Abstract
The pyrimidine trifluorothymidine (TFT) inhibits thymidylate synthase (TS) and can be incorporated into the DNA. TFT, as part of TAS‐102, is clinically evaluated in phase II studies as an oral chemotherapeutic agent. Erlotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that is often deregulated in colorectal cancer. This study investigated molecular mechanisms underlying the cytotoxic actions of the combination of an EGFR−tyrosine kinase inhibitor with TFT in colorectal cancer cells Caco2, WiDR, Lovo92, and Colo320. Drug interactions were examined by the sulforhodamine B assay and subsequent combination index (CI) analyses, cell cycle effects by FACS analysis of propidium iodide stained cells, Akt, MAPK and EGFR phosphorylation and expression levels by Western blotting and TS activity by the TS in situ assay. All combination schedules were synergistic in wt‐EGFR expressing (but with mutated downstream pathways) WiDR and Lovo92 (CI 0.4–0.8) and very synergistic in Caco2 cells (with wt‐EGFR and functional downstream pathways; CI 0.1–0.3), but in EGFR‐lacking Colo320 cells, no additional activity was found (CI 1.0–1.2). Synergism was mostly related to the induction of cell cycle arrest and an erlotinib‐mediated inhibition of the pro‐survival signaling through Akt and MAPK that was activated (phosphorylated) by TFT. Erlotinib inhibited TS activity in EGFR‐expressing cell lines, probably due to cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. TS activity was slightly lower in the combinations, probably due to cell cycle interference. Taken together, the combination of erlotinib with TFT seems to present a potential strategy in the field of molecular therapeutics. (Cancer Sci 2009)
Abbreviations
- 5FU
5‐fluorouracil
- CI
combination index
- CRC
colorectal cancer
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- NSCLC
non‐small‐cell lung cancer
- PI
propidium iodide
- SRB
sulforhodamine B
- TFT
trifluorothymidine
- TKI
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- TP
thymidine phosphorylase
- TS
thymidylate synthase
Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide. The standard therapy consists of 5FU and leucovorin, which is usually combined with either the topoisomerase I inhibitor irinotecan or the novel platinum analog oxaliplatin.( 1 ) Addition of the latter compounds substantially increased the median survival. Further improvement of therapy can be expected from drugs bypassing 5FU resistance. Therefore 5FU prodrugs are currently being investigated, including S‐1, UFT and capecitabine.( 2 ) Recently, we and others showed that another fluoropyrimidine, TFT, might be more effective in CRC cells to overcome (acquired) 5FU and/or 5‐fluoro‐2′‐deoxyuridine (FdUrd) resistance.( 3 , 4 ) TFT is part of the oral fluoropyrimidine formulation TAS‐102 and can be activated to its phosphate derivatives. When monophosphorylated, TFT can inhibit TS, thereby inhibiting the synthesis of new pyrimidines.( 3 ) In its triphosphate form, TFT can be incorporated into the DNA, causing DNA damage. Both events will lead to the induction of cell death. TAS‐102 is currently being tested in a phase II clinical trial against colon and gastric cancer.( 3 ) TAS‐102 is a promising novel formulation that also showed pronounced synergism with irinotecan and oxaliplatin.( 5 , 6 )
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed or deregulated in many human cancer types, including CRC.( 7 ) A high EGFR expression level has been related to a poor prognosis.( 8 , 9 ) Targeting EGFR might be a rational approach to treat CRC patients. EGFR inhibitors are under investigation, including the EGFR‐TKIs gefitinib and erlotinib. Erlotinib is a highly potent reversible inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR. It is an oral compound that is active against a wide range of colon cancers in vitro,( 10 ) but its clinical application is mostly limited to NSCLC in which it is active against patients with activating EGFR mutations and wild‐type k‐Ras. Erlotinib as a monotherapy has also shown activity in metastatic CRC patients,( 11 ) providing a basis for further studies in phase II in combination with chemotherapy. However, a proper analysis of the mechanism underlying the combination is essential. Although a combination of EGFR inhibition with chemotherapeutic regimens may enhance the anticancer response,( 12 , 13 ) the interaction might be dependent on schedule and concentration. The combination of the multitargeted TS inhibitor pemetrexed with erlotinib showed a sequence‐dependent synergistic interaction, for example, when cells were pre‐exposed to pemetrexed in NSCLC cell lines.( 14 , 15 ) Various combination studies with erlotinib are currently under investigation in advanced and metastatic CRC, including with capecitabine and oxaliplatin, capecitabine and irinotecan, but also with bevacizumab and 5FU, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin.( 16 , 17 , 18 )
The aim of our study was to investigate whether inhibition of EGFR could enhance the effect of TFT against CRC cells in vitro. We used erlotinib as a model TKI and investigated schedule dependency in relation to the phosphorylation levels of EGFR as well as that of the intracellular kinases Akt and MAPK. Furthermore, we assessed the effect on cell cycle distribution, modulation of TS activity, and the induction of DNA damage to gain insight into the mechanism underlying the synergistic effect of combination therapy with TFT and an EGFR‐TKI.
Materials and Methods
Cell lines and chemicals Human colon carcinoma cell lines WiDR, Colo320, Lovo92 and Caco2 were cultured as monolayers in DMEM supplemented with 10% heat‐inactivated FCS and 20 mM HEPES. Cells were maintained in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. TFT was provided by Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. (Tokushima, Japan).
Drug cytotoxicity assays Drug cytotoxicity was determined by the SRB assay as described previously.( 19 ) In 96‐well plates (Greiner Bio‐One, Frickenhausen, Germany), 5000 cells/well were seeded in 100 μL medium. After 24 h, 100 μL drug containing medium was added to the wells. After 72 h drug exposure, cells were precipitated for 1 h at 4°C with 25 μL 50% trichloroacetic acid and colored with SRB (0.4% SRB in 1% acetic acid [w/v]). The optical density was measured at 540 nm after reconstitution of the dye in 150 μL 10 mM Tris. The IC50 values were estimated from graphs and are given in means ± SEM. For combination experiments, a concentration range which was fitted according to CalcuSyn (Biosoft, Cambridge, UK) was used with a fixed ratio based on the IC50. Cells were either exposed concurrently to both TFT and erlotinib for 72 h or 24 h pre‐incubated with either TFT or erlotinib, followed by a 48 h exposure to the combination. The interaction was determined with the multiple drug effect method, in which a CI was calculated with CalcuSyn as described previously.( 5 ) This method is distinct from other methods by the fact that both “potency” and “shape” of dose–effect curves of drugs and their combinations are taken into account. For calculation of the CI, only values above a fraction affected of 0.5 were used, equivalent to 50–100% growth inhibition. Per experiment, CI values at fraction affected 0.5, 0.75, and 0.9 were averaged according to the guidelines( 5 ) and the mean was used for comparison of separate experiments. A CI <0.9 indicates synergism and >1.1 antagonism.
FACS analysis of cell cycle Cell cycle analysis and cell death measurement were carried out as described previously.( 19 ) The time‐course of cell cycle changes for various combinations with TFT was determined earlier, showing the most pronounced changes after 72 h. Therefore, we focused on 72 h treatment with IC50 concentrations of the drugs and drug combinations; this also enabled the cells to have completed enough cell cycles (at least three cycles) to determine statistically significant differences. In brief, 100 000 cells were seeded in six‐well plates. Cells were trypsinized, resuspended in medium collected from the matching sample, and centrifuged for 4 min at 1000g. Subsequently, cells were stained with PI (0.1 mg/mL) in the dark on ice. DNA content of the cells was analyzed by FACS (FACScan; BD Immunocytometry Systems, San Jose, CA, USA) with an acquisition of 10 000 events. Sub‐G1 peak was used as the indication of cell death induction.
Thymidylate Synthase in situ Activity
Inhibition of TS in intact cells was determined by measuring the conversion of [3H]‐dCyd to 3H2O, which is catalyzed by TS as described previously.( 20 ) Briefly, 1.106 cells were seeded and incubated with the IC50 concentrations of the different drugs and the simultaneous combination for 22 h. Subsequently, [3H]‐dCyd (final concentration, 1 μM; specific activity 4.9 Ci/mmol) was added to each sample for 2 h at 37°C. Blanks consisted of culture medium only and untreated cells were used as controls. The reaction was stopped by adding trichloroacetic acid and unconverted [3H]‐dCyd was removed by activated charcoal. After centrifugation, the supernatant was transferred to a liquid scintillation vial and counted.
Western blot analysis Cells were seeded in T25 culture flasks at a density of 1.5.106 cells. After 24 h, cells were exposed to IC50 concentrations of TFT or the various combination schedules (IC50 concentration) as described in the drugs cytotoxicity assay. After treatment for the indicated time‐points in the figures, cells were lysed in lysis buffer (10% glycerol, 5 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris‐HCl [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM β‐glycerophophate, 1% Triton X‐100, 0.04% protease inhibitor cocktail, 0.1% 1 M NaVO3) and centrifuged at 11 000g at 4°C for 10 min. Protein concentration in the supernatant was determined by carrying out a Bio‐Rad protein assay according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Bio‐Rad Laboratories, Veenendaal, the Netherlands). From each condition 30 μg of protein was separated on a 10–12% SDS–PAGE and electroblotted onto a PVDF membrane. Blots were blocked in 5% milk in TBST (0.15 M NaCl, 0.05% Tween‐20, 10 mM Tris–HCl [pH 8.0]) and subsequently incubated at 4°C overnight with the following antibodies: EGFR (#2232); phospho‐EGFR (Tyr1068 #2234); Akt (#9272); phospho‐Akt (Ser473 #9271); p42/44 MAPK (#9102); phospho‐p42/44 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204 #9101) (1 : 1000; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA); p53 (AB‐2; Oncogene Research Products, Cambridge, MA, USA); p21 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA); or phospho‐γ‐H2Ax (Ser139 #05‐636) (1 : 1000; Upstate, Billerica, MA, USA) and β‐Actin (#A5441) (1:10,000; Sigma Aldrich Chemicals, Deisenhofer, Germany) served as the loading control for protein amount. After the first antibody, secondary antibody was added and the signal was detected using ECL or ECL‐plus on hyperfilms (Amersham International, Chalfont St Giles, UK).
Results
Growth inhibition and combination analysis WiDR, Colo320, and Lovo92 cells showed comparable levels of sensitivity to TFT treatment as determined by the SRB assay (Table 1; Fig. 1). Cells were slightly more sensitive to TFT than to erlotinib. There was barely any difference in sensitivity to erlotinib in the three cell lines, which were all relatively insensitive with each IC50 in the μM range. This is probably because they have a different mutation status for several kinases, including EGFR (Table 1). Furthermore, they have different expression levels of p53 and p21 (Fig. 2). In WiDR cells, all combinations were synergistic. All combinations in Lovo92 cells were moderately synergistic, although at lower concentration ranges (growth inhibition <50%) the combinations were not synergistic (Fig. 1). However, we do not consider this low concentration range of therapeutic interest. In Colo320 cells the tested combinations were not synergistic, although antagonism was not observed. In contrast to previous experiences with erlotinib combined with a TS inhibitor,( 14 , 15 ) the order of administration of the combination schedule was not important to achieve synergism.
Table 1.
Characteristics of colorectal cancer cell lines used in this analysis
| EGFR | p53 | Braf | k‐Ras | PTEN | IC50 erlotinib (μM) | IC50 TFT (μM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WiDR | w.t. | mut | mut | w.t | w.t. | 8.2 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 0.3 |
| Lovo92 | w.t. | w.t. | w.t. | mut | w.t. | 4.4 ± 1.3 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| Colo320 | w.t. | w.t.† | w.t. | mut | w.t. | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| Caco2 | w.t. | w.t. | w.t. | w.t. | w.t. | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 25 ± 2.0 |
†Colo320 is w.t. p53, but lacks p21 (see Fig. 1) and therefore behaves as a mutant. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; mut, mutant; TFT, trifluorothymidine; w.t., wild type.
Figure 1.
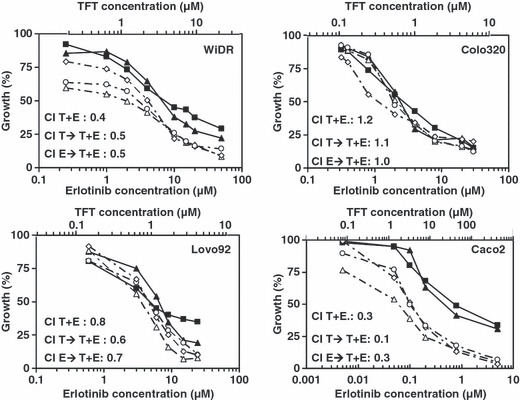
Growth inhibition curves of WiDR, Lovo92, Colo320 and Caco2 colorectal cancer cells exposed to trifluorothymidine (TFT) and erlotinib (E) alone or in combination. Cells were exposed for 72 h to TFT (T) (‐‐; scale on upper part), E (‐‐; scale on lower part), simultaneous combination (T + E; ‐◊‐), 24 h pre‐incubation with TFT followed by a 48 h combination (T → T + E; ‐Δ‐), or a 24 h pre‐incubation with E followed by a 48 h combination (E → T + E; ‐○‐). SEM was less than 20%. A mean combination index (CI) was calculated at fraction affected of 0.5, 0.75, and 0.9 and values are indicated in the graphs for each combination. CI values represent means of at least four independent experiments.
Figure 2.
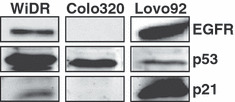
Characterization of the cell lines by Western blot analysis for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), p53, and p21 expression levels in WiDR, Lovo92, and Colo320 colorectal cancer cells.
In order to determine whether the sensitivity to erlotinib is important for synergism with TFT, we included Caco2, a cell line that is very sensitive to erlotinib (Fig. 1) due to a wild‐type EGFR expression and with no reported mutations in the genes of p53, Braf, k‐Ras, or PTEN. In addition, EGFR expression levels were higher in Caco2 than in WiDR cells.( 21 ) Caco2 cells were sensitive to erlotinib with an IC50 value in the nM range (Table 1; Fig. 1). In these cells, all three combination schedules were highly synergistic (Fig. 1).
Effects on cell cycle distribution To determine whether the synergistic actions were related to specific cell cycle effects, FACS analysis of PI stained cells was carried out using IC50 concentrations (Table 1; Fig. 3; Fig. S1, Supporting Information). TFT alone induced predominantly a G2/M‐phase arrest, although this was cell line‐ and time‐dependent. In WiDR and Lovo92, erlotinib alone increased cells in the G1‐phase, which was not time‐dependent. In contrast, in Colo320 cells, erlotinib caused no significant changes in the cell cycle distribution. The simultaneous exposure increased WiDR cells in the G1 phase to some extent. When preincubated with erlotinib, the combined treatment resulted in an increased S phase fraction. In Lovo92 cells, all drug combinations induced G1 phase arrest. In addition, in both WiDR and Lovo92 cells, the cell cycle distribution seen after combined drug treatments is more comparable to that of erlotinib alone than to that of TFT alone. When Colo320 cells were preincubated with erlotinib prior to addition of the combination, cells mostly accumulated in the S phase, whereas the other two combinations arrested cells mainly in the G2/M phase, comparable to TFT alone. Because of the different cell cycle distribution in the pre‐erlotinib schedule, erlotinib may have off‐target effects. In Colo320 cells the combinations were not synergistic. These different effects on cell cycle distribution between the various cell lines indicate that the interactions between the drugs are cell cycle mediated.
Figure 3.
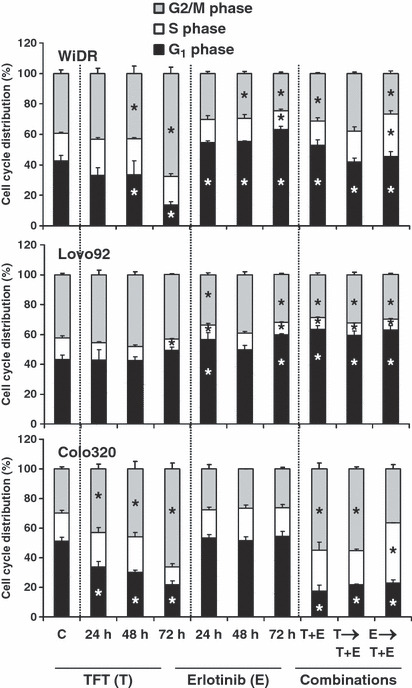
Cell cycle effects at IC50 concentrations of trifluorothymidine (TFT) (T), erlotinib (E), simultaneous combination (T + E), and the sequential combinations where cells were preincubated for 24 h with TFT (T → T + E) or E (E → T + E) followed by the T + E combination in WiDR, Lovo92 and Colo320 colorectal cancer cells. Values represent means of at least four independent experiments ± SEM. *Significant differences between treated and control (C) (P < 0.05).
Effects on cell death induction To determine whether the combinations resulted in an increase in cell death induction, we analyzed the sub‐G1‐fraction of PI stained cells. In order to determine apoptosis we also determined caspase activation, which might not be seen in the sub‐G1. The pattern of sub‐G1 accumulation agreed with caspase activation (data not shown). In all three cell lines, TFT induced cell death in a time‐dependent manner (Fig. 4). Erlotinib did not induce cell death directly. In WiDR, cell death was induced more strongly by the combinations compared to the control, although the combinations did not have a higher cell death than induced by 72 h TFT alone. In Lovo92 and Colo320 cells, cell death induced by the combination where TFT was given first was significantly higher than control levels, although lower than induced by TFT alone. As the combinations in EGFR expressing cells were synergistic, this may indicate that the combinations act by the induction of cell cycle arrest rather than cell death.
Figure 4.
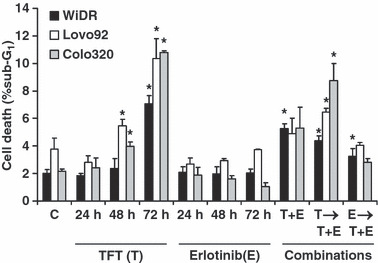
Cell death induction (sub‐G1) after exposure to IC50 concentrations of trifluorothymidine (TFT) (T), erlotinib (E). or the IC50‐ratio based combinations T + E, T → T + E (preincubated for 24 h with TFT, followed by T + E combination), or E → T + E (preincubated for 24 h with E, followed by T+E combination in WiDR, Lovo92, and Colo320 colorectal cancer cells. Values represent means of at least four independent experiments ± SEM. *Significant differences between treated and control (C) (P < 0.05).
Thymidylate synthase activity Thymidylate synthase is an important cell cycle enzyme that plays a limiting role in de novo pyrimidine deoxynucleotide synthesis. As the cell cycle effects seem to be important for the synergistic action of the combinations, and TS is one of the targets of TFT, we determined TS inhibition in intact cells treated with TFT and erlotinib (Table 2). Based on previous time‐course experiments with TS inhibitors in these cell lines, we chose 24 h to measure the inhibition.( 22 ) TFT markedly inhibited TS activity in all three cell lines. Erlotinib alone also inhibited TS activity in EGFR expressing WiDR and Lovo92 cells. After a simultaneous combination, TS was inhibited to a larger extent than by TFT alone. This level of inhibition was almost similar to the expected level of inhibition, although the decrease was not significant (Table 2). The effect of erlotinib alone on TS might be related to a cell cycle‐dependent activity of TS.( 15 , 23 )
Table 2.
Thymidylate synthase in situ activity in WiDR, Lovo92 and Colo320 colorectal cancer cells
| TFT | Erlotinib | Combination | Expected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WiDR | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 37.4 ± 4.8 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.8 |
| Lovo92 | 33.6 ± 2.2 | 64.3 ± 10.2 | 24.3 ± 4.8 | 21.6 |
| Colo320 | 20.4 ± 2.2 | 101.5 ± 7.2 | 13.2 ± 3.4 | 20.7 |
Thymidylate synthase in situ activity after 24 h exposure to IC50 concentrations of either trifluorothymidine (TFT), erlotinib, or the simultaneous combination. Values represent the percentage of untreated control cells and are expressed as means of at least three independent experiments ± SEM. Expected values are calculated by multiplying the percentage inhibition by erlotinib by the percentage activity of TFT alone. When the value is lower than the expected value, this means that thymidylate synthase inhibition is synergistic.
Effects on EGFR, MAPK and Akt phosphorylation Erlotinib inhibits EGFR phosphorylation and thereby its downstream targets, Akt and MAPK. To determine whether cell cycle arrest was related to inhibition of these important cell growth signalling pathways, Western blot analysis was carried out. Lovo92 strongly expressed EGFR, WiDR had a moderate EGFR expression, but Colo320 did not express EGFR (Fig. 2).
As effects on phosphorylation are direct, the phosphorylation status of these proteins was determined after 2 h exposure of the drugs and simultaneous drug combination (Fig. 5). Moreover, to determine whether erlotinib can effectively inhibit EGFR, EGF was added to the cultures 5 min prior to cell lysis. In this way, it can be determined whether the EGFR signalling pathway was inhibited. In WiDR and Lovo92 cells, EGFR, Akt, and MAPK phosphorylation increased after EGF stimulation. TFT slightly increased the phosphorylation levels of MAPK. Erlotinib alone increased EGFR phosphorylation, but prevented the stimulation by EGF. Erlotinib clearly prevented activation of the downstream kinase Akt and to a lesser extent that of MAPK. In the combination, phosphorylation of EGFR and Akt were inhibited almost completely, whereas the stimulation of MAPK by EGF and TFT was completely prevented. In Colo320 cells, EGFR, Akt, and MAPK phosphorylation levels did not change after stimulation with EGF. EGFR was not detectable and could not be upregulated to a detectable level by any of the tested drugs or drug combinations. Akt phosphorylation was slightly decreased after TFT alone. These results indicate that erlotinib can inhibit EGFR signalling in cells with an active EGFR, but has no effect on downstream signaling in cells with low or absent EGFR expression.
Figure 5.
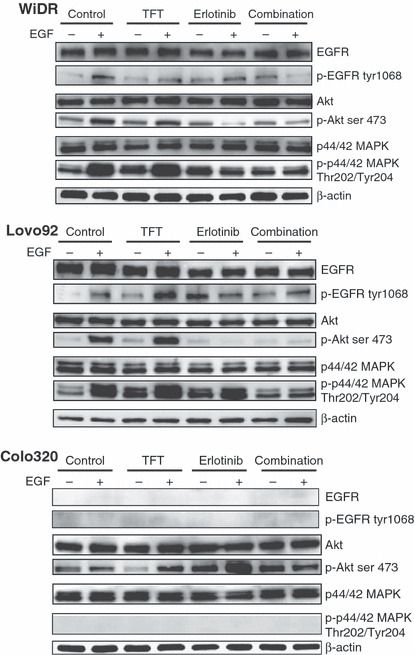
Western blot of expression levels of intracellular kinases in colorectal cancer cells after 2 h exposure to trifluorothymidine (TFT) alone, erlotinib (E) alone, or in simultaneous combination (T + E) with or without epidermal growth factor (EGF) to stimulate EGF receptor (EGFR)‐related signaling. The blots are representative of two or three independent experiments. Colo320 cells did not show any detectable expression of phosphorylated (p‐)EGFR or phosphorylated MAPK. E → T + E, cells preincubated with E, followed by T + E combination; T → T + E, cells preincubated with TFT, followed by T + E combination.
In order to investigate long‐term effects, and the effects in the sequential combinations, which can not be determined after 2 h and in which EGF addition does not play a role (data not shown), we also investigated the effects of the combination after 72 h (Fig. 6). Surprisingly, in WiDR and Lovo92 cells, after 48 h of TFT exposure phosphorylated EGFR increased, which was reduced after 72 h. In both WiDR and Lovo92 cells TFT increased phosphorylation levels of MAPK and Akt time‐dependently. Erlotinib barely affected Akt phosphorylation, but in WiDR cells, phosphorylated Akt increased after 24 h, which reduced in time.
Figure 6.
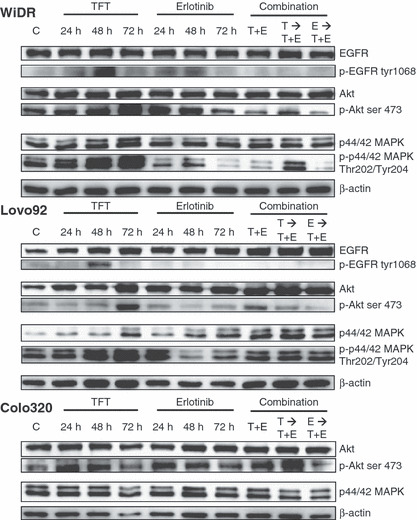
Western blot of expression levels of intracellular kinases after 24, 48, and 72 h exposure to trifluorothymidine (TFT) alone, erlotinib (E) alone, or in three combination schedules (72 h). The blots are representative of three independent experiments. Colo320 cells did not express detectable epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), phosphorylated (p‐)EGFR, or phosphorylated MAPK (Fig. 5), so blots have not been included in this figure. C, control; E → T + E, cells preincubated with E, followed by T + E combination; T → T + E, cells preincubated with TFT, followed by T + E combination; T + E, simultaneous combination of TFT and E.
In WiDR and Lovo92, addition of erlotinib prevented the pro‐survival signalling that was induced by TFT, even to lower levels than the control phosphorylation levels. Although after the sequential combination where TFT was given first, Akt and MAPK were still activated, this was reduced to control levels. In Colo320 cells, which did not express detectable EGFR or phosphorylated MAPK, no changes in expression and/or phosphorylation levels were observed after all different drugs and drug combinations. Overall, the inhibition of cell growth can be related to cell cycle effects, which in turn are related to the inhibition of the pro‐survival signals that are induced by TFT.
Effect on DNA damage Recent reports have indicated that EGFR inhibition might decrease DNA repair activity,( 24 , 25 ) therefore we determined the level of DNA damage after 72 h of drug incubation and whether DNA damage levels decreased (due to repair) after 48 h of growth in drug‐free medium (Fig. 7). DNA damage was monitored by determination of the phosphorylation status of histone γ–H2Ax, one of the first events in DNA damage response. Cells exposed to the drugs or drug combinations induced γ‐H2Ax phosphorylation, although for the combinations a less than additive effect was seen. In Lovo92 and WiDR cells, this DNA damage increased significantly (up to 55‐fold) following subsequent 48 h of culture in drug‐free medium. In Colo320 cells this accumulation did not increase, but may explain the observed cell cycle changes after exposure to the combination.
Figure 7.
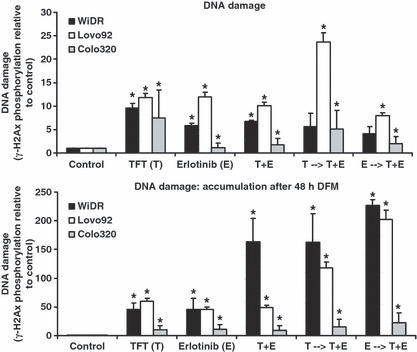
Phosphorylation levels of γ‐H2Ax as a marker for DNA damage induction in colorectal cancer cells. Western blot analysis was carried out after 72 h incubation with IC50 concentrations. DNA damage accumulation was measured after 72 h drug exposure then recovery for 48 h in drug‐free medium. Values represent means corrected for control phosphorylation levels (set to 1) ± SEM. *Significant differences between treated and control (P < 0.05). E, erlotinib; E → T + E, cells preincubated with E, followed by T + E combination; T → T + E, cells preincubated with trifluorothymidine (TFT), followed by T + E combination; T + E, simultaneous combination of TFT and E.
Discussion
This study shows that a combination of TFT with erlotinib is synergistic in EGFR expressing colon cancer cells, also in the presence of a k‐Ras mutation. This sensitization of moderately sensitive cells to erlotinib indicates the potential for evaluating the combination of TFT with EGFR‐TKIs. Ongoing clinical studies are confirming the promising therapeutic activity of second‐generation EGFR‐TKIs and multitargeted TKIs in several tumor types.( 26 , 27 ) The combination of TFT with erlotinib was strongly synergistic in Caco‐2 cells with a functional (e.g. wild‐type) EGFR signaling pathway, and the combination was synergistic in WiDR and Lovo92 cells that were moderately sensitive to erlotinib with mutations in the downstream EGFR pathway. The combination was not synergistic in cells that did not express EGFR. This underlines the importance of an active EGFR signaling pathway in the synergistic interaction. The mechanism underlying the synergistic interaction was probably due to inhibition of the downstream EGFR pro‐survival signaling pathway and the induction of DNA damage.
Synergistic actions with EGFR‐TKIs have previously been reported with cytotoxic agents such as 5FU and TS inhibitors (pemetrexed) and irinotecan, and with radiation.( 15 , 28 , 29 , 30 ) These cytotoxic agents and radiation could increase the phosphorylation level of EGFR, which possibly reflects the activation of pro‐survival signaling. This effect was blocked by addition of EGFR‐TKIs, explaining the synergistic activities. 5FU or pemetrexed‐induced activation of EGFR phosphorylation was prevented by gefitinib and erlotinib.( 15 , 31 ) In our study, such a synergistic interaction was only found for cells that constitutively expressed both EGFR and activated the pro‐survival signaling after exposure to TFT. TFT alone activated EGFR phosphorylation levels, and highly increased the phosphorylation levels of the pro‐survival kinases MAPK and Akt. This pro‐survival signaling could be inhibited by the addition of erlotinib, possibly explaining the synergistic interaction. In EGFR lacking Colo320 cells, erlotinib could inhibit cell growth and no synergism was found. In these cells TFT hardly activated pro‐survival signaling and erlotinib did not have any effect on the phosphorylation levels of the tested intracellular kinases or on the cell cycle. Therefore, it is likely that the mechanism of erlotinib in these cells do not involve changes in intracellular signaling in the examined routes.
All three cell lines were moderately sensitive to erlotinib. In NSCLC and CRC, mutations in k‐Ras and BRAF are potential biomarkers for erlotinib sensitivity. Mutations in these genes can cause constitutive activation of MAPK. The low EGFR expression in one cell line and k‐Ras mutations may explain the low sensitivity to erlotinib. However, independent of the mutations in k‐Ras, downstream signaling of Akt and MAPK was significantly inhibited in our cell lines. In addition, EGFR status is known not to be a predictive factor for responses to cetuximab, as responses were reported in patients with EGFR‐negative tumors.( 32 , 33 ) In addition, erlotinib has shown to have some off‐target effects in leukemia cells, in which the JAK2/STAT5 pathway was inhibited,( 34 ) and which were likely to be comparable to the off‐target effects of gefitinib.( 35 ) In the latter studies, differentiation and cell cycle blockade induced by EGFR antagonists exerting off‐target effects on Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) cells were not automatically linked to an apoptotic response.( 34 , 35 ) Our data indicate that erlotinib also has off‐target effects in colon cancer cells. Ongoing clinical studies, in which the responses to the new‐generation EGFR‐TKIs are evaluated, appear to be promising. In this respect, based on our current data, the inhibition of pro‐survival signaling by EGFR‐TKIs can enhance the efficacy of the chemotherapeutic agent and may be worthwhile to test in a clinical setting.
Recent studies reported that ERGF‐TKIs can decrease the expression levels and activity of TS in NSCLC, breast, and colorectal cancer cells( 15 , 23 , 36 ) and could be related to synergism. As erlotinib did not inhibit TS itself in cell‐free extracts,( 15 ) the decrease in TS can be explained by the G1/G0 cell cycle arrest that was induced by the EGFR‐TKI. TS is an enzyme that is only active in the S phase of the cell cycle. TS activity was decreased in the combinations, compared to TFT alone, which is possibly related to an increased inhibition of TS and the induced cell cycle arrest.( 15 )
Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors have been shown to stimulate the induction of apoptosis in various cell types.( 15 , 31 ) However, in our colon cancer cell line panel, erlotinib itself did not induce cell death, as shown by the sub‐G1 analysis. The lack of cell death is supported by the absence of caspase activation following erlotinib treatment. Erlotinib seems to act more on the cell cycle, arresting cells in the G0/G1 phase, which can be mediated by inhibition of pro‐survival signaling. As cell death was not involved in the synergistic actions, it is expected that the action of the combinations is more related to an induction of cell cycle arrest, possibly mediated by the induction of DNA damage. Previously it was reported that cell cycle modulation is important for the efficacy of the combination of EGFR‐TKIs with cytotoxic agents.( 15 , 37 ) Cellular damage induced by chemotherapeutic compounds can convert EGFR ligands from growth factors into survival factors for cancer cells that express functional EGFR.( 38 ) In this context, the blockade of EGFR signaling by EGFR‐TKI could prevent repair of cellular damage induced by cytotoxic drugs.
Inhibition of EGFR signaling has previously been shown to reduce DNA damage repair.( 39 ) TFT is a known inducer of DNA damage,( 5 , 6 ) therefore the combined treatment with erlotinib might cause persistent DNA damage induction, for example, TFT‐induced DNA damage can not be repaired due to inhibition of the DNA repair mechanisms by erlotinib.( 39 ) This notion is further strengthened by the finding that persistent DNA damage was only observed in EGFR expressing cells. This may also explain why erlotinib alone induced DNA damage, as it also affects basal repair levels. Thus, the synergism found between TFT and erlotinib might be explained by a diminished ability to repair TFT‐induced DNA damage lesions.
Thymidine phosphorylase plays a role in apoptosis, cell growth, and angiogenesis.( 40 ) Moreover, TP might be induced after exposure to EGFR‐TKIs and cytotoxic agents, which has been related to chemoresistance.( 23 ) TAS‐102 consists of TFT combined with thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor.( 3 ) This may be an additional advantage of a clinical combination of TAS‐102 with erlotinib. Further investigation is required to elucidate the role of TP in enhancement of responses to EGFR‐TKI, especially in vivo. In conclusion, the combination of TFT with EGFR‐TKI was synergistic, which was dependent on EGFR expression and probably mediated by cell cycle deregulation and not immediate cell death. Although further research is needed to fully elucidate this promising combination in CRC therapy, the concept of combined molecular targeting of EGFR and TFT seems to present a potential strategy in the field of molecular therapeutics.
Disclosure Statement
G. J. Peters received a research grant from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd; M. Fukushima is an employee of Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Supporting information
Fig. S1. Example of histrograms of cell cycle distribution by FACS analysis of WiDR colorectal cancer cells after 72 h exposure to trifluorothymidine (TFT) (T) alone, erlotinib (E) alone, or in combination. E → T + E, cells preincubated with E, followed by T + E combination; T → T + E, cells preincubated with trifluorothymidine (TFT) (T), followed by T + E combination; T + E, simultaneous combination of TFT and E.
Please note: Wiley‐Blackwell are not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting materials supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing material) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
Supporting info item
Acknowledgment
This study was financially supported by Tokushima Research Center, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Tokushima, Japan.
References
- 1. Thirion P, Michiels S, Pignon JP et al. Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: an updated meta‐analysis. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 3766–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Rich TA, Shepard RC, Mosley ST. Four decades of continuing innovation with fluorouracil: current and future approaches to fluorouracil chemoradiation therapy. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 2214–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Temmink OH, Emura T, De Bruin M, Fukushima M, Peters GJ. Therapeutic potential of the dual‐targeted TAS‐102 formulation in the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 779–89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Emura T, Murakami Y, Nakagawa F, Fukushima M, Kitazato KA. A novel antimetabolite, TAS‐102 retains its effect on FU‐related resistant cancer cells. Int J Mol Med 2004; 13: 545–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Temmink OH, Hoebe EK, Fukushima M, Peters GJ. Irinotecan‐induced cytotoxicity to colon cancer cells in vitro is stimulated by pre‐incubation with trifluorothymidine. Eur J Cancer 2007; 43: 175–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Temmink OH, Hoebe EK, Van Der Born K, Ackland SP, Fukushima M, Peters GJ. Mechanism of trifluorothymidine potentiation of oxaliplatin‐induced cytotoxicity to colorectal cancer cells. Br J Cancer 2007; 96: 231–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Amador ML, Hidalgo M. Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2004; 4: 51–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Hemming AW, Davis NL, Kluftinger A et al. Prognostic markers of colorectal cancer: an evaluation of DNA content, epidermal growth factor receptor, and Ki‐67. J Surg Oncol 1992; 51: 147–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Mayer A, Takimoto M, Fritz E, Schellander G, Kofler K, Ludwig H. The prognostic significance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, epidermal growth factor receptor, and mdr gene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer 1993; 71: 2454–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Yang JL, Qu XJ, Russell PJ, Goldstein D. Interferon‐alpha promotes the anti‐proliferative effect of Erlotinib (OSI‐774) on human colon cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett 2005; 225: 61–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Townsley CA, Major P, Siu LL et al. Phase II study of erlotinib (OSI‐774) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2006; 94: 1136–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Dassonville O, Bozec A, Fischel JL, Milano G. EGFR targeting therapies: monoclonal antibodies versus tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Similarities and differences. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2007; 62: 53–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Tortora G, Gelardi T, Ciardiello F, Bianco R. The rationale for the combination of selective EGFR inhibitors with cytotoxic drugs and radiotherapy. Int J Biol Markers 2007; 22: S47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Li T, Ling YH, Goldman ID, Perez‐Soler R. Schedule‐dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and erlotinib in human non‐small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 3413–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Giovannetti E, Lemos C, Tekle C et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic interaction of erlotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with the multitargeted antifolate pemetrexed in non‐small‐cell lung cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 2008; 73: 1290–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Bajetta E, Di Bartolomeo M, Buzzoni R, Ferrario E, Dotti KF, Mariani L, Bajetta R, Gevorgyan A, Venturino P, Galassi M. Dose finding study of erlotinib combined to capecitabine and irinotecan in pretreated advanced colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009; 64: 67–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Meyerhardt JA, Zhu AX, Enzinger PC, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Kulke MH, Earle CC, Vincitore M, Michelini A, Sheehan S, Fuchs CS. Phase II study of capecitabine, oxaliplatin, and erlotinib in previously treated patients with metastastic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 1892–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Meyerhardt J, Stuart K, Fuchs C, Zhu A, Earle C, Bhargava P, Blaszkowsky L, Enzinger P, Mayer R, Battu S, Lawrence C, Ryan D. Phase II study of FOLFOX, bevacizumab and erlotinib as first‐line therapy for patients with metastastic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 2007; 18: 1185–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Bijnsdorp IV, Kruyt FA, Gokoel S, Fukushima M, Peters GJ. Synergistic interaction between trifluorothymidine and docetaxel is sequence dependent. Cancer Sci 2008; 99: 2302–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Rots MG, Pieters R, Kaspers GJ et al. Circumvention of methotrexate resistance in childhood leukemia subtypes by rationally designed antifolates. Blood 1999; 94: 3121–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Lemos C, Kathmann I, Giovannetti E, Calhau C, Jansen G, Peters GJ. Impact of cellular folate status and epidermal growth factor receptor expression on BCRP/ABCG2‐mediated resistance to gefitinib and erlotinib. Br J Cancer 2009; 100: 1120–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Van der Wilt CL, Kuiper CM, Peters GJ. Combination studies of antifolates with 5‐fluorouracil in colon cancer cell lines. Oncol Res 1999; 11: 383–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Magné N, Fischel JL, Dubreuil A et al. ZD1893 (Iressa) modifies the activity of key enzymes linked to fluoropyrimidine activity: rational basis for a new combination therapy with capecitabine. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 4735–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yacoub A, McKinstry R, Hinman D, Chung T, Dent P, Hagan MP. Epidermal growth factor and ionizing radiation up‐regulate the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and ERCC1 in DU145 and LNCaP prostate carcinoma through MAPK signaling. Radiat Res 2003; 159: 439–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Li L, Wang H, Yang ES, Arteaga CL, Xia F. Erlotinib attenuates homologous recombinational repair of chromosomal breaks in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9141–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Gora‐Tybor J, Robak T. Targeted drugs in chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr Med Chem 2008; 15: 3036–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Nahleh ZA. Molecularly targeted therapy in breast cancer: the new generation. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 2008; 3: 100–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Okabe T, Okamoto I, Tsukioka S et al. Synergistic antitumor effect of S‐1 and the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib in non‐small cell lung cancer cell lines: role of gefitinib‐induced down‐regulation of thymidylate synthase. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 599–606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Koizumi F, Kanzawa F, Ueda Y, Koh Y, Tsukiyama S, Taguchi F, Tamura T, Saijo N, Nishio K. Synergistic interaction between the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (“Iressa”) and the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor CPT‐11 (irinotecan) in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2004; 108: 464–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Chinnaiyan P, Huang S, Vallabhaneni G, Armstrong E, Varambally S, Tomlins SA, Chinnaiyan AM, Harari PM. Mechanisms of enhanced radiation response following epidermal growth factor receptor signaling inhibition by erlotinib (Tarceva). Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3328–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Van Schaeybroeck S, Kyula J, Kelly DM et al. Chemotherapy‐induced epidermal growth factor receptor activation determines response to combined gefitinib/chemotherapy treatment in non‐small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 1154–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Chung KY, Shia J, Kemeny NE et al. Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 1803–1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Saltz L. Epidermal growth factor receptor‐negative colorectal cancer: is there truly such an entity? Clin Colorectal Cancer 2005; 5 (Suppl 2): S98–S100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Boehrer S, Adès L, Braun T et al. Erlotinib exhibits antineoplastic off‐target effects in AML and MDS: a preclinical study. Blood 2008; 111: 2170–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Boehrer S, Adès L, Galluzzi L et al. Erlotinib and gefitinib for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: a preclinical comparison. Biochem Pharmacol 2008; 76: 1417–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Budman DR, Soong R, Calabro A, Tai J, Diasio R. Identification of potentially useful combinations of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase antagonists with conventional cytotoxic agents using median effect analysis. Anticancer Drugs 2006; 17: 921–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Morelli MP, Cascone T, Troiani T et al. Sequence dependent antiproliferative effects of cytotoxic drugs and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Ann Oncol 2005; 16 (Suppl 4): iv 61–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 2000; 19: 6550–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Bandyopadhyay D, Mandal M, Adam L, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R. Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA‐dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 1568–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Liekens S, Bronckaers A, Pérez‐Pérez MJ, Balzarini J. Targeting platelet‐derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase for cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol 2007; 74: 1555–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Fig. S1. Example of histrograms of cell cycle distribution by FACS analysis of WiDR colorectal cancer cells after 72 h exposure to trifluorothymidine (TFT) (T) alone, erlotinib (E) alone, or in combination. E → T + E, cells preincubated with E, followed by T + E combination; T → T + E, cells preincubated with trifluorothymidine (TFT) (T), followed by T + E combination; T + E, simultaneous combination of TFT and E.
Please note: Wiley‐Blackwell are not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting materials supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing material) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
Supporting info item


