Fig. 5. Programmable excision of a non-sense mutation in the CFTR transcript restores translation.
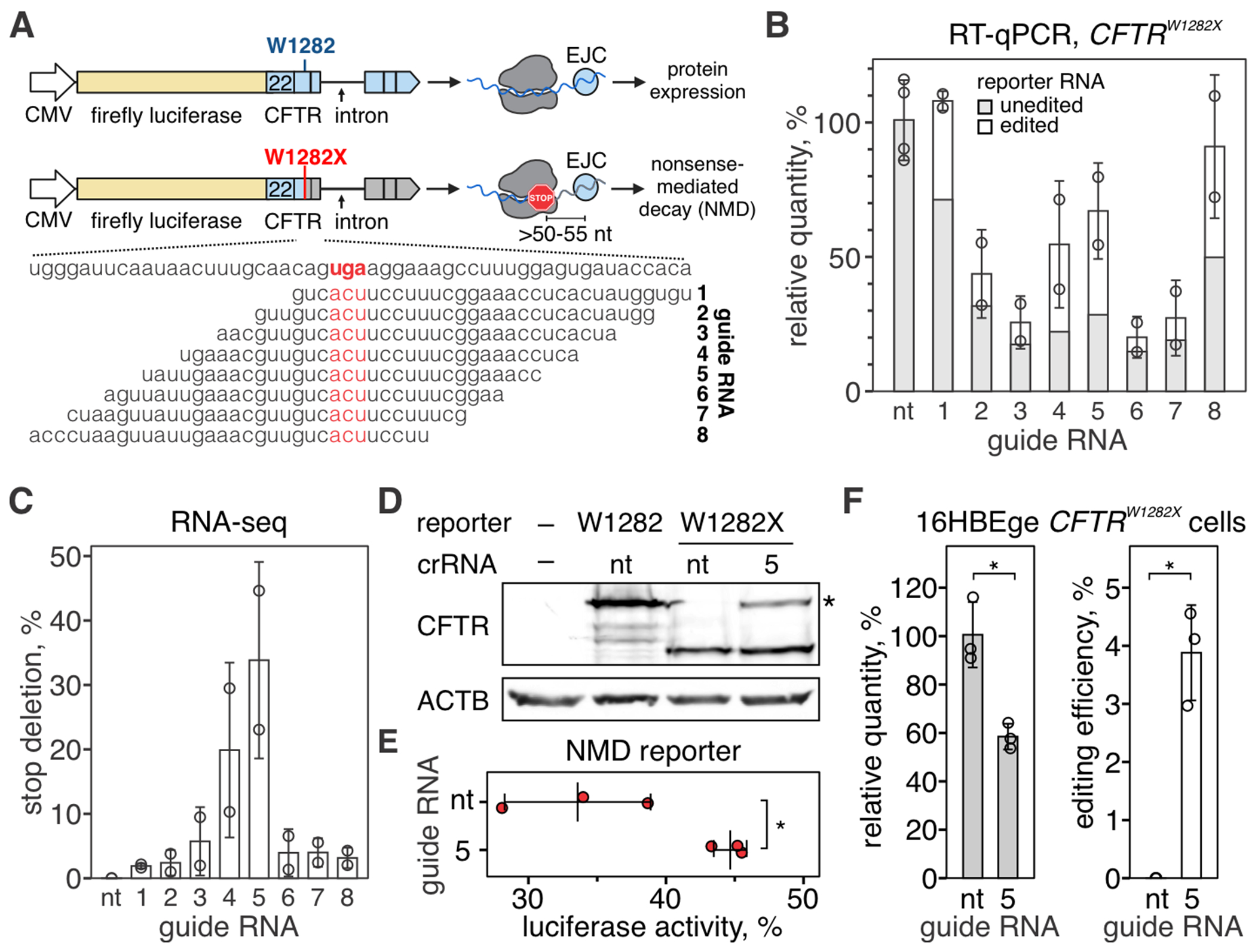
(A) Diagram of a luciferase-based reporter for CFTRW1282X mutation (fLuc-CFTR, top) and guide RNA design (bottom). Top: Firefly luciferase was genetically linked to exons 22-27 of the CFTR cDNA, and synthetic intron sequence was inserted between exons 24 and 25. See Methods for additional details. Bottom: Eight crRNAs were tiled across the mutation (W1282X) to guide the excision of the stop codon (UGA, highlighted with red). (B) RT-qPCR was used to quantify fLuc-CFTR transcript targeted with Csm complexes. Amplicons were deep-sequenced to quantify edited vs. unedited reporter RNA. See fig. S6A for sequencing depth plots. (C) Quantification of deletions that remove stop codon (W1282X). (D) Western blot with antibodies against CFTR amino acid residues 1204-1211 with lysates from 293T cells expressing fLuc-CFTR or fLuc-CFTRW1282X) and Csm complexes with non-targeting (nt) guide RNA or CFTR-targeting guide RNA 5. See fig. S6B for uncropped images. (E) Quantification of luciferase activity in 293T cells transfected with fLuc-CFTRW1282X and Csm complexes with non-targeting guide RNA or targeting guide RNA 5. Middle bar shows mean of three biological replicates (red dots). Error bars show mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, Welch’s t-test. (F) Left: RT-qPCR was used to quantify CFTR transcript in HBE16ge CFTRW1282X cells transfected with plasmids encoding for Csm complexes with non-targeting guide RNA (nt) or CFTR-targeting guide RNA 5. Right: qPCR amplicons were deep-sequenced, and deletions removing W1282X codon were quantified. See fig. S6C for depth plot. Data is shown as the mean of three biological replicates ± SD. *P < 0.05, Welch’s t-test.
