Abstract
We isolated novel reassortant avian influenza A(H5N6) viruses containing genes from clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 virus and low pathogenicity avian influenza viruses in carcasses of whooper swans and bean geese in South Korea during December 2023. Neuraminidase gene was from a clade 2.3.4.4b H5N6 virus infecting poultry and humans in China.
Keywords: avian influenza virus, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, H5N6, clade 2.3.4.4, wild bird, genomic surveillance, influenza, viruses, zoonoses
Infection caused by highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses (HPAIVs) have caused major economic losses in the poultry industry and pose a serious threat to public health. The A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996 (gs/GD) lineage of H5 HPAIV emerged in China in 1996 and diverged into 10 genetically independent hemagglutinin (HA) clades (0–9) and subclades (1). The gs/GD lineage of H5 HPAIV has caused outbreaks worldwide, infecting a range of wildlife, poultry, and humans (1). Clade 2.3.4.4 H5Nx HPAIV containing multiple neuraminidase (NA) subtypes (2) has dominated outbreaks worldwide from 2014 onwards and further divided into subclades 2.3.4.4a–h (3). Currently, clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 HPAIV is predominant globally after causing outbreaks in Europe in the fall of 2020 and in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Antarctica (4–7).
During October 2022–March 2023, a total of 16 different genotypes of H5N1 2.3.4.4b HPAIV caused outbreaks in South Korea, including 174 cases in wild birds (8). Based on the available surveillance data, no new virus incursions have occurred in South Korea during summer and fall 2023. National surveillance for HPAIV began in South Korea in the fall of 2023. We isolated 3 H5N6 HPAIVs from wild bird carcasses found in South Korea during December 2023 (A/whooper swan/Korea/23WC075/2023[H5N6], A/whooper swan/Korea/23WC116/2023[H5N6], and A/bean goose/Korea/23WC111/2023[H5N6]) (Appendix Table 1). We conducted next-generation sequencing of the isolates and shared complete genome sequences publicly. We conducted comparative phylogenetic analysis to infer the origin and evolution of the viruses.
All H5N6 isolates were identified as HPAIVs based on the presence of multiple basic amino acids at the HA proteolytic cleavage site (REKRRKR/GLF). BLAST inquiries of the GISAID database (https://www.gisaid.org) indicated all 8 genes shared the highest nucleotide sequence identity (99.77%–100%) with a clade 2.3.4.4b H5N6 virus identified from a peregrine falcon in 2023 in Japan (A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023[H5N6]), harboring the same genome constellation as the H5N6 viruses in South Korea (Table). The HA gene clustered with the major genotype a of the H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b HPAIV that circulated during 2022–2023 in South Korea (8). The NA gene of H5N6 virus clustered with H5N6 HPAIV from China, previously isolated in poultry and humans in 2018, but other internal genes were genetically distinct. Polymerase basic 1 and matrix protein genes also clustered with 2022–2023 H5N1 HPAIVs from South Korea. Polymerase basic 2, polymerase acidic, nucleoprotein, and nonstructural genes clustered with low-pathogenicity avian influenza viruses in Eurasia (Appendix Figure 2).
Table. Nucleotide sequence identities between gene segments of novel clade 2.3.4.4b highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N6) virus isolate A/whooper swan/Korea/23WC075/2023 from South Korea and nearest top 3 homologs in the GISAID EpiFlu database*.
| Gene | Top 3 query | Accession no. | Nucleotide identity | % Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB2 |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 1 (PB2) | EPI2898974 | 2280/2280 | 100.00 |
| A/environment/chongqing/1795/2023 (A/H9N2) segment 1 (PB2) | EPI2841012 | 2271/2280 | 99.61 | |
| A/environment/Kagoshima/KU-I6/2021 (H4N6) (A/H4N6) segment 1 (PB2) |
EPI2553141 |
2253/2280 |
98.82 |
|
| PB1 |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 2 (PB1) | EPI2898975 | 2273/2274 | 99.96 |
| A/egret/Korea/22WC394/2023 (A/H5N1) segment 2 (PB1) | EPI2743089 | 2271/2274 | 99.87 | |
| A/common buzzard/Korea/22WC336/2023 (A/H5N1) segment 2 (PB1) |
EPI2742993 |
2271/2274 |
99.87 |
|
| PA |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 3 (PA) | EPI2898976 | 2150/2151 | 99.95 |
| A/common teal/Amur region/92b/2020 (A/H6N2) segment 3 (PA) | EPI1849993 | 2142/2151 | 99.58 | |
| A/mallard/Russia Primorje/94T/2020 (A/H1N1) segment 3 (PA) |
EPI1849961 |
2141/2151 |
99.54 |
|
| HA |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 4 (HA) | EPI2898977 | 1700/1704 | 99.77 |
| A/environment/Kagoshima/KU-G4/2022 (H5N1) (A/H5N1) segment 4 (HA) | EPI2789597 | 1697/1704 | 99.59 | |
| A/environment/Kagoshima/KU-D4/2022 (H5N1) (A/H5N1) segment 4 (HA) |
EPI2789589 |
1697/1704 |
99.59 |
|
| NP |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 5 (NP) | EPI2898978 | 1496/1497 | 99.93 |
| A/gadwall/Novosibirsk region/3407k/2020 (A/H4N6) segment 5 (NP) | EPI1849870 | 1479/1497 | 98.80 | |
| A/mallard/Novosibirsk region/3286k/2020 (A/H4N6) segment 5 (NP) |
EPI1849878 |
1478/1497 |
98.73 |
|
| NA |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 6 (NA) | EPI2898979 | 1377/1380 | 99.78 |
| A/duck/Hunan/S40199/2021(H5N6) (A/H5N6) segment 6 (NA) | EPI1997201 | 1360/1380 | 98.55 | |
| A/Changsha/1/2022 (A/H5N6) segment 6 (NA) |
EPI2287050 |
1359/1380 |
98.48 |
|
| M |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 7 (MP) | EPI2898980 | 982/982 | 100.00 |
| A/northern pintail/Kagoshima/KU-64/2022 (H5N1) (A/H5N1) segment 7 (MP) | EPI2794001 | 980/982 | 99.80 | |
| A/environment/Kagoshima/KU-B4/2022 (H5N1) (A/H5N1) segment 7 (MP) |
EPI2789385 |
980/982 |
99.80 |
|
| NS |
A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023 (A/H5N6) segment 8 (NS) | EPI2898981 | 837/838 | 99.88 |
| A/bean goose/Korea/KNU-10/2022 (A/H10N7) segment 8 (NS) | EPI2873490 | 836/838 | 99.76 | |
| A/bean goose/Korea/KNU-14/2022 (A/H6N1) segment 8 (NS) |
EPI2873460 |
836/838 |
99.76 |
|
| *GISAID, https://www.gisaid.org; HA, hemagglutinin; P, matrix; NA, neuraminidase; NP, nucleoprotein; NS, nonstructural; PA, polymerase acidic; PB, polymerase basic. | ||||
Estimated time to most recent common ancestor (tMRCA) of each gene of the H5N6 viruses and the A/peregrine falcon/Saga/4112A002/2023(H5N6) ranged from February through November 2023 (Figure; Appendix Table 2). On the basis of overlap between the 95% highest posterior density intervals of tMRCA, we assume the novel reassortant H5N6 viruses emerged around August–October 2023 and were introduced into Japan and South Korea. Maximum clade credibility tree of the NA gene revealed the wild bird H5N6 viruses from Japan and South Korea shared a common ancestor with the human infection case of H5N6 virus (A/Changsha/1/2022) from China. Since 2014, a total of 90 human cases of H5N6 infection have been reported in China;w most infections were reported after 2021 (9; https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/375483). The tMRCA of the wild bird H5N6 viruses from Japan and Korea and the human infection H5N6 virus from China is estimated to be June 12, 2022 (95% highest posterior density December 7, 2021–November 10, 2022) (Figure; Appendix Table 2). The ancestral H5N6 HPAIV circulating in China potentially donated the NA gene to the clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 virus in late 2022. The N6 gene of current and ancestral H5N6 HPAIV possessed a stalk deletion potentially acquired during the circulation of viruses in domestic poultry (10).
Figure.
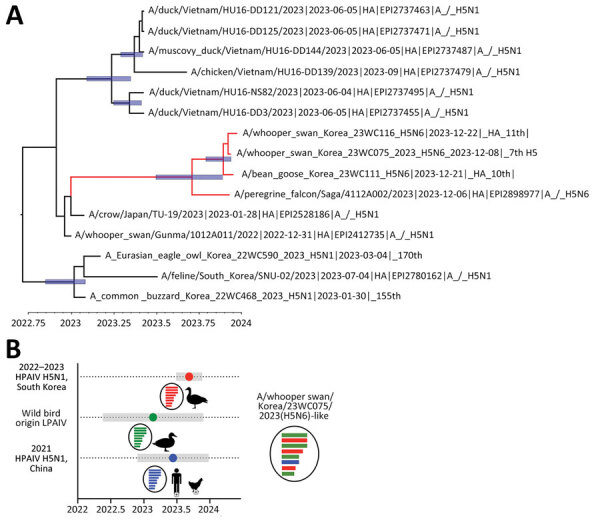
Exploration of most common ancestors for novel reassortant highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N6) clade 2.3.4.4 b isolates recovered from wild birds, South Korea. A) Maximum clade credibility tree of viruses found in the carcasses of whooper swans and bean geese in South Korea, December 2023. Tree was constructed using the hemagglutinin gene of the H5N6 viruses. Red indicates H5N6 isolates from South Korea and Japan. The timescale is shown on the horizontal axis in decimal years. Node bars represent 95% highest posterior density of the heights. Accession numbers beginning with EPI indicate isolates from the GISAID database (https://www.gisaid.org). B) Temporal schematic of the reassortant genome constellation of the novel reassortant H5N6 viruses from South Korea. Gene segments originating from H5N1 HPAIVs (red), LPAIVs (green), and H5N6 (blue) HPAIVs are indicated. Shade bars represent 95% highest posterior density range of time to most recent common ancestor. Circles represent the mean time to most recent common ancestor. HPAIV, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus; LPAIV, low-pathogenicity avian influenza viruses.
The H5N6 viruses possessed molecular markers T188, V210, Q222, and G224 in HA, which are associated with binding affinity to α-2,3 sialic acid receptors. We observed S133A and T156A mutations in HA, known to be associated with increased binding to α-2,6 sialic acid receptors. We observed L89V in polymerase basic 2, but not Q591K, E627K, and D701N. We also observed D622G in polymerase basic 1, N30D and I43M in matrix 1, and P42S in nonstructural protein 1, which are associated with increased virulence in mice (10).
Previous reports suggest the genomes of clade 2.3.4.4b are evolving through frequent genome reassortments, forming transient and diverse genome constellations change with no apparent pattern of gene segment association (8). Detection of H5N6 HPAIVs from wild birds in South Korea and Japan during the 2023–24 wintering season and our phylogenetic analysis suggest H5N6 HPAIVs most likely descended from clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 viruses circulating during 2022–2023, evolved from reassortment with other low-pathogenicity avian influenza viruses and HPAIVs, and were introduced into South Korea and Japan by wild birds during the fall migration season. Enhanced genomic surveillance of HPAIVs in wild birds is needed for early detection and monitoring of further evolution and spread of viruses.
Additional information about novel avian influenza A(H5N6) in wild birds, South Korea, 2023.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by a grant from National Institute of Wildlife Disease Control and Prevention (NIWDC) (grant no. 2023-016) and the Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea.
The datasets in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of repositories and accession numbers are available through the GISAID (https://www.gisaid.org) EpiFlu database (accession nos. EPI2976997–EPI2977029).
Biography
Mr. Cho is a PhD candidate at the College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University. His research interests include molecular epidemiology and development of vaccines against avian diseases.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Cho AY, Si Y-J, Kim D-J, Seo Y-R, Lee D-Y, Kim D, et al. Novel avian influenza A(H5N6) virus in wild birds, South Korea, 2023. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 June [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid3006.240192
These authors contributed equally to this article.
References
- 1.Wan XF. Lessons from emergence of A/goose/Guangdong/1996-like H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses and recent influenza surveillance efforts in southern China. Zoonoses Public Health. 2012;59(Suppl 2):32–42. 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2012.01497.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lee DH, Bertran K, Kwon JH, Swayne DE. Evolution, global spread, and pathogenicity of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5Nx clade 2.3.4.4. J Vet Sci. 2017;18(S1):269–80. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.S1.269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Health Organization. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of zoonotic influenza A viruses and development of candidate vaccine viruses for pandemic preparedness. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2020;95:525–39 https://www.who.int/publications/journals/weekly-epidemiological-record cited 2024 Feb 4. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bevins SN, Shriner SA, Cumbee JC Jr, Dilione KE, Douglass KE, Ellis JW, et al. Intercontinental movement of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4 virus to the United States, 2021. Emerg Infect Dis. 2022;28:1006–11. 10.3201/eid2805.220318 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baek YG, Lee YN, Lee DH, Shin JI, Lee JH, Chung DH, et al. Multiple reassortants of H5N8 clade 2.3.4.4b highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses detected in South Korea during the winter of 2020–2021. Viruses. 2021;13:490. 10.3390/v13030490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wu H, Peng X, Xu L, Jin C, Cheng L, Lu X, et al. Novel reassortant influenza A(H5N8) viruses in domestic ducks, eastern China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1315–8. 10.3201/eid2008.140339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fusaro A, Gonzales JL, Kuiken T, Mirinavičiūtė G, Niqueux É, Ståhl K, et al. ; European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Union Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza. Avian influenza overview December 2023-March 2024. EFSA J. 2024;22:e8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Seo Y-R, Cho AY, Si Y-J, Lee S-I, Kim D-J, Jeong H, et al. Evolution and spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus in wild birds, South Korea, 2022–2023. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024;30:299–309. 10.3201/eid3002.231274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang P, Sun L, Li J, Wu Q, Rezaei N, Jiang S, et al. Potential cross-species transmission of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 subtype (HPAI H5) viruses to humans calls for the development of H5-specific and universal influenza vaccines. Cell Discov. 2023;9:58. 10.1038/s41421-023-00571-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suttie A, Deng YM, Greenhill AR, Dussart P, Horwood PF, Karlsson EA. Inventory of molecular markers affecting biological characteristics of avian influenza A viruses. Virus Genes. 2019;55:739–68. 10.1007/s11262-019-01700-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional information about novel avian influenza A(H5N6) in wild birds, South Korea, 2023.


