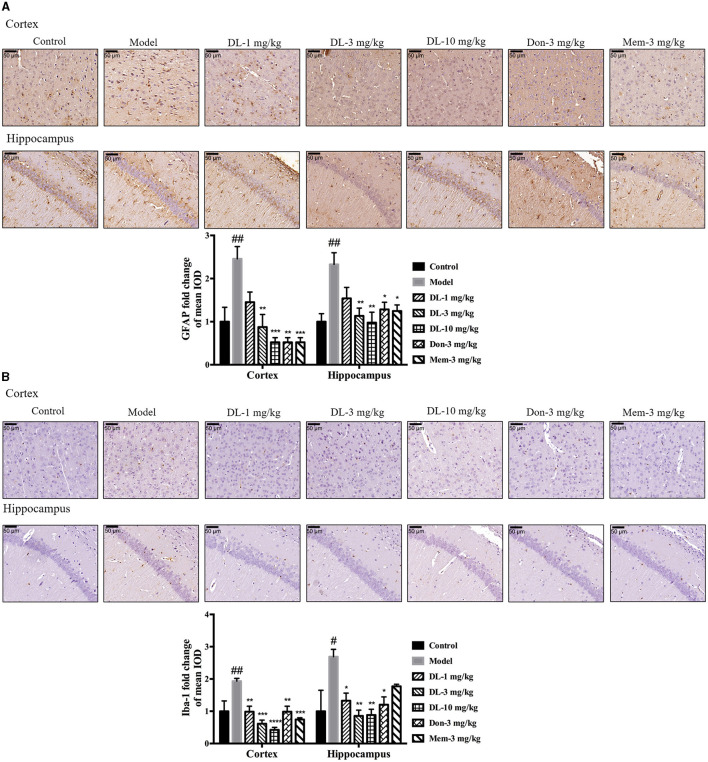
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 as published. The representative pictures for GFAP staining in the hippocampus were identical for both model group and Don-3 mg/kg group, in which the picture in Model group was used by mistake. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
Figure 5.
DL0410 decreased the activation of astrocytes and microglia in the hippocampus and cortex. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 3). DL0410 decreased the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1), and decreased the activation of astrocytes (A) and microglia (B) in the hippocampus and cortex [GFAP: cortex F(6, 14) = 7.660, p = 0.0009, hippocampus F(6, 14) = 4.969, p = 0.0064; Iba-1: cortex F(6, 14) = 8.685, p = 0.0005, hippocampus F(6, 13) = 4.182, p = 0.0146]. Scale bar = 50 μm, and magnification = 400 × . #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. model group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.