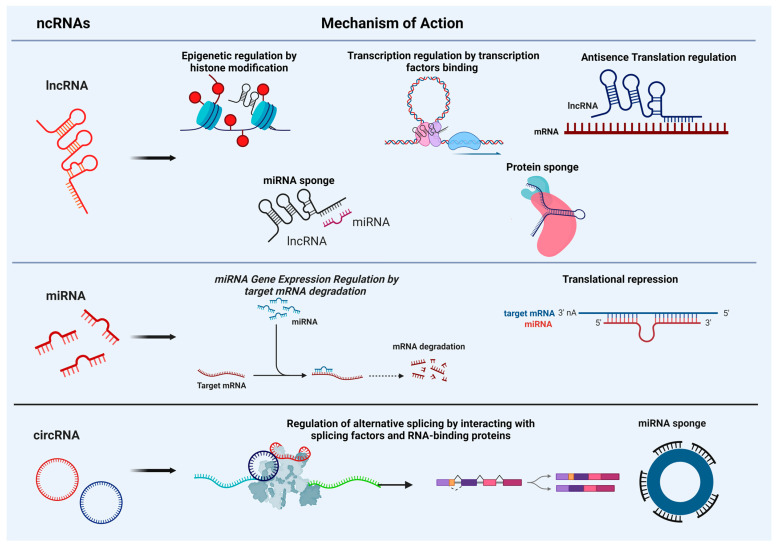
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation illustrating the multifaceted mechanisms of action of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), microRNA (miRNA), and circular RNA (circRNA). LncRNA can play a regulatory role by acting as epigenetic regulators, influencing chromatin remodeling and histone modification; scaffolds for the assembly of transcriptional regulatory complexes; regulating gene expression by forming RNA duplex with mRNA and modulating translation; miRNA and protein sponges. MiRNA functions as a post-transcriptional regulator by binding to target mRNA, leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression. CircRNAs regulate alternative splicing by interacting with splicing factors or RNA-binding proteins, acting as miRNA sponges, thus sequestering miRNAs and preventing them from targeting mRNA transcripts. (Figure generated by Biorender).