Abstract
Keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in epidermis are well-controlled and essential for reacting to stimuli such as ultraviolet light. Imbalance between proliferation and differentiation is a characteristic feature of major human skin diseases such as psoriasis and squamous cell carcinoma. However, the effect of keratinocyte metabolism on proliferation and differentiation remains largely elusive. We show here that the gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) promotes differentiation while inhibits proliferation of keratinocyte and suppresses psoriasis development. FBP1 is identified among the most upregulated genes induced by UVB using transcriptome sequencing and is elevated especially in upper epidermis. Fbp1 heterozygous mice exhibit aberrant epidermis phenotypes with local hyperplasia and dedifferentiation. Loss of FBP1 promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of keratinocytes in vitro. Mechanistically, FBP1 loss facilitates glycolysis-mediated acetyl-CoA production, which increases histone H3 acetylation at lysine 9, resulting in enhanced transcription of proliferation genes. We further find that the expression of FBP1 is dramatically reduced in human psoriatic lesions and in skin of mouse imiquimod psoriasis model. Fbp1 deficiency in mice facilitates psoriasis-like skin lesions development through glycolysis and acetyl-CoA production. Collectively, our findings reveal a previously unrecognized role of FBP1 in epidermal homeostasis and provide evidence for FBP1 as a metabolic psoriasis suppressor.
Subject terms: Cell biology, Diseases
Introduction
The epidermis of mammalian skin serves as a water-impermeable barrier which is essential for keeping harmful insults out. Cells from a basal proliferative layer of epidermis commit to differentiate and move upward during normal tissue homeostasis or after exposure to stimuli such as ultraviolet light. Disturbances in epidermal homeostasis are associated with various skin diseases such as psoriasis. Psoriatic lesions are characterized by epidermal acanthosis (thickening of viable layers), hyperkeratosis (thickened cornified layer), and parakeratosis (cell nuclei present in the cornified layer), which are due to increased proliferation and aberrant terminal differentiation of keratinocytes [1, 2]. The keratinocyte response is triggered by dysregulated cellular immune system, with T cells, dendritic cells, and various immune-related cytokines and chemokines implicated in pathogenesis [2].
Glycolysis, as an important metabolic pathway in cells, provides energy, reducing equivalents and materials for the synthesis of cellular biomass to maintain cell division. It has been proven that epidermis is a glycolytic tissue [3, 4]. Recent evidences demonstrate that the glycolytic enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) is required for proliferation and inhibits differentiation in epidermal keratinocytes, implicating glycolysis directly regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation [5]. The glycolytic enzymes are also increasingly proven to participate in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, as psoriatic lesions exhibit increased proliferating keratinocytes [6]. For example, glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) is elevated in psoriatic epidermis from the patient and imiquimod (IMQ) induced psoriasis mouse model, genetic and pharmacological Glut1 inactivation decreased hyperplasia in mouse models of psoriasis-like disease [7]; pyruvate kinase M2 contributes to psoriasis progression by promoting proliferation and mediating interleukin-17 signaling in keratinocytes [8, 9]. These studies have examined aerobic glycolysis in keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation; however, gluconeogenesis has not been fully studied.
As a rate-limiting gluconeogenic enzyme, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBP1), catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate. Recent studies demonstrate that FBP1 also functions as a protein phosphatase to dephosphorylate histone H3 and IκBα [10, 11]. An autosomal recessive inherited disorder of FBP1 deficiency is characterized by hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis, which often results in sudden infant death [12]. FBP1 is increasingly identified as a tumor suppressor as loss of FBP1 expression has been shown to promote tumor progression by enhancing aerobic glycolysis, thereby resulting in poor prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma [13–16]. FBP1 also plays important role in pathophysiology of diabetes, obesity and insulin hyperresponsiveness [17–20]. However, to our knowledge, the role of FBP1 in epidermal homeostasis and psoriasis has not been studied.
Here we identify FBP1 is among the most upregulated genes induced by UVB and is elevated especially in upper epidermis. Functional studies demonstrate Fbp1 loss disturbs epidermal homeostasis with increased hyperplasia and reduced differentiation using genetic mice model. Mechanistically, FBP1 depletion promotes glycolysis-mediated acetyl-CoA production, which increases histone acetylation and subsequent growth-related genes transcription in keratinocytes. We also find FBP1 is dramatically reduced in human psoriatic lesions and Fbp1 deficient mice are more prone to develop IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions, demonstrating FBP1 participates in psoriasis pathogenesis. Our results uncover a previously unrecognized role of FBP1 in epidermal homeostasis and suggest that restoring FBP1 in psoriatic lesions might be a promising approach for treating psoriasis.
Result
UVB irradiation causes epidermal differentiation and metabolic changes in human epidermal equivalents
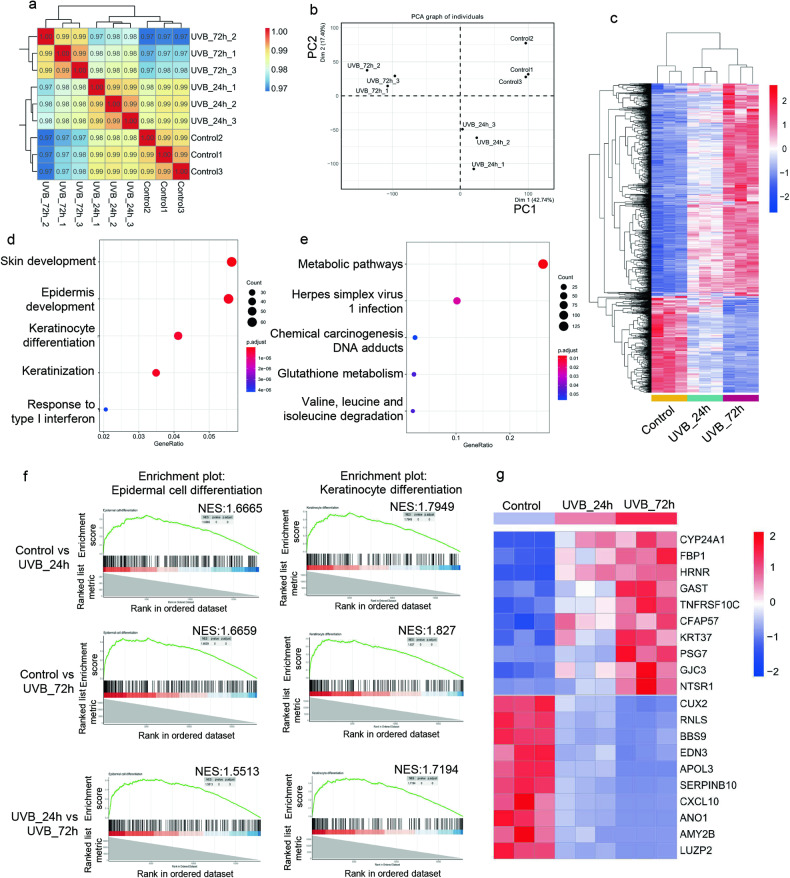
To investigate the transcriptional response to UVB radiation in human epidermis, we utilized human primary keratinocytes to generate human epidermal equivalents, which were then irradiated with 500 mJ/cm2 UVB and collected 24 h (UVB_24 h) or 72 h (UVB_72 h) after irradiation. The non-irradiated epidermis serves as control. Gene expression in irradiated and non-irradiated epidermis was characterized by RNA-Seq technique. A total of 17,929 genes were detected in these samples. Samples of the same group clustered closely evaluated by Spearman’s correlation coefficient method, suggesting high fidelity of RNA-Seq data (Fig. 1a). Principal component analysis (PCA) demonstrated a clear separation of transcriptional signatures induced by UVB irradiation (Fig. 1b). To further characterize differentially expressed genes from RNA-Seq data, we set the threshold with Q-value < 0.001 and |log2FC| > 1 by DESeq2 R package. A total of 2672 genes were identified differentially expressed among three groups. We further narrowed down the differentially expressed genes to 1515 by excluding genes of average Fragment Per Kilobase of transcript, per Million mapped reads (FPKM) <1. Among the 1515 genes, 25.3% (383/1515) exhibited a continuously increased expression pattern while 55.7% (844/1515) exhibited a continuously decreased expression pattern (Fig. 1c). Over-representation analysis of Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways using the 1227 continuously changing genes revealed a significant enrichment in the skin development, epidermis development, keratinocyte differentiation (Fig. 1d) and metabolic pathways (Fig. 1e). Gene set enrichment analysis based on the entire transcriptome data identified GO enrichment in epidermal cell differentiation and keratinocyte differentiation in all three comparisons (Fig. 1f). Thus, UVB irradiation induces keratinocyte differentiation and metabolic changes in human epidermal equivalents.
Fig. 1. UVB irradiation causes epidermal differentiation and metabolic changes in human epidermal equivalents.
a Sample correlation analysis of the transcriptome of human epidermal equivalents from the control group, UVB_24 h group and UVB_72 h group. b Principal component analysis of the transcriptome of human epidermal equivalents from the control group, UVB_24 h group and UVB_72 h group. c Clustering heatmap of the 1227 differentially expressed genes based on FPKM. d, e Over-representation analysis of GO (d) and KEGG pathways (e) based on the 1227 differentially expressed genes. The size indicates the gene numbers and the color corresponds to the P value. f Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of differentially expressed genes in the UVB_24 h group relative to the control group, UVB_72 h group relative to the control group and UVB_72 h group relative to the UVB_24 h group. g Expression heatmap of the top 10 changed genes.
FBP1 expression is induced by UVB irradiation
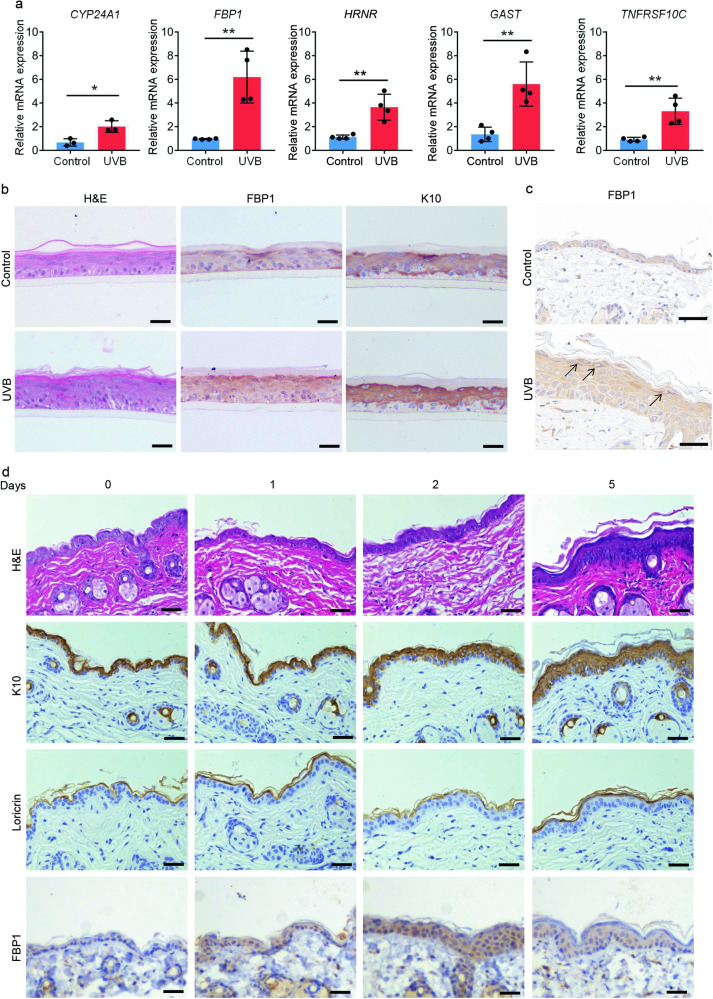
We further examined the top 10 upregulated genes induced by UVB irradiation (Fig. 1g). Among these genes, CYP24A1 (cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1) is a vitamin D3 hydroxylating enzyme which can be induced by UVB irradiation in wavelength-dependent manner in human keratinocytes [21–23]. Hornerin (HRNR) is a component of the epidermal cornified cell envelopes and its expression is induced by UVB irradiation [24, 25]. Thus, the increased expression of UVB-responsive genes detected in irradiated samples indicated our transcriptomic data were convincing. Indeed, the RT-qPCR analysis confirmed the increased transcription levels of CYP24A1, FBP1, HRNR, GAST (gastrin) and TNFRSF10C (TNF receptor superfamily member 10c) (Fig. 2a). As FBP1 is a rate-limiting gluconeogenic enzyme and its role in epidermis was unknown, we selected FBP1 for further studies. UVB irradiation promoted the stratification process, increased the thickness, and induced FBP1 expression in human epidermis equivalents (Fig. 2b). Fbp1 expression was also upregulated in UVB-irradiated mice skin, especially in upper epidermis (Fig. 2c). We further detected FBP1 levels in mice skin at various times after UVB irradiation. UVB promoted epidermal differentiation and inflammation as the expression of the differentiation marker keratin10 (K10), loricrin cornified envelope precursor protein (Loricrin) and the cytokines interleukin 1 beta (Il1b), interleukin 6 (Il6), interleukin 8 (Il8) were elevated (Fig. 2d and Supplementary Fig. 1a, b). Meanwhile, FBP1 level was slightly elevated 1 day after UVB irradiation and significantly elevated 2 days after UVB irradiation (Fig. 2d and Supplementary Fig. 1b). In summary, UVB induced Fbp1 expression, concomitant with the increased epidermal differentiation and inflammation.
Fig. 2. FBP1 expression is induced by UVB irradiation.
a Relative mRNA levels of CYP24A1, FBP1, HRNR, GAST and TNFRSF10C in control (0 mJ/cm2) and UVB-irradiated (500 mJ/cm2) human epidermal equivalents collected 72 h after irradiation, n = 3 or 4 independent experiments. b Representative H&E staining or immunohistochemical staining (FBP1, K10) of control (0 mJ/cm2) or UVB (500 mJ/cm2) irradiated human epidermal equivalents collected 72 h after irradiation. Scale bars: 50 μm. c Representative immunohistochemical staining for FBP1 of control (0 mJ/cm2) or UVB (500 mJ/cm2) irradiated mice skin collected 72 h after irradiation. Scale bars: 50 μm. Arrows indicated deep-stained upper epidermis. d Representative H&E staining or immunohistochemical staining of mice skin collected at indicated days after irradiation. Scale bars: 50 μm. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Statistical analyses in (a) were performed with Student’s t-tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
We also investigated the regulation of FBP1 expression. As IL-6 is induced by UVB irradiation and is known to activate the expression of pyruvate carboxylase 1, another gluconeogenesis enzyme, in the liver [26], we hypothesized IL-6 might be one of the regulators of FBP1. However, FBP1 levels were not changed upon IL-6 knockdown (Supplementary Fig. 1c). Additionally, the transcription factor for PFKFB3, p63 [5], also did not control FBP1 expression (Supplementary Fig. 1c). As UVB activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and NF-κB pathways [27, 28], we further detected whether theses pathways participated in regulating FBP1. Indeed, inhibition of p38 MAPK pathways by adezmapimod or inhibition of NF-κB pathways by BAY 11-7082 slightly downregulated FBP1 expression, demonstrating these two pathways partially regulate FBP1 levels (Supplementary Fig. 1d).
FBP1 is essential for epidermal homeostasis and response to UVB irradiation
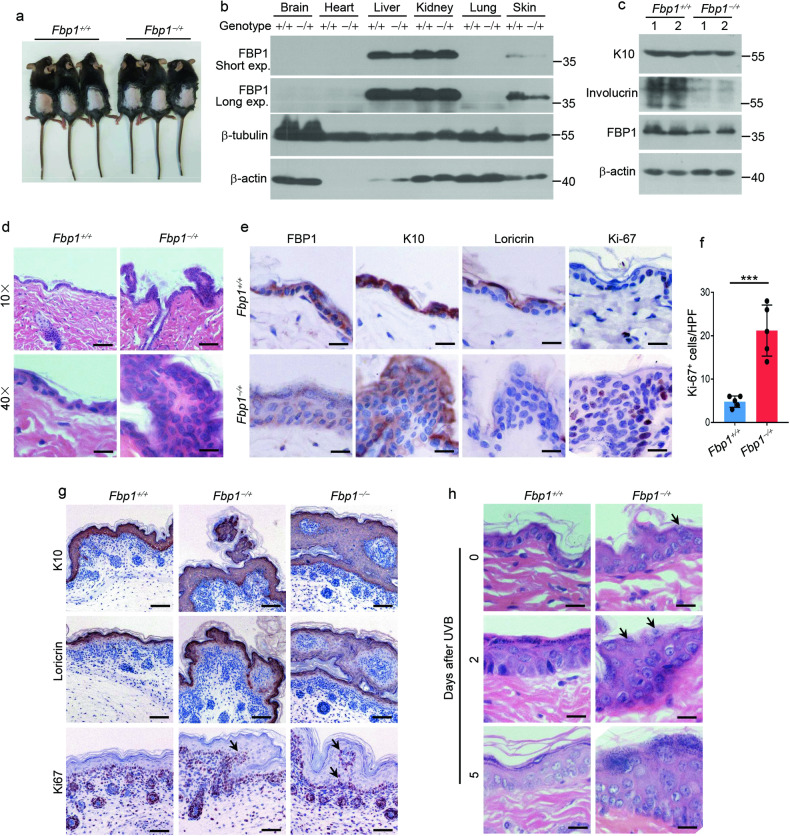
To elucidate the role of FBP1 in epidermis, we utilized genetic mice model. By using CRISPR-Cas9 technology, we deleted the exon 2–4 (5120 bp) of the murine Fbp1 gene (Supplementary Fig. 2a). We designed primers outside (F1, R1) and inside (F2, R2) the deletion region (Supplementary Fig. 2b,c), and verified Fbp1 genotypes by PCR (Supplementary Fig. 2d). Although Fbp1 homozygous (Fbp1−/−) newborn mice were morphologically indistinguishable from WT littermates (Fbp1+/+) (Supplementary Fig. 2e), they died several days after birth, which might be caused by hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis observed in FBP1 deficient human infants [12]. Thus, we further analyzed the Fbp1 heterozygous mice (Fbp1−/+). Six-week-old heterozygous mice exhibited normal morphology compared with their WT littermates (Fig. 3a). Western blot demonstrated that Fbp1 was strongly expressed in liver and kidney, weakly expressed in skin and not expressed in brain, heart and lung (Fig. 3b). Fbp1 expression was ~50% lower in heterozygous liver and skin (Fig. 3b). Surprisingly, skin of Fbp1 heterozygous mice exhibited focal hyperplasia with disorganized keratinocytes and enlarged nuclei (Fig. 3d). The expression of epidermal K10 and Loricrin were decreased while proliferation marker Ki-67 was increased in these skin lesions, suggesting decreased epidermal differentiation and increased proliferation (Fig. 3c, e, f). We further analyzed skin of neonatal Fbp1 homozygous mice and also found disorganized focal lesions (Fig. 3g), demonstrating that FBP1 is essential for maintaining skin homeostasis. We next tested whether FBP1 was necessary for the epidermal response to UVB irradiation. Many areas of Fbp1 heterozygous mice skin showed abnormal stratification with retained cell nuclei in the cornified layer after UVB irradiation (Fig. 3h). MB05032, a specific inhibitor of FBP1 [29], also reduced the expression of keratin10 and loricrin in human epidermal equivalents with or without UVB treatment (Supplementary Fig. 2f, g). In summary, FBP1 is essential for epidermal homeostasis and response to UVB irradiation.
Fig. 3. FBP1 is essential for epidermal homeostasis and response to UVB irradiation.
a Photos of 6-week-old Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice. b Western blot analysis of the expression of FBP1, β-tubulin and β-actin in indicated organs obtained from Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice. Exp exposure. c Western blot analysis of the expression of K10, involucrin, FBP1 and β-actin in skin tissue from Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice. d Representative H&E staining of skin from 6-week-old Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice. Scale bars in upper images: 100 μm, scale bars in lower images: 25 μm. e Immunohistochemical staining for FBP1, K10, loricrin and Ki-67 of skin from 6-week-old Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice. Scale bars: 25 μm. f The quantification of Ki-67+ keratinocytes in skin sections from 6-week-old Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice, n = 3 mice per genotype. HPF high-power field. g Immunohistochemical staining for K10, loricrin and Ki-67 of skin from neonatal Fbp1+/+, Fbp1−/+ and Fbp1−/− mice. Scale bars: 100 μm. Arrows indicated protruding Ki-67+ basal keratinocytes. h Representative H&E staining of skin from 6-week-old Fbp1+/+ and Fbp1−/+ mice collected at indicated days after irradiation. Scale bars: 50 μm. Arrows indicated retained cell nuclei in the cornified layer. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Statistical analyses in (f) were performed with Student’s t-tests. ***p < 0.001.
FBP1 promotes differentiation and inhibits proliferation of keratinocytes
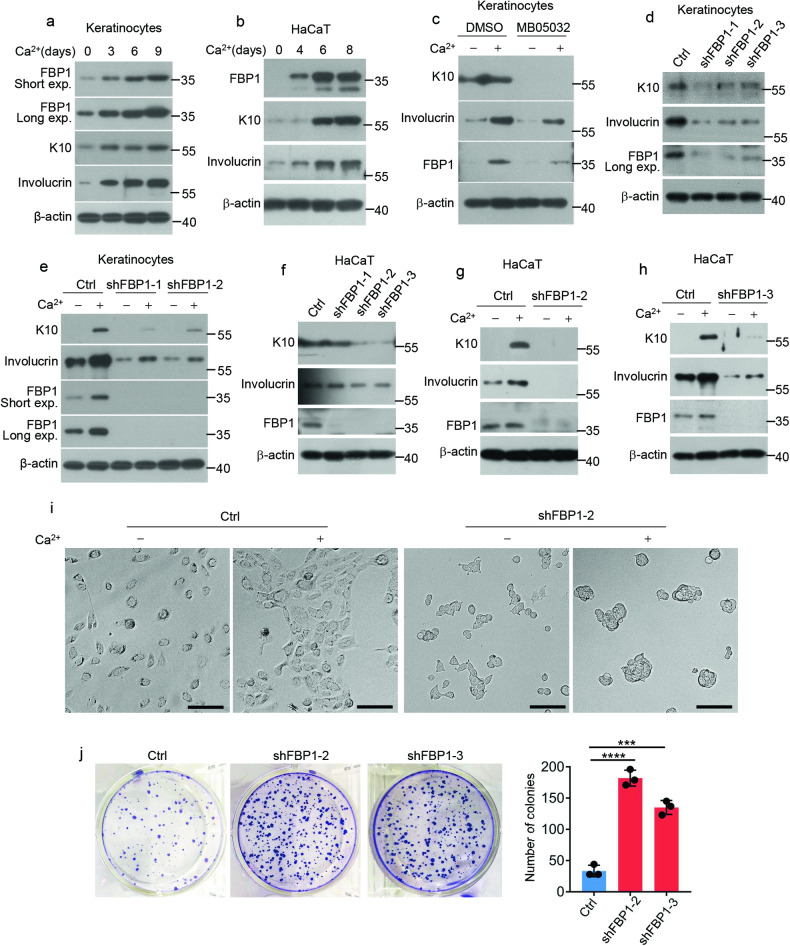
As Fbp1 deficient mice exhibits disturbed epidermal homeostasis with increased hyperplasia and reduced differentiation, we hypothesized that FBP1 might participate in keratinocytes differentiation and proliferation. We next utilized human primary keratinocytes and HaCaT cells to clarify the role of FBP1. FBP1 gradually accumulated during calcium-induced differentiation of human primary keratinocytes and HaCaT cells (Fig. 4a, b), implicating FBP1 was involved in keratinocytes differentiation. To investigate whether FBP1 regulated keratinocytes differentiation, we treated human primary keratinocytes with DMSO or MB05032 and induced differentiation with calcium. Compared with DMSO, MB05032 significantly suppressed the expression of differentiation genes (Fig. 4c). We further depleted intracellular FBP1 using short hairpin RNAs (shFBP1) (Fig. 4d). FBP1 depletion significantly inhibited K10 and involucrin levels under basal condition and calcium-induced differentiation condition (Fig. 4d, e). We also depleted FBP1 in immortalized HaCaT keratinocytes (Fig. 4f). Similarly, both K10 and involucrin levels were significantly inhibited in shFBP1 cells compared with control cells cultured in basal medium or differentiation medium (Fig. 4f–h). Interestingly, we found morphology of HaCaT cells changed dramatically upon FBP1 depletion. Control cells exhibited polygonal shape and changed from scattered to closely arranged state with calcium treatment, while shFBP1 cells exhibited a small, rounded shape and formed clusters upon calcium treatment (Fig. 4i), indicating the dedifferentiation of shFBP1 cells. We further tested whether shFBP1 cells showed proliferation changes. The growth of shFBP1 HaCaT cells markedly increased compared with that of control cells, on the basis of crystal violet staining and cell numbers (Fig. 4j), indicating FBP1 inhibited keratinocytes proliferation. Additionally, the expression of cytokines IL1B and IL-6 was suppressed in shFBP1 cells under basal condition or after UVB irradiation (Supplementary Fig. 3a–c). Collectively, these results demonstrate that FBP1 promotes differentiation while inhibits proliferation of keratinocytes.
Fig. 4. FBP1 promotes differentiation and inhibits proliferation of keratinocytes.
a Human primary keratinocytes were treated with CaCl2 (1.2 mM) for 0, 3, 6 or 9 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. Exp, exposure. b HaCaT cells were treated with CaCl2 (1.2 mM) for 0, 4, 6 or 8 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. c Human primary keratinocytes were treated with DMSO or 40 μM MB05032 for 2 days and then exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 3 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. d Ctrl shRNA or FBP1 shRNAs (shFBP1-1, shFBP1-2, shFBP1-3) were packaged into lentiviral particles and transduced into keratinocytes. The positive clones were selected by puromycin (2 µg/ml). The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. Exp, exposure. e Keratinocytes stably expressing Ctrl shRNA or FBP1 shRNAs (shFBP1-1, shFBP1-2) were exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 3 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. Exp, exposure. f Ctrl shRNA or FBP1 shRNAs (shFBP1-1, shFBP1-2, shFBP1-3) were packaged into lentiviral particles and transduced into HaCaT cells. The positive clones were selected by puromycin (2 µg/ml). The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. g, h HaCaT cells stably expressing Ctrl, shFBP1-2 (g) or shFBP1-3 (h) were exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 6 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. i HaCaT cells stably expressing Ctrl or shFBP1-2 were exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 3 days before observation by microscopy. Scale bars: 50 µm. j HaCaT cells stably expressing Ctrl or shFBP1-2 were plated (1000 cells/well) and cultured for 2 weeks. The colonies were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted, n = 3 independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Statistical analyses in (j) were performed with Student’s t-tests. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
FBP1 regulates keratinocyte proliferation/differentiation in glycolysis-dependent manner
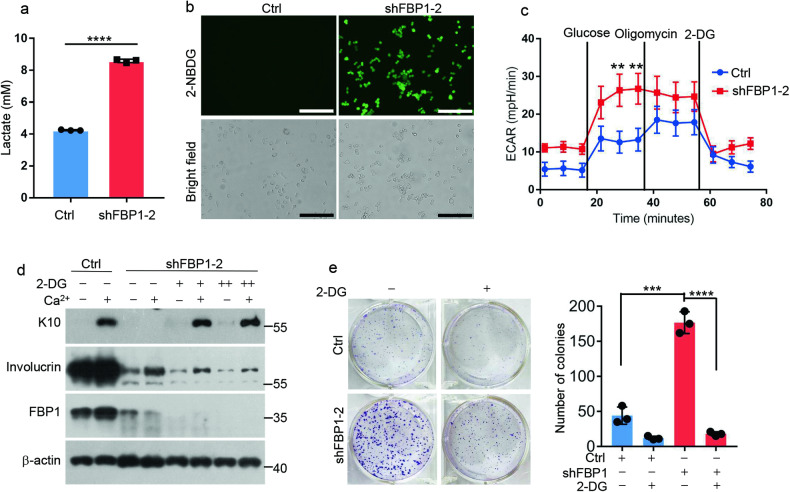
As a rate-limiting gluconeogenic enzyme, FBP1 inhibits glucose uptake and glycolysis. To determine whether FBP1 regulates glycolytic metabolism in keratinocytes, we compared glycolysis between control and shFBP1 HaCaT cells. Depletion of FBP1 dramatically promoted lactate production and glucose uptake (Fig. 5a, b). To further examine the ability of shFBP1 cells to metabolize glucose, we measured the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) using a Seahorse XF extracellular flux instrument. ShFBP1 cells exhibited enhanced ECAR compared with control cells upon the addition of glucose to the culture media (Fig. 5c). Furthermore, injection of oligomycinA, which inhibits mitochondrial ATP production and induces maximal glycolytic rates, failed to further increase ECAR in shFBP1 cells, indicating shFBP1 cells maintained the maximum glycolytic capacity in the presence of glucose (Fig. 5c). These experiments suggested that FBP1 loss enhanced glycolysis in keratinocytes. To investigate whether FBP1 regulated keratinocytes proliferation/differentiation in glycolysis-dependent manner, we treated shFBP1 cells with 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG), a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism. Inhibition of K10 expression in shFBP1 cells was fully reversed by administration of 2-DG (Fig. 5d). However, the involucrin levels were not altered by 2-DG treatment in shFBP1 cells. One possible reason was that 2-DG induced the unfolded protein response and affected protein translation as 2-DG is also chemically identical with 2-deoxymannose [5, 30]. Meanwhile, the increased growth of shFBP1 HaCaT cells was suppressed by 2-DG treatment, assessed by crystal violet staining and cell numbers (Fig. 5e). Thus, FBP1 regulates keratinocytes proliferation/differentiation through glycolysis.
Fig. 5. FBP1 regulates keratinocyte proliferation/differentiation in glycolysis-dependent manner.
a Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were incubated for an additional 24 h in growth medium 3 days after plating. Medium was collected and lactate content was measured, n = 3 independent experiments. b Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were treated with 2-NBDG (100 μM) for 30 min and images were taken with an excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 535 nm. Scale bars: 100 µm. c Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) of Ctrl and shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were detected using a Seahorse XF extracellular flux instrument, n = 3 independent experiments. d Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were treated with 0 mM (−), 1 mM (+) or 2 mM (++) 2-DG for 2 days, and then exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 6 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. e Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were plated (1000 cells/well) and cultured with or without 1 mM 2-DG for 2 weeks. The colonies were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted, n = 3 independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Statistical analyses in (a), (c) and (e) were performed with Student’s t-tests. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
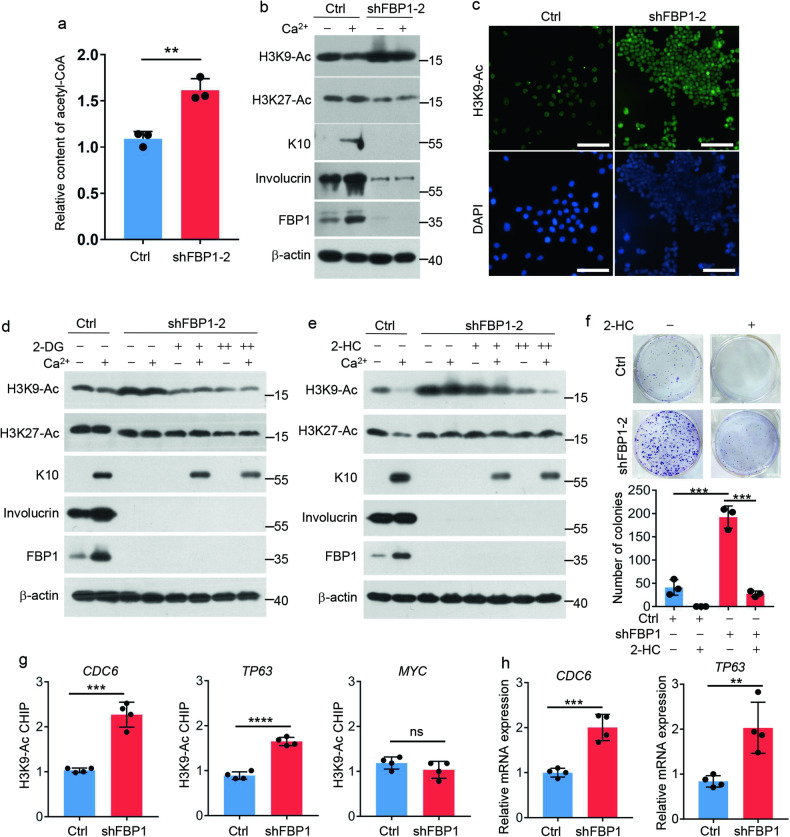
FBP1 loss promotes acetyl-CoA production and histone acetylation
In mammalian cells, glycolysis drives synthesis of citrate, which is converted to acetyl-CoA by ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY). As a critical second messenger, acetyl-CoA controls key cellular processes, including energy metabolism, mitosis, and autophagy through influencing the acetylation profile of several proteins [31]. Thus, we detected whether enhanced glycolysis promoted acetyl-CoA production in FBP1-depleted cells. Indeed, acetyl-CoA levels were higher in shFBP1 cells compared to control cells (Fig. 6a). Acetyl-CoA was shown to be rate limiting for histone acetylation [31], thus, we speculated increased acetyl-CoA in shFBP1 cells might affect the histone acetylation state. To test this hypothesis, we detected global histone 3 acetylation at lysine K9 (H3K9-Ac) and K27 (H3K27-Ac), marks that are associated with chromatin opening and transcription. We observed increased H3K9-Ac in shFBP1 cells compared with control cells (Fig. 6b, c). Indeed, intracellular acetyl-CoA levels were reported to induce the Gcn5-catalyzed H3K9-Ac [32, 33]. However, H3K27-Ac had no obvious changes upon FBP1 depletion, even slightly downregulated (Fig. 6b). These results demonstrated that FBP1 loss promoted acetyl-CoA production and H3K9-Ac. Next, we sought to link the change in histone acetylation to the shift in glycolysis and acetyl-CoA in FBP1-depleted cells. Inhibition of glycolysis by 2-DG or inhibition of acetyl-CoA production by 2-hydroxycitrate (2-HC), a competitive inhibitor of ACLY, decreased H3K9-Ac levels in shFBP1 cells (Fig. 6d,e), suggesting increased histone acetylation in FBP1-depleted cells was through glycolysis-mediated acetyl-CoA. Furthermore, 2-HC significantly reversed both the suppressed differentiation and accelerated proliferation in shFBP1 cells, as detected by K10 expression and clone numbers (Fig. 6e, f), demonstrating FBP1 regulates keratinocytes proliferation/differentiation in acetyl-CoA-dependent manner.
Fig. 6. FBP1 loss promotes acetyl-CoA production and histone acetylation.
a 1 × 106 Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were harvested and acetyl-CoA levels in HaCaT cells were detected by acetyl-CoA Assay. Values were expressed as fold differences compared to Ctrl, n = 3 independent experiments. b Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 6 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. c Immunostaining for H3K9-Ac (green) in Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells. The nuclei were stained by DAPI. Scale bars: 100 μm. d Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were treated with 0 mM (−), 1 mM (+) or 2 mM (++) 2-DG for 2 days, and then exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 6 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. e Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were treated with 0 mM (−), 2.5 mM (+) or 5 mM (++) 2-HC for 2 days, and then exposed to 0.06 mM (−) or 1.2 mM (+) calcium for 6 days before collection. The indicated proteins were detected by western blots. f Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells were plated (1000 cells/well) and cultured with or without 2.5 mM 2-HC for 2 weeks. The colonies were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted, n = 3 independent experiments. g H3K9-ac abundance on indicated genes in Ctrl or shFBP1-2 HaCaT cells was detected by H3K9-ac immunoprecipitation and qPCR. Values were expressed as fold differences compared to Ctrl, n = 4 independent experiments. h Relative mRNA levels of CDC6 and TP63 in Ctrl and shFBP1 HaCaT cells, n = 4 independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Statistical analyses in (a), (f), (g) and (h) were performed with Student’s t-tests. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns not significant.
Intracellular acetyl-CoA levels had been reported to induce the H3K9-Ac at genes important for growth, thereby enabling their rapid transcription and commitment to growth [32]. To examine the abundance of H3K9-Ac at growth genes, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation–qPCR (ChIP–qPCR) analysis. Compared with control cells, H3K9-Ac at CDC6 (cell division cycle 6) and TP63 (tumor protein p63) genes were more abundant in shFBP1 cells (Fig. 6g), in accord with the increased transcript levels of CDC6 and TP63 in shFBP1 cells (Fig. 6h), which explained the rapid proliferation and dedifferentiation phenotype of FBP1-depleted keratinocytes. Together, these results demonstrate that FBP1 loss promotes acetyl-CoA production, which increases H3K9-Ac at growth-related genes such as CDC6 and TP63, thus enabling their rapid transcription and cell proliferation.
Fbp1 deficiency aggravates psoriasis models
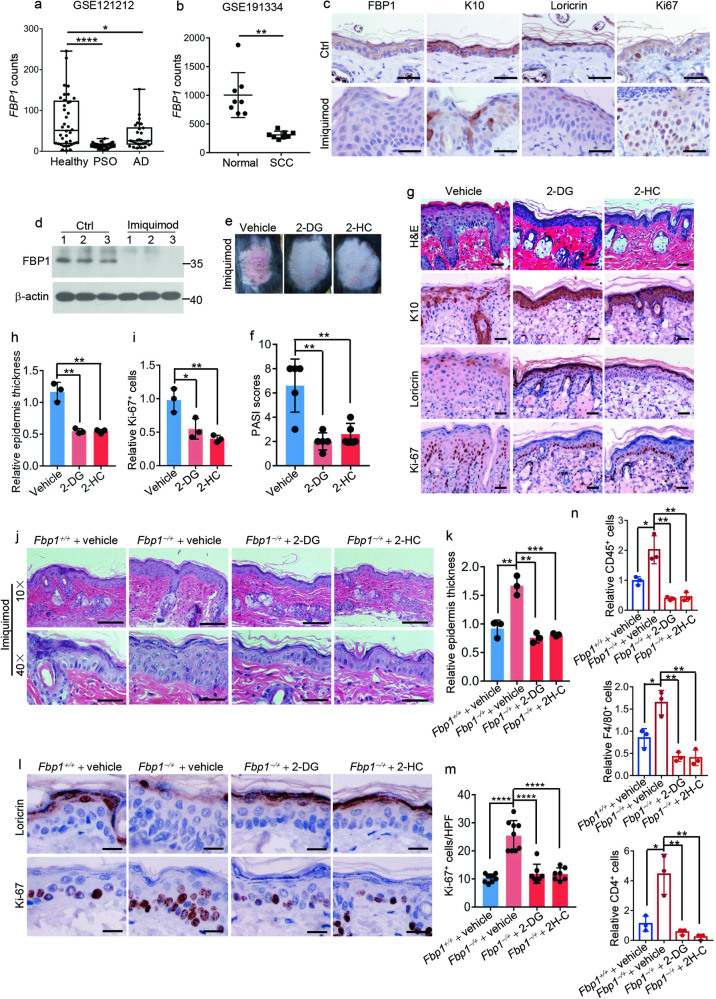
Psoriasis is a chronic cytokine-driven, inflammatory skin disease characterized by hyperplasia and abnormal differentiation of the epidermis that presents as thickened and scaly plaques. Keratinocyte hyperproliferation is triggered pathologically in psoriasis. To explore whether FBP1 participated in psoriasis pathogenesis, we examined FBP1 expression in biopsies from people with psoriasis and healthy controls using a publicly available RNA-seq dataset (Gene Expression Omnibus database: accession no. GSE121212). In comparison with healthy controls, FBP1 expression significantly decreased in skin lesions from patients with psoriasis, and to a less extent, decreased in skin lesions from patients with atopic dermatitis (Fig. 7a). Meanwhile, the LORICRIN expression was downregulated while the CDC6 expression was upregulated in skin lesions from patients with psoriasis, demonstrating reduced differentiation and increased proliferation in psoriatic lesions (Supplementary Fig. 4a, b). Additionally, we also found FBP1 and CDC6 levels were dramatically reduced in skin lesions from patients with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) using dataset GSE191334 (Fig. 7b and Supplementary Fig. 4c), implicating FBP1 might also participate in SCC development. We further established the mice model of psoriasis through topical application of imiquimod. The imiquimod-treated mice developed psoriasiform lesions characterized by epidermal acanthosis (Supplementary Fig. 4d), with reduced expression of differentiation marker K10, Loricrin and increased expression of proliferation marker Ki-67 (Fig. 7c). Fbp1 expression was downregulated in psoriasiform lesions of imiquimod-treated mice (Fig. 7c, d). The imiquimod-induced psoriasiform lesions were alleviated by topical application of 2-DG or 2-HC (Fig. 7e, f) compared to vehicle-treated mice, demonstrating glycolysis and acetyl-CoA production participated in this progress. 2-DG or 2-HC application also decreased psoriasiform hyperplasia, epidermis thickness and proliferating (Ki-67+) cells, while increased differentiation markers (K10, Loricrin) expression in psoriasiform lesions (Fig. 7g–i) compared to vehicle-treated mice. Furthermore, the number of infiltrated leukocytes (CD45+), macrophages (F4/80+) and T cells (CD4+) in psoriasiform skin lesions were also significantly reduced by 2-DG or 2-HC treatment (Supplementary Fig. 4e, f) compared to vehicle-treated mice. Thus, inhibition of glycolysis or acetyl-CoA production largely normalized keratinocyte proliferation/differentiation and decreased immune cell infiltration in mice psoriasis model.
Fig. 7. Fbp1 deficiency aggravates psoriasis models.
a FBP1 levels in healthy skin, psoriatic lesions or atopic dermatitis lesions based on RNA-Seq datasets from public databases GSE121212. b FBP1 levels in normal skin or squamous cell carcinoma based on GSE191334. c Immunohistochemical staining for FBP1, K10, loricrin and Ki-67 of skin from Ctrl or imiquimod-treated mice. Scale bars: 50 μm. d Western blot analysis of the expression of FBP1 and β-actin in skin tissues from Ctrl or imiquimod-treated mice. e Photos of skin lesions from vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated mice after 8 days treatment with imiquimod. f The Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score for imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated mice, n = 5 mice per group. g Representative H&E staining or immunohistochemical staining for K10, loricrin and Ki-67 of imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated mice. Scale bars: 50 μm. h Relative epidermis thickness for imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated mice, n = 3 mice per group. i Relative Ki-67+ keratinocytes for imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated mice, n = 3 mice per group. j Representative H&E staining of skin lesions from vehicle pretreated Fbp1+/+ mice, vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated Fbp1−/+ mice after 5 days treatment with imiquimod. Scale bars in upper images: 200 μm, scale bars in lower images: 50 μm. k Relative epidermis thickness for imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle pretreated Fbp1+/+ mice, vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated Fbp1−/+ mice, n = 3 mice per group. l Immunohistochemical staining for loricrin and Ki-67 of imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle pretreated Fbp1+/+ mice, vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated Fbp1−/+ mice. Scale bars: 25 μm. m The quantification of Ki-67+ keratinocytes in imiquimod-induced skin lesions from vehicle pretreated Fbp1+/+ mice, vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated Fbp1−/+ mice, n = 3 mice per group. HPF high-power field. n Relative leukocytes (CD45+), macrophages (F4/80+) or T cells (CD4+) numbers of imiquimod-induced skin lesions (8 days) from vehicle pretreated Fbp1+/+ mice, vehicle, 2-DG or 2-HC pretreated Fbp1−/+ mice, n = 3 mice per group. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Statistical analyses in (a), (b), (f), (h), (i), (k), (m), (n) were performed with Student’s t-tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
We further tested whether Fbp1 deficiency affect the development of pathological hyperplasia in psoriasis models. Fbp1−/+ mice exhibited increased scales and higher PASI scores in comparison to Fbp1+/+ mice (Supplementary Fig. 4g, h). Histological analysis demonstrated aggravated psoriasiform hyperplasia and increased epidermis thickness in Fbp1−/+ mice compared with Fbp1+/+ mice (Fig. 7j,k). Furthermore, the skin of Fbp1−/+ mice showed lower Loricrin expression and higher Ki-67 numbers than that of Fbp1+/+ mice (Fig. 7l, m), demonstrating decreased differentiation and increased proliferation in psoriasiform lesions of Fbp1−/+ mice. The number of infiltrated immune cells was also increased in psoriasis-like skin lesions of Fbp1−/+ mice (Fig. 7n and Supplementary Fig. 4i). These results suggest that Fbp1 deficiency aggravates psoriasis-like phenotype in imiquimod-treated mice.
We next examined whether 2-DG or 2-HC alleviated psoriasis-like phenotype in Fbp1−/+ mice. Indeed, topical application of 2-DG or 2-HC decreased scale, inhibited psoriasiform hyperplasia and skin thickening (Supplementary Fig. 4g, h and Fig. 7j, k) compared to vehicle-treated Fbp1−/+ mice. The skin lesions of 2-DG or 2-HC treated Fbp1−/+ mice showed higher Loricrin expression and lower Ki-67 staining than that of vehicle-treated Fbp1−/+ mice (Fig. 7l, m). The infiltration of leukocytes (CD45+), macrophages (F4/80+) and T cells (CD4+) was also attenuated by 2-DG or 2-HC treatment compared to vehicle treatment (Fig. 7n and Supplementary Fig. 4i). Thus, Fbp1 loss aggravates psoriasis-like skin lesions partially through glycolysis and acetyl-CoA production.
Discussion
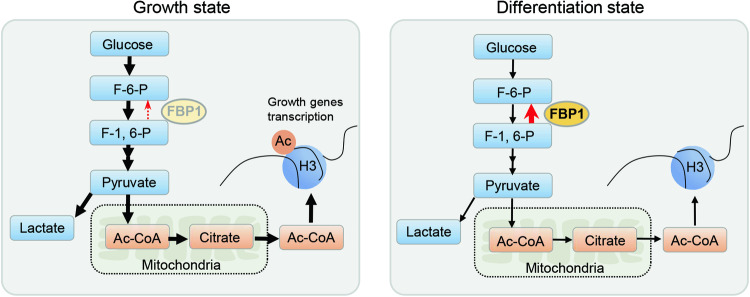
The epidermis is a self-renewal tissue that protects the body against environmental insults and excess water loss. Emerging studies reveal glycolytic enzymes contribute to this essential process [34]. However, the role of gluconeogenic enzymes in epidermis has not been explored. Here we provide genetic evidence that the gluconeogenic enzyme FBP1 participates in epidermal homeostasis and response to UVB irradiation. FBP1 loss promotes proliferation and maintains dedifferentiation state of keratinocytes. Mechanistically, FBP1 deficiency facilitates glycolysis-mediated acetyl-CoA production, thereby resulting in increased H3K9 acetylation and enhanced transcription of proliferation genes (Fig. 8). Moreover, Fbp1 loss aggravates psoriasis-like skin lesions through glycolysis and acetyl-CoA in the mice imiquimod psoriasis model.
Fig. 8. Working model for cell state transition controlled by FBP1.
FBP1 controls keratinocyte state through regulating glycolysis and acetyl-CoA production, which determines histone acetylation level at growth genes.
We provide several evidences that FBP1 regulates proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes. First, FBP1 expression is induced by UVB irradiation, especially in upper epidermis and parallels the expression of epidermal differentiation marker. Second, genetic ablation of Fbp1 in mice results in local epidermal hyperplasia featured by increased proliferation and decreased differentiation of keratinocytes. Third, FBP1 loss promotes proliferation and maintains the dedifferentiation state of keratinocytes in vitro. Additionally, we also found FBP1 depletion abolishes expression of inflammation cytokines IL1B and IL-6 in keratinocytes. As IL-1 and IL-6 play key roles in inflammatory responses to triggers and wound healing [35–39], FBP1 may also participate in these processes which need further investigation.
Metabolites generated during glycolytic and oxidative processes are utilized in enzymatic reactions leading to epigenetic modifications and transcriptional regulation, thus facilitating the transition from one cell type to another (e.g., differentiation) [40–42]. Metabolic reprogramming of epigenetics is involved in a variety of processes such as cell fate, development, cancer and trained immunity [40, 43, 44]. The link between metabolism and epigenetic machinery in keratinocytes is less clarified. Here we find the increased metabolite acetyl-CoA accounts for the elevated H3K9 acetylation in FBP1 deficient keratinocytes, which is essential for growth-related genes transcription and cell proliferation.
Psoriasis is a common skin disorder characterized by abnormal immune cell infiltration and cytokine-driven epidermal hyperplasia [45]. Although many therapies can reduce symptoms, psoriasis has no known cure [1]. Several studies have shown that dysregulated metabolic pathways are linked to psoriasis pathogenesis. Compared with healthy individuals, patients with psoriasis have higher levels of lactic acid and amino acids, indicating the involvement of glycolysis and amino acid metabolic pathway [46, 47]. Indeed, dimethyl fumarate, an immunomodulatory drug used to treat psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, was recently shown to mediate anti-inflammatory effects through inactivating the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in activated myeloid and lymphoid cells [48]. Here we find FBP1 is dramatically reduced in human psoriatic lesions and in skin of mice imiquimod psoriasis model, in vivo study demonstrates Fbp1 deficiency facilitates psoriasis-like skin lesions development through glycolysis and acetyl-CoA. Fbp1 deficiency also promotes the inflammatory infiltration in animal models of psoriasis in glycolysis and acetyl-CoA-dependent manner. Consistent with previously reported roles for glycolysis in T lymphocyte activation [49, 50], we speculate that Fbp1 deficiency might also facilitate glycolysis in other cell types in the skin, including infiltrating lymphocytes, and thereby aggravate inflammation in vivo. Thus, targeting glycolysis or acetyl-CoA production may represent potential treatment for psoriasis patients with reduced FBP1 expression in skin lesions. Additionally, the glycolytic enzyme PFKFB3 is overexpressed in the skin of psoriasis patients, and in the skin of IMQ-mouse model [5, 51], which may well be involved in the activation of glycolysis, together with the downregulation of FBP1. Moreover, consistent with the decreased expression of FBP1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma [13–16], we find FBP1 is also downregulated in SCC, implicating the tumor suppressive role of FBP1 in skin carcinoma. Furthermore, the exact role of FBP1 in other proliferative skin diseases also deserves future exploration.
Using pathway specific inhibitors, we find FBP1 expression is partially regulated by p38 MAPK pathways and NF-κB pathways. However, other mechanisms may also exist as these inhibitors cannot completely silence FBP1 expression. For example, promoter methylation may also participate in regulating FBP1 levels in skin as FBP1 promoter exhibits higher methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma than in normal liver tissues [15]. Importantly, elucidating the reason why FBP1 is downregulated in psoriasis may help to restore FBP1 level and alleviate psoriasis in the future.
Since Fbp1 gene is inactivated in the whole mouse in this study, some of the observed phenotype in Fbp1−/+ mice might be due to the deficiency of the enzyme in other types of cells and not only in keratinocytes, for example, immune cells, thus keratinocyte-specific ablation of Fbp1 in mice should be conducted in the future to elucidate the exact role of FBP1 in keratinocytes in vivo.
In summary, our study reveals that FBP1 plays critical role in normal skin homeostasis and response to external stimuli, and identifies that FBP1 loss promotes cell state transition and facilitates psoriasis-like skin lesions through metabolite-mediated epigenetic alteration.
Material and methods
Animals
Fbp1 heterozygous (Fbp1−/+) mice, generated through the CRISPR-Cas9-mediated deletion of exon 2 to exon 4 of the Fbp1 gene, were bought from GemPharmatech (Nanjing, Jiangsu, China). Fbp1 homozygous (Fbp1−/−) mice were obtained by crossing female and male Fbp1−/+ mice. All mice were on the C57BL/6 J background and maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions. All experimental procedures in mice were approved by the Laboratory Animal Center of Chinese Academy of Military Medical Sciences and complied with all relevant ethical regulations. They were conducted according to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. For the imiquimod-induced psoriasiform hyperplasia model, 6-week-old mice were shaved and chemically depilated. The shaved dorsal-skin samples were treated topically with 50 mg of 5% imiquimod (Aldara, 3 M Pharmaceuticals) daily. Skin tissues were harvested after 5 or 8 days of treatment. 2-DG (D807272, Macklin, Shanghai, China) or 2-HC (P815515, Macklin, Shanghai, China) was dissolved in water. For 2-DG or 2-HC treatment, mice were randomly assigned to receive 2-DG (0.5%, 100 μl), 2-HC (1%, 100 μl), or water vehicle control (100 μl), respectively. The treatment was applied topically immediately before imiquimod treatment.
Cell culture and transfection
Human primary keratinocytes were bought from Biocell Biotechnology (Guangdong, China), and grown in ready-to-use keratinocyte growth medium (PromoCell, C-20011) supplemented with Supplement Mix (PromoCell, C-20011) and 0.06 mmol/L CaCl2. HaCaT cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and cultured in calcium free MEM (Sigma, M0518) supplemented with 0.06 mmol/L CaCl2 and 10% FBS in which calcium was removed by Chelex 100 (Macklin, I832447). For differentiation of keratinocytes, CaCl2 was added to the medium to 1.2 mmol/L. For IL-6 or TP63 knockdown, cells were transfected with indicated siRNA using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen) reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Cells were collected and indicated proteins were analyzed by western blot 72 h after transfection. SiRNA target sequences were listed in Supplementary Table. For adezmapimod (MCE, HY-10256) or BAY 11-7082 (MCE, HY-13453) treatment, cells were collected and indicated proteins were analyzed by western blot 48 h after treatment.
Human epidermis equivalents
Keratinocytes harvested and suspended in ice-cold medium (PromoCell, C-20011) containing 1.2 mM calcium were seeded on polycarbonate culture inserts (0.4 μm pores in diameter, Snapwell permeable supports, Costar, 3407). After 24 h of incubation at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2, cells were exposed to the air–liquid interface, and 50 μg/ml vitamin C (Sigma, A92902) and 10 ng/ml keratinocyte growth factor (PeproTech, 100-19) were added to the medium in the lower compartment. The medium was renewed every day during the air–liquid interface culture.
UVB irradiation
The TL 20W/12RS fluorescent lamp (Philips, Eindhoven, Holland) was used to irradiate the mice, human epidermis equivalents or keratinocytes. The power of the lamp was 431 μW/cm2 detected by a UV-AB meter (Tenmars, TM-213). The mice or human epidermis equivalents were placed 40 cm below the light source and irradiated. Vertical movement of mice was restrained by a wire screen.
RNA-seq data analysis
Reference genome and gene model annotation files were downloaded from genome website browser Ensembl directly. Indexes of the reference genome were built using Bowtie v2.0.6 and paired-end clean reads were aligned to the reference genome using TopHat v2.0.9. Cufflinks v2.1.1 was used to count the fragment numbers mapped of each gene. And then FPKM of each gene was calculated based on the length of the gene and fragments count mapped to this gene. Differential expression analysis between three groups (Control, UVB_24 h and UVB_72 h) was performed using the DESeq2 R package (1.32.0). Genes with Q-value < 0.001 and log2FC > 1 found by DESeq2 were selected. Correlation was determined using the cor. test function in R with method = “Pearson”. Pathway analyses were performed using GSEA software (4.0.3) and Cluster Profiler (4.4.2) package in R (4.1.1).
Histology
Paraffin-embedded skin specimens were sectioned, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and visualized using a light microscope (Nikon, Eclipse 80i, Japan). Epidermal thickness was measured using ImageJ software.
Immunohistochemistry
For immunohistochemical analysis, 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed sections were blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin and incubated with primary antibodies against FBP1 (Proteintech, 12842-1-AP), keratin 10 (Abcam, ab76318), loricrin (Abcam, ab198994), IL-1β (Abclonal, A16288), IL-8 (Proteintech, 27095-1-AP), Ki-67 (Cell Signaling Technology, 12202), CD45 (Abcam, ab10558), F4/80 (Abcam, ab6640), CD4 (Abcam, ab183685) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue sections were incubated with biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG (Vector Laboratories, BA-1000) for 30 min at room temperature. The antigen–antibody binding was detected by 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (Solarbio, DA1016) system. Tissue sections were briefly immersed in hematoxylin for counterstaining and were covered with cover glasses.
Immunocytochemistry
For immunocytochemical analysis, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton-X-100/PBS and blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin. Cells were incubated with primary antibodies against H3K9-ac (Zen-bio, 340016) overnight at 4 °C. Cells were then incubated with the corresponding CoraLite488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Proteintech, SA00013) for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were mounted with mounting medium with DAPI. Images were taken using Cytation 5 Cell Imaging Multimode Reader (Biotek).
Western blots
For western blots, samples of cells or tissues were separated on SDS–PAGE gels, transferred to PVDF membranes and probed with primary antibodies to the following proteins: keratin 10 (Abcam, ab76318), involucrin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-21748), FBP1 (Proteintech, 12842-1-AP), β-actin (Proteintech, 20536-1-AP), IL-1β (Proteintech, 16806-1-AP), IL-6 (Proteintech, 21865-1-AP), H3K9-ac (Zen-bio, 340016), β-tubulin (Zen-bio, 200608), H3K27-ac (Abclonal, A7253), p63 (Zen-bio, 381215). Samples were then stained with secondary antibodies conjugated to HRP at a dilution of 1:5000 (Santa Cruz, donkey anti-rabbit, SC2077 and donkey anti-mouse, SC2096) and detected with an ECL system (PerkinElmer, NEL104001EA). Full and uncropped western blots can be found in the Supplementary Material.
Reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from epidermal preparations using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, 15596026). Two micrograms total RNA was reverse transcribed using TransScript One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (TransGen Biotech, AT311-02). Gene expression analysis was performed on Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher). Gene expression was analyzed using TransStart Green qPCR SuperMix (TransGen Biotech, AQ101-01) at the following conditions: 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation (95 °C for 5 s), annealing and extension (30 s at temperature experimentally determined for each primer pair). Amplification differences between samples and controls were calculated based on the Ct (ΔΔCt) method and normalized to GAPDH. RT-qPCR primers were listed in Supplementary Table.
Lentivirus packaging and infection
Lentiviral vectors (GV248) carrying FBP1 shRNA were from GeneChem Company (China). The vector was transfected into HEK293T cells together with pSPAX.2 and pMD.2G for 24 h, and cell culture media were collected and filtered. The viral particles were precipitated by Polyethylene glycol 8000 (0.05 g/ml) and then used to infect cells. Cells were cultured in medium containing 2 μg/ml puromycin (MCE, HY-B1743A) for the selection of stable clones 3 days post infection. The positive clones were identified and verified by western blots. The FBP1 shRNA target sequences were as follows: shFBP1-1: 5′-CCTTGATGGATCTTCCAACAT-3′, shFBP1-2: 5′-CGACCTGGTTATGAACATGTT-3′, shFBP1-3: 5′-CAGCAGTCAAAGCCATCTCTT-3′.
Glucose uptake assay
Glucose uptake in HaCaT cells was measured by analysis of 2-NBDG taken up by cells using 2-NBDG Glucose Uptake Assay Kit (BioVision, K682-50). Images were taken using Cytation 5 Cell Imaging Multimode Reader (Biotek) with an excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 535 nm.
Lactate measurement
HaCaT cells were incubated for an additional 24 h in fresh growth medium 3 days after plating. Medium was collected on ice, centrifuged for 10 min at 2500 r.p.m. at 4 °C and lactate contents were measured by cobas c311 analyzer (Roche) according to the operator’s manual. The values were normalized to the total cellular protein level.
ECAR measurement
ECAR was measured using Agilent Seahorse XF Glycolysis Stress Test Kit (Agilent Technologies, 103020-100). Briefly, HaCaT cells were resuspended with MEM medium and plated into Seahorse XFe Microplate by 10,000 cells/well, then the plate was incubated at 37 °C overnight. Glucose (10 mM, Sigma, G8644), oligomycin (10 µM, Sigma, 75351) and 2-DG (50 mM, Sigma, D8375) solution was sequentially added into the appropriate ports of a hydrated sensor cartridge. To evaluate ECAR, the calibration plate was replaced with the cell culture microplate, and the “Start” button was pressed.
Acetyl-CoA assay
Acetyl-CoA levels in HaCaT cells were determined by Acetyl-Coenzyme A Assay Kit (Sigma, MAK039). Fluorescence intensity was detected using Cytation 5 Cell Imaging Multimode Reader (Biotek) with an excitation wavelength of 535 nm and an emission wavelength of 587 nm. Values were expressed as fold differences compared to control.
Colony formation assay
For colony formation assay, HaCaT cells were diluted to the single cell suspension and 1000 cells were cultured in every well of six-well plate at 5% CO2 incubator for 2 weeks. Then the colonies were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay and qPCR
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were performed using the Simple ChIP Plus Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kit (Cell Signaling Technology, 9005) according to the product manual. Quantitative Real-Time PCR was used to measure the amount of enrichment of a particular DNA sequence by histone H3 (Cell Signaling Technology, 4620) or H3K9ac (Zen-bio, 340016) immunoprecipitation. Ct value detected from H3K9ac immunoprecipitates were normalized by Ct value from histone H3 immunoprecipitates. Amplification differences between samples and controls were calculated based on the Ct (ΔΔCt) method. QPCR primers were list in Supplementary Table.
Statistical analysis
The statistical significance of differences between two groups was calculated with the two-tailed Student’s t-test, and error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (s.d.). Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 7. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Innovation Team and Talents Cultivation Program of the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ZYYCXTD-D-202207, YG), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2021-QNRC1-03, WZ) and Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Toxicology, Grant/Award Number: 2020HJDL04.
Author contributions
PZ and XL performed all of the experiments with the assistance of CH, PS and LZ. JY and YT drafted the manuscript. ZB, CX, GL and LZ read and revised the manuscript. WZ and YG designed this study. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Data availability
Gene expression profile of human epidermal equivalents has been deposited into Figshare (10.6084/m9.figshare.21299496.v1).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Chinese Academy of Military Medical Sciences and carried out in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (US NIH, 2011).
Footnotes
Edited by Massimiliano Agostini
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Pengfei Zhang, Ju Yang, Xiong Liu.
Contributor Information
Wei Zhou, Email: zhouweisyl802@163.com.
Yue Gao, Email: gaoyue@bmi.ac.cn.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41419-024-06706-6.
References
- 1.Boehncke WH, Schon MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983–94. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61909-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lowes MA, Bowcock AM, Krueger JG. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature. 2007;445:866–73. doi: 10.1038/nature05663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cruickshank CN, Trotter MD. The oxygen uptake, glucose utilization and lactic acid production of guinea-pig skin in relation to oxygen tension. Biochemical J. 1956;62:57–61. doi: 10.1042/bj0620057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cruickshank CN, Trotter MD, Cooper JR. Studies on the carbohydrate metabolism of skin. Biochemical J. 1957;66:285–9. doi: 10.1042/bj0660285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hamanaka RB, Mutlu GM. PFKFB3, a direct target of p63, is required for proliferation and inhibits differentiation in epidermal keratinocytes. J Investig Dermatol. 2017;137:1267–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.12.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhou X, Chen Y, Cui L, Shi Y, Guo C. Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: from keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:81. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04523-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang Z, Zi Z, Lee EE, Zhao J, Contreras DC, South AP, et al. Differential glucose requirement in skin homeostasis and injury identifies a therapeutic target for psoriasis. Nat Med. 2018;24:617–27. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0003-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu YZ, Xu MY, Dai XY, Yan L, Li L, Zhu RZ, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 mediates glycolysis contributes to psoriasis by promoting keratinocyte proliferation. Front Pharm. 2021;12:765790. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.765790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Veras FP, Publio GA, Melo BM, Prado DS, Norbiato T, Cecilio NT, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammation. Cell Rep. 2022;41:111897. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang Z, Li M, Jiang H, Luo S, Shao F, Xia Y, et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 functions as a protein phosphatase to dephosphorylate histone H3 and suppresses PPARalpha-regulated gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat Cell Biol. 2022;24:1655–65. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-01009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhu W, Chu H, Zhang Y, Luo T, Yu H, Zhu H, et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 dephosphorylates IkappaBalpha and suppresses colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 2023;33:245–57. doi: 10.1038/s41422-022-00773-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Emery JL, Howat AJ, Variend S, Vawter GF. Investigation of inborn errors of metabolism in unexpected infant deaths. Lancet. 1988;2:29–31. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(88)92955-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li B, Qiu B, Lee DS, Walton ZE, Ochocki JD, Mathew LK, et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase opposes renal carcinoma progression. Nature. 2014;513:251–5. doi: 10.1038/nature13557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dong C, Yuan T, Wu Y, Wang Y, Fan TW, Miriyala S, et al. Loss of FBP1 by Snail-mediated repression provides metabolic advantages in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:316–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.01.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hirata H, Sugimachi K, Komatsu H, Ueda M, Masuda T, Uchi R, et al. Decreased expression of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase associates with glucose metabolism and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016;76:3265–76. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li F, Huangyang P, Burrows M, Guo K, Riscal R, Godfrey J, et al. FBP1 loss disrupts liver metabolism and promotes tumorigenesis through a hepatic stellate cell senescence secretome. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:728–39. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0511-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.van Poelje PD, Potter SC, Chandramouli VC, Landau BR, Dang Q, Erion MD. Inhibition of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase reduces excessive endogenous glucose production and attenuates hyperglycemia in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Diabetes. 2006;55:1747–54. doi: 10.2337/db05-1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kebede M, Favaloro J, Gunton JE, Laybutt DR, Shaw M, Wong N, et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase overexpression in pancreatic beta-cells results in reduced insulin secretion: a new mechanism for fat-induced impairment of beta-cell function. Diabetes. 2008;57:1887–95. doi: 10.2337/db07-1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Visinoni S, Khalid NF, Joannides CN, Shulkes A, Yim M, Whitehead J, et al. The role of liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in regulating appetite and adiposity. Diabetes. 2012;61:1122–32. doi: 10.2337/db11-1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gu L, Zhu Y, Watari K, Lee M, Liu J, Perez S, et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is a nonenzymatic safety valve that curtails AKT activation to prevent insulin hyperresponsiveness. Cell Metab. 2023;35:1009–21.e1009. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tanaka Y, Castillo L, DeLuca HF. The 24-hydroxylation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Biol Chem. 1977;252:1421–4. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)40673-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bikle DD, Nemanic MK, Gee E, Elias P. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 production by human keratinocytes. Kinetics and regulation. J Clin Investig. 1986;78:557–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI112609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bar M, Domaschke D, Meye A, Lehmann B, Meurer M. Wavelength-dependent induction of CYP24A1-mRNA after UVB-triggered calcitriol synthesis in cultured human keratinocytes. J investig Dermatol. 2007;127:206–13. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Henry J, Hsu CY, Haftek M, Nachat R, de Koning HD, Gardinal-Galera I, et al. Hornerin is a component of the epidermal cornified cell envelopes. FASEB J. 2011;25:1567–76. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-168658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Makino T, Yamakoshi T, Mizawa M, Shimizu T. Ultraviolet B irradiation induces the expression of hornerin in xenotransplanted human skin. Acta Histochem. 2014;116:20–4. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2013.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dumas SN, Guo CA, Kim JK, Friedline RH, Ntambi JM. Interleukin-6 derived from cutaneous deficiency of stearoyl-CoA desaturase- 1 may mediate metabolic organ crosstalk among skin, adipose tissue and liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:87–91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Peus D, Vasa RA, Beyerle A, Meves A, Krautmacher C, Pittelkow MR. UVB activates ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways via reactive oxygen species in cultured keratinocytes. J Investig Dermatol. 1999;112:751–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lewis DA, Spandau DF. UVB-induced activation of NF-kappaB is regulated by the IGF-1R and dependent on p38 MAPK. J Investig Dermatol. 2008;128:1022–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Erion MD, van Poelje PD, Dang Q, Kasibhatla SR, Potter SC, Reddy MR, et al. MB06322 (CS-917): a potent and selective inhibitor of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase for controlling gluconeogenesis in type 2 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:7970–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502983102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xi H, Kurtoglu M, Lampidis TJ. The wonders of 2-deoxy-D-glucose. IUBMB Life. 2014;66:110–21. doi: 10.1002/iub.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pietrocola F, Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Madeo F, Kroemer G. Acetyl coenzyme A: a central metabolite and second messenger. Cell Metab. 2015;21:805–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cai L, Sutter BM, Li B, Tu BP. Acetyl-CoA induces cell growth and proliferation by promoting the acetylation of histones at growth genes. Mol Cell. 2011;42:426–37. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jin Q, Yu LR, Wang L, Zhang Z, Kasper LH, Lee JE, et al. Distinct roles of GCN5/PCAF-mediated H3K9ac and CBP/p300-mediated H3K18/27ac in nuclear receptor transactivation. EMBO J. 2011;30:249–62. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cibrian D, de la Fuente H, Sanchez-Madrid F. Metabolic pathways that control skin homeostasis and inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26:975–86. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2020.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Murphy JE, Robert C, Kupper TS. Interleukin-1 and cutaneous inflammation: a crucial link between innate and acquired immunity. J Investig Dermatol. 2000;114:602–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Palmer G, Talabot-Ayer D, Kaya G, Gabay C. Type I IL-1 receptor mediates IL-1 and intracellular IL-1 receptor antagonist effects in skin inflammation. J Investig Dermatol. 2007;127:1938–46. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gallucci RM, Simeonova PP, Matheson JM, Kommineni C, Guriel JL, Sugawara T, et al. Impaired cutaneous wound healing in interleukin-6-deficient and immunosuppressed mice. FASEB J. 2000;14:2525–31. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0073com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lin ZQ, Kondo T, Ishida Y, Takayasu T, Mukaida N. Essential involvement of IL-6 in the skin wound-healing process as evidenced by delayed wound healing in IL-6-deficient mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:713–21. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0802397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Luckett-Chastain LR, Gallucci RM. Interleukin (IL)-6 modulates transforming growth factor-beta expression in skin and dermal fibroblasts from IL-6-deficient mice. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:237–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ryall JG, Cliff T, Dalton S, Sartorelli V. Metabolic reprogramming of stem cell epigenetics. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17:651–62. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lu C, Thompson CB. Metabolic regulation of epigenetics. Cell Metab. 2012;16:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reid MA, Dai Z, Locasale JW. The impact of cellular metabolism on chromatin dynamics and epigenetics. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:1298–306. doi: 10.1038/ncb3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kinnaird A, Zhao S, Wellen KE, Michelakis ED. Metabolic control of epigenetics in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:694–707. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fanucchi S, Dominguez-Andres J, Joosten LAB, Netea MG, Mhlanga MM. The intersection of epigenetics and metabolism in trained immunity. Immunity. 2021;54:32–43. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Greb JE, Goldminz AM, Elder JT, Lebwohl MG, Gladman DD, Wu JJ, et al. Psoriasis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2016;2:16082. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kamleh MA, Snowden SG, Grapov D, Blackburn GJ, Watson DG, Xu N, et al. LC-MS metabolomics of psoriasis patients reveals disease severity-dependent increases in circulating amino acids that are ameliorated by anti-TNFalpha treatment. J Proteome Res. 2015;14:557–66. doi: 10.1021/pr500782g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kang H, Li X, Zhou Q, Quan C, Xue F, Zheng J, et al. Exploration of candidate biomarkers for human psoriasis based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry serum metabolomics. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:713–22. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kornberg MD, Bhargava P, Kim PM, Putluri V, Snowman AM, Putluri N, et al. Dimethyl fumarate targets GAPDH and aerobic glycolysis to modulate immunity. Science. 2018;360:449–53. doi: 10.1126/science.aan4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gerriets VA, Kishton RJ, Nichols AG, Macintyre AN, Inoue M, Ilkayeva O, et al. Metabolic programming and PDHK1 control CD4+ T cell subsets and inflammation. J Clin Investig. 2015;125:194–207. doi: 10.1172/JCI76012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Xu K, Yin N, Peng M, Stamatiades EG, Chhangawala S, Shyu A, et al. Glycolytic ATP fuels phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling to support effector T helper 17 cell responses. Immunity. 2021;54:976–87.e977. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Telang S, Clem BF, Klarer AC, Clem AL, Trent JO, Bucala R, et al. Small molecule inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase suppresses t cell activation. J Transl Med. 2012;10:95. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Gene expression profile of human epidermal equivalents has been deposited into Figshare (10.6084/m9.figshare.21299496.v1).