Abstract
Currently available data indicate the potential application of rapamycin and its analogues in the clinic as anticancer therapeutic agents through inhibiting tumor cell growth and tumor angiogenesis. However, whether rapamycin can directly suppress tumor metastasis remains unclear. In the present study, we demonstrated that rapamycin treatment results in reduced formation of metastatic nodules in the lung by B16 cells. This is due to two mechanisms. First, the expression of αv integrin is down‐regulated by rapamycin treatment, and subsequently, the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is reduced. Second, rapamycin promotes apoptosis by up‐regulating the proapoptotic molecules Bid and Bax and down‐regulating Bcl‐xL. Blocking the apoptosis pathway by pan‐caspase inhibitor zVAD partially reversed the suppression of rapamycin in B16 metastasis. Interestingly, rapamycin up‐regulates Bax and Bid in B16 cells via the S6K1 pathway and down‐regulates the expression of αv integrin via other pathway(s). In addition, our data showed that autophagy was not involved in the mechanisms of rapamycin‐mediated metastasis suppression. Our findings demonstrate a potential anti‐metastatic effect of rapamycin via down‐regulating αv integrin expression and up‐regulating apoptosis signaling, suggesting that rapamycin might be worthy of clinical evaluation as an antimetastatic agent. (Cancer Sci 2009)
The development of metastases is the major cause of death for cancer patients. However, effective treatment and prevention of metastases remains unavailable. The molecular mechanisms involved in tumor metastases are incompletely understood, although it is generally accepted that tumor metastases are associated with tumor cell‐matrix adhesion, with the degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and with the survival of tumor cells in blood stream.( 1 , 2 ) Hence, these steps provide potential targets against tumor metastasis.
Integrin signaling pathways play a fundamental role in tumor cell‐matrix adhesion and metastasis.( 3 , 4 , 5 ) The engagement of integrins with ECM components such as fibronectin, collagen, and laminin results in tumor cell adhesion, mobility and migration, proliferation, and survival. Integrins are membrane‐spanning heterodimers composed of α and β subunits. Tumor cells commonly express altered integrins on their surface. For instance, αvβ3 integrin is not expressed in normal mammary epithelium; however, altered expression of αvβ3 integrin is frequently observed in various types of tumors, including breast,( 6 , 7 ) prostate,( 8 ) ovary,( 9 ) melanomas,( 10 , 11 ) and gliomas.( 12 ) Notably, αv integrin is required for melanoma metastasis and targeting the αv integrin signaling pathway inhibits the metastatic potential of melanoma. ( 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ) It has been shown that the engagement of αvβ3 integrin with its ligand can alter cellular behavior through the recruitment and activation of signaling protein such as focal adhesion kinase (FAK), leading to tumor cell migration and invasion.( 19 , 20 ) In addition, up‐regulation of cdc2, a downstream target molecule of the αvβ3 signaling pathway, also promotes tumor cell migration.( 20 , 21 , 22 )
ECM degradation, mediated by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) such as MMP‐2 and MMP‐9,( 23 , 24 ) is another prerequisite for tumor metastasis. As a consequence of ECM degradation, tumor cells have the chance to interact with and enter into blood vessels. In the bloodstream, which is different from the primary tumor microenvironment, the dynamic flow conditions are dangerous for circulating tumor cells. Such tumor cells have to be subjected to shear forces and most of them are cleared from circulation through the apoptosis pathway.( 25 ) Therefore, apoptosis‐resistance is critical for the survival of circulating tumor cells.
Rapamycin, a lipophilic macrolide antibiotic, was originally identified as a fungicide and immunosuppressant.( 26 ) However, studies have revealed that rapamycin can potently arrest the growth of cells derived from a broad spectrum of cancers.( 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 ) Rapamycin has been shown to specifically inhibit its target mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin), which is a key player in tumor development and progression.( 33 ) Rapamycin binds the immunophilin FK506 binding protein (FKBP12) to form the FKBP12‐rapamycin complex, which then interacts with mTOR and inhibits the mTOR‐mediated phosphorylation of S6K1 and 4E‐BP1.( 33 ) In addition, rapamycin is the best characterized drug that enhances autophagy,( 34 , 35 , 36 ) a process of “self‐eating” that involves both cancer cell death and survival. Therefore, rapamycin might interfere with different aspects of the tumor.
It has been noted that rapamycin can impede tumor metastasis by suppressing tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.( 37 , 38 , 39 ) However, the direct effects of rapamycin on tumor metastasis remain unclear. In this study, we demonstrate that rapamycin directly suppresses tumor metastasis through down‐regulating αv integrin and up‐regulating apoptosis signaling in a mouse model of melanoma lung metastasis. Our data also indicate that autophagy is not involved in the rapamycin‐mediated suppression of metastasis.
Materials and Methods
Animals and the cell line. Six‐ to 8‐week‐old C57BL/6 mice were purchased from the Center of Medical Experimental Animals of Hubei Province (Wuhan, China) for studies approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji Medical College. Mouse melanoma tumor cell line B16 F1 was purchased from the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC; Wuhan, China), and cultured according to the guidelines.
Reagents. Rapamycin, 3‐methyladenine (3‐MA), and wortmannin (WM) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). The apoptosis inhibitor zVAD was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). The antagonist Cyclo(Arg‐Gly‐Asp‐D‐Phe‐Val) of αv integrin was purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA, USA). The recombinant polypeptide with cell‐binding domain (CBD) and Hep II domain of human fibronectin (FN), designated as CH50, was preserved in our laboratory, which may function to inhibit αv integrin signaling.( 21 ) The concentrations used in this study have described in the figure legends.
Melanoma model of lung metastasis. B16 melanoma tumor cells were treated with different agents for 24 h. Then 2 × 105 treated cells were injected into the mice via the tail vein. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and the black melanoma nodules on the lungs were calculated.
Analysis of gene expression by real‐time RT‐PCR. Total RNA was extracted from cells with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For real‐time RT‐PCR assays, the cDNA sequences of all detected genes were retrieved from the NCBI database. The primers were designed with Oligo Primer Analysis 4.0 software and the sequences were blasted (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/). One hundred ng of total RNA was used for reverse transcription using Superscript II RNase H reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) in a volume of 25 μL. Then 2 μL of cDNA was amplified with SYBR Green Universal PCR Mastermix (Bio‐Rad, Richmond, CA, USA) in duplicate. For sample analysis, the threshold was set based on the exponential phase of products, and the cycle threshold (CT) value for samples was determined. The resulting data were analyzed with the comparative CT method for relative gene expression quantification against the housekeeping gene GAPDH.
MMP assay by gelatin zymography. The assay of MMPs in protein samples was performed as described previously.( 15 ) Briefly, proteins prepared from B16 cells of each group were separated by 7.5% SDS‐PAGE containing 1% gelatin. The gels were incubated in MMP activation buffer containing 50 mm Tris (pH8.0) and 10 mm CaCl2 at 37°C overnight, and then stained with 1% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R‐250 for 3 h and destained in 10% (V/V) methanol and 5% (V/V) acetic acid.
Western blot analysis. Cell lysates (30 μg of total protein) and prestained molecular weight markers were separated by SDS‐PAGE followed by transfer onto nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in TBST (Tris‐buffered saline with 0.5% of Triton X‐100) containing 5% nonfat milk, and probed with primary antibodies. After incubation with the secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase, membranes were extensively washed, and the immunoreactivity was visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence according to the manufacturer’s protocol (ECL kit; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Antibody LC3 was purchased from Novus Biologicals (Littleton, CO, USA); antibodies mTOR, phospho‐mTOR (Ser2448) S6K1 and phospho‐S6K (Thr421/Ser424) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA); and other antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology.
Construction of B16 tumor cell line expressing S6K1‐siRNA. The S6K1‐siRNA sequence (gagccttagggatgaagtg) and its control siRNA (gagccttagcgatcaagtg) were inserted into RNAi‐Ready pSIREN‐RetroQ expressing vector with U6 promoter (BD Biosciences, Clontech, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The recombinant siRNA‐expressing plasmids and control plasmids were transfected into B16 tumor cells using FuGENE 6 transfection reagent (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, USA) for stable expression after selection.
Construction of B16 tumor cell line overexpressing αv integrin. The full length of cDNA of mouse αv integrin gene was inserted into eukaryotic expressing vector pcDNA3.1. The recombinant vector and mock plasmid were transfected into B16 cells with G418 selection.
Apoptosis assay. B16 melanoma tumor cells were cultured in the presence or absence of rapamycin (0.5 μg/mL) for 24, 48, or 72 h. Then cells were stained with phycoerythrin (PE)‐conjugated Annexin V (BD Biosciences) and analyzed by flow cytometry.
In vitro migration assay. A Transwell system that incorporated a polycarbonate filter membrane with a diameter of 6.5 mm and pore size of 8 μm (Corning, Corning, NY, USA) was used to assess the migration of B16 cells. The Matrigel (5 μg in 10 μL serum‐free 1640) was added to the filter to form a thin gel layer, and the lower membrane was coated with fibronectin (5 μg in 10 μL serum‐free 1640), dried in a hood overnight. Cells (1 × 105) were suspended in 100 μL of medium in the presence of different agents as indicated and then added to the upper chamber of the Transwell insert. The lower chamber was filled with 600 μL of the same medium as in the upper chamber. After 12 h of incubation at 37°C, cells on the upper surface of the filter were removed by using a cotton swab. The cells that penetrated to the lower surface of the filter were fixed in methanol, and then sections were stained with hematoxylin–eosin and observed under a microscope.
Data analysis. Results were presented as mean values ± SD and interpreted by repeated‐measure anova. Differences were considered to be statistically significant when the P‐value was less than 0.05.
Results
Rapamycin suppresses lung metastasis of circulating B16 melanoma cells. To evaluate the direct effects of rapamycin on tumor metastasis, we used a well‐characterized model of experimental lung metastasis by i.v. injection of B16 melanoma cells.( 40 , 41 ) B16 cells were treated with 0.5 μg/mL rapamycin for 24 h and then injected into mice via the tail vein. This condition was chosen because no obvious apoptosis was induced by rapamycin (Fig. 1a). Twenty‐one days after B16 cell injection, the mice were sacrificed and assayed. As shown in Figure 1(b,c), rapamycin treatment significantly suppressed B16 cell lung metastasis, compared to control. Furthermore, in another experiment, we found that the survival of mice of rapamycin group was significantly prolonged (P < 0.001, Fig. 1d). To further confirm our in vivo data, we conducted an in vitro Transwell assay, and we found that the migrating ability of rapamycin‐treated B16 cells was reduced (Fig. 1e). In addition, we here also tested the direct pharmacological activity of rapamycin in vivo. Mice were administrated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg/kg rapamycin by i.p. injection once daily for 7 days. Four hours after the first injection of rapamycin, the mice were injected with 2 × 105 B16 tumor cells. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and assayed. The result showed a dose‐dependent reduction of B16 cell lung metastasis (Fig. 1f). Taken together, these data suggested that rapamycin directly effects B16 tumor cells and suppresses B16 lung metastasis.
Figure 1.
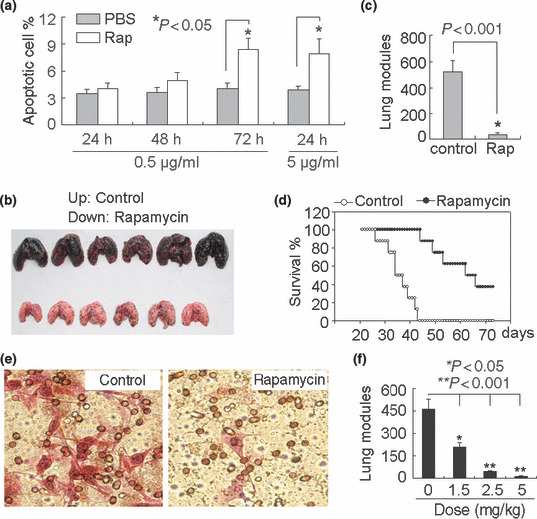
Rapamycin suppresses the lung metastasis of circulating B16 melanoma cells. (a) Influence of rapamycin on B16 cell apoptosis. B16 cells were treated with 0.5 or 5 μg/mL rapamycin for different time periods. The cells were harvested and stained with phycoerythrin (PE)‐conjugated Annexin V for apoptosis detection by flow cytometry. (b,c) Rapamycin suppresses lung metastasis of B16 cells. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin (0.5 μg/mL) in vitro for 24 h, and then i.v. injected into mice. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed. The data shown are the representative photograph of lungs from three independent experiments (b); and the number of lung tumor nodules (c). (d) Long‐term survival of mice after injection of rapamycin‐treated B16 cells. The survival period of tumor‐bearing mice in the rapamycin group was significantly prolonged, compared with that in the control group (n = 16; P < 0.001, Kaplan–Meier analysis). (e) Rapamycin inhibited the migration of B16 cells. The migration of rapamycin‐treated B16 cells by Transwell assay was determined as described in the Materials and Methods. The data shown are the representative from three reproducible experiments. (f) Rapamycin administration inhibited the lung metastasis of circulating B16 cells. Mice were administrated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg/kg rapamycin by i.p. injection once daily for 7 days. Four hours after the first injection of rapamycin, the mice were injected with 2 × 105 B16 tumor cells. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and the number of lung tumor nodules was counted.
Autophagy is not involved in rapamycin‐mediated suppression of B16 metastasis. Autophagy is a process of self‐degradation of cellular components, such as long‐lived proteins and organelles.( 34 ) Though autophagy has become an important area in cancer research, its role in the tumor may be variable and depends on the context.( 42 , 43 ) Taking into account the positive regulation of rapamycin on autophagy,( 34 , 35 , 36 ) we initially hypothesized that rapamycin suppressed B16 metastasis through the up‐regulation of autophagy. As shown in Figure 2(a), the induction of autophagy by rapamycin was observed in B16 cells. Therefore, we expected that the decrease of autophagy should reverse the effect of rapamycin and facilitate metastasis. To test this, a B16 tumor cell line expressing Beclin 1‐siRNA was used here to interfere with the formation of autophagosome, since Beclin 1 plays an important role in the initiation of autophagosome. The efficiency of Beclin 1 knockdown in B16 cells was proved in our previously study.( 44 ) Beclin 1‐siRNA and control cell lines were treated with rapamycin and then i.v. injected into mice. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and assayed. Nevertheless, the inhibition of autophagy by beclin 1 knockdown did not alter the negative effect of rapamycin on B16 lung metastasis (Fig. 2b). Consistently, the decrease of autophagy by knockdown Beclin 1 did not inhibit the suppression of rapamycin on B16 cell migration in in vitro assay (Fig. 2c), suggesting that the autophagic pathway is not involved in rapamycin‐mediated suppression of B16 metastasis. In addition, we also used autophagy inhibitors to counteract the proautophagic effect of rapamycin. As shown in Figure 2(d), the treatment of B16 cells with rapamycin plus autophagy inhibitor, either wortmannin ( 34 ) or 3‐methyladenine,( 34 ) did not enhance B16 lung metastasis. Taken together, these data suggested that rapamycin suppresses B16 lung metastasis through autophagy‐independent mechanism(s).
Figure 2.
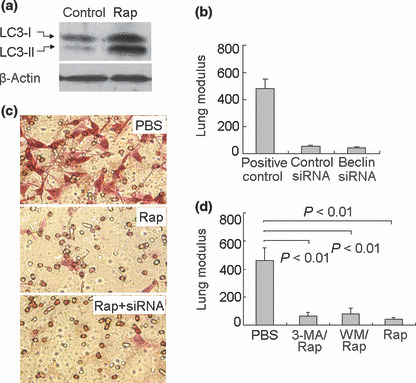
Autophagy is not involved in the suppression of B16 metastasis by rapamycin. (a) Effect of rapamycin on autophagy in B16 cells. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin (0.5 μg/mL) in vitro. Twenty‐four hours later, the cells were harvested to determine LC3 by Western blotting. (b) Inhibition of autophagy by beclin 1 knockdown did not alter the effect of rapamycin on B16 lung metastasis. Beclin 1 siRNA‐ or control siRNA‐expressing B16 cells, treated with rapamycin, were injected into mice via the tail vein. Twenty‐one days later, mice were sacrificed and the lung tumor nodules were counted. PBS‐treated B16 cells were used as positive control. (c) Knockdown of Beclin 1 did not inhibit the suppression of rapamycin on B16 cell migration in vitro. Beclin 1 siRNA‐ or control siRNA‐expressing B16 cells were treated with rapamycin. The Transwell assay was determined as described in the Materials and Methods. (d) Autophagy inhibitors did not inhibit rapamycin‐mediated suppression of B16 cell lung metastasis. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin plus autophagy inhibitor wortmannin (WM, 100 nm) or 3‐methyladenine (3‐MA, 3 mm) for 24 h. The treated cells were injected into mice. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and the number of lung tumor nodules was enumerated. The data shown are the representative from two independent experiments.
Rapamycin suppresses tumor metastasis by down‐regulating αv integrin signaling. Enhanced levels of expression of certain integrins, and a consequent increase in specific integrin signals, have been linked to cancer cell progression and metastasis.( 3 , 4 ) We previously reported that αvβ3 integrin signaling plays an important role in B16 lung metastasis.( 20 , 21 ) Here, we wondered whether rapamycin mediated metastatic suppression via influencing the αvβ3 integrin signaling pathway. First, we examined the expression of αvβ3 integrin in rapamycin‐treated B16 cells by real‐time RT‐PCR and Western blotting. We found that rapamycin had no effect on β3 expression, but effectively down‐regulated αv expression (Fig. 3a,b). Notably, the withdrawal of rapamycin in the culture medium did not cause the recovery of αv expression until 4 h later (data not shown). Next, we analyzed the activation of FAK, a critical mediator of integrin signaling,( 19 ) and the expression of cdc2, a downstream molecule of the αvβ3 signaling pathway.( 22 ) Consistently, rapamycin treatment reduced phosphorylated but not total FAK (Fig. 3c) and the mRNA and protein levels of cdc2 (Fig. 3d). In addition to regulating integrin signaling, we also wondered whether rapamycin was capable of regulating MMPs, another group of important molecules for metastasis. For this purpose, the production of MMP‐2 and MMP‐9 was determined by real‐time RT‐PCR and zymography assay. The results showed that rapamycin did not affect the production of MMPs (Fig. 3e,f).
Figure 3.
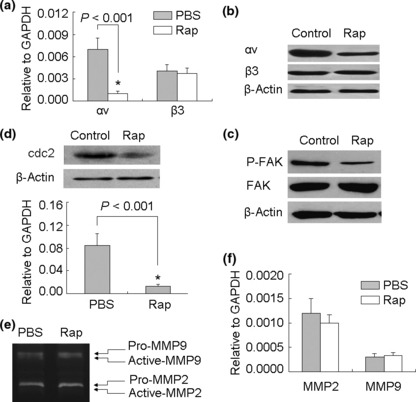
Rapamycin inhibits αv integrin signaling of B16 cells. (a,b) Rapamycin down‐regulated the expression of αv integrin in B16 cells. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin in vitro. Twenty‐four hours later, the cells were harvested for the detection of αv and β3 expression by real‐time RT‐PCR (a); or 24 h later, the cells were used for Western blot analysis (b). (c) Rapamycin inhibited the activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK). B16 cells were treated with rapamycin for 24 h. The phosphorylated FAK and total FAK were analyzed by Western blotting. (d) Assay of cdc2 expression. The rapamycin‐treated cells were used for total RNA isolation and cell lysate preparation. The expression of cdc2 was analyzed by real‐time RT‐PCR (bottom) and Western blotting (up). (e,f) Assay of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)‐2 and MMP‐9 production. B16 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of rapamycin for 24 h. MMP‐2 and MMP‐9 in supernatants were detected by zymography assay (e). The relative mRNA levels of MMP‐2 and MMP‐9 were detected by real‐time RT‐PCR (f).
To further confirm that down‐regulation of αv integrin was required for rapamycin‐mediated metastasis suppression, we constructed an αv integrin‐overexpressing B16 cell line (Fig. 4a). We found that rapamycin did not inhibit the expression of αv integrin (Fig. 4b), suggesting that the rapamycin signaling pathway might not have effects on exogenous expressing vector in B16 cells. Such conditions partially reversed the inhibitory effect of rapamycin on lung metastasis of B16 cells (Fig. 4c). We previously reported that a recombinant CBD‐HepII (heparin II domain) polypeptide of fibronectin (designated as CH50) effectively suppresses αvβ3 signaling, leading to the suppression of B16 cell lung metastasis.( 20 , 21 ) Here, we further compared the suppressive effects among rapamycin, CH50, and commercial αv integrin antagonist Cyclo(Arg‐Gly‐Asp‐D‐Phe‐Val). Interestingly, despite the down‐regulation of both αv and β3 by CH50, rapamycin was showed stronger suppression against B16 lung metastasis, compared to CH50 as well as αv integrin antagonist (Fig. 4d), suggesting that rapamycin might be an ideal agent targeting αv integrin signaling.
Figure 4.
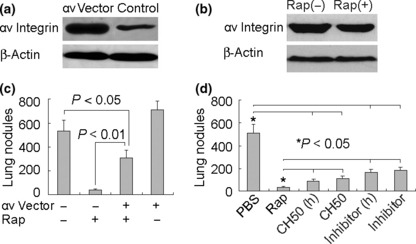
Down‐regulation of αv integrin is required for rapamycin‐mediated suppression of B16 metastasis. (a) Construction of αv integrin‐overexpressing B16 cell line. αv Integrin‐expressing plasmid was transfected to B16 cells. The stably transfected cells were used to analyze αv integrin expression by Western blotting. (b) Rapamycin did not inhibit the exogenous expression of αv integrin. (c) Overexpression of αv integrin partly reversed the suppression of rapamycin in lung metastasis. αv‐Overexpressing or mock B16 cells, treated with rapamycin, were injected into mice via the tail vein. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and the lung tumor nodules were counted. (d) Comparison of the effect on B16 cell metastasis among rapamycin, CH50, and αv integrin antagonist. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin (0.5 μg/mL), CH50 (10 μg/mL), or high‐dose CH50 (25 μg/mL); or αv integrin antagonist (10 μg/mL) or high dose (25 μg/mL) for 24 h. Then the cells were injected to the mice. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and the lung tumor nodules were counted.
Rapamycin suppresses tumor metastasis by up‐regulating apoptosis signaling. Because the rapamycin‐mediated suppression of tumor metastasis could be partially reversed by overexpressing αv integrin and rapamycin exhibited a stronger suppressive effect than that of CH50 or αv integrin antagonist, we hypothesized that other pathway(s) might be involved in rapamycin‐mediated metastasis suppression besides down‐regulation of integrin signaling. The acquirement of apoptosis resistance is critical for the survival of circulating tumor cells and subsequent metastasis. In this regard, we further questioned whether rapamycin suppressed B16 lung metastasis through the apoptosis pathway. To address this question, B16 cells were treated with pan‐caspase inhibitor zVAD to block apoptosis. Under this condition, the suppressive effect of rapamycin on metastasis declined (Fig. 5a). In line with these data, the proapoptotic molecules Bid and Bax were up‐regulated and the antiapoptotic member Bcl‐xL was down‐regulated in B16 cells by rapamycin (Fig. 5b,c). Taken together, these findings suggested that rapamycin might enhance the apoptosis of circulating tumor cells, thus suppressing tumor metastasis.
Figure 5.
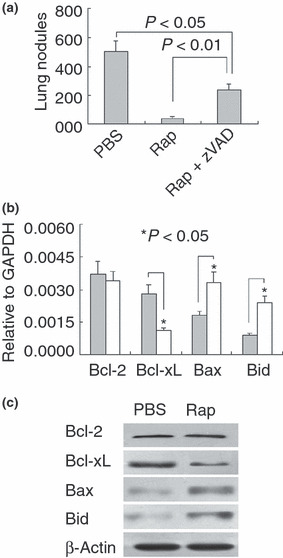
Rapamycin suppresses tumor metastasis by up‐regulating apoptosis signaling. (a) Inhibition of apoptosis declined the effect of rapamycin on B16 cell metastasis. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin in the presence or absence of zVAD (10 μm), and then injected to mice via the tail vein. Twenty‐one days later, the mice were sacrificed and the lung tumor nodules were counted. (b,c) Rapamycin increased the apoptosis potential of B16 cells. B16 cells were treated with rapamycin for 24 h. The cells were harvested for RNA isolation. The expressions of Bcl‐2, Bcl‐xL, Bax, and Bid were determined by real‐time RT‐PCR (b); or the cells were used for protein analysis by Western blotting (c).
S6K1 is involved in the up‐regulation of Bax and Bid but not the down‐regulation of αv integrin in B16 cells. Although S6K1 and 4E‐BP1 are the downstream targets of mTOR, reports have indicated that rapamycin selectively inhibits the phosphorylation of S6K1 rather than that of 4E‐BP1 in many cells.( 45 , 46 , 47 ) Here, by generating an S6K1 siRNA‐expressing B16 cell line (Fig. 6a), we further asked whether rapamycin regulated αv integrin, Bid, and Bax through the S6K1 pathway. As shown in Figure 6(b,c), S6K1 knowndown could up‐regulate the expressions of Bax and Bid in B16 cells, suggesting that the mTOR/S6K1 pathway is involved in the regulation of the expressions of Bax and Bid. Taking into account the inhibition of the mTOR/S6K1 pathway by rapamycin,( 45 , 46 , 47 ) it was reasonable that rapamycin might up‐regulate Bax and Bid expression through suppressing the mTOR/S6K1 pathway. In line with this, the addition of rapamycin to S6K1 knockdown B16 cells did not alter Bax and Bid expression, compared to addition of rapamycin to S6K1‐expressing B16 cells (Fig. 6b,c). On the other hand, as shown in Figure 6(d), S6K1 knowndown had no effect on αv integrin expression and did not inhibit the down‐regulation of αv integrin by rapamycin. Moreover, the inhibition of mTOR and S6K1 by rapamycin was also observed under the same conditions (Fig. 6e). These data suggested that rapamycin may use the S6K1 pathway to up‐regulate Bax and Bid, but another pathway to down‐regulate αv integrin in B16 cells.
Figure 6.
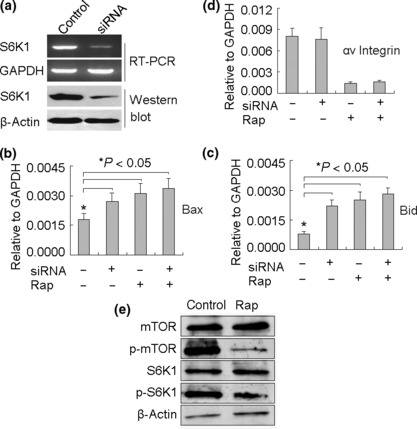
S6K1 is involved in the up‐regulation of Bax and Bid, but not in the down‐regulation of αv integrin in B16 cells. (a) siRNA silenced S6K1 expression. After stable transfection of S6K1 siRNA vector into the B16 cell line, S6K1 mRNA and protein expression was examined by RT‐PCR and Western blotting. (b–d) The influence of S6K1 knockdown on the expressions of Bax, Bid, and αv integrin in B16 cells. S6K1 or control siRNA‐expressing B16 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of rapamycin. Twenty‐four hours later, cells were harvested for RNA isolation. The real‐time RT‐PCR was performed to analyze the expression of Bax (b), Bid (c), and αv integrin (d). (e) The inhibition of mTOR and S6K1 by rapamycin. B16 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of rapamycin. Twenty‐four hours later, cells were harvested to determine mTOR and S6K1 by Western blotting.
Discussion
The major finding in the present study is that rapamycin directly suppresses the lung metastasis of circulating B16 melanoma cells through mechanisms of down‐regulating αv integrin expression and up‐regulating apoptosis signaling. Our data also indicate that autophagy is not involved in rapamycin‐mediated metastasis suppression.
Intense studies on the antitumor effects of rapamycin have been mainly focused on the inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Here, we provide additional evidence that rapamycin can directly suppress tumor metastasis. Even though it has been shown that mTOR has versatile effects on cancer development and progression, we first identified that rapamycin targets integrin, the critical signaling pathway required for tumor cell migration and metastasis. Our convincing evidence includes (i) both mRNA and protein levels of αv integrin were decreased in B16 cells after rapamycin treatment; (ii) the phosphorylation of downstream signal molecule FAK declined; and (iii) the mRNA level of effector molecule cdc2 was decreased. The members of the αv integrin family are widely expressed in various types of tumor cells, which involve tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. There are five recognized αv integrin receptors: αvβ1, αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6, and αvβ8.( 48 ) Among them, agents targeting the αvβ3 integrin receptor are now in clinical development for treating solid tumors.( 49 , 50 , 51 ) Therefore, targeting αv integrin by rapamycin may have important clinical significance. In addition, although we confirm here that αv integrin is targeted by rapamycin, our ongoing study is trying to elucidate whether other integrin(s) is also targeted by rapamycin and the underlying mechanism(s).
By complexing with FKBP‐12, rapamycin binds to mTOR and inhibits the mTOR‐mediated phosphorylation of downstream targets S6K1 and 4E‐BP1. However, S6K1 and 4E‐BP1 seem not to regulate integrin expression, considering that the activities of S6K1 and 4E‐BP1 are related to cell growth and cell cycle progression.( 52 , 53 ) In support of this, our data show that the knockdown of S6K1 by specific siRNA does not decrease the expression of αv integrin in B16 cells (Fig. 6d), suggesting that other target(s) of mTOR might be involved in the regulation of integrin expression. Therefore, a closer examination of the regulation of integrin by mTOR signaling should be useful for the comprehensive evaluation of the tumor therapeutic value of rapamycin.
Besides the inhibition of metastasis through down‐regulating integrin signaling, the present study also reveals that rapamycin can suppress metastasis through up‐regulating apoptosis signaling. To succeed in metastasis, circulating cancer cells have to pass through several stressful and highly selective steps, including survival in the bloodstream, arrest in the capillary bed, and resumption of proliferation in distant organs. The acquirement of apoptosis resistance is a prerequisite for tumor cells to realize these goals. It has been reported that Bcl2 overexpression is associated with a 10‐fold decrease in the number of apoptotic tumor cells at the secondary site 1 h after intravenous injection,( 54 ) and with an increase in metastasis formation.( 55 ) Therefore, the increase of apoptosis potential by rapamycin may play an important role in rapamycin‐mediated metastasis suppression. Actually, our in vivo data clearly show that blockade of apoptosis pathway by pan‐caspase inhibitor zVAD effectively declines the suppression of rapamycin in B16 lung metastasis (Fig. 5a).
The occurrence of metastasis may be unpredictable after surgical excision of primary tumor. Therefore the prevention of metastasis should be a long‐term event. Considering the multiple effects on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and tumor angiogenesis, and the safety of long‐term oral administration, rapamycin might be a good candidate agent for tumor metastasis prevention. However, the immunosuppressive property of rapamycin should be considered. Rapamycin exerts its potent immunosuppressive effects in part through direct effects on antigen‐specific lymphocytes; however, rapamycin also modulates adaptive immunity through its effects on innate immune cells, including dendritic cells and macrophages, and others.( 56 , 57 ) Although clinical sequels of immunosuppression do not seem to be a major concern in the current clinical evaluation of rapamycin in cancer, the long‐term effects might have a negative consequence. In this context, combining other immune modulators to overcome such pitfalls may be of benefit when using rapamycin in the prevention of tumor metastasis.
The regulation of autophagy by rapamycin hints at a possible mechanism involving rapamycin‐mediated metastasis suppression. However, the inhibition of autophagosome formation by Beclin1 knockdown did not change the inhibitory effect of rapamycin on metastasis, suggesting that autophagy is not involved in rapamycin‐mediated suppression of B16 metastasis. However, considering the role of autophagy in energy metabolism and the requirement of energy for cell mobility, it is still possible that autophagy participates in tumor cell migration and metastasis by increasing the energy supply of tumor cells.
In summary, a novel finding in the present study is that rapamycin may directly effect tumor cells and suppresses their metastasis by regulating integrin expression and apoptosis signaling. Our data and others( 31 , 32 , 33 ) together suggest that rapamycin and its analogues are worthy of clinical evaluation as an antimetastatic agent.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET‐08‐0219), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30871020), and Special Research Foundation for Universities affiliated with the Chinese Ministry of Education (Z2009005).
References
- 1. Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massagué J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ‐specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 274–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 563–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hood JD, Cheresh DA. Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 91–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Felding‐Habermann B. Integrin adhesion receptors in tumor metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 2003; 20: 203–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kuphal S, Bauer R, Bosserhoff AK. Integrin signaling in malignant melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2005; 24: 195–222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Liapis H, Flath A, Kitazawa S. Integrin αvβ3 expression by bone‐residing breast cancer metastases. Diagn Mol Pathol 1996; 5: 127–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Pignatelli M, Cardillo MR, Hanby A, Stamp GW. Integrins and their accessory adhesion molecules in mammary carcinomas: loss of polarization in poorly differentiated tumors. Hum Pathol 1992; 23: 1159–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Cooper CR, Chay CH, Pienta KJ. The role of a(v)h(3) in prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia 2002; 4: 191–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Carreiras F, Denoux Y, Staedel C, Lehmann M, Sichel F, Gauduchon P. Expression and localization of av integrins and their ligand vitronectin in normal ovarian epithelium and in ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 1996; 62: 260–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Albelda SM, Mette SA, Elder DE et al. Integrin distribution in malignant melanoma: association of the h3 subunit with tumor progression. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 6757–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Natali PG, Hamby CV, Felding‐Habermann B et al. Clinical significance of a(v)h3 integrin and intercellular adhesion molecule‐1 expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma lesions. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 1554–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Gingras MC, Roussel E, Bruner JM, Branch CD, Moser RP. Comparison of cell adhesion molecule expression between glioblastoma multiforme and autologous normal brain tissue. J Neuroimmunol 1995; 57: 143–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Felding‐Habermann B, Fransvea E, O’Toole TE, Manzuk L, Faha B, Hensler M. Involvement of tumor cell integrin alpha v beta 3 in hematogenous metastasis of human melanoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 2002; 19: 427–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Voura EB, Ramjeesingh RA, Montgomery AM, Siu CH. Involvement of integrin alpha(v)beta(3) and cell adhesion molecule L1 in transendothelial migration of melanoma cells. Mol Biol Cell 2001; 12: 2699–710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Qian F, Zhang ZC, Wu XF, Li YP, Xu Q. Interaction between integrin alpha(5) and fibronectin is required for metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 333: 1269–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Popkov M, Rader C, Gonzalez B, Sinha SC, Barbas CF III. Small molecule drug activity in melanoma models may be dramatically enhanced with an antibody effector. Int J Cancer 2006; 119: 1194–207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ramos OH, Kauskot A, Cominetti MR et al. A novel alpha(v)beta (3)‐blocking disintegrin containing the RGD motive, DisBa‐01, inhibits bFGF‐induced angiogenesis and melanoma metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 2008; 25: 53–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gong W, Liu Y, Huang B et al. Recombinant CBD‐HepII polypeptide of fibronectin inhibits alphavbeta3 signaling and hematogenous metastasis of tumor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 367: 144–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD. Integrin‐regulated FAK‐Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2006; 18: 516–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Gong W, Zhang GM, Liu Y et al. IFN‐gamma withdrawal after immunotherapy potentiates B16 melanoma invasion and metastasis by intensifying tumor integrin alphavbeta3 signaling. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 702–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Liu Y, Huang B, Yuan Y et al. Inhibition of hepatocarcinoma and tumor metastasis to liver by gene therapy with recombinant CBD‐HepII polypeptide of fibronectin. Int J Cancer 2007; 121: 184–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Manes T, Zheng DQ, Tognin S, Woodard AS, Marchisio PC, Languino LR. αvβ3 integrin expression up‐regulates cdc2, which modulates cell migration. J Cell Biol 2003; 161: 817–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 161–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Fridman R, Toth M, Chvyrkova I, Meroueh SO, Mobashery S. Cell surface association of matrix metalloproteinase‐9 (gelatinase B). Cancer Metastasis Rev 2003; 22: 153–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Mehlen P, Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 449–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Vézina C, Kudelski A, Sehgal SN. Rapamycin (AY‐22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. I. Taxonomy of the producing streptomycete and isolation of the active principle. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975; 28: 721–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Dilling MB, Dias P, Shapiro DN, Germain GS, Johnson RK, Houghton PJ. Rapamycin selectively inhibits the growth of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma cells through inhibition of signaling via the type I insulin‐like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 903–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Huang S, Liu LN, Hosoi H, Dilling MB, Shikata T, Houghton PJ. p53/p21(CIP1) cooperate in enforcing rapamycin‐inducedG (1) arrest andd etermine the cellular response to rapamycin. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3373–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Ogawa T, Tokuda M, Tomizawa K et al. Osteoblastic differentiation is enhanced by rapamycin in rat osteoblast‐like osteosarcoma (ROS 17/2.8) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 249: 226–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Shah SA, Potter MW, Ricciardi R, Perugini RA, Callery MP. FRAP‐p70s6K signaling is requiredfor pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. J Surg Res 2001; 97: 123–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hultsch T, Martin R, Hohman RJ. The effect of the immunophilin ligands rapamycin and FK506 on proliferation of mast cells andother hematopoietic cell lines. Mol Biol Cell 1992; 3: 981–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gottschalk AR, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Quintans J. Identification of immunosuppressant‐induced apoptosis in a murine B‐cell line andits prevention by bcl‐x but not bcl‐2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994; 91: 7350–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Bjornsti MA, Houghton PJ. The TOR pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 335–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yin XM, Ding WX, Gao W. Autophagy in the liver. Hepatology 2008; 47: 1773–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Iwamaru A, Kondo Y, Iwado E et al. Silencing mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by small interfering RNA enhances rapamycin‐induced autophagy in malignant glioma cells. Oncogene 2007; 26: 1840–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Paglin S, Lee NY, Nakar C et al. Rapamycin‐sensitive pathway regulates mitochondrial membrane potential, autophagy, and survival in irradiated MCF‐7 cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 11061–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Luan FL, Ding R, Sharma VK, Chon WJ, Lagman M, Suthanthiran M. Rapamycin is an effective inhibitor of human renal cancer metastasis. Kidney Int 2003; 63: 917–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Guba M, Von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M et al. Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor growth by antiangiogenesis: involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. Nat Med 2002; 8: 128–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Kobayashi S, Kishimoto T, Kamata S, Otsuka M, Miyazaki M, Ishikura H. Rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin, suppresses lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 726–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Maeda M, Suga T, Takasuka N, Hoshi A, Sasaki T. Effect of bis(bilato)‐1,2‐cyclohexanediammineplatinum(II) complexes on lung metastasis of B16–F10 melanoma cells in mice. Cancer Lett 1990; 55: 143–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kolber DL, Knisely TL, Maione TE. Inhibition of development of murine melanoma lung metastases by systemic administration of recombinant platelet factor 4. J Natl Cancer Inst 1995; 87: 304–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Hippert MM, O’Toole PS, Thorburn A. Autophagy in cancer: good, bad, or both? Cancer Res 2006; 66: 9349–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Ogier‐Denis E, Codogno P. Autophagy: a barrier or an adaptive response to cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2003; 1603: 113–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Li B, Lei Z, Lichty BD et al. Autophagy facilitates major histocompatibility complex class I expression induced by IFN‐γ in B16 melanoma cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2009; doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0752-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Choo AY, Yoon SO, Kim SG, Roux PP, Blenis J. Rapamycin differentially inhibits S6Ks and 4E‐BP1 to mediate cell‐type‐specific repression of mRNA translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008; 105: 17414–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Feldman ME, Apsel B, Uotila A et al. Active‐site inhibitors of mTOR target rapamycin‐resistant outputs of mTORC1 and mTORC2. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Thoreen CC, Kang SA, Chang JW et al. An ATP‐competitive mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor reveals rapamycin‐resistant functions of mTORC1. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 8023–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Nemeth JA, Nakada MT, Trikha M et al. Alpha‐v integrins as therapeutic targets in oncology. Cancer Invest 2007; 25: 632–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Gutheil JC, Campbell TN, Pierce PR et al. Targeted antiangiogenic therapy for cancer using Vitaxin: a humanized monoclonal antibody to the integrin alphavbeta3. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 3056–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Patel SR, Jenkins J, Papadopolous N et al. Pilot study of vitaxin–an angiogenesis inhibitor‐in patients with advanced leiomyosarcomas. Cancer 2001; 92: 1347–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Posey JA, Khazaeli MB, DelGrosso A et al. A pilot trial of Vitaxin, a humanized antivitronectin receptor (anti alpha v beta 3) antibody in patients with metastatic cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2001; 16: 125–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Ma XM, Blenis J. Molecular mechanisms of mTOR‐mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 307–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Inoki K, Ouyang H, Li Y, Guan KL. Signaling by target of rapamycin proteins in cell growth control. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2005; 69: 79–100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Wong CW, Lee A, Shientag L et al. Apoptosis: an early event in metastatic inefficiency. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 333–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Del Bufalo D, Biroccio A, Leonetti C, Zupi G. Bcl‐2 overexpression enhances the metastatic potential of a human breast cancer line. FASEB J 1997; 11: 947–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Thomson AW, Turnquist HR, Raimondi G. Immunoregulatory functions of mTOR inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 324–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Janes MR, Fruman DA. Immune regulation by rapamycin: moving beyond T cells. Sci Signal 2009; 2: pe25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


