Abstract
Delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (aSAH) is a singular pathological entity necessitating early diagnostic approaches and both prophylactic and curative interventions. This retrospective before-after study investigates the effects of a management strategy integrating perfusion computed tomography (CTP), vigilant clinical monitoring and standardized systemic administration of milrinone on the occurrence of delayed cerebral infarction (DCIn). The period included 277 patients, and the one 453. There was a higher prevalence of Modified Fisher score III/IV and more frequent diagnosis of vasospasm in the period. Conversely, the occurrence of DCIn was reduced with the management strategy (adjusted OR 0.48, 95% CI [0.26; 0.84]). Notably, delayed ischemic neurologic deficits were less prevalent at the time of vasospasm diagnosis (24 vs 11%, ), suggesting that CTP facilitated early detection. In patients diagnosed with vasospasm, intravenous milrinone was more frequently administered (80 vs 54%, ) and associated with superior hemodynamics. The present study from a large cohort of aSAH patients suggests, for one part, the interest of CTP in early diagnosis of vasospasm and DCI, and for the other the efficacy of CT perfusion-guided systemic administration of milrinone in both preventing and treating DCIn.
Subject terms: Medical research, Cerebrovascular disorders
Introduction
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) presents with an incidence of 8–10/100,000 inhabitants/year1–3. It most often affects women, with a female to male ratio of 3/2, and a mean age of occurrence of 55–62 years3–5. During the last couple of decades, mortality rates showed no tendency to overall improvement2,6, and nowadays outcome remains poor, resulting in mortality or severe handicap in 30% of patients4,7,8.
In this context, delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI), a major risk factor for poor clinical outcome as frequent as in 25–30% of aSAH patients, appears to be a singular pathological entity with a time course eligible to both prophylactic and curative treatments4,9,10. Commonly diagnosed on computed-tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) scans when irreversible delayed cerebral infarction (DCIn) is established11, DCI can also be suspected early using transcranial Doppler (TCD)12–14 or perfusion CT (CTP) in order to diagnose vasospasm and measure its impact on cerebral perfusion before the infarct has formed12,15–17.
Even though those diagnostic tools are widely accepted, consensual treatments are very few18,19, and first consist in non-pharmacological approaches aiming at optimizing systemic and ergo cerebral hemodynamics, mainly through euvolemia20,21 and elevated blood pressure22,23. The principal drug used in prophylaxis is nimodipine, which systemic administration has been shown to improve patients outcome24,25.
Other less consensual treatments include direct arterial dilation via intra-arterial administration of pharmacological agents26–28 including milrinone29–32 or percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA)28,33,34, as well as systemic intravenous (IV) administration of milrinone5. This last option, mainly based on inodilation, has these past few years received particular attention. Indeed, it has been repeatedly suggested that IV milrinone could be both efficient and safe for improving aSAH patients’ clinical outcome35–37. However, data are still sparse and come from studies of small sample sizes31,38–40, leading the most recent USA Guidelines for aSAH patients management to conclude that “the role of milrinone, although promising, requires further investigation”5.
In this before-after study, we aimed at assessing the effects of a new management strategy, comprising systematic CTP follow-up and the administration of IV milrinone, on the occurrence of DCIn in aSAH patients.
Materials and methods
Study population
This retrospective, before-after, monocentric study was conducted in an academic center in Montpellier, France. French adult patients hospitalized for aSAH confirmed by angio-CT (CTA) during two distinct periods, from 2014 to 2016 (“before”) and from 2018 to 2021 (“after”) were included.
Management protocol
Strategy common to the two periods
Aneurysm exclusion was performed according to the current guidelines for aSAH management5. Endovascular or surgical securization procedure was collegially decided by neurosurgeons and neuroradiologists. Surgical procedures including external ventricular drainage (EVD), intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) evacuation or decompressive craniectomy were performed when necessary. Comatose patients were sedated and assisted with mechanical ventilation to control oxygenation and ventilation (PaO2 75 mmHg, PaCO2 between 35 and 40 mmHg). Body temperature was maintained between 36 and 38 C. All patients received nimodipine, administered either orally every 4 h in a total daily dose of 360 mg, or intravenously in a dose of 2 mg/h when the oral route was not available. Patients were under continuous nurse supervision and regular physician examination notably to detect neurological deterioration associated with DCI. When suspected after TCD and/or clinical examination, angiographic vasospasm and DCI were evaluated on CT or MR scans. In patients with angiographic vasospasm and/or DCI, cerebral perfusion pressure was optimized by maintaining normovolemia and inducing hypertension using norepinephrine when necessary.
Rescue therapy during the “before” period
Patients diagnosed with angiographic vasospasm presenting either a prolonged neurological deficit or a persistent vasospasm when unconscious were treated with intra-arterial administration of both nimodipine and milrinone. As a last resort, PTA was considered when vasospasm concerned the proximal portion of the middle cerebral artery. Most severe vasospasms, i.e. diffuse or recurrent, were treated with continuous intravenous infusion of milrinone.
Preventive and rescue therapies during the “after” period
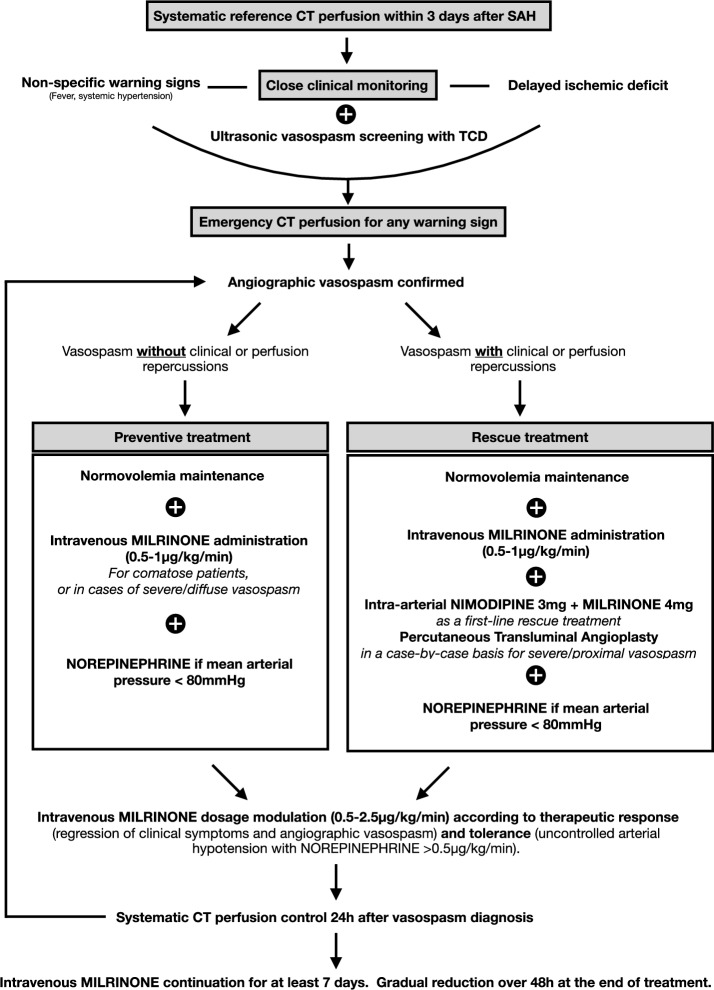
The “after” management strategy protocol used is depicted on Fig. 1. It was based on a systematic baseline CTP, followed by close clinical and TCD monitoring. Hypoperfusion was defined as , as calculated from the CTP sequences using automated RapidAI software (Rapid CTP for Stroke, IschemaView, Inc., Menlo Park, CA). In the following days, ultrasonic vasospasm and/or DCI suspicion led to an additional diagnostic CTP to confirm angiographic vasospasm and search for associated hypoperfusion. Preventive treatment (left arm of the algorithm): in comatose patients, or in cases of severe and diffuse vasospasm, IV milrinone was used even in the absence of DIND or hypoperfusion. Rescue treatment (right arm of the algorithm): when DIND or a hypoperfusion was present, IV milrinone was administered and direct arterial dilation was also performed using at least pharmacological agents, and through PTA after case-by-case evaluation. Raising blood pressure was not the primary goal of the “after” management, the emphasis was instead on inodilation. Any occurrence of hypotension was addressed by adding IV norepinephrine to ensure a mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) above 80 mmHg. When IV milrinone was poorly tolerated in this regard, IV milrinone dosage was reduced or administration was stopped. Clinical monitoring and routine follow-up CTP scans were performed to adjust the dose of milrinone.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of practice guidelines in the “ after” period.
Data collection
The following data were recorded for every patient: age, sex, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) at admission, presence of ICH, aneurysm size and location, modified Fisher score, World Federation of Neurosurgeons Score (WFNS), type of aneurysm securing procedure and EVD placement.
Vasospasm occurrence was defined as a reduction in arteries diameter of at least one-third compared to baseline caliber, measured on either CTA or digital subtraction angiography (DSA) at any time.
Delayed ischemic neurologic deficit (DIND) was defined as a delayed clinical deterioration due to delayed cerebral ischemia (i.e. focal neurological impairment or a decrease of at least 2 points on the GCS that lasts for at least 1 h that cannot be attributed to another cause).
Indication, administration, timing and duration of IV milrinone, IA vasodilators, and PTA were recorded. For a 5-day period divided into 6-h subperiods starting at the time of vasospasm diagnosis, minimal mean arterial pressure, maximum norepinephrine dose, and maximal IV milrinone dose were noted. Mechanical ventilation, ICU and hospital stays durations, as well as vital status at hospital discharge were recorded.
Outcome
Delayed cerebral infarction (DCIn) was defined as the presence of a cerebral infarction 1) de novo on the last available CT or MR scan at the time of discharge from the ICU, i.e. excluding early brain injuries (EBI) already present in either CT or MR scans performed within the first 72 h following aneurysm rupture, 2) not attributable to any other cause.
Methodological compliance and ethics
This observational study was performed according to the STROBE guidelines. The study was validated by Montpellier ethics committee (IRB-MTP_2023_01_202301324) in accordance with French regulation and registered on the Health Data Hub study registration platform (N F20230217101049). Since there was no invasive procedure in addition to French ICUs standard of care, patients or their family were informed and could opt out of the study, according to French law41.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses carried out in this article are of two types. First, descriptive statistics were used to compare the variables of interest according to the groups “before” (2014-2016) and “after” (2018-2021) practices modifications, throughout the entirety of the study’s sample population, as well as within the subset of individuals who experienced vasospasm. Continuous variables were presented as means with their associated standard deviations (SD) and categorical variables with their frequencies and associated percentage. Distributions between groups were compared using the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test to compare continuous variables and Pearson’s Chi-Square test for categorical variables (or exact Fisher test for small sample size with ). Computed p-values were given in each table.
Second, to account for imbalances between groups in confounding factors, we used a propensity score to adjust for between-group differences through a matching procedure. The propensity score was calculated using logistic regression to balance the distribution of covariates between groups of patients before and after practices modifications, allowing to reduce potential bias in the estimates of the treatment effect42. The following covariates were included in the score because of their clinical relevance : age, sex, modified Fisher score, WFNS, aneurysm location, aneurysm exclusion, intracerebral hemorrhage and EVD. The initial sample included two pools of patients, totalizing 730 observations. Using the optimal 1:1 pair matching method, the balanced sample consisted of 554 matched pairs. Validity of the produced score and balance of covariates were assessed using standardized mean differences, propensity score histograms and with statistical comparison of the “before” and “after” populations after matching. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) based on the propensity score was used in a logistic regression model to explore the effect of the changes in practice on DCIn occurrence. Unadjusted odds-ratio and IPTW adjusted odds-ratio (OR) are presented with their 95% confidence interval, as well as the corresponding p-value.
All statistical analyses were conducted using R software, version 4.2.1. A p-value threshold of less than 0.05 was adopted for all tests for statistical significance.
Ethics approval
This study was validated by Montpellier ethics committee (IRB-MTP_2023_01_202301324) in accordance with French regulation and registered on the Health Data Hub study registration platform (N F20230217101049).
Consent to participate
Since there was no invasive procedure in addition to French ICUs standard of care, patients or their family were informed and could opt out of the study.
Results
The “before” period spanned from 2014 to 2016 and enrolled 277 patients, the “after” one from 2018 to 2021 and included 453 patients. Six patients were excluded because of refusal. Patients and aSAH characteristics in both periods are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Descriptive table for groups “before” and “after” practices modifications
| Whole population | After matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before, N = 277 | After, N = 453 | p-value | Before, N = 277 | After, N = 277 | p-value | |
| Age* | 55.22 (13.38) | 56.21 (12.19) | 0.2 | 55.22 (13.38) | 55.58 (12.36) | 0.6 |
| Gender* | 0.3 | 0.2 | ||||
| Female | 184 (66%) | 283 (62%) | 184 (66%) | 170 (61%) | ||
| Male | 93 (34%) | 170 (38%) | 93 (34%) | 107 (39%) | ||
| Modified Fisher score* | ||||||
| I/II | 101 (36%) | 109 (24%) | 101 (36%) | 102 (37%) | ||
| III/IV | 176 (64%) | 344 (76%) | 176 (64%) | 175 (63%) | ||
| WFNS* | 0.12 | 0.8 | ||||
| I/II | 163 (59%) | 240 (53%) | 163 (59%) | 160 (58%) | ||
| III/IV/V | 114 (41%) | 213 (47%) | 114 (41%) | 117 (42%) | ||
| Aneurysm localisation* | 0.8 | |||||
| ACA/Acom | 104 (38%) | 177 (39%) | 104 (38%) | 102 (37%) | ||
| IC/Pcom | 67 (24%) | 108 (24%) | 67 (24%) | 63 (23%) | ||
| MCA | 63 (23%) | 94 (21%) | 63 (23%) | 68 (25%) | ||
| Other localization | 8 (2.9%) | 21 (4.6%) | 8 (2.9%) | 9 (3.2%) | ||
| Vertebrobasilar territory | 35 (13%) | 53 (12%) | 35 (13%) | 35 (13%) | ||
| Aneurysm exclusion* | 0.2 | |||||
| No treatment | 12 (4.3%) | 34 (7.5%) | 12 (4.3%) | 12 (4.3%) | ||
| Clipping | 31 (11%) | 49 (11%) | 31 (11%) | 31 (11%) | ||
| Coiling | 234 (84%) | 370 (82%) | 234 (84%) | 234 (84%) | ||
| Aneurysm size (cm) | 0.2 | 0.067 | ||||
| 5 | 64 (30%) | 160 (37%) | 64 (30%) | 104 (39%) | ||
| ]5–10[ | 100 (47%) | 194 (45%) | 100 (47%) | 119 (45%) | ||
| 10 | 47 (22%) | 78 (18%) | 47 (22%) | 42 (16%) | ||
| (Missing data) | 66 | 21 | 66 | 12 | ||
| Rebleeding | 35 (13%) | 63 (14%) | 0.6 | 35 (13%) | 37 (13%) | 0.8 |
| ICH* | 81 (29%) | 147 (32%) | 0.4 | 81 (29%) | 79 (29%) | 0.9 |
| Early brain injury | 82 (30%) | 144 (32%) | 0.5 | 82 (30%) | 86 (31%) | 0.7 |
| EVD | 120 (43%) | 214 (47%) | 0.3 | 120 (43%) | 125 (45%) | 0.7 |
| Vasospasm | 118 (43%) | 259 (57%) | <0.001 | 118 (43%) | 154 (56%) | 0.002 |
| Length of MV, days | 18.70 (17.56) | 15.01 (15.72) | 0.015 | 18.70 (17.56) | 15.31 (16.51) | 0.032 |
| Death | 0.2 | |||||
| No | 233 (84%) | 363 (80%) | 233 (84%) | 232 (84%) | ||
| Yes | 44 (16%) | 90 (20%) | 44 (16%) | 45 (16%) | ||
| Hospital LOS, days | 29.25 (26.03) | 29.28 (25.12) | 0.4 | 29.25 (26.03) | 29.73 (26.34) | 0.4 |
| ICU LOS, days | 26.18 (24.07) | 19.55 (19.14) | 0.008 | 26.18 (24.07) | 20.29 (19.94) | 0.040 |
WFNS World Federation of Neurological Surgeons, ACA Anterior cerebral artery, Acom Anterior communicating artery, IC Internal carotid, Pcom Posterior communicating artery, MCA Middle cerebral artery, ICH Intracerebral hemorrhage, EVD External ventricular drainage, MV Mechanical ventilation, LOS Length of stay, ICU Intensive Care Unit. Mean (SD); n (%), Wilcoxon rank sum test, Pearson’s Chi-squared test. Fisher exact test. Variables denoted with a * were included in the matching procedure.
Significant values are in bold.
Patients age and sex ratio were similar, WFNS and aneurysm characteristics were comparable, and EBI was as frequent in the two groups. There was no difference regarding aneurysm treatment (i.e. embolization vs surgery). At the time of admission, only the modified Fisher score differed between groups, being more frequently III/IV during the “after” period. After adjustment, the baseline variables distributions are well balanced between the two groups. Besides, vasospasm was more frequently diagnosed during the “after” than in the “before” period (56% vs 43% respectively, ). Length of mechanical ventilation and ICU length of stay were reduced in the “after” period. All-cause mortality was similar between the two periods.
Table 2 presents the OR for DCIn in the “after” compared to the “before” period, both unadjusted (0.64, IC95=[0.39; 1.01] and adjusted (0.48, IC95= [0.26; 0.84]), showing a reduction in DCIn occurrence when the new management strategy was established.
Table 2.
Effect of change in practice on DCIn occurrence after population matching (N=544). OR=Odds ratio, CI=Confidence interval.
| Without adjustment | Adjusted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCIn | OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value |
| Period | ||||||
| Before | – | – | – | – | ||
| After | 0.63 | 0.39, 1.01 | 0.055 | 0.48 | 0.26, 0.84 | 0.013 |
In order to explore the effective management of vasospasm and DCI in the two periods, the remaining of the study focuses on the subpopulation of patients diagnosed with vasospasm, before statistical matching. This subpopulation’s characteristics are presented in Table 3. Patients and aneurysm features were all similar in the two periods of time. However, DCIn and DIND, both at the time of vasospasm diagnosis and at any time during the stay, were less frequent in the “after” than in the “before” period (15 vs 31% , 11 vs 24% , 15 vs 26% respectively).
Table 3.
Descriptive table of the vasospasm subpopulation (N=377)
| Before, N = 118 | After, N = 259 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 54.55 (12.52) | 55.66 (11.55) | 0.4 |
| Sex | 0.4 | ||
| Female | 81 (69%) | 165 (64%) | |
| Male | 37 (31%) | 94 (36%) | |
| Modified Fisher score | 0.2 | ||
| I/II | 27 (23%) | 45 (17%) | |
| III/IV | 91 (77%) | 214 (83%) | |
| WFNS | |||
| I/II | 60 (51%) | 131 (51%) | |
| III/IV/V | 58 (49%) | 128 (49%) | |
| Aneurysm localisation | 0.9 | ||
| ACA/Acom | 48 (41%) | 104 (40%) | |
| IC/Pcom | 30 (25%) | 64 (25%) | |
| MCA | 28 (24%) | 55 (21%) | |
| Other localization | 2 (2%) | 8 (3%) | |
| Vertebrobasilar territory | 10 (8%) | 28 (11%) | |
| Aneurysm exclusion | 0.7 | ||
| No treatment | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Clipping | 12 (10%) | 30 (11%) | |
| Coiling | 105 (89%) | 228 (88%) | |
| Intracerebral hemorrhage | 44 (37%) | 88 (34%) | 0.5 |
| External ventricular drainage | 65 (55%) | 162 (63%) | 0.2 |
| Delayed cerebral infarction (DCIn) | 37 (31%) | 40 (15%) | <0.001 |
| DIND at vasospasm diagnosis | 28 (24%) | 28 (11%) | 0.001 |
| DIND during the stay | 31 (26%) | 40 (15%) | 0.013 |
WFNS World Federation of Neurological Surgeons, ACA Anterior cerebral artery, Acom Anterior communicating artery, IC Internal carotid, Pcom Posterior communicating artery, MCA Middle cerebral artery, DIND Delayed ischemic neurologic deficit. Mean (SD); n (%), Wilcoxon rank sum test, Pearson’s Chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test.
Significant values are in bold.
The treatments administered in patients with vasospasm are shown in Table 4. First, indication for treatment was different in the two periods. Indeed, DIND and DCIn were less frequently a motive in the “after” period, being only 8 versus 21% and 1 versus 9% respectively (). Accordingly, vasodilation was more frequently undertaken as a preventive treatment in the “after” period (71 vs 51%). Second, IV milrinone was in fact more frequently administered in the “after” period (80 vs 54%, ), although at the same mean dose (0.84 vs 0.83g/kg/min, ). IA administration of vasodilators was similar in the two periods, while PTA was less frequently performed in the “after” one (6.6 vs 16%, ).
Table 4.
Profile of treatments used in the vasospasm subpopulation (N=377).
| Before, N = 118 | After, N = 259 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated vasospasm | 39 (33%) | 51 (20%) | <0.005 |
| IV milrinone administration | 64 (54%) | 208 (80%) | <0.001 |
| IA milrinone administration | 49 (42%) | 83 (32%) | 0.074 |
| IA nimodipine administration | 50 (42%) | 83 (32%) | 0.052 |
| PTA | 19 (16%) | 17 (6.6%) | 0.003 |
| Indication for vasospasm treatment | <0.001 | ||
| Delayed ischemic neurologic deficit (DIND) | 17 (21%) | 16 (8%) | |
| Hypoperfusion on perfusion CT | 15 (19%) | 44 (21%) | |
| Delayed cerebral infarction (DCIn) | 7 (9%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Prevention | 40 (51%) | 147 (70%) |
IV Intravenous, IA Intra-arterial, PTA Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. n (%), Pearson’s Chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test.
Significant values are in bold.
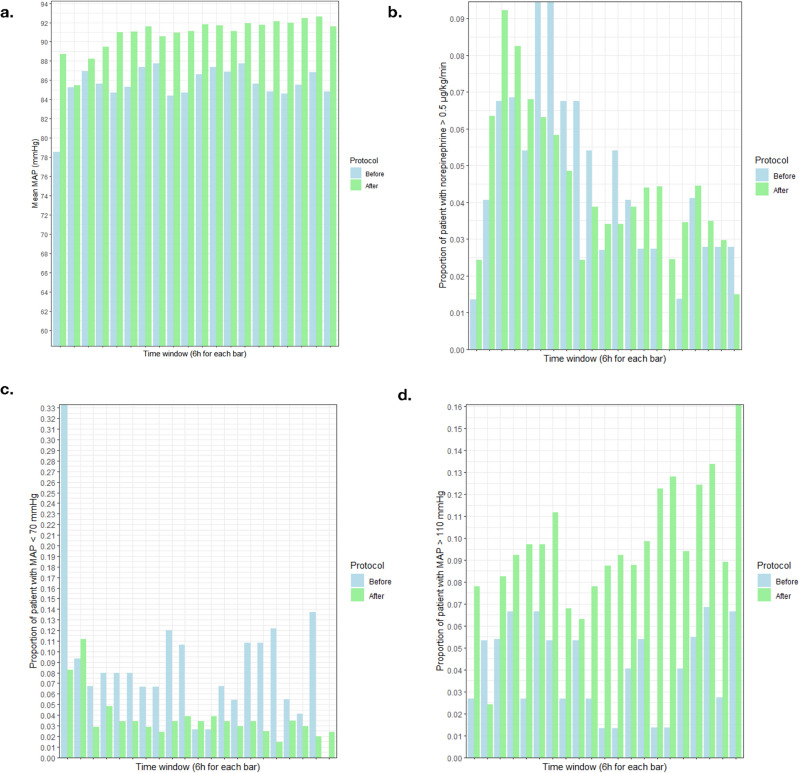
Finally, we report indicators of systemic hemodynamics in Fig. 2. In the “after” period, mean MAP was slightly higher (91 vs 86 mmHg, , see Fig. 2a), and less patients presented with MAP<70 mmHg and more with MAP>110 mmHg (Fig. 2c, d). In order to achieve and maintain elevated blood pressure, no more patients required a dose of norepinephrine higher than 0.5g/kg/mn in the “after” period (Fig. 2b), even though the mean dose was slightly higher (0.35 vs 0.28g/kg/min, ).
Figure 2.
Indicators of systemic hemodynamics in the 5-day period following vasospasm diagnosis, in the “before”(blue) and “after”(green) groups. (a) Mean arterial blood pressure (MAP). (b) Proportion of patients in whom norepinephrine exceeded 0.5g/kg/mn. (c) Proportion of patients showing a MAP lower than 70 mmHg. (d) Proportion of patients showing a MAP higher than 110 mmHg.
Discussion
This before-after study shows a reduction in delayed cerebral infarction associated with a management strategy based on systematic early CTP guiding systemic administration of milrinone in aSAH patients.
Patients and aSAH characteristics were comparable in the two periods, except for high Fisher scores and vasospasm diagnosis, both more frequent in the “after” period. It is possible that vasospasm was more frequently diagnosed because of the management strategy. Alternately, it could actually have been more frequent, which would be consistent with the distribution of Fisher scores43. In either case, these findings can only strengthen the conclusions on the positive effects of the new strategy on the outcome.
In details, this strategy led to early asymptomatic vasospasm diagnosis, allowing neurological deficit and established infarction to be less frequent at the time of treatment initiation. Additionally, intravenous milrinone reduced the need for PTA, and was accompanied by superior systemic hemodynamics.
Of course, the nature of the study leads to limitations, mainly concerning long-term neurological outcome, the record of which was not available. All the same, we present real-world data from unselected patients together with detailed management description, such that our bundle of care can easily be reproduced or adapted in other centers to achieve the low incidence of DCIn seen in our cohort.
There are several putative explanations for the reduced occurrence of DCIn with the new strategy. First, early asymptomatic diagnosis due to systematic and following CTP could have triggered early treatment, plausibly associated with regression or compensation of pathological mechanisms. This interest of CTP in the early phase of delayed ischemia has already been suggested in previous studies16,44,45. However, the clinical impact of early diagnosis using this method had not yet been conclusively demonstrated. We report here arguments in favor of this strategy, adding data from critically ill patients, lacking from the literature44.
Second, the proactive approach combining first-line milrinone with limited doses of norepinephrine could maximize the positive effects of milrinone on cerebral hemodynamics by prioritizing cerebral vasodilation over the achievement of systemic arterial hypertension, even though this strategy is still a matter of debate39,46,47. It is suggested that milrinone systemic effects on hemodynamics, namely increased cardiac output and increased venous return, can reasonably improve brain perfusion when associated with cerebral arteries dilation35,48. Indeed, the Lassen curve could be shifted upwards and rightwards after milrinone administration, leading to a greater cerebral blood flow for a given cerebral perfusion pressure35.
Third, systemic administration of milrinone can have several other consequences on disease progression. For instance, pharmacological vasodilation of cerebral arteries is with this approach not limited to large vessels diagnosed with vasospasm. It is likely that small arteries and arterioles, at the core of recent pathophysiological theories for DCI and not accessible to PTA, benefit from milrinone effects on smooth muscle cells49–52. Another postulated mechanism involves anti-inflammatory properties of milrinone through inhibition of cytokines production35, since inflammation is also suspected to play a role in DCI development53. For instance, perivascular macrophage have been shown to participate in microvascular spasms in experimental models, and could therefore be a cellular target for milrinone non-vascular effects54.
Conclusion
Even though the underlying causes for the observed effects remain mainly speculative, the present study shows data from a large cohort of 730 patient suggesting, for one part, the interest of CTP in early diagnosis of vasospasm and DCI, and for the other the efficacy of CT perfusion-guided systemic administration of milrinone in prevention and treatment of DCIn.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our entire medical team of intensive care physicians and anaesthesiologists, as well as all the neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists and rehabilitation specialists involved in the care of the patients.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: K.C., O.G., V.S. Data curation: K.C., S.B., O.G. Formal analysis: F.K., N.M. Methodology: K.C., N.M., O.G., V.S. Resources: C.D., F.P., V.C. Supervision: PFP, VC. Writing - original draft: VS, KC. Writing – review & editing: CD, VC, PFP
Funding:
No funding was provided for this study.
Data availability
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Suarez, J. I. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med.1010.1056/NEJMra052732 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Mackey J, et al. Stable incidence but declining case-fatality rates of subarachnoid hemorrhage in a population. Neurology. 2016;87:2192–2197. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Neifert SN, et al. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: The last decade. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021;12:428–446. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chalard K, et al. Long-term outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage requiring mechanical ventilation. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0247942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoh BL, et al. 2023 guideline for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2023 doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wahood W, et al. Trends in admissions and outcomes for treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the United States. Neurocrit. Care. 2022;37:209–218. doi: 10.1007/s12028-022-01476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Molyneux AJ, et al. Risk of recurrent subarachnoid haemorrhage, death, or dependence and standardised mortality ratios after clipping or coiling of an intracranial aneurysm in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT): Long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:427–433. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70080-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cinotti R, et al. Evolution of neurological recovery during the first year after subarachnoid haemorrhage in a French University Centre. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2019;38:251–257. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2018.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rowland MJ, Hadjipavlou G, Kelly M, Westbrook J, Pattinson KTS. Delayed cerebral ischaemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage: Looking beyond vasospasm. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012;109(3):315–329. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Galea JP, Dulhanty L, Patel HC. Predictors of outcome in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients: Observations from a multicenter data set. Stroke. 2017;48(11):2958–2963. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vergouwen MDI, et al. Definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as an outcome event in clinical trials and observational studies proposal of a Multidisciplinary Research Group. Stroke. 2010;41(10):2391–2395. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.589275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Westermaier T, et al. Value of transcranial doppler, perfusion-CT and neurological evaluation to forecast secondary ischemia after aneurysmal SAH. Neurocrit. Care. 2014;20:406–412. doi: 10.1007/s12028-013-9896-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kumar G, Shahripour RB, Harrigan MR. Vasospasm on transcranial Doppler is predictive of delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2016;124:1257–1264. doi: 10.3171/2015.4.JNS15428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen HY, et al. Combining transcranial Doppler and EEG data to predict delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology. 2022;98:e459–e469. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000013126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van der Schaaf I, et al. CT after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Relation of cerebral perfusion to delayed cerebral ischemia. Neurology. 2006;66(10):1533–1538. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000216272.67895.d3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cremers CHP, et al. Different CT perfusion algorithms in the detection of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 2015;57:469–474. doi: 10.1007/s00234-015-1486-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Malinova V, et al. Early whole-brain CT perfusion for detection of patients at risk for delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2016;125:128–136. doi: 10.3171/2015.6.JNS15720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.de Oliveira Manoel AL, et al. The critical care management of poor-grade subarachnoid haemorrhage. Crit. Care. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1193-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Francoeur CL, Mayer SA. Management of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit. Care. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1447-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lennihan L, et al. Effect of hypervolemic therapy on cerebral blood flow after subarachnoid hemorrhage a randomized controlled trial. Stroke. 2000;31(2):383–391. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.31.2.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Duangthongphon P, Souwong B, Munkong W, Kitkhuandee A. Results of a preventive rebleeding protocol in patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysm: A retrospective cohort study. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2019;14:748–753. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_32_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gathier CS, et al. Induced hypertension for delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A randomized clinical trial. Stroke. 2018;49:76–83. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Haegens NM, et al. Induced hypertension in preventing cerebral infarction in delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2018;49:2630–2636. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pickard JD, et al. Effect of oral nimodipine on cerebral infarction and outcome after subarachnoid haemorrhage: British aneurysm nimodipine trial. Br. Med. J. 1989;298(6674):636–642. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6674.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hao G, et al. Clinical effectiveness of nimodipine for the prevention of poor outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022;13:982498. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.982498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Biondi A, et al. Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of symptomatic cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Preliminary results. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1067–1076. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Linfante I, et al. Angiographic and hemodynamic effect of high concentration of intra-arterial nicardipine in cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:1080–1087. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000327698.66596.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Weiss M, et al. Intraarterial nimodipine versus induced hypertension for delayed cerebral ischemia: A modified treatment protocol. Stroke. 2022;53:2607–2616. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.038216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shankar JJS, Santos MPd, Deus-Silva L, Lum C. Angiographic evaluation of the effect of intra-arterial milrinone therapy in patients with vasospasm from aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 2010;53(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/s00234-010-0720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Romero CM, et al. Milrinone as a rescue therapy for symptomatic refractory cerebral vasospasm in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care. 2009;11:165–171. doi: 10.1007/s12028-008-9048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fraticelli AT, Cholley BP, Losser M-R, Saint Maurice J-P, Payen D. Milrinone for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2008;39(3):893–898. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.492447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jentzsch J, et al. Nimodipine versus milrinone—Equal or complementary use? A retrospective analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022;13:939015. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.939015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zwienenberg-Lee M, et al. Effect of prophylactic transluminal balloon angioplasty on cerebral vasospasm and outcome in patients with fisher grade III subarachnoid hemorrhage: Results of a phase II multicenter, Randomized, clinical trial. Stroke. 2008;39:1759–1765. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schacht H, et al. Transluminal balloon angioplasty for cerebral vasospasm after spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage: A single-center experience. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020;188:105590. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Castle-Kirszbaum M, et al. Intravenous milrinone for treatment of delayed cerebral ischaemia following subarachnoid haemorrhage: A pooled systematic review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021;44:3107–3124. doi: 10.1007/s10143-021-01509-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Santos-Teles AG, et al. Efficacy and safety of milrinone in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Revista Brasileira de Terapia Intensiva. 2020 doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20200097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lannes M, Zeiler F, Guichon C, Teitelbaum J. The use of milrinone in patients with delayed cerebral ischemia following subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Can. J. Neurol. Sci./J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2017;44(02):152–160. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2016.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lannes M, Teitelbaum J, del Pilar Cortés M, Cardoso M, Angle M. Milrinone and homeostasis to treat cerebral vasospasm associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage: The montreal neurological hospital protocol. Neurocrit. Care. 2012;16(3):354–362. doi: 10.1007/s12028-012-9701-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lakhal K, et al. Intravenous milrinone for cerebral vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage: The MILRISPASM controlled beforeâ€-after study. Neurocrit. Care. 2021;35:669–679. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01331-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bernier TD, et al. Treatment of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-associated Delayed Cerebral Ischemia With Milrinone: A review and proposal. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2021 doi: 10.1097/ANA.0000000000000755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Toulouse E, et al. French legal approach to clinical research. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2018;37(6):607–614. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2018.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Austin PC, Stuart EA. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat. Med. 2015;34:3661–3679. doi: 10.1002/sim.6607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Claassen JAHR, Thijssen DHJ, Panerai RB, Faraci FM. Regulation of cerebral blood flow in humans: Physiology and clinical implications of autoregulation. Physiol. Rev. 2021;101:1487–1559. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sun H, Li W, Ma J, Liu Y, You C. CT perfusion diagnoses delayed cerebral ischemia in the early stage of the time-window after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neuroradiol. 2017;44:313–318. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2016.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Abdulazim A, Heilig M, Rinkel G, Etminan N. Diagnosis of delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and triggers for intervention. Neurocrit. Care. 2023;39:311–319. doi: 10.1007/s12028-023-01812-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Abulhasan YB, Ortiz Jimenez J, Teitelbaum J, Angle MR. Role of induced hypertension and intravenous milrinone after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Is it time to shift the paradigm? Neurocrit. Care. 2021;35:920–921. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lakhal K, Hivert A, Rozec B, Cadiet J. Induced hypertension or intravenous milrinone for cerebral vasospasm: Why choose? Neurocrit. Care. 2021;35:922–923. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01378-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mathew R, et al. Milrinone as compared with dobutamine in the treatment of cardiogenic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;385:516–525. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Friedrich B, Müller F, Feiler S, Schöller K, Plesnila N. Experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage causes early and long-lasting microarterial constriction and microthrombosis: An in-vivo microscopy study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32(3):447–455. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Terpolilli NA, Brem C, Bühler D, Plesnila N. Are we barking up the wrong vessels?: Cerebral microcirculation after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2015;46(10):3014–3019. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.006353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.El Amki M, et al. Long-lasting cerebral vasospasm, microthrombosis, apoptosis and paravascular alterations associated with neurological deficits in a mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018;55(4):2763–2779. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Anzabi M, et al. Capillary flow disturbances after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage: A contributor to delayed cerebral ischemia? Microcirculation. 2019;26:e12516. doi: 10.1111/micc.12516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.de Oliveira Manoel, A. L. & Macdonald, R. L. Neuroinflammation as a target for intervention in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front. Neurol.9. 10.3389/fneur.2018.00292 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Lin X, et al. Perivascular macrophages mediate microvasospasms after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2023;54:2126–2134. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.042290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.