The title compound forms a sheet structure of dimers exhibiting intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, organic, co-former
Abstract
The structure of the title compound, C8H7IO3, at 90 K has monoclinic (P21/c) symmetry. The extended structure is layered and displays intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonding arising from the same OH group.
Structure description
2-Hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester (C8H8O3), commonly known as methyl salicylate, and its derivatives have been shown to display biological effects such as anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal, and process signaling (Yoon et al., 2019 ▸; Li et al., 2016 ▸; Park et al., 2007 ▸). It can also be found in various foods (Duthie & Wood, 2011 ▸). The title compound, 2-hydroxy-4-iodobenzoic acid methyl ester (methyl 4-iodosalicylate, C8H7IO3) allows for an effective way of incorporating the said methyl salicylates within larger organic molecules, using such methodologies as McClure protocols (Franchi et al., 2010 ▸; McClure et al., 2001 ▸), Stille (Yoon et al., 2019 ▸; Stille, 1986 ▸) and Suzuki–Miyaura reactions (Fracaroli et al., 2014 ▸; Miyaura et al., 1979 ▸), which take advantage of the iodine atom at the 4-position of the aromatic ring for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The iodine atom is also capable of forming supramolecular synthons, which may be useful for crystal engineering (Desiraju, 1995 ▸; Cherukuvada et al., 2016 ▸; Mitchell et al., 2023 ▸).
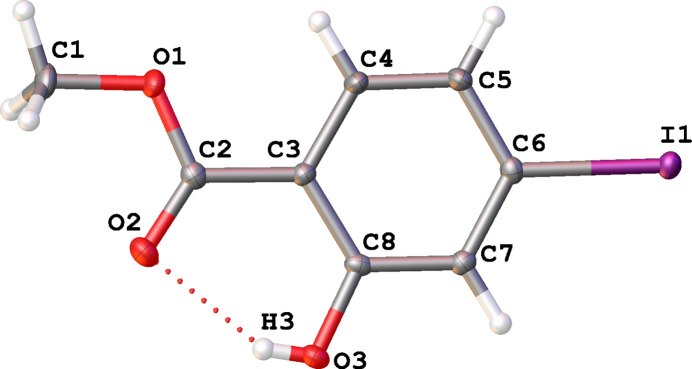
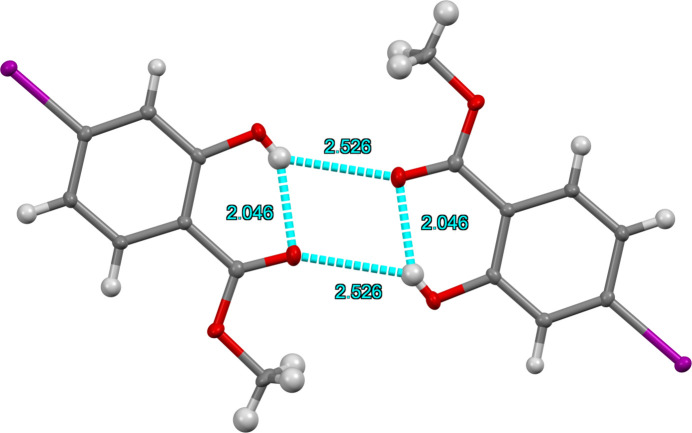
At 90 K the title compound displays monoclinic (P21/c) symmetry with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). Intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions occur between the hydroxy groups of one molecule and the carbonyl oxygen atom of the methyl ester of an adjacent molecule to form a centrosymmetric dimeric pair (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸) with H⋯O = 2.53 (4) Å. An O3—H3⋯O2 intramolecular hydrogen bond also exists with an H⋯O distance of 2.05 (4) Å. The C5⋯C8 [3.326 (3) Å] and O3⋯H1C (2.51 Å) interactions provide the only short contacts between the stacks of offset (
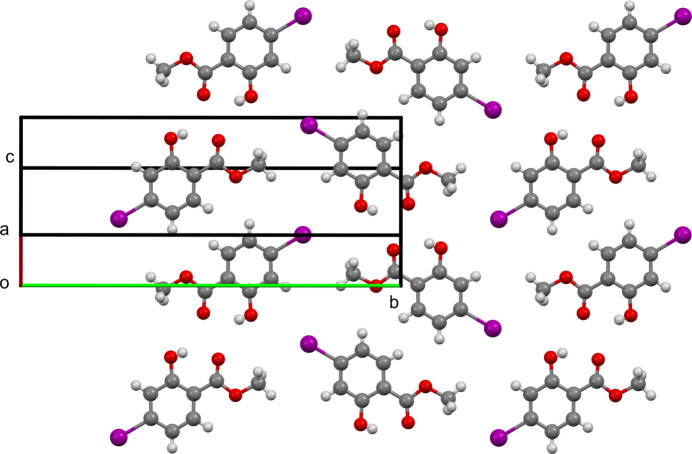
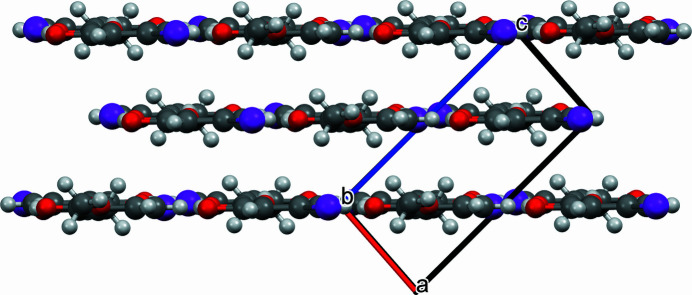
 02) parallel sheets, which make up the crystal (Fig. 3 ▸). These sheets, in turn, contain the inversion-generated hydrogen-bonded dimers (Fig. 2 ▸). The non-hydrogen atoms of the molecule are essentially coplanar with no displacement from the mean molecular plane greater than 0.132 Å (Fig. 4 ▸).
02) parallel sheets, which make up the crystal (Fig. 3 ▸). These sheets, in turn, contain the inversion-generated hydrogen-bonded dimers (Fig. 2 ▸). The non-hydrogen atoms of the molecule are essentially coplanar with no displacement from the mean molecular plane greater than 0.132 Å (Fig. 4 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing 50% displacement ellipsoids. The intramolecular hydrogen bond is indicated by a red dashed line.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O2 | 0.70 (4) | 2.05 (4) | 2.670 (3) | 149 (4) |
| O3—H3⋯O2i | 0.70 (4) | 2.53 (4) | 3.087 (2) | 139 (4) |
Symmetry code: (i)
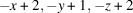 .
.
Figure 2.
The dimer of title compound showing intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds depicted with blue dashed lines with corresponding O⋯H distances for each O—H⋯O interaction.
Figure 3.
Packing diagram viewed perpendicular to (
 02).
02).
Figure 4.
Packing diagram viewed along b-axis and parallel to (
 02).
02).
Crystallization
Methyl 4-iodosalicylate (32.8 mg, 0.118 mmol) was added to a 20 ml scintillation vial to which benzene (∼2 ml) was added, and the vial shaken until the compound dissolved. The resulting solution was then left undisturbed, lightly capped, and in the dark for one week to allow for crystal formation while the solvent slowly evaporated.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection, and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C8H7IO3 |
| M r | 278.04 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 90 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 4.3286 (8), 21.334 (4), 9.2941 (16) |
| β (°) | 93.744 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 856.4 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 3.70 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.80 × 0.20 × 0.02 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.564, 0.747 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 23320, 3651, 3315 |
| R int | 0.049 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.809 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.030, 0.057, 1.11 |
| No. of reflections | 3651 |
| No. of parameters | 114 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.27, −1.92 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003948/hb4468sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003948/hb4468Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003948/hb4468Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2352344
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C8H7IO3 | F(000) = 528 |
| Mr = 278.04 | Dx = 2.156 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 4.3286 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 6811 reflections |
| b = 21.334 (4) Å | θ = 2.9–34.1° |
| c = 9.2941 (16) Å | µ = 3.70 mm−1 |
| β = 93.744 (4)° | T = 90 K |
| V = 856.4 (3) Å3 | Plate, pale yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.80 × 0.20 × 0.02 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3315 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.049 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | θmax = 35.1°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Tmin = 0.564, Tmax = 0.747 | h = −6→6 |
| 23320 measured reflections | k = −33→34 |
| 3651 independent reflections | l = −14→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.057 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + 1.660P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.11 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3651 reflections | Δρmax = 1.27 e Å−3 |
| 114 parameters | Δρmin = −1.92 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. The O-bound H atom was located in a difference map and its position was freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å) and refined as riding atoms. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.05964 (3) | 0.25795 (2) | 0.54095 (2) | 0.01430 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.7859 (4) | 0.39459 (9) | 0.91310 (18) | 0.0170 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.4603 (4) | 0.56516 (8) | 0.72915 (18) | 0.0180 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.7790 (4) | 0.51960 (9) | 0.89865 (19) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.2313 (5) | 0.34266 (10) | 0.6295 (2) | 0.0127 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.4516 (5) | 0.34172 (10) | 0.7453 (2) | 0.0128 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.522507 | 0.302965 | 0.785568 | 0.015* | |
| C8 | 0.5675 (5) | 0.39821 (10) | 0.8018 (2) | 0.0121 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.5827 (6) | 0.62513 (11) | 0.7783 (3) | 0.0203 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.499780 | 0.658300 | 0.713823 | 0.030* | |
| H1B | 0.809060 | 0.624553 | 0.777897 | 0.030* | |
| H1C | 0.522278 | 0.633151 | 0.876394 | 0.030* | |
| C5 | 0.1189 (5) | 0.39860 (11) | 0.5688 (2) | 0.0161 (4) | |
| H5 | −0.033554 | 0.398522 | 0.490504 | 0.019* | |
| C3 | 0.4577 (5) | 0.45534 (10) | 0.7425 (2) | 0.0123 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.5823 (5) | 0.51534 (11) | 0.7990 (2) | 0.0144 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.2359 (5) | 0.45406 (10) | 0.6259 (2) | 0.0156 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.163744 | 0.492573 | 0.584857 | 0.019* | |
| H3 | 0.836 (8) | 0.4252 (17) | 0.929 (4) | 0.025 (9)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.01408 (6) | 0.01099 (7) | 0.01764 (7) | −0.00031 (5) | −0.00056 (4) | −0.00134 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0153 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | −0.0061 (6) | −0.0004 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0104 (7) | 0.0188 (8) | −0.0031 (6) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0204 (9) | 0.0211 (8) | −0.0015 (6) | −0.0083 (6) | −0.0031 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0114 (8) | 0.0128 (9) | 0.0138 (9) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0009 (7) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0128 (9) | 0.0120 (9) | 0.0136 (9) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0103 (8) | 0.0155 (9) | 0.0105 (8) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0114 (10) | 0.0211 (11) | −0.0062 (8) | 0.0005 (9) | −0.0021 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0178 (10) | 0.0137 (10) | 0.0158 (9) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0061 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0132 (9) | 0.0108 (9) | 0.0128 (9) | 0.0003 (7) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0140 (9) | 0.0152 (10) | 0.0138 (9) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0007 (7) | −0.0011 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0179 (10) | 0.0104 (9) | 0.0177 (10) | 0.0002 (7) | −0.0053 (8) | 0.0012 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C6 | 2.101 (2) | C8—C3 | 1.407 (3) |
| O3—C8 | 1.357 (3) | C1—H1A | 0.9800 |
| O3—H3 | 0.70 (4) | C1—H1B | 0.9800 |
| O1—C1 | 1.447 (3) | C1—H1C | 0.9800 |
| O1—C2 | 1.336 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C2 | 1.220 (3) | C5—C4 | 1.379 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.391 (3) | C3—C2 | 1.472 (3) |
| C6—C5 | 1.394 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.400 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.395 (3) | ||
| C8—O3—H3 | 107 (3) | H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| C2—O1—C1 | 115.15 (18) | H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—I1 | 119.85 (16) | C6—C5—H5 | 121.0 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.9 (2) | C4—C5—C6 | 118.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—I1 | 118.20 (15) | C4—C5—H5 | 121.0 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 | C8—C3—C2 | 120.44 (19) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.4 (2) | C4—C3—C8 | 118.89 (19) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.3 | C4—C3—C2 | 120.63 (19) |
| O3—C8—C7 | 116.94 (19) | O1—C2—C3 | 113.23 (18) |
| O3—C8—C3 | 123.3 (2) | O2—C2—O1 | 122.9 (2) |
| C7—C8—C3 | 119.80 (19) | O2—C2—C3 | 123.8 (2) |
| O1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C5—C4—C3 | 122.0 (2) |
| O1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C5—C4—H4 | 119.0 |
| O1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C3—C4—H4 | 119.0 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | ||
| I1—C6—C7—C8 | 178.99 (15) | C8—C3—C2—O1 | 178.4 (2) |
| I1—C6—C5—C4 | −179.01 (17) | C8—C3—C2—O2 | −1.0 (3) |
| O3—C8—C3—C2 | 1.0 (3) | C8—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (3) |
| O3—C8—C3—C4 | 178.8 (2) | C1—O1—C2—O2 | 1.2 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—O3 | −178.90 (19) | C1—O1—C2—C3 | −178.26 (19) |
| C6—C7—C8—C3 | 0.9 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.9 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 178.8 (2) |
| C7—C6—C5—C4 | 0.8 (3) | C4—C3—C2—O1 | 0.6 (3) |
| C7—C8—C3—C2 | −178.8 (2) | C4—C3—C2—O2 | −178.8 (2) |
| C7—C8—C3—C4 | −0.9 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O2 | 0.70 (4) | 2.05 (4) | 2.670 (3) | 149 (4) |
| O3—H3···O2i | 0.70 (4) | 2.53 (4) | 3.087 (2) | 139 (4) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+2.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: National Science Foundation (award No. DMR-2003932).
References
- Bruker (2016). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cherukuvada, S., Kaur, R. & Guru Row, T. N. (2016). CrystEngComm, 18, 8528–8555.
- Desiraju, G. R. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 2311–2327.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Duthie, G. G. & Wood, A. D. (2011). Food Funct. 2, 515–520. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fracaroli, A. M., Furukawa, H., Suzuki, M., Dodd, M., Okajima, S., Gándara, F., Reimer, J. A. & Yaghi, O. M. (2014). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 8863–8866. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Franchi, L., Rinaldi, M., Vignaroli, G., Innitzer, A., Radi, M. & Botta, M. (2010). Synthesis, pp. 3927–3933.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, J., Yin, Y., Wang, L., Liang, P., Li, M., Liu, X., Wu, L. & Yang, H. (2016). Molecules, 21, 1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- McClure, M. S., Glover, B., McSorley, E., Millar, A., Osterhout, M. H. & Roschangar, F. (2001). Org. Lett. 3, 1677–1680. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, T. B., Zhang, X., Jerozal, R. T., Chen, Y.-S., Wang, S. & Benedict, J. B. (2023). IUCrJ, 10, 694–699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Miyaura, N., Yamada, K. & Suzuki, A. (1979). Tetrahedron Lett. 20, 3437–3440.
- Park, S.-W., Kaimoyo, E., Kumar, D., Mosher, S. & Klessig, D. F. (2007). Science, 318, 113–116. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Stille, J. K. (1986). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 25, 508–524.
- Yoon, M., Kim, M., Kim, M. H., Kang, J.-G., Sohn, Y. & Kim, I. T. (2019). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 495, 119008.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003948/hb4468sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003948/hb4468Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003948/hb4468Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2352344
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report