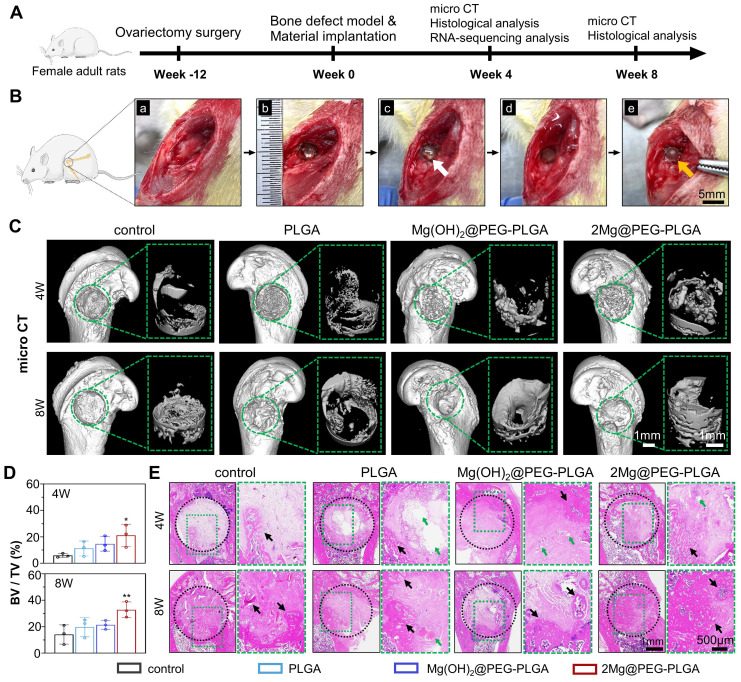
Figure 6.
Osteoporotic bone defect repair efficacy of the 2Mg@PEG-PLGA hydrogel. (A) Schematic timeline of the in vivo study. (B) The surgical process of in situ implantation of the 2Mg@PEG-PLGA hydrogel in osteoporotic bone defects. (a-b) The construction of bone defects (3 mm in diameter × 3 mm in depth) on the lateral epicondyle of the femur. (c-e) The implanted 2Mg@PEG-PLGA hydrogel was solidified after immersion in saline for 5 min. The white and red arrows indicate gelatinous and solidified 2Mg@PEG-PLGA gels, respectively. (C) Micro-CT 3D-reconstructed images of the distal femur of rats and the newly formed bone within the bone defect at 4 and 8 weeks. The green circle marks the bone defects. (D) BV/TV analysis of the newly formed bone within the bone defect via micro-CT. (E) HE staining of rat femurs from different groups at 4 and 8 weeks. The black circle marks the bone defects. The green arrows indicate residual materials. The black arrows indicate the newly formed bone. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.