Correction: Acta Neuropathol Commun (2022) 10:180 10.1186/s40478-022-01480-y
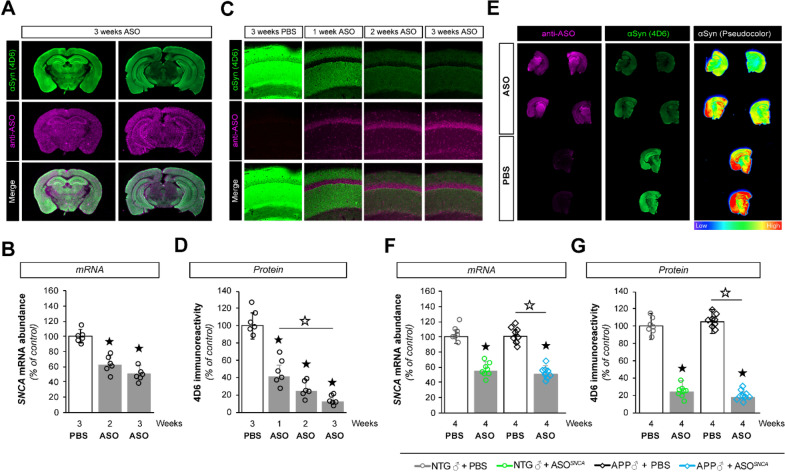
Following the publication of the original article [1], it was noted that due to a technical error Fig. 1c was incorrect. The images presented in Fig. 1C for the “2 weeks ASO” and “3 weeks ASO” groups are identical. Unfortunately, this was not detected prior to publication. The authors have reviewed the original images and raw data files for this experiment and they can confirm that the published images for the “2 week ASO” group are not consistent with the original raw files but depict the raw images corresponding to the "3 weeks ASO” group. The correct figure is given hereafter.
Fig. 1.
ASO1 disperses throughout the brain and lowers SNCA gene expression. A Infra-red imaging documenting the widespread distribution of ASOs 3 weeks after injection using anti- ASO (pink) and anti-αSyn (4D6, green) antibodies. B Reduction in SNCA mRNA at 2 and 3 weeks post-injection as determined by RT-qPCR. C Confocal imaging illustrating the presence of ASO1 (pink) and a corresponding decrease in αSyn (green) in mouse hippocampi. D Quantification of hippocampal 4D6 immunoreactivity in ASO1 or PBS treated mice. E Infra-red imaging detectedαSyn (green) and ASO (pink) in coronal brain sections from PBS and ASO treated mice. The relative αSyn signal was lower in ASO-injected animals than in PBS-injected animals (pseudocolor). F, G Measurements of SNCA mRNA abundance by RT-qPCR (F) and αSyn protein amounts by immunofluorescence (G) in transgenic (APP) and non-transgenic (NTG) animals treated with PBS or ASO. Histogram bars represent mean ± SEM. ★P < 0.05 compared to NTG + PBS, ☆P < 0.05 compared to APP + PBS
The correction does not change the conclusions of the published work.
The incorrect Fig. 1(C) reads:
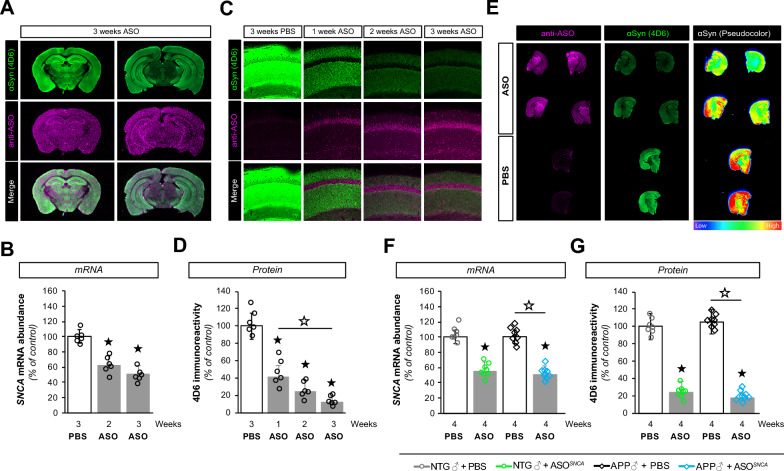
The correct Fig. 1(C) should read:
Fig. 1.
ASO1 disperses throughout the brain and lowers SNCA gene expression. A Infra-red imaging documenting the widespread distribution of ASOs 3 weeks after injection using anti- ASO (pink) and anti-αSyn (4D6, green) antibodies. B Reduction in SNCA mRNA at 2 and 3 weeks post-injection as determined by RT-qPCR. C Confocal imaging illustrating the presence of ASO1 (pink) and a corresponding decrease in αSyn (green) in mouse hippocampi. D Quantification of hippocampal 4D6 immunoreactivity in ASO1 or PBS treated mice. E Infra-red imaging detectedαSyn (green) and ASO (pink) in coronal brain sections from PBS and ASO treated mice. The relative αSyn signal was lower in ASO-injected animals than in PBS-injected animals (pseudocolor). F, G Measurements of SNCA mRNA abundance by RT-qPCR (F) and αSyn protein amounts by immunofluorescence (G) in transgenic (APP) and non-transgenic (NTG) animals treated with PBS or ASO. Histogram bars represent mean ± SEM. ★P < 0.05 compared to NTG + PBS, ☆P < 0.05 compared to APP + PBS
The correct figure has been included in this correction, and the original article [1] has been corrected.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference
- 1.Brown JL, Hart DW, Boyle GE, et al. NCA genetic lowering reveals differential cognitive function of alpha-synuclein dependent on sex. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022;10:180. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01480-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]