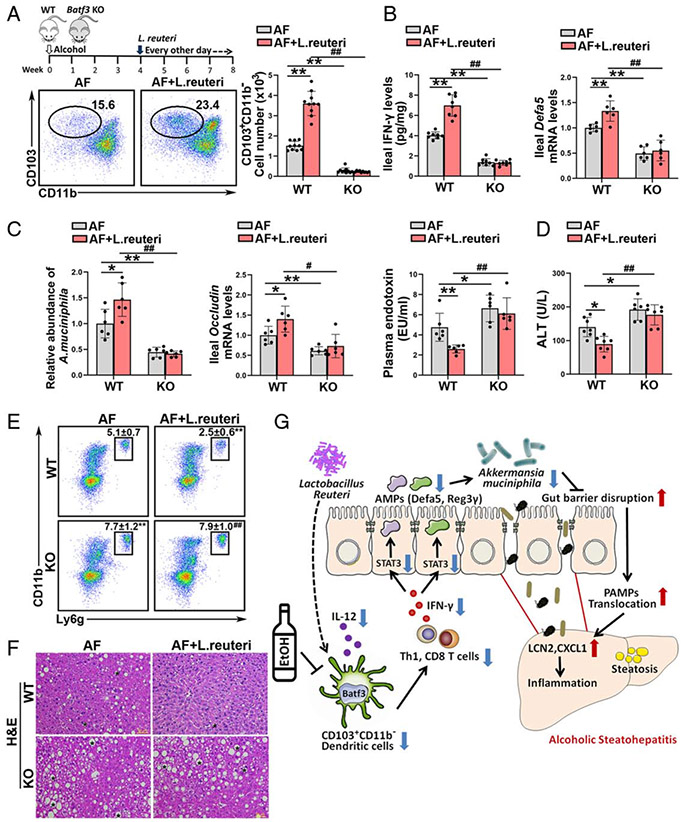
FIGURE 8.
Intestinal conventional type 1 DCs (cDC1s) are required for the protective role of Lactobacillus reuteri in alcohol-induced steatohepatitis. Alcohol-fed C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) mice and Batf3−/− mice were administrated with or without L. reuteri, respectively. (A) The dot plot and relative frequency of ileal CD103+CD11b− cDC1s (n = 10). (B) Ileal interferon gamma (IFN-γ) protein levels (n = 8) and the ileal mRNA levels of Defa5 (n = 6). (C) Relative A. muciniphila abundance (n = 6), mRNA levels of ileal Occludin (n = 6), and plasma LPS levels (n = 6). (D) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (n = 7). (E) Representative dot plot and frequency of neutrophils in the liver (n = 10). (F) Liver histopathological changes shown by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Scale bars: 50 μm. Asterisks: lipid droplets. (G) Summarized figure of this study. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus WT/alcohol-fed (AF) mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus WT/AF+L. reuteri. LPS, lipopolysaccharide.