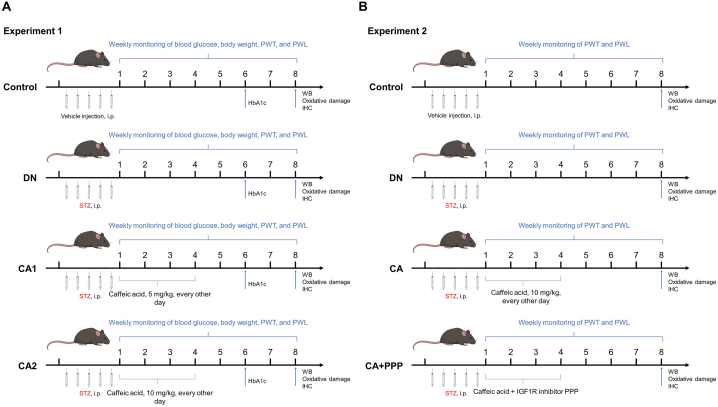
Fig. 1.
Overview of experimental design. (A) Experiment 1 examines the effects of different caffeic acid dosages on diabetic neuropathy, oxidative stress, and inflammation in mouse models. The Control group was given vehicle (citrate buffer, 50 μL) via intraperitoneal injections for five days. The Diabetic Neuropathy (DN) group received STZ solution (50 mg/kg) intraperitoneally for five days. The CA1 group mirrored the DN protocol but also received oral caffeic acid (5 mg/kg) every other day for four weeks post-final STZ injection. The CA2 group followed the CA1 regime but with caffeic acid dosed at 10 mg/kg. (B) Experiment 2 seeks to establish the IGF-1 signaling pathway's role in caffeic acid's protective effects. The Control and DN groups replicated the Experiment 1 protocol. The CA group was given STZ solution (50 mg/kg) for five days and then caffeic acid (10 mg/kg) orally every other day for four weeks. The CA + PPP group mirrored the CA group, but with an added intraperitoneal dose of IGF-1R inhibitor, Picropodophyllin (PPP) (1 mg/kg), given 20 min before each caffeic acid dosage.