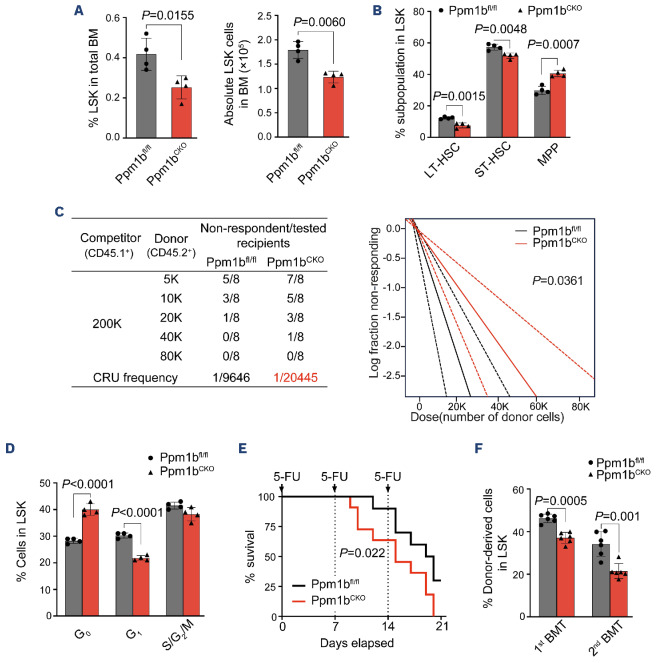
Figure 3.
Loss of Ppm1b leads to the suppression of phenotypic hematopoietic stem cell expansion in vivo. (A) Statistical analysis of the percentage (left) and number (right) of Lin-Sca-1+c-Kit+ (LSK) cells in 8-week-old Ppm1bCKO and Ppm1bfl/fl mice. (A) N=4. (B) Statistical analysis of the percentage of LT-HSC, ST-HSC and MPP cells (all gated from LSK) (N=4). (C) Limiting dilution transplantation assays were performed by transplanting different doses of bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMC) from indicated mice. (Left) The number of functional hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) in bone marrow (BM) of Ppm1bCKO and Ppm1bfl/fl mice was measured by flow cytometry after 16 weeks of transplantation. Recipients with <2% donor-derived cells in BM were defined as non-respondent (N=8). (Right) Fraction of HSC in BM of Ppm1bCKO and Ppm1bfl/fl mice by Poisson statistical analysis of the data using L-Calc software. Solid lines indicate the best-fit linear model for each dataset. Dashed lines for 95% Confidence Intervals; χ2 test=4.39; P=0.0361. (D) Cell cycle analysis of LSK cells from indicated mice by flow cytometry using Hoechst 33342 and Ki67 staining (N=4). (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of Ppm1bCKO and Ppm1bfl/fl mice treated thrice with 5-FU (150 mg/kg) (N=12). (F) Percentage of donor-derived LSK cells in the BM of the primary and secondary recipient mice (N=6). Two-tailed unpaired Student t test was used to generate the P values. The significance for survival analyses was calculated by logrank (Mantel-Cox) test. See also Online Supplementary Figure S3. BMT: bone marrow transplantation; CRU: competitive repopulating units.