Fig. 3. Repair of concurrent RNA breaks results in large RNA excisions.
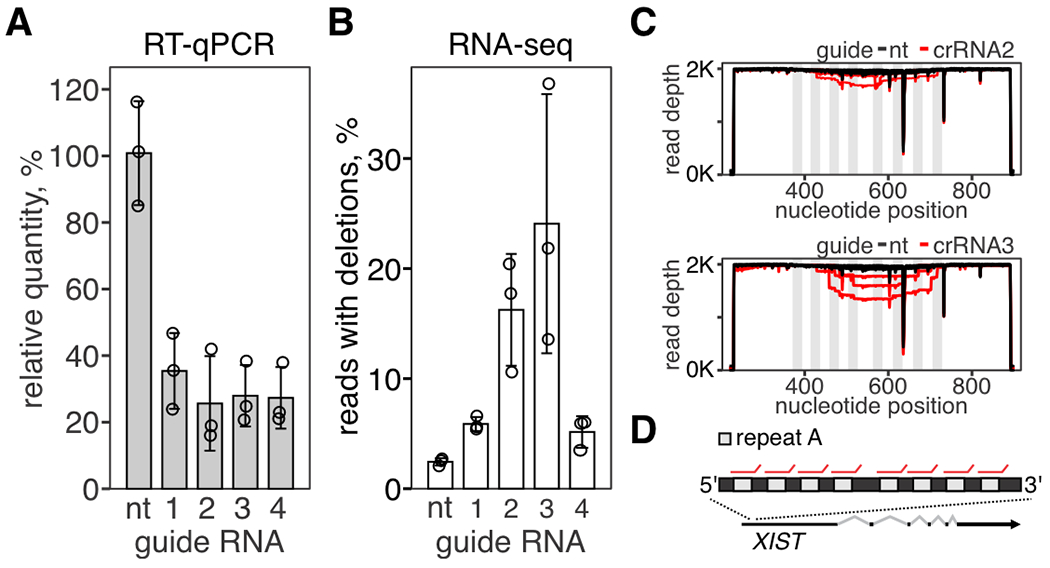
(A) Repetitive region (repeat A) in XIST transcript was targeted with SthCsm complex with four different guide RNAs. Knockdown of XIST was quantified with RT-qPCR. Data is shown as the mean of three biological replicates ± SD. B) Amplicon-seq was used to quantify programmed RNA deletions in XIST. C) Repeat A was amplified and deep-sequenced. Reads were aligned to the reference sequence (NR_001564.2, GenBank). Graphs show sequencing depth (y-axes) at the amplified region of the transcript (x-axes). Every line shows a biological replicate (n = 3). Vertical light gray rectangles indicate the position of repeats targeted by Csm complexes. D) Repeat A architecture in XIST lncRNA. Red lines show binding sites for Csm complexes.
