In adults a tachycardia is any heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute. Supraventricular tachycardias may be divided into two distinct groups depending on whether they arise from the atria or the atrioventricular junction. This article will consider those arising from the atria: sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia. Tachycardias arising from re-entry circuits in the atrioventricular junction will be considered in the next article in the series.
Supraventricular tachycardias
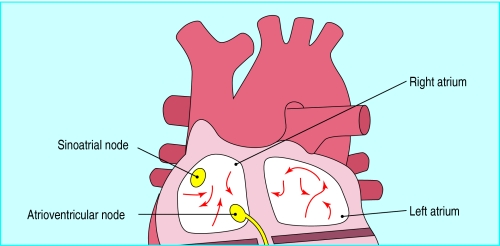
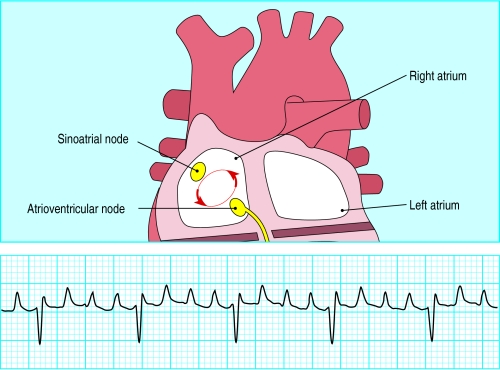
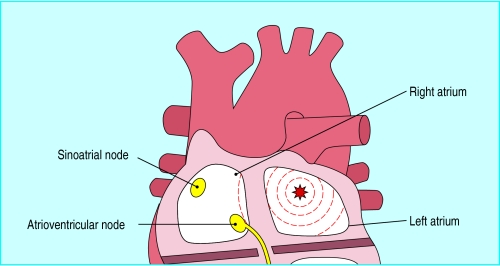
From the atria or sinoatrial node
Sinus tachycardia
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial flutter
Atrial tachycardia
From the atrioventricular node
Atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia
Atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia
Clinical relevance
The clinical importance of a tachycardia in an individual patient is related to the ventricular rate, the presence of any underlying heart disease, and the integrity of cardiovascular reflexes. Coronary blood flow occurs during diastole, and as the heart rate increases diastole shortens. In the presence of coronary atherosclerosis, blood flow may become critical and anginal-type chest pain may result. Similar chest pain, which is not related to myocardial ischaemia, may also occur. Reduced cardiac performance produces symptoms of faintness or syncope and leads to increased sympathetic stimulation, which may increase the heart rate further.
Electrocardiographic characteristics of atrial arrhythmias
Sinus tachycardia
P waves have normal morphology
Atrial rate 100-200 beats/min
Regular ventricular rhythm
Ventricular rate 100-200 beats/min
One P wave precedes every QRS complex
Atrial tachycardia
Abnormal P wave morphology
Atrial rate 100-250 beats/min
Ventricular rhythm usually regular
Variable ventricular rate
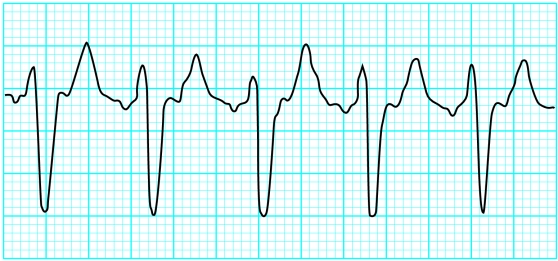
Atrial flutter
Undulating saw-toothed baseline F (flutter) waves
Atrial rate 250-350 beats/min
Regular ventricular rhythm
Ventricular rate typically 150 beats/min (with 2:1 atrioventricular block)
4:1 is also common (3:1 and 1:1 block uncommon)
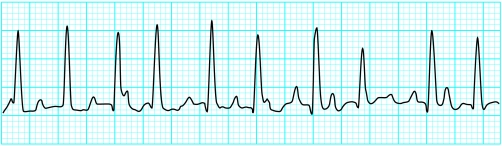
Atrial fibrillation
P waves absent; oscillating baseline f (fibrillation) waves
Atrial rate 350-600 beats/min
Irregular ventricular rhythm
Ventricular rate 100-180 beats/min
As a general rule the faster the ventricular rate, the more likely the presence of symptoms—for example, chest pain, faintness, and breathlessness. Urgent treatment is needed for severely symptomatic patients with a narrow complex tachycardia.
Electrocardiographic features
Differentiation between different types of supraventricular tachycardia may be difficult, particularly when ventricular rates exceed 150 beats/min.
Electrocardiographic analysis should include measurement of the ventricular rate, assessment of the ventricular rhythm, identification of P, F, or f waves , measurement of the atrial rate, and establishment of the relation of P waves to the ventricular complexes
Knowledge of the electrophysiology of these arrhythmias will assist correct identification. Evaluation of atrial activity on the electrocardiogram is crucial in this process. Analysis of the ventricular rate and rhythm may also be helpful, although this rate will depend on the degree of atrioventricular block. Increasing atrioventricular block by manoeuvres such as carotid sinus massage or administration of intravenous adenosine may be of diagnostic value as slowing the ventricular rate allows more accurate visualisation of atrial activity. Such manoeuvres will not usually stop the tachycardia, however, unless it is due to re-entry involving the atrioventricular node.
Sinus tachycardia
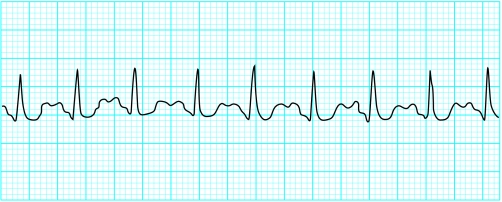
Sinus tachycardia is usually a physiological response but may be precipitated by sympathomimetic drugs or endocrine disturbances.
The rate rarely exceeds 200 beats/min in adults. The rate increases gradually and may show beat to beat variation. Each P wave is followed by a QRS complex. P wave morphology and axis are normal, although the height of the P wave may increase with the heart rate and the PR interval will shorten. With a fast tachycardia the P wave may become lost in the preceding T wave.
Causes of sinus tachycardia
Physiological—Exertion, anxiety, pain
Pathological—Fever, anaemia, hypovolaemia, hypoxia
Endocrine—Thyrotoxicosis
Pharmacological—Adrenaline as a result of phaeochromocytoma; salbutamol; alcohol, caffeine
Recognition of the underlying cause usually makes diagnosis of sinus tachycardia easy. A persistent tachycardia in the absence of an obvious underlying cause should prompt consideration of atrial flutter or atrial tachycardia.
Causes of atrial fibrillation
| • Ischaemic heart disease | • Cardiomyopathy (dilated or hypertrophic) |
| • Hypertensive heart disease | • Sick sinus syndrome |
| • Rheumatic heart disease | • Post-cardiac surgery |
| • Thyrotoxicosis | • Chronic pulmonary disease |
| • Alcohol misuse (acute or | • Idiopathic (lone) |
| chronic) | |
Rarely the sinus tachycardia may be due to a re-entry phenomenon in the sinoatrial node. This is recognised by abrupt onset and termination, a very regular rate, and absence of an underlying physiological stimulus. The electrocardiographic characteristics are otherwise identical. The rate is usually 130-140 beats/min, and vagal manoeuvres may be successful in stopping the arrhythmia.
Atrial fibrillation
This is the most common sustained arrhythmia. Overall prevalence is 1% to 1.5%, but prevalence increases with age, affecting about 10% of people aged over 70. Causes are varied, although many cases are idiopathic. Prognosis is related to the underlying cause; it is excellent when due to idiopathic atrial fibrillation and relatively poor when due to ischaemic cardiomyopathy.
Atrial fibrillation is caused by multiple re-entrant circuits or “wavelets” of activation sweeping around the atrial myocardium. These are often triggered by rapid firing foci. Atrial fibrillation is seen on the electrocardiogram as a wavy, irregular baseline made up of f (fibrillation) waves discharging at a frequency of 350 to 600 beats/min. The amplitude of these waves varies between leads but may be so coarse that they are mistaken for flutter waves.
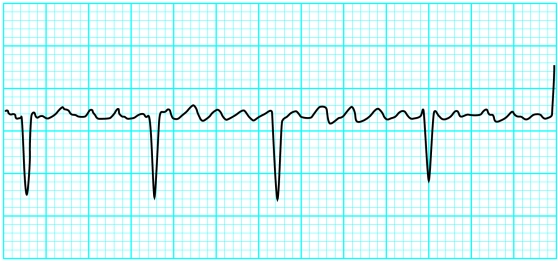
Conduction of atrial impulses to the ventricles is variable and unpredictable. Only a few of the impulses transmit through the atrioventricular node to produce an irregular ventricular response. This combination of absent P waves, fine baseline f wave oscillations, and irregular ventricular complexes is characteristic of atrial fibrillation. The ventricular rate depends on the degree of atrioventricular conduction, and with normal conduction it varies between 100 and 180 beats/min. Slower rates suggest a higher degree of atrioventricular block or the patient may be taking medication such as digoxin.
Fast atrial fibrillation may be difficult to distinguish from other tachycardias. The RR interval remains irregular, however, and the overall rate often fluctuates. Mapping R waves against a piece of paper or with calipers usually confirms the diagnosis.
Atrial fibrillation may be paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent. It may be precipitated by an atrial extrasystole or result from degeneration of other supraventricular tachycardias, particularly atrial tachycardia and/or flutter.
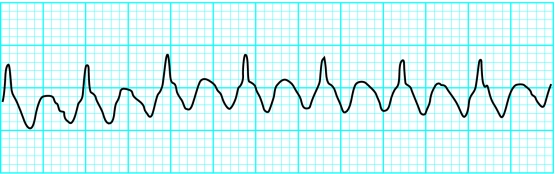
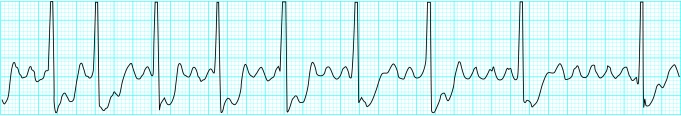
Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter is due to a re-entry circuit in the right atrium with secondary activation of the left atrium. This produces atrial contractions at a rate of about 300 beats/min—seen on the electrocardiogram as flutter (F) waves. These are broad and appear saw-toothed and are best seen in the inferior leads and in lead V1.
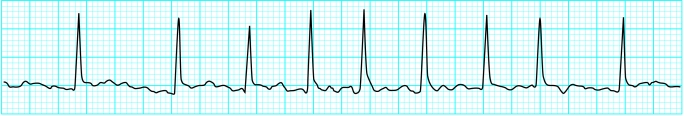
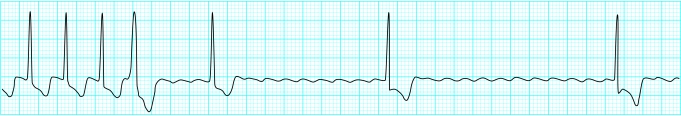
The ventricular rate depends on conduction through the atrioventricular node. Typically 2:1 block (atrial rate to ventricular rate) occurs, giving a ventricular rate of 150 beats/min. Identification of a regular tachycardia with this rate should prompt the diagnosis of atrial flutter. The non-conducting flutter waves are often mistaken for or merged with T waves and become apparent only if the block is increased. Manoeuvres that induce transient atrioventricular block may allow identification of flutter waves.
The causes of atrial flutter are similar to those of atrial fibrillation, although idiopathic atrial flutter is uncommon. It may convert into atrial fibrillation over time or, after administration of drugs such as digoxin.
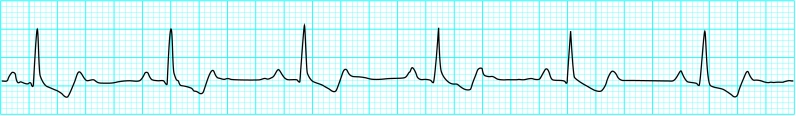
Atrial tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia typically arises from an ectopic source in the atrial muscle and produces an atrial rate of 150-250 beats/min—slower than that of atrial flutter. The P waves may be abnormally shaped depending on the site of the ectopic pacemaker.
Types of atrial tachycardia
Benign
Incessant ectopic
Multifocal
Atrial tachycardia with block (digoxin toxicity)
The ventricular rate depends on the degree of atrioventricular block, but when 1:1 conduction occurs a rapid ventricular response may result. Increasing the degree of block with carotid sinus massage or adenosine may aid the diagnosis.
There are four commonly recognised types of atrial tachycardia. Benign atrial tachycardia is a common arrhythmia in elderly people. It is paroxysmal in nature, has an atrial rate of 80-140 beats/min and an abrupt onset and cessation, and is brief in duration.
Incessant ectopic atrial tachycardia is a rare chronic arrhythmia in children and young adults. The rate depends on the underlying sympathetic tone and is characteristically 100-160 beats/min. It can be difficult to distinguish from a sinus tachycardia. Diagnosis is important as it may lead to dilated cardiomyopathy if left untreated.
Conditions associated with atrial tachycardia
Cardiomyopathy
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Ischaemic heart disease
Rheumatic heart disease
Sick sinus syndrome
Digoxin toxicity
Multifocal atrial tachycardia occurs when multiple sites in the atria are discharging and is due to increased automaticity. It is characterised by P waves of varying morphologies and PR intervals of different lengths on the electrocardiographic trace. The ventricular rate is irregular. It can be distinguished from atrial fibrillation by an isoelectric baseline between the P waves. It is typically seen in association with chronic pulmonary disease. Other causes include hypoxia or digoxin toxicity.
Atrial tachycardia with atrioventricular block is typically seen with digoxin toxicity. The ventricular rhythm is usually regular but may be irregular if atrioventricular block is variable. Although often referred to as “paroxysmal atrial tachycardia with block” this arrhythmia is usually sustained.
Figure.
Sinus tachycardia
Figure.
Atrial fibrillation is the result of multiple wavelets of depolarisation (shown by arrows) moving around the atria chaotically, rarely completing a re-entrant circuit
Figure.
Atrial fibrillation waves seen in lead V1
Figure.
Rhythm strip in atrial fibrillation
Figure.
Atrial flutter is usually the result of a single re-entrant circuit in the right atrium (top); atrial flutter showing obvious flutter waves (bottom)
Figure.
Rhythm strip in atrial flutter (rate 150 beats/min)
Figure.
Atrial flutter (rate 150 beats/min) with increasing block (flutter waves revealed after administration of adenosine)
Figure.
Atrial flutter with variable block
Figure.
Atrial tachycardia is initiated by an ectopic atrial focus (the P wave morphology therefore differs from that of sinus rhythm)
Figure.
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block (note the inverted P waves)
Figure.
Multifocal atrial fibrillation
Figure.
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block in patient with digoxin toxicity
Footnotes
The ABC of clinical electrocardiography is edited by Francis Morris, consultant in emergency medicine at the Northern General Hospital, Sheffield; June Edhouse, consultant in emergency medicine, Stepping Hill Hospital, Stockport; William J Brady, associate professor, programme director, and vice chair, department of emergency medicine, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, USA; and John Camm, professor of clinical cardiology, St George's Hospital Medical School, London. The series will be published as a book in the summer.
Steve Goodacre is health services research fellow in the accident and emergency department at the Northern General Hospital, Sheffield; Richard Irons is consultant in accident and emergency medicine at the Princess of Wales Hospital, Bridgend.