Abstract

Provided herein are novel furopyridine and furopyrimidine compounds as PI4K inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions, use of such compounds in treating malaria and viral infections, and processes for preparing such compounds.
Important Compound Classes

Title
Furopyridin and Furopyrimidin, Inhibitors of PI4K, for Use in the Treatment of Parasite Infection and Malaria
Patent Publication Number
WO 2024/033280 A1
Publication Date
February 15, 2024
Priority Application
US 63/370,838 and US 63/480,808
Priority Date
August 9, 2022 and January 20, 2023
Inventors
Kulkarni, S.; Spangenberg, T.; Cabrera, D. G.; Kandepedu, N.; Von Geldern, T. W.; Basarab, G.
Assignee Company
Merck Patent GmbH, Germany
Disease Area
Malaria and viral infection
Biological Target
PI4K
Summary
Malaria represents a major global health burden with an estimated 229 million new cases and nearly 409,000 deaths in 2019. It is a vector-borne infectious disease caused by the hematoprotozoan parasite of genus Plasmodium. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), Plasmodium falciparum was responsible for most of the malaria related morbidity and mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Plasmodium kinases are attractive targets for new generation antimalarials as both protein and lipid kinases are involved in key signaling pathways at various stages of the parasite lifecycle. Lipid kinases are important in all stages of Plasmodium lifecycle, this includes phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase (PI4K) that catalyzes the conversion of phosphatidylinositol (PI) to phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P). Therefore, PI4K inhibitors show great potential for the treatment of PI4K-related disorders such as malaria and viral infections.
The present application describes a series of novel furopyridine and furopyrimidine compounds as PI4K inhibitors for the treatment of malaria and viral infections. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
R = AR1 or HT1;
Q =  ,
,  , or
, or  ; and
; and
Z = CH, CHal, CAlk2, CCHal3 or N.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The in vitroPlasmodium falciparum growth inhibition assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit growth and propagation of the Plasmodium falciparum parasite. The IC50 (nM) are shown in the following Table.
Biological Data
The Table below shows representative
compounds that were tested for their ability to inhibit growth and
propagation of the Plasmodium falciparum parasite.
The biological data obtained from testing representative examples
are listed in the following Table.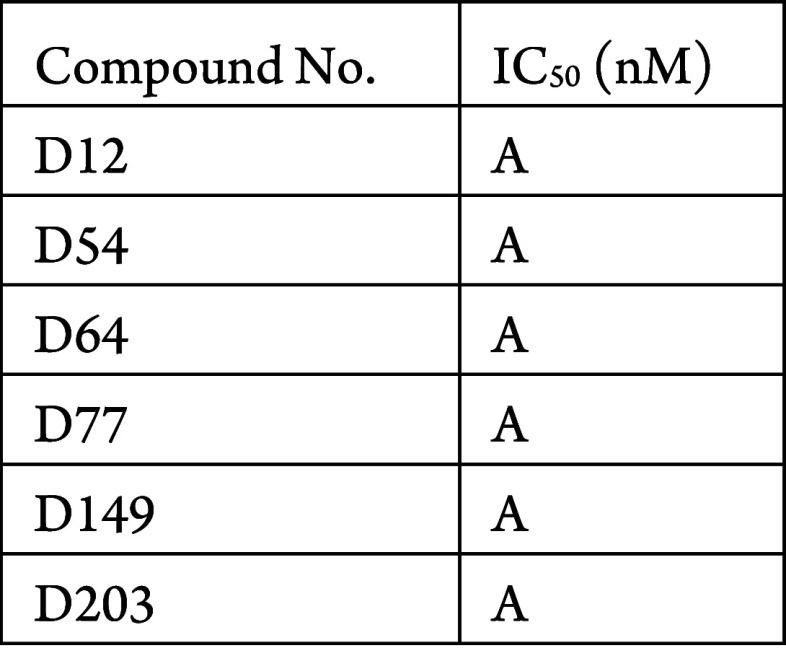
For IC50: A means <10 nM.
Claims
Total claims: 29
Compound claims: 20
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 6
Method of treatment claims: 3
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Li G.; Wu Y.; Zhang Y.; Wang H.; Li M.; He D.; Guan W.; Yao H. Research progress on phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115993. 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papur O. S.; Glatz J. F. C.; Luiken J. J. F. P. Protein kinase-D1 and downstream signaling mechanisms involved in GLUT4 translocation in cardiac muscle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119748. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. P. S.; Manjunatha U. H.; Mikolajczak S.; Ashigbie P. G.; Diagana T. T. Drug discovery for parasitic diseases: powered by technology, enabled by pharmacology, informed by clinical science. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 260–271. 10.1016/j.pt.2023.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey B. L.; Nguyen W.; Cowman A. F.; Sleebs B. E. Chemo-proteomics in antimalarial target identification and engagement. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 2303–2351. 10.1002/med.21975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow-Busch I.; Shaw A. L.; Burke J. E. PI4KA and PIKfyve: Essential phosphoinositide signaling enzymes involved in myriad human diseases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2023, 83, 102207. 10.1016/j.ceb.2023.102207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



