a mutated gene encoding either Rho-GAP (SRK) or ADP-RT (S2ED)-deficient protein (Fig. 5c). All the complemented strains secreted the wild-type or the mutant proteins at a level similar to that of the parental strain (Fig. 5d). An ExoS protein devoid of Rho-GAP activity (mutant SRK [33]) behaved essentially as the wild-type ExoS protein, whereas the S2ED mutant, impaired in its ADP-RT activity [34], completely lost its effects on H2AX and c-Jun phosphorylation (Fig. 5e). These experiments identified the ADP-RT activity of ExoS as an essential component in H2AX phosphorylation pathways induced by P. aeruginosa infection.
Signaling pathways involved in H2AX phosphorylation upon infection
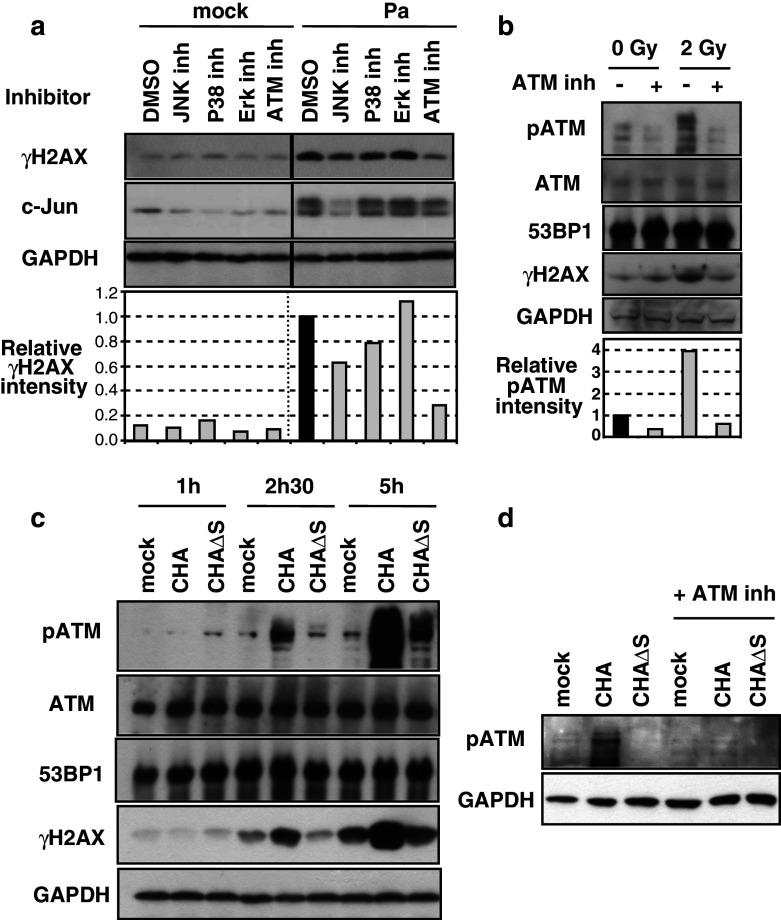
The utilization of specific anti-H2AX S139 antibody, combined with dephosphorylation experiments (Fig. 1b), confirmed that following P. aeruginosa infection, γH2AX was phosphorylated. To gain insight into the host signaling pathways affected by this bacterium, we tested various chemical inhibitors directed against kinases known to be involved in the c-jun and H2AX phosphorylation pathways. c-Jun is phosphorylated by the MAP kinase family whereas H2AX is reported to be phosphorylated by the ATM kinase family (ATM, ATR, DNA-PK, [2]) and also by JNK upon genotoxic stress induced by ionizing radiation or UV [4, 35]. Our experiments indicated that P. aeruginosa-induced H2AX phosphorylation was impaired in the presence of ATM kinase inhibitor KU55933 (Fig. 6a), which could also inhibit ATM activation by autophosphorylation on serine 1981 upon irradiation (Fig. 6b). We also obtained a 40 % decrease of H2AX phosphorylation in the presence of JNK inhibitor, whereas p38 and Erk inhibitors had a modest (p38 inhibitor) or no effect (Erk inhibitor) on H2AX phosphorylation upon infection (Fig. 6a). As predicted, JNK inhibitor greatly inhibited P. aeruginosa-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73 (Fig. 6a and not shown). Therefore, these data strongly suggested that P. aeruginosa-dependent H2AX phosphorylation is mostly mediated via ATM kinase. Thus we analyzed the phosphorylation status of this kinase during the course of infection. Like H2AX phosphorylation, ATM activation by phosphorylation on serine 1981 (pATM) was detected 2.5 h after infection, with the wild-type CHA strain but not the CHAΔExoS mutant, while total ATM or 53BP1 levels remained constant during the time course of infection (Fig. 6c). This induced ATM autophosphorylation was lost in the presence of ATM inhibitor (Fig. 6d), like that observed upon γ-irradiation (Fig. 6b). Much higher levels of both H2AX and ATM phosphorylation were detected 5 h after infection. In this later case, however, the entire effect was probably not due to ExoS alone since ATM phosphorylation above background level was still observed despite the deletion of exoS (Fig. 6c). Other virulence systems than the T3SS present in P. aeruginosa might activate that ATM pathway after an extended exposure to the bacteria.
Fig. 6.
Activation of ATM kinase by P. aeruginosa. a Effect of kinase chemical inhibitors. HL60 macrophages were pre-treated with the indicated kinase inhibitors (inh, as listed in “Materials and methods”, 10 μM each, final concentration) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 h before infection by P. aeruginosa CHA at a MOI of 10 or a mock treatment. Cell extracts were prepared 2.5 h after the infection and analyzed by Western blot. Relative intensity of γH2AX is set to 1 (dark bar) in macrophage treated with vehicle (DMSO) infected by P. aeruginosa. b Efficiency of ATM kinase inhibitor in HL60 macrophages. Cells were pre-treated (+) or not (−) with 10 μM KU55933 and then irradiated at 2 Gy or mock treated (0 Gy). Cell extracts, prepared 1 h after irradiation, were analyzed by Western blot. Relative pATM normalized to GAPDH level was set to 1 (dark bar) in mock macrophages (vehicle DMSO, no irradiation). c ExoS is required for early ATM kinase activation by phosphorylation. HL60 macrophages were infected with CHA or CHAΔExoS (MOI 10) for various periods of time. Cells extracts were prepared and ATM phosphorylation status was analyzed by Western blot. d Inhibition of ATM phosphorylation on serine 1981 by ATM kinase inhibitor upon infection by wild-type CHA or exoS-deficient bacteria (CHAΔS)
P. aeruginosa induces γH2AX in lung cancer-derived epithelial cells
To extend the interest of our findings, we used another cell line to analyze cell response to P. aeruginosa infection. Unlike HL60 macrophages that are at a terminally differentiated stage, the human non-small cell lung carcinoma H1299 cells display an epithelial cell morphology and they proliferate actively. Immunostaining on mock and infected H1299 (MOI 100, 1.5 h) cells indicated that infection with P. aeruginosa triggered an increase in γH2AX foci formation and a re-localization of 53BP1 to these foci, as what happened after a γ-irradiation at 2 Gy (Fig. 7a). Fragmented/apoptotic nuclei were not detected by microscopic examination of DNA staining. Closer analysis by confocal microscopy showed a co-localization of the two proteins in these foci (supplemental Fig. S3). As what we observed in HL60 macrophages, not all the cells were positive for γH2AX staining upon infection in contrast to γ-irradiated cells. Interestingly, we also obtained an accumulation of discrete γH2AX foci containing 53BP1 at the nucleus periphery, near the nuclear envelop. Finally, we quantified γH2AX expression by Western-blot analysis of H1299 cell extracts infected by P. aeruginosa. Cells were infected for 1 or 2.5 h with wild-type strain at a MOI of 10 and 100. γH2AX-increased expression was easily detected at a MOI of 100 at 2.5 h (sixfold increase) and even at 1 h after infection in comparison to mock-treated cells (Fig. 7b). More γH2AX was also observed 2.5 h after infection at the lower MOI of 10. Together, these data confirmed that P. aeruginosa-induced γH2AX expression and DNA repair foci formation in lung-derived adenocarcinoma epithelial cells, a model different from human HL60 macrophages, but still relevant to P. aeruginosa infection.
Fig. 7.
P. aeruginosa induces γH2AX/53BP1 foci formation in lung epithelial cells. a Human H1299 lung epithelial cells, derived from a non-small cells lung cancer, were grown in LabTek chambers, infected by P. aeruginosa (MOI 100 for 1.5 h) and immunostained for γH2AX (red), 53BP1 (green), and DNA (blue). As a positive control for γH2AX induction, H1299 cells were irradiated at 2 Gy and immunostained 1 h later (lower panel). Confocal microscopy analysis, scale bar 10 μm. b H1299 cells were infected (or mock-treated) with wild-type CHA strain at a MOI of 10 or 100. Cell extracts were prepared 1 h or 2.5 h after infection and analyzed by Western blot. γH2AX relative intensity is set to 1 (dark bar) for mock H1299 at 2.5 h
Discussion
This study was aimed at unraveling some of the potential genotoxic effects of P. aeruginosa in host-infected cells. As predicted from earlier studies, we showed that P. aeruginosa infection induced a hyperphosphorylation of c-Jun very rapidly and at a very low MOI in macrophages. Thus, we used this very sensitive test as a marker of macrophage infection. We observed DNA strand breaks after infection and a strong induction of H2AX phosphorylation, which required the ExoS toxin from P. aeruginosa. γH2AX co-localizes with 53BP1 into discrete nuclear foci that are usually associated with DNA damage and repair, both in terminally differentiated macrophages and in actively proliferating lung cancer epithelial cells. The protein modifications described in this report are not a general reaction of macrophages once they are in contact with bacteria, but they are specific to the T3SS, as an E. coli laboratory strain or a T3SS-defective mutant had no effect on c-Jun or γH2AX under similar conditions. Moreover, ExoS toxin was the most important toxin in this process.
Once injected into the host cytoplasm, ExoS goes to endosomes, then to the endoplasmic reticulum, and to the Golgi apparatus [36]. It is present at the perinuclear region but absent from the nucleus. ExoS does not have any nuclease activity, excluding the possibility of its direct action on the genome. It is known that Gram-negative bacteria, through their external lipopolysaccharides, induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) production that can contribute to genotoxicity. Indeed, studies indicated that ROS and RNS participate in DNA damage during infection by Gram-negative Helicobacter pylori bacteria [37, 38]. It is possible that ROS and RNS might have a role in DNA DSB induced by P. aeruginosa. A Gram-negative non-pathogenic E. coli laboratory strain harboring LPS at its surface or a T3SS-deficient P. aeruginosa mutant, yet harboring LPS, did not trigger H2AX phosphorylation. Thus, the ultimate mechanisms leading to DNA damage induced by P. aeruginosa infection remain elusive. Very recently, it was shown that synthesis of the DNA repair protein OGG1 is induced in lung epithelial cells and in mice infected by P. aeruginosa PAO1 strain [13]. Comet assays also indicated that DNA breaks occurred rapidly in infection and infection of OGG1-deficient mice confirmed that DNA repair proteins such as OGG1 played a critical role in the host response to P. aeruginosa. Together with our study, these data indicate that P. aeruginosa infection is genotoxic for the host cell and that it can generate multiple types of DNA damages and initiate several DNA repair pathways.
H2AX phosphorylation requires an intact ADP-RT domain of ExoS, highlighting the fact that ADP ribosylation of one or several ExoS substrates is involved in the pathway leading to γH2AX induction. ExoT, the ExoS-related T3SS toxin, had only a modest effect on the c-Jun and H2AX phosphorylation status. A major difference between ExoS and ExoT is the nature of the substrates that are ADP-ribosylated by these two enzymes. Indeed, ExoT has a limited number of targets, mainly the CrkI and CrkII proteins, whereas ExoS has numerous identified substrates (about 20 proteins [16]). Therefore, identification of the ADP-ribosylated targets of ExoS that lead to the nuclear modifications observed on c-Jun and H2AX will represent a crucial step toward the understanding of the genotoxic activity associated with ExoS.
Experiments with chemical kinase inhibitors allowed us to identify several kinases whose inactivation impaired H2AX phosphorylation after P. aeruginosa infection. Inhibition of the activity of ATM and JNK, but not that of Erk, triggered decreased H2AX phosphorylation in macrophages. p38 inhibitor tended to reduce γH2AX but its effect was only minor. The most effective kinase, by far, is ATM, a kinase known to participate in DSB signaling and in cell cycle control [2]. A more moderate diminution (40 %) was obtained in the presence of JNK inhibitor. JNK has been reported to phosphorylate H2AX in response to UV irradiation and subsequent apoptosis induction [31]. However, we did not measure an increase in apoptosis at early stages of infection, possibly meaning that the infected cells are trying to repair their DNA. This is in agreement with previous studies that detected apoptosis (caspase-3 activity) at 5 h after infection [27] or at 36 h after transfection of host cells with an exoS-expressing plasmid (about 35 % of condensed chromatin and fragmented nuclei [39]) or at a very high MOI (16 % dead/apoptotic cells at 3 h, MOI 1000 [23]). In contrast, our study takes place in the earliest steps of host cell reaction, at the time of the initial DNA damage. Depending on the extent of DNA injuries, cells will either repair their DNA or they will undergo cell death when genome integrity is irreversibly compromised after multiple DNA lesions [40]. We showed that P. aeruginosa infection induced activation of ATM by phosphorylation on serine 1981. Together, these data revealed that induced phosphorylation of H2AX by P. aeruginosa is mainly dependent on ATM kinase, at least in the early stages of contact with bacteria, indicating that the ATM-dependent DNA damage cascade is activated upon infection.
Are P. aeruginosa-induced foci exactly the same as irradiation-induced foci (IRIF)? We can not completely answer that question yet, although it appears that some crucial steps are common to both stresses: ATM phosphorylation, H2AX phosphorylation and foci formation, recruitment of 53BP1 to these foci. Additional work will be necessary to further characterize the nature of P. aeruginosa-induced foci and their long term evolution, by videomicroscopy for example. Along the same lines, we have not investigated so far the chemical modifications appearing on damaged DNA upon infection. This should help to gain new information on the molecular mechanisms involved in DNA attack and repair.
Not all the cells will die following a P. aeruginosa attack, especially when combined antibiotic treatments are used to fight the infection and only small amounts of bacteria are involved. The surviving cells repair their DNA and continue to live and divide. However, if the repair is imperfect, as has been described during infection with E. coli expressing the genotoxin colibactin, chromosome aberrations can appear and generate chromosomal instability and increased gene mutation frequency [7]. These events could contribute to the development of intestinal cancer [7], specifically in the context of chronic inflammation. Similarly, the carcinogenic bacteria H. pylori, that chronically infect the human gastric mucosa, directly compromise the genome integrity of its host cells by triggering DNA DSB and a DNA damage response [41]. Immunocompromised patients with cancer are prone to P. aeruginosa infection, but to date, there is no study or evidence for a role for this pathogen in cancer biology. Our study highlights possible new routes for further investigation of P. aeruginosa toxicity.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. F. Boulay for very helpful scientific discussions, I. Attrée for advice and critical reading of the manuscript, J. Gaffé for discussion and corrections, H.P. Schweizer for the gift of mini-CTX1, Prof. B. Toussaint and Prof. B. Polack for the CHAΔTlox and CHAΔSTlox strains, D. Dacheux for the exoS mutagenesis, B. Schaack for annexin labeling reagents, J. Baudier for H1299 cells, P. Obeid for her advice on comet assays and E. Lebel for technical help. Images were obtained at the confocal microscopy facility of the “Institut de Recherches en Technologies et Sciences pour le Vivant” (iRTSV, CEA-Grenoble). Irradiations were performed in the “Anémome/Bio” irradiator in the “ARC -Nucléart” facility at the CEA-Grenoble. Part of the work of S. Elsen, V. Collin-Faure and C. Lemercier was performed in the former laboratory CEA-iRTSV-LBBSI, CNRS UMR5092 directed by Dr. F. Boulay. This work was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), the Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique et aux Energies Renouvelables (CEA), the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) and the Université Joseph Fourier (UJF Grenoble).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
- ADP-RT
ADP ribosyl transferase
- ATM
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated
- DSB
Double-strand breaks
- OGG1
8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase
- Crk
CT-10 regulator of kinase
- MOI
Multiplicity of infection
- PI
Propidium iodide
- CDT
Cytolethal distending toxin
- CIP
Calf intestine phosphatase
- T3SS
Type III secretion system
References
- 1.Ciccia A, Elledge SJ. The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell. 2010;40:179–204. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Derheimer FA, Kastan MB. Multiple roles of ATM in monitoring and maintaining DNA integrity. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:3675–3681. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.05.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kinner A, Wu W, Staudt C, Iliakis G. Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:5678–5694. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bonner WM, Redon CE, Dickey JS, Nakamura AJ, Sedelnikova OA, et al. Gamma H2AX and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:957–967. doi: 10.1038/nrc2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mah LJ, El-Osta A, Karagiannis TC. GammaH2AX: a sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia. 2010;24:679–686. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nougayrède JP, Homburg S, Taieb F, Boury M, Brzuszkiewicz E, et al. Escherichia coli induces DNA double-strand breaks in eukaryotic cells. Science. 2006;313:848–851. doi: 10.1126/science.1127059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cuevas-Ramos G, Petit CR, Marcq I, Boury M, Oswald E, et al. Escherichia coli induces DNA damage in vivo and triggers genomic instability in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:11537–11542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001261107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lara-Tejero M, Galán JE. A bacterial toxin that controls cell cycle progression as a deoxyribonuclease I-like protein. Science. 2000;290:354–357. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5490.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li L, Sharipo A, Chaves-Olarte E, Masucci MG, Levitsky V, et al. The Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin activates sensors of DNA damage and repair complexes in proliferating and non-proliferating cells. Cell Microbiol. 2002;4:87–99. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2002.00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Oswald E, Nougayrède JP, Taieb F, Sugai M. Bacterial toxins that modulate host cell-cycle progression. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kunz AN, Brook I. Emerging resistant Gram-negative aerobic bacilli in hospital-acquired infections. Chemotherapy. 2010;56:492–500. doi: 10.1159/000321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kerr KG, Snelling AM. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a formidable and ever-present adversary. J Hosp Infect. 2009;73:338–344. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2009.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu M, Huang H, Zhang W, Kannan S, Weaver A, et al. Host DNA repair proteins in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in lung epithelial cells and in mice. Infect Immun. 2011;79:75–87. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00815-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.David SS, O’Shea VL, Kundu S. Base-excision repair of oxidative DNA damage. Nature. 2007;447:941–950. doi: 10.1038/nature05978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Veesenmeyer JL, Hauser AR, Lisboa T, Rello J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and therapy: evolving translational strategies. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:1777–1786. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819ff137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Roy-Burman A, Savel RH, Racine S, Swanson BL, Revadigar NS, et al. Type III protein secretion is associated with death in lower respiratory and systemic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1767–1774. doi: 10.1086/320737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hauser AR, Cobb E, Bodi M, Mariscal D, Vallés J, et al. Type III protein secretion is associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Crit Care Med. 2002;30:521–528. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200203000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hauser AR. The type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: infection by injection. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7:654–665. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Deng Q, Barbieri JT. Molecular mechanisms of the cytotoxicity of ADP-ribosylating toxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008;62:271–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fink SL, Cookson BT. Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 2005;73:1907–1916. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.1907-1916.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grassmé H, Jendrossek V, Gulbins E. Molecular mechanisms of bacteria induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2001;6:441–445. doi: 10.1023/A:1012485506972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aude-Garcia C, Collin-Faure V, Bausinger H, Hanau D, Rabilloud T, et al. Dual roles for MEF2A and MEF2D during human macrophage terminal differentiation and c-Jun expression. Biochem J. 2010;430:237–244. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rovera G, Santoli D, Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1979;76:2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Toussaint B, Delic-Attree I, Vignais PM. Pseudomonas aeruginosa contains an IHF-like protein that binds to the algD Promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;196(1):416–1421. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Weston CR, Davis RJ. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:142–149. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jia J, Alaoui-El-Azher M, Chow M, Chambers TC, Baker H, et al. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated signaling is essential for Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoS-induced apoptosis. Infect Immun. 2003;71:3361–3370. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3361-3370.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jendrossek V, Grassmé H, Mueller I, Lang F, Gulbins E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced apoptosis involves mitochondria and stress-activated protein kinases. Infect Immun. 2001;69:2675–2683. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2675-2683.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rucks EA, Olson JC. Characterization of an ExoS Type III translocation-resistant cell line. Infect Immun. 2005;73:638–643. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.638-643.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bridge DR, Novotny MJ, Moore ER, Olson JC. Role of host cell polarity and leading edge properties in Pseudomonas type III secretion. Microbiology. 2010;156:356–373. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.033241-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Smeal T, Binetruy B, Mercola DA, Birrer M, Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991;354:494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dacheux D, Toussaint B, Richard M, Brochier G, Croize J, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolates induce rapid, type III secretion-dependent, but ExoU-independent, oncosis of macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 2000;68:2916–2924. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2916-2924.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yahr TL, Mende-Mueller LM, Friese MB, Frank DW. Identification of type III secreted products of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S regulon. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:7165–7168. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.22.7165-7168.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Goehring UM, Schmidt G, Pederson KJ, Aktories K, Barbieri JT. The N-terminal domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S is a GTPase-activating protein for Rho GTPases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:36369–36372. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.51.36369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Radke J, Pederson KJ, Barbieri JT. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S is a biglutamic acid ADP-ribosyltransferase. Infect Immun. 1999;67:1508–1510. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.3.1508-1510.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lu C, Zhu F, Cho YY, Tang F, Yoga T, et al. Cell apoptosis: requirement of H2AX in DNA ladder formation, but not for the activation of caspase-3. Mol Cell. 2006;23:121–132. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Deng Q, Zhang Y, Barbieri JT. Intracellular trafficking of Pseudomonas ExoS, a type III cytotoxin. Traffic. 2007;8:1331–1345. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Katsurahara M, Kobayashi Y, Iwasa M, Ma N, Inoue H. Reactive nitrogen species mediate DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Helicobacter. 2009;14:552–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2009.00719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.HirakuY Kawanishi S, Ichinose T, Murata M. The role of iNOS-mediated DNA damage in infection- and asbestos-induced carcinogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1203:15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jia J, Wang Y, Zhou L, Jin S. Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin ExoS effectively induces apoptosis in host cells. Infect Immun. 2006;74:6557–6570. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00591-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zio DD, Cianfanelli V, Cecconi F. New insights into the link between DNA damage and apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Toller IM, Neelsen KJ, Steger M, Hartung ML, Hottiger MO, et al. Carcinogenic bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori triggers DNA double-strand breaks and a DNA damage response in its host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:14944–14949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100959108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.