Abstract
Brain clocks, which quantify discrepancies between brain age and chronological age, hold promise for understanding brain health and disease. However, the impact of multimodal diversity (geographical, socioeconomic, sociodemographic, sex, neurodegeneration) on the brain age gap (BAG) is unknown. Here, we analyzed datasets from 5,306 participants across 15 countries (7 Latin American countries -LAC, 8 non-LAC). Based on higher-order interactions in brain signals, we developed a BAG deep learning architecture for functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI=2,953) and electroencephalography (EEG=2,353). The datasets comprised healthy controls, and individuals with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. LAC models evidenced older brain ages (fMRI: MDE=5.60, RMSE=11.91; EEG: MDE=5.34, RMSE=9.82) compared to non-LAC, associated with frontoposterior networks. Structural socioeconomic inequality and other disparity-related factors (pollution, health disparities) were influential predictors of increased brain age gaps, especially in LAC (R2=0.37, F2=0.59, RMSE=6.9). A gradient of increasing BAG from controls to mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease was found. In LAC, we observed larger BAGs in females in control and Alzheimer’s disease groups compared to respective males. Results were not explained by variations in signal quality, demographics, or acquisition methods. Findings provide a quantitative framework capturing the multimodal diversity of accelerated brain aging.
The brain undergoes dynamic functional changes with age1–3. Accurately mapping the trajectory of these changes and how they relate to chronological age is critical for understanding the aging process, multilevel disparities4,5, and brain disorders1 such as the Alzheimer’s disease continuum, which includes mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and related disorders like behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD)6. Brain clocks or brain age models have emerged as dimensional, transdiagnostic metrics that measure brain health influenced by a range of factors7–9, suggesting that they may be able to capture multimodal diversity10. Notably, underrepresented populations from Latin American countries (LAC) exhibit higher genetic diversity and distinct physical, social and internal exposomes11,12 that impact brain phenotypes4,13,14. Income and socioeconomic inequality15,16, high levels of air pollution17, limited access to timely and effective healthcare18, increased prevalence of communicable diseases19, rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases19,20, and low education attaiment21,22, are determinants of brain health in LAC18. Thus, although measuring the brain age gap (BAG) could enhance our understanding of disease risk and its impact on accelerated aging23, there is a lack of research on brain age models in underrepresented populations with increased socioeconomic and health disparities18,24,25.
Sex and gender differences emerge as critical factors influencing brain changes. Studies on atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease continuum reveal a faster rate of brain atrophy in females than in males26. Moreover, country-level gender inequality is associated to sex differences in cortical thickness27. Structural gender inequality further impacts brain health, with adverse environments affecting dendritic branching and synapse formation28. However, no studies to date have explored the spectrum of brain age abnormalities, including the effects of demographic heterogeneity across geographical regions, sexes, and the continuum from brain health to disease. Further, most studies have been conducted with participants from the global north, resulting in a lack of generalization to underrepresented populations from LAC24,29–31.
Multimodal machine learning studies show promise in brain aging23; however, most rely on structural MRI, overlooking brain network dynamics. Complex spatiotemporal dimensions can be tracked with spatial accuracy through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and millisecond precision using electroencephalogram (EEG)32. Given the complementary strengths of fMRI and EEG, it is crucial to cross-validate existing brain clock models using these techniques. However, no studies have simultaneously applied EEG and fMRI to replicate brain age effects. Additionally, standard machine learning approaches are less generalizable than deep learning methods33. Brain age indices has been restricted by the predominant use of MRI or PET, which are less accessible and affordable in LAC, leading to selection biases34. EEG offers a solution due to its cost-effectiveness, portability, and ease of implementation in aging and dementia35,36. However, few studies have combined accessible techniques with deep learning to develop scalable brain age markers. The application of EEG is hindered by heterogeneity in recordings, electrode layouts, acquisition systems, processing pipelines, and small sample sizes37. These standardization challenges have impeded the integration of fMRI and EEG in extensive, multicenter brain age research.
We adopted a framework to tackle diversity by including datasets from LAC and non-LAC regions (n = 5306), utilizing graph convolutional networks (GCN) to functional connectivity of fMRI and EEG signals. We hypothesized that, across fMRI and EEG imaging, models would accurately predict BAGs and be sensitive to the impacts of multimodal diversity, including geographical and sociodemographic effects, sex differences, health disparities, and exposome influences. By testing this hypothesis, we aimed to assess the effectiveness of high-order interactions and deep learning in predicting brain age differences across diverse and heterogeneous populations of healthy aging and neurocognitive disorders.
Results
We employed resting-state fMRI (n = 2953) and EEG (n = 2353) signals separately to evaluate whether a deep-learning computational pipeline (Fig. 1) captures differences in brain aging across heterogeneous populations. We included fMRI data from 2953 participants from Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and Peru (LAC) and the USA, China, and Japan (non-LAC). The EEG dataset involved 2353 participants from Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, and Cuba (LAC), and Greece, Ireland, Italy, Turkey, and the UK (non-LAC). Healthy controls, MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, and bvFTD groups were included. We focused on the Alzheimer’s disease and bvFTD as these conditions represent the most common late-onset and early-onset causes of dementia38,39. We included the Alzheimer’s disease continuum, which encompasses MCI, to capture the prodromal stages of the disease39. Raw fMRI and EEG signals were preprocessed to remove artifacts and then normalized. Based on multivariate information theory, we calculated high-order interactions1. Weighted graphs were used as inputs for a graph convolutional deep learning network trained to predict brain age, employing one model for fMRI and another for EEG.
Fig. 1. Datasets characterization and analysis pipeline.
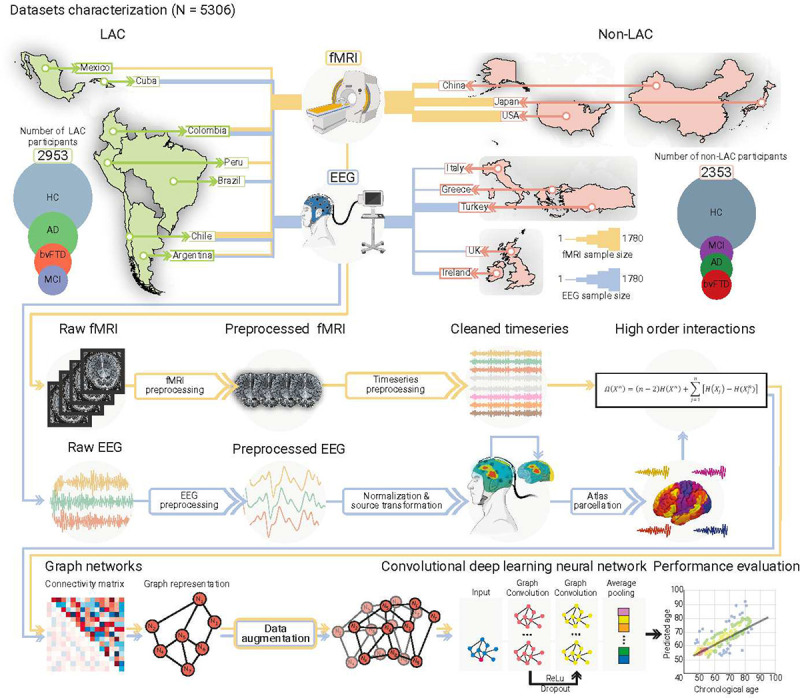
Datasets included Latin American countries (LAC) and non-LAC healthy controls (HC, total N = 3509) and participants with Alzheimer’s disease (AD, total N = 828), behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD, total N = 463), and mild cognitive impairment (MCI, total N = 517). The functional magnetic resonance imaging dataset (fMRI, yellow lines) included 2953 participants from LAC (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and Peru) as well as non-LAC (the USA, China, and Japan). The electroencephalography dataset (EEG, blue lines) involved 2353 participants from Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, and Cuba (LAC) as well as Greece, Ireland, Italy, Turkey, and the UK (non-LAC). Circles represent the number of participants per group, scaled between the number of participants in the largest and smallest groups for each region to facilitate visualization. Line thickness represents the number of participants with fMRI (yellow lines) and EEG (blue lines) per country. The raw fMRI and EEG signals were preprocessed by filtering and artifact removal and the EEG signals were normalized to project them into source space. A parcellation using the automated anatomical labeling (AAL) atlas for both the fMRI and EEG signals was performed to build the nodes from which we calculated the high-order interactions using the Ω-information metric. A connectivity matrix was obtained for both modalities, which was later represented by graphs. Data augmentation was performed only in the testing dataset. The graphs were used as input for a graph convolutional deep learning network (architecture shown in the last row), with separate models for EEG and fMRI. Finally, age prediction was obtained, and the performance was measured by comparing the predicted vs. the chronological ages. This figure was partially created using Biorender under Team license.
BAG across LAC and non-LAC datasets
We used the fMRI and EEG signals from the control’s datasets (i.e., LAC and non-LAC) to train and test brain-aging models. We employed 80% cross-validation with a 20% hold-out testing split. As shown in Figs. 2a and 3a, our models predicting brain age obtained adequate goodness of fit (fMRI: R2 = 0.52, p < 0.001, F2 = 1.07; EEG: R2 = 0.45, p < 0.001, F2 = 0.83). We implemented the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) to evaluate models’ fit, obtaining acceptable brain age predictions (fMRI-RMSE = 7.24, EEG-RMSE = 6.45). For both, fMRI and EEG, the main predictive brain-regional features included hubs in frontoposterior networks (nodes in precentral gyrus, the middle occipital gyrus, and the superior and middle frontal gyri; Fig. 2a and 3a). Additional nodes for the fMRI model included the inferior frontal gyri, and the anterior and median cingulate and paracingulate gyri (Fig. 2a.). For EEG, key nodes also comprised the superior and inferior parietal gyri and the inferior occipital gyrus (Fig. 3a). Thus, for both fMRI and EEG the models showed an adequate fit and predictive performance, with key predictive features involving frontoposterior networks in the brain.
Fig. 2. fMRI training and testing the deep learning model in different samples.
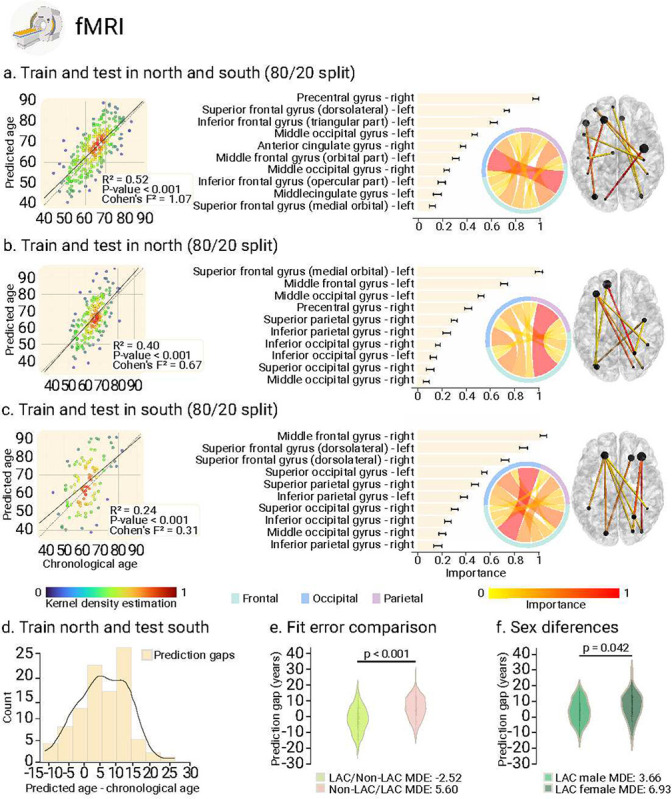
(a) Ordinary least squares (OLS) regression comparing chronological age vs. predicted age with the feature importance list for training and testing in the whole sample. (b) Regression comparing chronological age vs. predicted age with the feature importance list for training and testing in the non-LAC dataset. (c) Regression comparing chronological age vs. predicted age with the feature importance list for training and testing in the LAC dataset. For (a), (b) and (c), data point colors indicate the kernel density estimation to provide a visual representation of the density of prediction errors across different values of chronological age. The bars show the brain region feature importance list in descending order, with ring plots and glass brain representations of the most important network-edge connections. (d) Histogram of the prediction error when training in non-LAC dataset and testing in LAC dataset. (e) Violin plot of the distribution and statistical comparison of training and testing with different regions using a permutation test (5000 iterations). (f) Violin plot of the distribution and statistical comparison of testing the models on females and males using a permutation test (5000 iterations). LAC = Latin American countries.
Fig. 3. EEG training and testing the deep learning model in different samples.
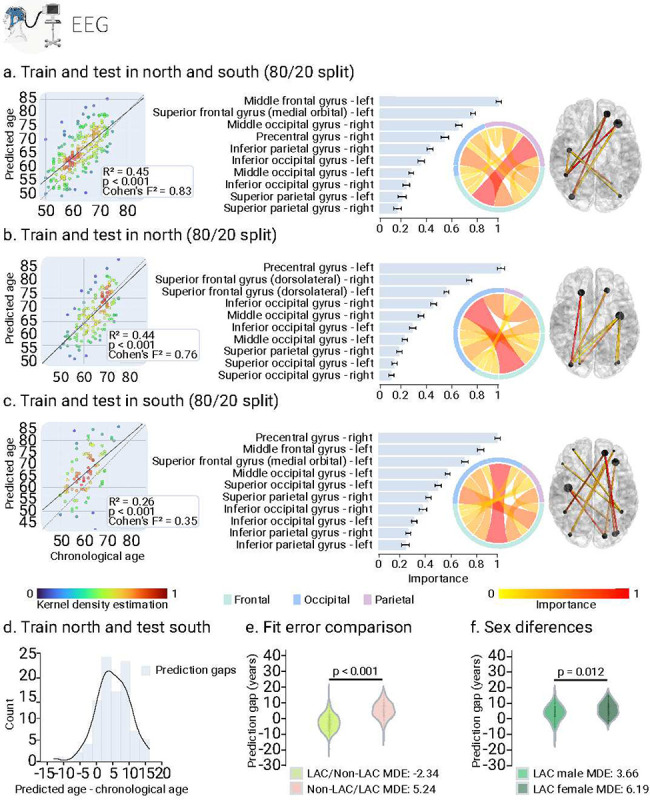
(a) Ordinary least squares (OLS) regression comparing chronological age vs. predicted age with the feature importance list for training and testing in the whole sample. (b) Regression comparing chronological age vs. predicted age with the feature importance list for training and testing in the non-LAC dataset. (c) Regression comparing chronological age vs. predicted age with the feature importance list for training and testing in the LAC dataset. For (a), (b) and (c), data point colors indicate the kernel density estimation to provide a visual representation of the density of prediction errors across different values of chronological age. The bars show the brain region feature importance list in descending order, with ring plots and glass brain representations of the most important network-edge connections. (d) Histogram of the prediction error when training in non-LAC dataset and testing in LAC dataset. (e) Violin plot of the distribution and statistical comparison of training and testing with different regions using a permutation test (5000 iterations). (f) Violin plot of the distribution and statistical comparison of testing the models on females and males using a permutation test (5000 iterations). LAC = Latin American countries.
BAG in non-LAC datasets
Using the same data split ratio, we trained and tested the models in non-LAC datasets. As shown in Figs. 2b and 3b, our models predicting brain age yielded considerable goodness of fit (fMRI: R2 = 0.40, p < 0.001, F2 = 0.67; EEG: R2 = 0.43, p < 0.001, F2 = 0.76). RMSE values were also adequate (fMRI-RMSE = 8.66; EEG-RMSE = 6.54). Mean Directional Errors (MDE) for fMRI and EEG were 0.69 and 1.07, respectively. For both fMRI and EEG, the main predictive features included hubs in frontoposterior networks including the superior frontal gyrus (dorsolateral), the precentral gyrus, and the middle occipital gyrus (Fig. 2b and 3b). Additional critical nodes for the fMRI model included the inferior and middle frontal gyri, and the anterior and median cingulate and paracingulate gyri (Fig. 2b). For EEG, key nodes also comprised the superior and inferior occipital gyri, and the superior parietal gyrus (Fig. 3b). In brief, models trained on non-LAC datasets exhibited strong fit values and predictive features as in the overall dataset analysis.
BAG in LAC datasets
When trained and tested in the LAC datasets (Figs. 2c and 3c), models demonstrated moderate goodness of fit indexes but were less precise, as indicated by higher RMSE values (fMRI = 11.91; EEG = 9.82). We observed increased positive biases in the MDE measures compared to the non-LAC models (fMRI = 3.18; EEG = 5.34). Again, the main features involved frontoposterior networks. Common nodes for fMRI and EEG included the superior and middle occipital gyri, the superior and inferior parietal gyri, and the superior and middle frontal gyri (Fig. 2c and 3c). For EEG, the model also highlighted the precentral gyrus, and the inferior occipital gyrus (Fig. 3c). Thus, models trained on LAC datasets showed moderate fit and positive biases (older brain age) in frontotemporal nodes (fMRI and EEG), compared to non-LAC models.
Cross-regional effects in model generalization
We investigated the effects of cross-region training and testing with data from non-LAC and LAC. Training with non-LAC data and testing on LAC data led to biases predicting older brain ages than chronological ages as shown by positive MDE values (Figs. 2d and 3d; fMRI: MDE = 5.60, RMSE = 9.44; EEG: MDE = 5.24, RMSE = 7.23). On the contrary, training on LAC and testing on non-LAC resulted in negative age biases predicting younger brain age shown by the MDE (Figs. 2d and 3d; LAC/non-LAC fMRI: MDE = −2.52, RMSE = 8.41; LAC/non-LAC EEG: MDE = −2.34, RMSE = 5.69). Sex differences were observed in the BAG when training in the non-LAC and testing in LAC (Figs. 4a and 4b). Specifically, female participants in LAC exhibited a greater bias towards older brain age than males (fMRI: p = 0.04; EEG: p = 0.03). In conclusion, training with non-LAC data and testing on LAC data resulted in a bias towards predicting older brain ages, especially for female participants in LAC.
Fig. 4. Groups, sex, and macrosocial influences in BAGs.
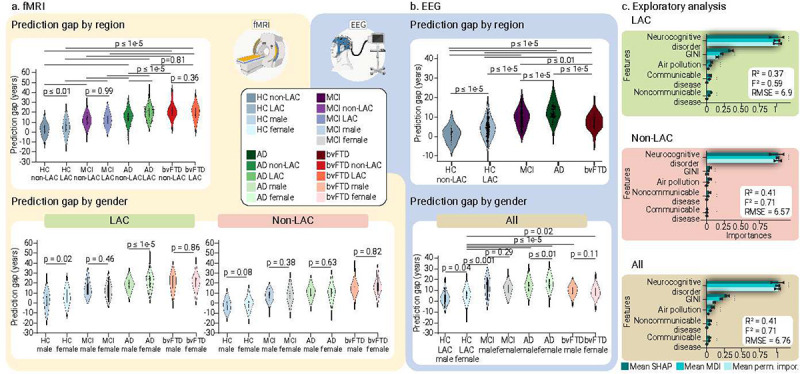
Violin plots for the distribution of prediction gaps for different groups and sex effects using (a) fMRI and (b) EEG datasets. The statistical comparisons were calculated using subsample permutation testing with 5000 iterations. (c) Associations between macrosocial and disease disparity factors with BAGs were assessed with a multi-method approach comprising SHAP values, feature importance (mean decrease in impurity, MDI), and permutation importance. Plots show the mean importance values for each method, along with their 99% confidence interval, as well as the average R-squared and Cohen’s F2. * = Significant predictors. Shaded bars indicate significance across the three methods. LAC = Latin American countries, HC non-LAC = Healthy controls from non-LAC, HC LAC = Healthy controls from LAC, MCI = mild cognitive impairment, AD = Alzheimer’s disease, bvFTD = behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia, M = Males. F = Females, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Accelerated aging in MCI, Alzheimer’s disease and bvFTD
We investigated the effects of testing the controls-trained model (80%) on different subsamples, matched by age, sex, and education, from other groups (i.e., controls non-LAC, controls LAC, MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, and bvFTD, Table 1). Permutation subsample analyses with 5000 iterations revealed statistically significant BAGs between the non-LAC and LAC control groups (Figs. 4a and 4b, fMRI: p < 0.01; EEG: p < 1e-5). This difference was also observed for Alzheimer’s disease in the fMRI dataset (p < 1e-5). Additionally, for fMRI, we found significant differences between controls from non-LAC and all clinical groups from the same region [MCI (p < 1e-5), Alzheimer’s disease (p < 1e-5), and bvFTD (p < 1e-5)]. Similarly, for both fMRI and EEG, we observed significant differences between controls from LAC and all the clinical groups [fMRI: MCI (p < 1e-5), Alzheimer’s disease (p < 1e-5), and bvFTD (p < 1e-5); EEG: MCI (p < 1e-5), Alzheimer’s disease (p < 1e-5), and bvFTD (p < 0.01)]. Across fMRI and EEG datasets, both LAC and non-LAC, we observed a gradient of increasing brain age from controls to MCI to Alzheimer’s disease. The MCI groups significantly differed from Alzheimer’s disease (fMRI and EEG: p < 1e-5) and bvFTD (fMRI: p < 1e-5; EEG: p < 0.01), with older brain ages for Alzheimer’s disease and bvFTD. For the fMRI and EEG non-LAC datasets, the Alzheimer’s disease group also showed an older brain age than the bvFTD group (p < 0.01). Thus, larger brain age gaps were observed in LAC compared to non- LAC groups and across clinical groups, with a gradient of increasing brain age from controls to MCI to dementia.
Table 1.
Demographics for fMRI and EEG datasets
| Full dataset | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All participants n = 5306 | HCs = 3509 | MCI = 517 | AD = 828 | bvFTD = 463 | |||
| fMRI dataset | |||||||
| Variable | HCs Non-LAC n = 967 LAC n = 477 | MCI Non-LAC n = 215 LAC n = 169 | AD Non-LAC n = 214 LAC n = 505 | bvFTD Non-LAC n = 190 LAC n = 216 | Statistics Non-LAC vs. LAC | Post-hoc comparisons | |
| Sex (F:M) | Non-LAC | 470:497 | 114:101 | 112:102 | 98:92 | χ2 = 2.19 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 |
| LAC | 261:216 | 84:85 | 262:243 | 105:111 | χ2 = 2.76 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 | |
| Age (years) | Non-LAC | 53.55 | 59.62 | 76.59 | 73.14 | F = 3.13 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 |
| LAC | 65.34 | 66.53 | 77.52 | 73.15 | F = 3.62 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 | |
| Years of Education | Non-LAC | 13.15 | 14.15 | 13.12 | 11.16 | F = 2.19 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 |
| LAC | 12.11 | 11.52 | 8.89 | 7.89 | F = 1.31 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 | |
| EEG dataset | |||||||
| HCs Non-LAC n = 569 LAC n = 1486 | MCI LAC n = 133 | AD LAC n = 108 | bvFTD LAC n = 57 | Statistics Non-LAC vs. LAC | Post-hoc comparisons | ||
| Sex (F:M) | Non-LAC | 470:99 | - | - | - | χ2 = 64.62 | - |
| LAC | 954:532 | 111:22 | 85:23 | 39:18 | χ2 = 28.05 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 | |
| Age (years) | Non-LAC | 58.98 | - | - | - | t = 4.21 | - |
| LAC | 66.74 | 62.54 | 78.62 | 71.05 | F = 7.62 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 | |
| Years of Education | Non-LAC | 14.85 (4.91 | - | - | - | t = 3.54 | - |
| LAC | 13.92 | 8.12 | 10.75 | 14.38 | F = 6.31 | HC-MCI: p > 0.05 | |
Results are presented as mean (SD). Asterisks (*) indicate an alpha level of p < 0.05. Demographic data comparing non-LAC and LAC groups were assessed using unpaired t-tests, while data for pathological groups were analyzed using ANOVAs followed by Tukey post-hoc pairwise comparisons, except for sex, which was analyzed using Pearson’s chi-squared (χ2) test. Effect sizes were calculated using partial eta squared (ηp2). Abbreviations: HC = healthy control, MCI = mild cognitive impairment, AD = Alzheimer’s disease, bvFTD = behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia.
Sex differences in neurocognitive disorders
For fMRI, we analyzed the differences between male and female participants with the same diagnosis for the non-LAC and LAC datasets. There were no significant differences among groups from non-LAC datasets (Figs 4a and 4b). However, Alzheimer’s disease females from LAC exhibited significantly greater BAGs compared to males (fMRI: p < 1e-3, EEG: p < 0.001). No other significant effects were observed. We conducted a supplementary analysis incorporating country-level gender inequality (GII indexes), sex, region (LAC vs. non-LAC), and individual neurocognitive status (HC vs. MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, or bvFTD) as predictors of BAGs. The model demonstrated good performance (R2 = 0.40, F2 = 0.66, RMSE = 6.85, p < 1e-15) and all predictors were influential. Having a neurocognitive disorder and being a female living in countries with high gender inequality – particularly from LAC – were associated with higher BAGs (Extended Data Fig.1 and Supplementary Table 1). Overall, females with Alzheimer’s disease from LAC exhibited significantly greater brain age gaps compared to males, influenced by high gender inequality in their countries.
Exposome determinants of BAGs
We employed gradient boosting regression models to explore the influence of physical and social exposomes, as well as disease disparity factors on BAGs. Predictors included aggregate country-level measures of air pollution (PM2.5), socioeconomic inequality (GINI index), and burdens of communicable, maternal, prenatal, and nutritional conditions, and non-communicable diseases. We also leveraged the individual neurocognitive status (HC versus Alzheimer’s disease, MCI, or bvFTD). We assessed predictors’ importance using a multi-method approach comprising permutation importance, mean decrease in impurity (MDI), and SHAP values (Fig. 4c). Across both LAC and non-LAC datasets, the models (R2 = 0.41, F2 = 0.71, RMSE = 6.76, F = 304.25, p < 1e-15) identified neurocognitive disorders (MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, or bvFTD) and higher socioeconomic inequality (GINI index) as the most influential and consistent predictors of increased BAGs (Fig. 4c). High levels of pollution and burden of non-communicable and communicable diseases were also predictive of increased BAGs, albeit less impactful. Stratified models for LAC (R2 = 0.37, F2 = 0.59, RMSE = 6.9, F = 138.78, p < 1e-15) and non-LAC (R2 = 0.41, F2 = 0.71, RMSE = 6.57, F = 135.91, p < 1e-15) also showed good performance, with neurocognitive disorders being the most influential predictor in both. In LAC, higher socioeconomic inequality was the second most consistent and influential predictor of larger BAGs across the three models. Air pollution and burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases were also influential. None of these variables was influential predictors in the non-LAC models. Predictors’ estimation coefficients are presented in Supplementary Table 2. In sum, neurocognitive disorders, followed by macrosocial factors linked to socioeconomic inequality, air pollution, and health disparities, were influential predictors of increased brain age gaps, especially in LAC.
Sensitivity analyses
We performed multiple tests to assess the validity of the results. First, we investigate whether variations in fMRI or EEG data quality explained the differences in brain age between the non-LAC and LAC. Subsample permutation tests with 5000 iterations showed no significant differences between any of the groups for fMRI (Fig. 5a) or EEG (Fig. 5b) data quality metrics. In addition, a linear regression examining scanner type effects showed that the fMRI data quality metric did not predict the BAGs (R2 = 0.001, p = 0.18, Cohen’s F2 = 0.001, Fig. 5c). To further test for scanner effects, we implemented a harmonization strategy by normalizing the BAG variable within each scanner type. We used the min-max scaler to ensure consistent minimum and maximum values across scanners. Results using this harmonization (Fig. 5d) and our initial approach were very similar. Additional analyses controlling for datasets collected with eyes open versus eyes closed protocols revealed no significant differences in BAGs across any groups (Extended Data Fig. 2).
Fig. 5. Sensitivity analysis.
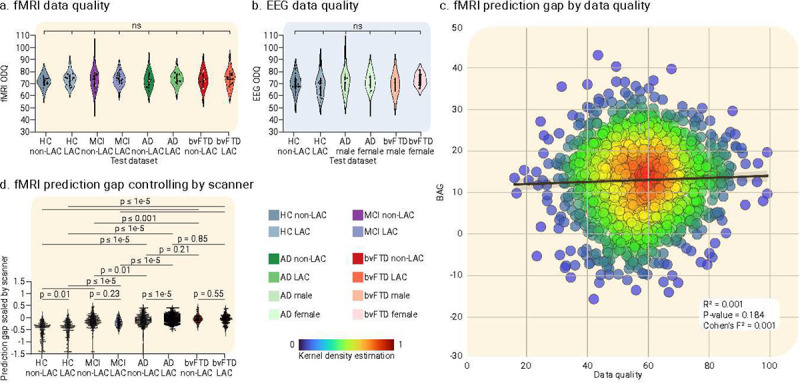
Violin plots for the distribution of data quality metrics of (a) fMRI and (b) EEG datasets. Both panels indicate null results between groups in terms of data quality. (c) Linear regression effects of scanner type, evidencing that the fMRI data quality was not significantly associated with fMRI BAGs differences. (d) fMRI BAG differences across groups controlling for scanner differences. The statistical comparisons were calculated using subsample permutation testing with 5000 iterations. LAC = Latin American countries, HC = Healthy controls, MCI = mild cognitive impairment, AD = Alzheimer’s disease, bvFTD = behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia.
We also controlled for effects of age and years of education on fMRI and EEG BAGs by including them as covariates in the group comparisons. All reported group differences remained significant after covariate adjustment (Supplementary Table 3). Years of education did not change the results for any analyses. In eight of the nine analyses, age did not have a significant effect. Considering the chronological age differences between Alzheimer’s disease and MCI groups, we performed a sensitivity analysis using a subset of MCI participants (fMRI: n = 254, mean age = 73.287 +/− 7.517; EEG: n = 52, mean age = 63.231 +/− 6.549) age matched to Alzheimer’s disease participants (fMRI: n = 254, mean age = 72.295 +/− 7.530, p = 0.13; EEG: n = 52, mean age = 62.769 +/− 6.302, p = 0.71). These results (Extended Data Fig. 3) confirmed those reported for the overall MCI and Alzheimer’s disease datasets (Figs. 4a and 4b). For both fMRI and EEG datasets, we found significantly larger BAGs in Alzheimer’s disease compared to MCI (fMRI: p < 1e-5; EEG: p < 0.01). For fMRI, these differences were observed in both LAC (p < 1e-5) and non-LAC (p < 1e-5) datasets. We also found differences between MCI participants from LAC vs. non-LAC (p < 1e-5) and Alzheimer’s disease participants from LAC vs. non-LAC (p < 1e-5). Thus, controlling for data quality, scanner effects, age, and education confirmed that the reported effects in brain age gaps remained the same.
Discussion
Our study used brain clocks to capture diversity and disparity across LAC and non-LAC datasets using fMRI and source-space EEG techniques. Despite heterogeneity in signal acquisition and methods, we captured patterns of brain age modulations in healthy aging from diverse datasets and participants with MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, and bvFTD. Models trained and tested on non-LAC data showed greater convergence with chronological age. Conversely, models applied to LAC datasets indicated larger BAGs, suggesting accelerated aging. We observed a gradient of BAGs from controls to MCI to Alzheimer’s disease. Sex differences revealed an increased BAG in females in control and Alzheimer’s disease groups. Most brain clock patterns were independently confirmed and replicated across fMRI and EEG. Aggregate-level macrosocial factors, including socioeconomic inequality, pollution, and burden of communicable/non-communicable conditions modulated the BAG, especially in LAC. Variations in signal quality, demographics, or acquisition methods did not account for the results. The findings offer a framework that captures the multimodal diversity associated with accelerated aging in various global settings.
Our results suggest that being from LAC is associated with accelerated aging. The better fit of the non-LAC compared to the LAC models supports the notion that universal models of brain phenotypes do not generalize well to underrepresented populations24,29,40. Diversity-related factors associated with different exposome and disease disparities4,10,24,41 may influence the BAGs in LAC and non-LAC. Neurocognitive disorders played a crucial role4,42. However, structural socioeconomic inequality, a distinctive characteristic of LAC15, increased levels air pollution43, and the burden of non-communicable19,20 and communicable18,44 diseases also have an significant impact on BAGs. The fact that these effects were larger in LAC suggests that underlying inequalities and adverse environmental and health conditions play a macrosocial, structural driving role11 in the observed regional differences. Immigration may also influence brain age through social determinants of health45 and genetic diversity. In LAC, tricontinental admixtures lead to significant ancestral diversity within and across countries46, impacting dementia prevalence and brain phenotypes41. Future studies should consider these potential effects in BAGs.
Selective brain networks were associated with larger BAG in the clinical groups. Both fMRI and EEG models of BAGs yielded large-scale frontoposterior high-order interactions1, consistent with models of brain age involving long-range connections between frontal, cingular, parietal, and occipital hubs, which may be more vulnerable to aging effects47–49. Also consistent with the cumulative nature of neurobiological changes over time50, BAGs increased from controls through MCI to Alzheimer’s disease. A previous deep learning study using MRI and PET in participants with MCI and dementia also indicated increased brain age associated with disease progression23. Our results point to the brain age of MCI as being an intermediate stage between healthy aging and dementia39, and suggest that both fMRI and EEG markers of brain age may help identify groups at greater risk of progressing to dementia.
Sex and gender have been linked to poorer brain health outcomes27,51. Larger BAGs in controls and Alzheimer’s disease females from LAC may relate to sex-specific conditions such as menopause, which involves brain volume reduction and increased amyloid-beta deposition52,53. Females also exhibit disproportionate tau brain burden54, pronounced inflammatory dysregulation55 and lower basal autophagy56, all of which increase Alzheimer’s disease risk. Such sex-specific factors are intertwined with environmental factors and gender inequalities51. Females in countries with higher gender inequality exhibit greater cortical atrophy27. Our sex effects were specific for Alzheimer’s disease and LAC, consistent with the impacts of environmental41 versus genetic risks57 in Alzheimer’s disease and bvFTD, respectively. Despite advances in gender equality, women in LAC still face significant obstacles58 including lower education, less income and healthcare access, and greater caregiving burden, potentially exacerbating brain health issues and Alzheimer’s disease risk59,60. Previous models for brain age have been conducted predominantly in high-income settings, ignoring sex and gender differences triggered by region-specific influences30,31. Thus, the inclusion of diverse samples can help to better understand the biological and environmental interaction of sex and gender disparities.
Our study had different strengths. We used diverse datasets across LAC and non-LAC including 15 countries, featuring large sample sizes, and replicated results across fMRI and EEG. Geographical and sex differences modulated brain clocks across fMRI and EEG models, with more accelerated aging observed in controls and Alzheimer’s disease females from LAC, contributing to the understanding of the effects of sex and diversity in aging. We used an integrative approach to analyze fMRI and EEG data across a large and geographically diverse sample. The convergence of two neuroimaging techniques and population heterogeneity enhanced the generalizability of our findings, making a significant contribution to computational models that capture diversity10. Brain clocks based on high-order interactions capture many risks to brain health, and thus, offer a new approach to personalized medicine, particularly for underrepresented populations. Our framework combines multiple dimensions of diversity in brain health, the Alzheimer’s disease continuum and related disorders within a single measure of brain clocks, which is relevant for global health policies, generalizable computational models, and public health strategies. Incorporating EEG offers affordable and scalable solutions for disadvantaged settings, such as those in LAC, compared to traditional neuroimaging techniques1,35. Accessible metrics of accelerated aging can offer personalized assessments of diversity, aging, and neurocognitive disorders.
This study has multiple limitations. Our EEG dataset lacks representation from clinical groups in non-LAC, which may limit the generalizability. This issue is partially mitigated by the consistent results from the fMRI data, which included MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, and bvFTD groups from both regions. Our BAG approach is unimodal. Future research should adopt multimodal approaches to deepen our understanding of brain aging across different pathophysiological mechanisms1. We leveraged two independent training and test datasets with fMRI and EEG, with out-of-sample validation yielding consistent results across geographical comparisons, sex effects, and clinical conditions. These datasets involve multimodal settings and recording parameters, suggesting that our results are strong across highly variable conditions. However, future research should include more regions to further validate and strengthen our findings. Additionally, we did not include individual-level data on gender identity, socioeconomic status, and ethnic stratification. Future research incorporating these variables could further enrich our understanding of brain age across diverse populations. Lastly, the sex differences observed between controls from LAC and non-LAC exhibited moderate effect sizes. Further research should assess sex differences in other regions.
In conclusion, brain clock models were sensitive to the impact of multimodal diversity involving geographical, sex, macrosocial, and disease-based factors from diverse populations, despite the heterogeneity in data acquisition and processing. Utilizing an deep learning architecture of the brain’s high-order interactions1 across fMRI and EEG signals, combined with globally accessible and affordable data, our study paves the way for more inclusive tools to assess disparities and diversity in brain aging. These tools can be vital in identifying MCI, Alzheimer’s disease and bvFTD risk factors, as well as to characterizing and staging disease processes. In the future, personalized medicine approaches could leverage models of BAGs to establish worldwide protocols for aging and neurocognitive disorders.
Methods
The total dataset consisted of 5306 participants, with 2953 undergoing fMRI and 2353 EEG acquisitions. Of these, 3509 were controls, 517 had MCI, 828 Alzheimer’s disease, and 463 bvFTD.
fMRI dataset
The fMRI study involved 2953 participants from both non-LAC (USA, China, Japan) and LAC (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, Peru), including 1444 healthy controls (HC). Two hundred fifteen participants met the Petersen criteria for MCI with a 24 MMSE cut-off value, 719 were diagnosed as probable AD61, and 402 fulfilled the diagnostic criteria for bvFTD62. LAC participants were recruited from the Multi-Partner Consortium to Expand Dementia Research in Latin America (ReDLat, with participants from Mexico, Colombia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina)63. Non-LAC participants were non-Latino individuals from ReDLat, the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), and the Neuroimaging in Frontotemporal Dementia (NIFD) repository. The datasets were matched on sex, age, and years of education (Table 1). Sex information was determined by self-report. No information regarding gender was inquired. To ensure data reliability, we excluded subjects who reported a history of alcohol/drug abuse or psychiatric or other neurological illnesses. No participants reported a history of alcohol/drug abuse, psychiatric, or other neurological illnesses.
EEG dataset
The total dataset involved 2353 participants. Controls comprised 1183 participants, including 737 from non-LAC (Turkey, Greece, Italy, United Kingdom, and Ireland) and 446 from LAC (Cuba, Colombia, Brazil, Argentina, and Chile). The participants presenting with clinical conditions were recruited from a multisite study with harmonized assessments25,36,63 in LAC (Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Colombia). This dataset included 133 patients with MCI, 108 with Alzheimer’s disease, and 57 with bvFTD. The controls datasets were matched on age, sex, and years of education concerning the clinical groups (MCI, Alzheimer’s disease, and bvFTD) (Table 1). Sex information was determined by self-report. No information regarding gender was inquired. The Petersen criteria defined the MCI group with a 24 MMSE cut-off value. All individuals with Alzheimer’s disease met the criteria for probable disease following international diagnostic guidelines61. The bvFTD group met the diagnostic criteria for probable bvFTD62. No subject in any of the clinical conditions reported a history of alcohol/drug abuse, psychiatric, or other neurological illnesses.
Ethics approval
The local institutions that contributed EEGs and/or fMRIs to this study approved the acquisitions and protocols (Supplementary Data S1), and all participants signed a consent form following the declaration of Helsinki. The overall study was approved by the consortium under multiple IRBs (FWA00028264, FWA00001035, FWA00028864, FWA00001113, FWA00010121, FWAA00014416, FWA00008475, FWA00029236, FWA00029089, and FWA00000068). Data collection and analysis posed no risks concerning stigmatization, incrimination, discrimination, animal welfare, environmental, health, safety, security, or personal concerns. No transfer of biological materials, cultural artifacts, or traditional knowledge occurred. The authors reviewed pertinent studies from all countries while preparing the manuscript.
fMRI preprocessing
The images were obtained from different scanners and in distinct acquisition settings (Supplementary Table 4). We included two resting-state recordings, closed and open eyes, to increase the sample size for rs-fMRI data. The type of resting-state recording was controlled by a dummy variable (open or closed eyes) when employing the functional connectivity metric64. The resting state of fMRI preprocessing was conducted using the fmriprep toolbox (version 22.0.2). Furthermore, additional preprocessing was performed using the toolbox CONN2264. The CONN toolbox preprocessing included smoothing with a Gaussian kernel of 6 × 6 × 6 mm, the signal denoising through linear regression to account for confounding effects of white matter, cerebrospinal fluid, realignment, and scrubbing. A band-pass filter (0.008–0.09) Hz was also applied. After time-series preprocessing, we employed region-of-interest (ROI) analysis based on the brain regions of the Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL90) atlas to reduce the dimensionality of the fMRI data for machine learning algorithms.
EEG preprocessing
EEGs were processed offline using procedures implemented in a custom, automatic pipeline for computing brain functional connectivity in the EEG using a mesh model for multiple electrode arrays and source space estimation (see Supplementary Table 5 for acquisition parameters). The pipeline allows for the multicentric assessment of rsEEG connectivity and has been validated in a large-scale evaluation of connectivity in dementia65. Recordings were re-referenced to the average reference and band-pass filtered between 0.5 and 40 Hz using a zero-phase shift Butterworth filter of order 8. Data were downsampled to 512 Hz, referenced using the reference electrode standardization technique (REST), and corrected for cardiac, ocular, and muscular artifacts using two methods based on Independent Component Analysis (ICA). ICLabel (a tool for classifying EEG independent components into signals and different noise categories)66, and EyeCatch (a tool for identifying eye-related ICA scalp maps) were used67. Data were visually inspected after artifact correction, and malfunctioning channels were identified and replaced using weighted spherical interpolations.
EEG normalization: Following guidelines for multicentric studies37, EEG was rescaled to reduce cross-site variability. The normalization was carried out separately for each dataset and consisted of the Z-score transformation of the EEG time series. The Z-score describes the position of raw data in terms of its distance from the mean when measured in standard deviation units. The Z-score transformed EEG connectivity matrices display more prominent interhemispheric asymmetry and reinforced long-distance connections than unweighted connectivity representations65.
EEG source space estimation: The source analysis of the rsEEG was conducted using the standardized Low-Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography method (sLORETA). sLORETA allows estimating the standardized current density at each of the predefined virtual sensors located in the cortical gray matter and the hippocampus of a reference brain (MNI 305, Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurologic Institute) based on the linear, weighted sum of a particular scalp voltage distribution or the EEG cross-spectrum at the sensor level. sLORETA is a distributed EEG inverse solution method based on an appropriate standardized version of the minimum norm current density estimation. sLORETA overcomes problems intrinsic to the estimation of deep sources of EEG and provides exact localization to test seeds, albeit with a high correlation between neighboring generators.
The different electrode layouts were registered onto the scalp MNI152 coordinates. A signal-to-noise ratio of 1 was chosen for the regularization method used to compute the sLORETA transformation matrix (forward operator for the inverse solution problem). The standardized current density maps were obtained using a head model of three concentric spheres in a predefined source space of 6242 voxels (voxel size = 5mm3) of the MNI average brain. A brain segmentation of 82 anatomic compartments (subcortical and cortical areas) was implemented using the automated anatomical labeling (AAL90) atlas. Current densities were estimated for the 153600 voltage distributions comprising the five minutes of rsEEG (sampled at 512 Hz). The voxels belonging to the same AAL region were averaged such that a single (mean) time series was obtained for each cortical region32,68,69.
High-order interactions
After preprocessing 82 time-series from the AAL brain parcellation for each modality (fMRI and EEG), we calculated the high-order interactions across triplets composed of a region i and region j and a set comprising all the brain regions without i and j. To this end, we evaluated high-order interactions using the organizational information (Ω) metric. It is a multivariate extension of Shannon’s mutual information, which assesses the dominant characteristic of multivariate systems (i.e., high-order interactions). In this case, to operationalize the Shannon Entropy, we used the Gaussian copula approximation, which estimates the differential Shannon’s entropy from the covariance matrix of the Gaussian copula transformed data70. This is a mixture of a parametric and a non-parametric approach, as the copula is preserved in a non-parametric way but is then used to generate Gaussian marginals. The Ω quantifies the balance between redundancy and synergy in high-order interactions among brain regions. By definition, Ω > 0 implies that the interdependencies are better described as shared randomness, indicating redundancy dominance. Conversely, Ω < 0 suggests that the interdependencies are better explained as collective constraints, indicating synergy dominance. After normalization, its magnitude ranges from −1 to 1. The Ω can be expressed as:
| (1) |
where Xn is the random vector that describes the system, and H is the Shannon’s entropy. When n is reduced to three variables (x, y, and z), Ω can be expressed as
| (2) |
To analyze brain activity, z can be considered a multivariate time series representing the activity of all brain regions except for x and y. Therefore, O info measures how synergistic or redundant is the relationship between two brain regions concerning the rest of the regions.
Model input preprocessing
As input to the models, the weighted adjacency matrix corresponding to the Ω metric was converted to a graph. This matrix defines the edges in the graph, where the weight of each edge reflects the Ω value between the corresponding regions. The feature vectors at each graph node are derived from the O-info matrix; specifically, each node’s feature vector is the corresponding row in the Ω matrix. To this end, the connectivity matrices were first converted to tensors using the PyTorch deep learning library, enabling their efficient manipulation. Subsequently, these tensors were reshaped, organizing the connectivity data into a structure where each tensor represented the features of nodes within a graph. This transformation preserved the relational information from the original matrices, making it accessible for analysis by graph neural networks. To ensure the integrity of the data, graphs containing NaN values, either in their features or target values, were filtered out. The remaining graphs were then split into training and validation sets using a stratified split to ensure a balanced representation of age groups in both sets.
Data augmentation
We employed augmentation tailored for connectivity matrices to make the model more resilient to heterogeneity and generalizability. Linear interpolation between matrices corresponding to neighboring age values was used, in contrast to traditional image augmentation techniques such as random rotations or crops that are inappropriate for connectivity data.
Given two matrices, M1 and M2, representing fMRI or EEG connectivity at ages a1 and a2, respectively, the interpolation to produce a matrix for a target age where a1 < at < a2 was conducted using the formula:
| (3) |
Here, represents the interpolation factor.
This augmentation method enabled the generation of fMRI and EEG connectivity matrices for age values previously absent in the data set. The derived matrices, through interpolation, ensure a smooth transition in the fMRI and EEG patterns from one age value to another, thereby maintaining the inherent physiological significance of the original data—preliminary validation against a hold-out dataset showed improvements in model fit against dataset heterogeneity. We included 500 samples with data augmentation only the training datasets for both modalities, half for the non-LAC and half for the LAC samples.
The architecture of the models
Two Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs)71 were designed for this study, specifically tailored to process graph-structured data. We employed the PyTorch Geometric code library based on the PyTorch library to develop and train the models. Two models were created, one for the fMRI data and another for the EEG data. Unlike traditional convolutional networks suited for neuroimaging data, functional connectivity demands a specialized approach since neighboring data points are not necessarily close in native space (i.e., adjacent brain areas). The GCN employs adjacency matrices of graphs as inputs comprised of node features. Each node in the graph aggregates features from its neighbors through a series of operations, including multiplication by a normalized adjacency matrix, transformation using a weight matrix, and applying an activation function, here the ReLU72. The architecture employed in our work consisted of two Graph Convolutional layers. The input features (O-info matrix) were passed through the first convolutional layer, followed by a ReLU activation function and a dropout layer for regularization. The features were then passed through the second convolutional layer. Finally, average pooling was used to aggregate the output features. To train the two models, we combined Mean Squared Error (MSE) as the loss function and the Adam optimizer. Given the variability in the data and potential model configurations, we implemented a hyperparameter tuning process using a grid search over specified learning rates and epoch numbers. For each model for the controls, the data was initially split into 80% for training and validation, and 20% for hold-out testing. Within the 80% training and validation set, we applied 5-fold cross-validation to determine the optimal hyperparameters for the model. After determining the best hyperparameters through this cross-validation process, the final model’s performance was evaluated on the remaining 20% hold-out test set to assess its generalization capability73.
Statistical analyses
Following hyperparameter tuning, each model was retrained using the best hyperparameters on the training set and evaluated on the test set. For a more comprehensive assessment, the predicted age values were compared to the actual age values using Pearson’s correlation coefficient, R-squared, and Cohen’s f2 effect size for each model74. We used the method outlined below to evaluate if the model was predicting increased or decreased ages concerning the actual chronological age.
The Mean Directional Error (MDE) is a diagnostic metric used to evaluate the prediction accuracy of the models, specifically focusing on the direction of prediction gaps rather than their magnitude to detect bias. It is calculated as follows:
| (4) |
The function “sign” yields a value of +1 if the prediction is above the actual value, −1 if below, and 0 if they are equal. yi is the real age of subject i and ŷi is the predicted age. An MDE value close to zero suggests a balanced number of overestimations and underestimations. Positive or negative values indicate systematic biases in the prediction method, where a positive MDE means the model generally overpredicts, and a negative MDE indicates underprediction.
In our analysis when comparing models, we sought to examine potential regional biases in predictive accuracy and compare possible sex effects or signal acquisition noise. The statistical approach involved conducting permutation tests (5,000 subsample iterations each), a non-parametric statistical test that does not assume a specific distribution of the data, thus offering flexibility in handling non-normal distributions. Given the nature of the permutation test, our analysis constituted two-sided tests, assessing the likelihood of observing the obtained difference under the null hypothesis of no difference between the models. While the permutation test alleviates the need for normality assumptions, making it resilient to deviations from normal distribution, it inherently addresses multiple comparison concerns by evaluating the empirical distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis.
We compared the adequacy of the models employing the root mean square error (RMSE). This is a metric to quantify the discrepancies between predicted and observed values in modeling, given by the formula:
| (6) |
In this equation, yi is the observed value, ŷi is the predicted value, and N is the total number of observations. RMSE measures the average magnitude of errors between predicted and actual observations. The squaring process results in a higher weight to outliers, making it a useful measure to evaluate if a model is robust to outliers.
To evaluate feature importance, we employed bootstrapping to assess the significance of individual nodes (i.e., brain areas) and edges (i.e., connections between brain nodes/regions) within the graph neural network. With this approach, we executed a two-step process to quantify the node and its edge’s impact on the model’s predictions. Initially, the model’s output was calculated with all nodes and its edges present to establish a baseline performance metric. Subsequently, the analysis was repeated after removing each node and edge at a time, thus simulating network information absence. The difference in the model’s output, with and without each area and edge was quantified, providing a measure of the network node importance. This process was repeated across multiple bootstrap testing dataset samples (n=5000) to calculate confidence intervals. Finally, a feature importance list of nodes was generated in descending order of importance for brain age prediction. This methodological framework allowed for an analysis of network-level contributions to each model’s overall predictive performance.
Gradient boosting regression models
We used gradient boosting regression models75 to investigate the impact of factors associated with the physical and social exposomes, and disease disparities, on BAGs between LAC and non-LAC populations. As predictors, we included country-level measures of: (i) air pollution (PM2.5 exposure), (ii) socioeconomic inequality (the GINI index)76, (iii) the burden of communicable, maternal, prenatal, and nutritional conditions, and (iv) the burden of non-communicable diseases. These indicators were sourced from the updated country-specific data provided on the World Bank’s platform (https://databank.worldbank.org/). Additionally, individual neurocognitive status (being controls versus having Alzheimer’s disease, MCI, or bvFTD) was included as predictor. BAGs from fMRI and EEG datasets were the outcomes.
Models were trained using 90% of the dataset and subsequently tested on an independent 10% subset, employing a 10-fold cross-validation framework. The cross-validation was repeated 10 times. Within each iteration, estimation coefficients for the predictors, as well as the R-squared, Cohen’s f277, and RMSE, were computed. We assessed feature importance using a multi-method approach incorporating permutation importance, features importance based on the mean decrease in impurity (MDI), and SHAP values78. We provided the mean importance values for each method, along with their 99% confidence interval, as well as the average R-squared and Cohen’s f277. Features whose lower confidence interval boundary crosses zero are considered non-significant. In order to optimize Ridge’s hyperparameters, Bayesian optimization was employed. Following the same multi-method approach, we conducted gradient boosting regressions to explore the effect of gender inequality and sex on BAGs. As predictors, we included: (i) the country level gender inequality index (GII), a composite metric measuring reproductive health, empowerment and the labor market, (ii) sex, (iii) region (LAC vs non-LAC) and (iv) individual neurocognitive status (HC versus Alzheimer’s disease, MCI, or bvFTD). BAGs from fMRI and EEG were the outcomes
Data quality assessment
For the fMRI overall data quality (ODQ) metric, each timeseries was segmented in 20 repetition time (TR) length to evaluate the temporal signal-to-noise ratio (tSNR)79, which is calculated as the mean fMRI signal divided by its standard deviation within each segment. Segments with tSNR above a threshold of 50 were classified as high quality79. As additional evaluations to consider overall acquisition quality, we checked the variability of the tSNR segments of all the time series in the brain to check for spatial consistency. Lastly, we checked for remaining outliers as signal spikes from movement or transient gradient artifacts. Thus, the fMRI ODQ was computed as a percentage of good segments considering its tSNR, low spatial variability, and the number of segments not having spikes from movement or transient gradient remaining artifacts.
For the EEG data quality assessment, we followed the method proposed by Zhao et al80. The EEG signals were divided into 1-second segments, and the quality of each segment was evaluated using four specific metrics. These metrics included the detection of weak or constant signals based on standard deviation, the identification of artifacts through signal amplitude ratios, the presence of high-frequency noise, and low correlation between channels. The EEG ODQ was then calculated as the percentage of segments exhibiting good quality. A value of 0 indicated that all segments were of poor quality, while a value of 100 indicated that all segments were of high quality.
Sensitivity analyses
We examined whether variations in fMRI or EEG data quality explained the differences in brain age between the non-LAC and LAC, comparing different groups’ fMRI79 and EEG80 data quality metrics, with subsample permutation tests with 5000 iterations for each comparison. In addition, we conducted a linear regression to examine the association between the fMRI data quality metrics and the BAGs. To further control for scanner effects, we implemented an additional harmonization strategy in the fMRI training dataset. This method involves normalizing the BAG variable within each scanner type by scaling the data to a fixed range using the min-max scaler14. This ensures that the minimum and maximum values of the BAG variable are consistent across different scanners, thereby reducing variability due to scanner differences. Additionally, we accounted for the sign of the BAG after normalization to maintain the interpretability of positive and negative values. This procedure adjusts for location and scale differences (e.g., mean and variance) across sites, minimizing scanner-related variability.
We used permutation tests (5000 subsample iterations each) to compare the BAGs between subsamples of participants undergoing fMRI with open versus closed eyes. We included 124 controls with closed eyes and 86 with open eyes, 269 Alzheimer’s disease with closed eyes and 164 with open eyes, and 88 bvFTD with closed eyes and 69 with open eyes. Notably, all MCI participants underwent fMRI with open eyes. Our findings revealed no significant differences in BAGs when analyzing data from open versus closed eyes conditions across all group comparisons (permutation test = 5000 iterations).
Ethics and inclusion statement
This work involved a collaboration between researchers in multiple countries. Contributors from different sites are included as coauthors according to their contributions. Researchers residing in LMIC were involved in study design, study implementation, methodological procedure, writing and reviewing processes. The current research is locally relevant due to the larger disparities observed in LAC. Roles and responsibilities were agreed among collaborators ahead of the research. Ethics committees approved all research involving participants. To prevent any stigmatization, all identifying information has been removed to preserve the privacy of individuals. We endorse the Nature Portfolio journals’ guidance on LMIC authorship and inclusion. Authorship was based on the intellectual contribution, commitment, and involvement of each researcher in this study. We included authors born in LMICs and other underrepresented countries.
Extended Data
Extended Data Fig. 1. Associations of sex and gender inequality with BAGs.
Multi-method approach comprising SHAP values, features and permutation importance. Plot shows the mean importance values for each method, along with their 99% confidence interval, as well as the average R-squared and Cohen’s F2. Having a neurocognitive disorder, being female, and living in countries with larger gender inequality (particularly from LAC), were associated with higher BAGs. LAC = Latin American countries.
Extended Data Fig. 2. Prediction gaps between fMRI datasets with either eyes open or eyes closed protocols.
No significant differences were observed between participants with open vs. closed eyes within the same groups (permutation test = 5000 iterations). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. LAC = Latin American countries, OE = open eyes, CE = closed eyes.
Extended Data Fig. 3. BAGs between subsamples of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) groups matched by chronological age.
Results were similar to those reported for the total MCI and Alzheimer’s disease datasets in Figs. 4a and b (permutation test = 5000 iterations).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Latin American Brain Health Institute (BrainLat) # BL-SRGP2020-02 awarded to MAP and AI. AI is supported by grants from ReDLat [National Institutes of Health and the Fogarty International Center (FIC), National Institutes of Aging (R01 AG057234, R01 AG075775, AG021051, R01 AG083799, CARDS-NIH 75N95022C00031), Alzheimer’s Association (SG-20-725707), Rainwater Charitable Foundation, The Bluefield project to cure FTD, and Global Brain Health Institute)], ANID/FONDECYT Regular (1210195, 1210176 and 1220995); and ANID/FONDAP/15150012. AMG is partially supported by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (R01AG075775, R01AG083799, 2P01AG019724); ANID (FONDECYT Regular 1210176, 1210195); and DICYT-USACH (032351G_DAS). The contents of this publication are solely the author’s responsibility and do not represent the official views of these institutions.
Footnotes
Additional Declarations: There is NO Competing Interest.
Code availability
The code used to preprocess and analyze the data of this work is available in an Open Science Foundation repository at the following address: https://osf.io/8zjf4/
Competing Interest Statement
None of the authors have competing financial or non-financial interests as defined by Nature Portfolio.
Supplementary Files
This is a list of supplementary files associated with this preprint. Click to download.
Data availability
All preprocessed data are openly available at: https://osf.io/8zjf4/. The fMRI and EEG datasets comprise sources (a) currently publicly available for direct download after registration and access application, (b) available after contacting the researcher, or (c) accessible after IRB approval of formal data-sharing agreement in a process that can last up to 12 weeks. The fMRI sources that are publicly available for direct download are the following: Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (USA) (ida.loni.usc.edu/collaboration/access/appLicense.jsp), Chinese Human Connectome Project (CHCP) (China) (scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=f512d085f3d3452a9b14689e9997ca94#p2), The frontotemporal lobar degeneration neuroimaging initiative (FTLDNI) (USA) (ida.loni.usc.edu/collaboration/access/appLicense.jsp), and Japanese Strategic Research Program for the Promotion of Brain Science (SRPBS) (Japan) (bicr-resource.atr.jp/srpbsopen/). The fMRI sources available after contacting the researcher include ReDLat USA by contacting Bruce Miller at UCSF through datasharing@ucsf.edu. The fMRI sources that require IRB approval and a formal data sharing agreement include: ReDLat pros (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, Peru) by contacting Agustín Ibañez at agustin.ibanez@gbhi.org, Centro de Gerociencia Salud Mental y Metabolismo (GERO) (Chile) by contacting Andrea Slachevsky at andrea.slachevsky@uchile.cl, ReDLat pre (Argentina) by contacting Agustín Ibañez at agustin.ibanez@gbhi.org, ReDLat pre (Peru) by contacting Nilton Custodio at ncustodio@ipn.pe, ReDLat pre (Colombia) by contacting Diana Matallana at dianamat@javeriana.edu.co, ReDLat pre (Colombia -II) by contacting Felipe Cardona at felipe.cardona@correounivalle.edu.co, ReDLat pre (Mexico) by contacting Ana Luisa Sosa at drasosa@hotmail.com, ReDLat pre (Chile) by contacting María Isabel Behrens at behrensl@uchile.cl, and ReDLat pre (Chile) by contacting Andrea Slachevsky at andrea.slachevsky@uchile.cl. The EEG sources that are publicly available for direct download are Centro de Neurociencias de Cuba (CHBMP) (Cuba) (www.synapse.org/Synapse:syn22324937). The EEG sources that are available after contacting the researcher include BrainLat (Argentina) by contacting Agustina Legaz at alegaz@udesa.edu.ar, BrainLat (Chile) by contacting Agustina Legaz at alegaz@udesa.edu.ar, Izmir University of Economics (Turkey) by contacting Gorsev Gener at gorsev.yener@ieu.edu.tr, Trinity College Dublin (Ireland) by contacting Francesca Farina at francesca.farina@northwestern.edu, Universidad de Antioquia (Colombia) by contacting Francisco Lopera at floperar@gmail.com, Universidad de Sao Paulo (Brazil) by contacting Mario Parra at mario.parra-rodriguez@strath.ac.uk, Universidad de Roma La Sapienza (Italy) by contacting Susana Lopez at susanna.lopez@uniroma1.it, University of Strathclyde (UK) by contacting Mario Parra at mario.parra-rodriguez@strath.ac.uk, Istanbul Medipol University (Turkey) by contacting Tuba Aktürk at takturk@medipol.edu.tr, and Takeda (Chile) by contacting Daniela Olivares at danielaolivaresvargas@gmail.com. For additional details, see Supplementary Data S1.
References
- 1.Ibanez A., Kringelbach M. & Deco G. A synergetic turn in cognitive neuroscience of brain diseases. Trends in Cognitve Sciences (2023). 10.1016/j.tics.2023.12.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tian Y. E. et al. Heterogeneous aging across multiple organ systems and prediction of chronic disease and mortality. Nat Med (2023). 10.1038/s41591-023-02296-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hou Y. et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 15, 565–581 (2019). 10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Santamaria-Garcia H. et al. Factors associated with healthy aging in Latin American populations. Nature medicine 29, 2248–2258 (2023). 10.1038/s41591-023-02495-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Walters H. Diverse factors shape healthy aging in Latin America. Nature Aging 3, 1175–1175 (2023). 10.1038/s43587-023-00508-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tseng W. I., Hsu Y. C. & Kao T. W. Brain Age Difference at Baseline Predicts Clinical Dementia Rating Change in Approximately Two Years. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD 86, 613–627 (2022). 10.3233/JAD-215380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mukadam N., Sommerlad A., Huntley J. & Livingston G. Population attributable fractions for risk factors for dementia in low-income and middle-income countries: an analysis using cross-sectional survey data. Lancet Glob Health 7, e596–e603 (2019). 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30074-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boyle P. A. et al. The “cognitive clock”: A novel indicator of brain health. Alzheimer’s & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. 17 12 (2021). 10.1002/alz.12351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Parra M. A. et al. Dementia in Latin America: Paving the way toward a regional action plan. Alzheimers Dement 17, 295–313 (2021). 10.1002/alz.12202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ibanez A. & Zimmer E. Time to synergize mental health with brain health. Nature Mental Health (2023). 10.1038/s44220-023-00086-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ibanez A. et al. Neuroecological links of the exposome and One Health. Neuron (2024). 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.04.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ibanez A. et al. Healthy aging metanalyses and scoping review of risk factors across Latin America reveal large heterogeneity and weak predictive models. Nature Aging (2024). 10.1038/s43587-024-00648-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Migeot J. et al. Allostasis, health, and development in Latin America. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 105697 (2024). 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fittipaldi S. et al. Heterogeneous factors influence social cognition across diverse settings in brain health and age-related diseases. Nature Mental Health 2, 63–75 (2024). 10.1038/s44220-023-00164-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gasparini L. & Cruces G. The Changing Picture of Inequality in Latin America: Evidence for Three Decades. (United Nations Development Programm (UNDP), 2022). [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chan M. Y. et al. Socioeconomic status moderates age-related differences in the brain’s functional network organization and anatomy across the adult lifespan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115, E5144–e5153 (2018). 10.1073/pnas.1714021115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fuller R. et al. Pollution and health: a progress update. Lancet Planet Health 6, e535–e547 (2022). 10.1016/s2542-5196(22)00090-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ibanez A., Legaz A. & Ruiz-Adame M. Addressing the gaps between socioeconomic disparities and biological models of dementia. Brain In press (2023). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bilal U. et al. Life expectancy and mortality in 363 cities of Latin America. Nat Med 27, 463–470 (2021). 10.1038/s41591-020-01214-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mullachery P. H. et al. Mortality amenable to healthcare in Latin American cities: a cross-sectional study examining between-country variation in amenable mortality and the role of urban metrics. Int J Epidemiol 51, 303–313 (2022). 10.1093/ije/dyab137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Breton T. R. & Canavire-Bacarreza G. Low test scores in Latin America: poor schools, poor families or something else? Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education 48, 733–748 (2018). 10.1080/03057925.2017.1342530 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gonzalez-Gomez R. et al. Educational disparities in brain health and dementia across Latin America and the United States. Alzheimer’s & Dementia (2024). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee J. et al. Deep learning-based brain age prediction in normal aging and dementia. Nature aging 2, 412–424 (2022). 10.1038/s43587-022-00219-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Baez S., Alladi S. & Ibanez A. Global South research is critical for understanding brain health, ageing and dementia. Clinical and Translational Medicine 13 (2023). 10.1002/ctm2.1486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Maito M. A. et al. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia using routine clinical and cognitive measures across multicentric underrepresented samples: A cross sectional observational study. Lancet Reg Health Am 17 (2023). 10.1016/j.lana.2022.100387 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ardekani B. A., Convit A. & Bachman A. H. Analysis of the MIRIAD Data Shows Sex Differences in Hippocampal Atrophy Progression. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD 50, 847–857 (2016). 10.3233/JAD-150780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zugman A. et al. Country-level gender inequality is associated with structural differences in the brains of women and men. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120, e2218782120 (2023). 10.1073/pnas.2218782120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nithianantharajah J. & Hannan A. J. Enriched environments, experience-dependent plasticity and disorders of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 7, 697–709 (2006). 10.1038/nrn1970 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Greene A. S. et al. Brain-phenotype models fail for individuals who defy sample stereotypes. Nature 609, 109–118 (2022). 10.1038/s41586-022-05118-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Khayretdinova M. et al. Predicting age from resting-state scalp EEG signals with deep convolutional neural networks on TD-brain dataset. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 14, 1019869 (2022). 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1019869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Al Zoubi O. et al. Predicting Age From Brain EEG Signals-A Machine Learning Approach. Frontiers in aging neuroscience. 10 184 (2018). 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Herzog R. et al. Genuine high-order interactions in brain networks and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 175, 105918 (2022). 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shen D., Wu G. & Suk H. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering 19, 221–248 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fry A. et al. Comparison of Sociodemographic and Health-Related Characteristics of UK Biobank Participants With Those of the General Population. American journal of epidemiology 186, 1026–1034 (2017). 10.1093/aje/kwx246 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hernandez H. et al. Brain health in diverse settings: How age, demographics and cognition shape brain function. Neuroimage 295, 120636 (2024). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Coronel-Oliveros C. et al. Viscous dynamics associated with hypoexcitation and structural disintegration in neurodegeneration via generative whole-brain modeling. Alzheimers Dement 20, 3228–3250 (2024). 10.1002/alz.13788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Prado P. et al. Dementia ConnEEGtome: Towards multicentric harmonization of EEG connectivity in neurodegeneration. Int J Psychophysiol 172, 24–38 (2022). 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2021.12.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ducharme S. et al. Recommendations to distinguish behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia from psychiatric disorders. Brain 143, 1632–1650 (2020). 10.1093/brain/awaa018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gustavsson A. et al. Global estimates on the number of persons across the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimers Dement 19, 658–670 (2023). 10.1002/alz.12694 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Moguilner S. et al. Biophysical models applied to dementia patients reveal links between geographical origin, gender, disease duration, and loss of neural inhibition. Alzheimers Res Ther 16, 79 (2024). 10.1186/s13195-024-01449-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Babulal G. M. et al. Perspectives on ethnic and racial disparities in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias: Update and areas of immediate need. Alzheimers Dement 15, 292–312 (2019). 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.09.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nianogo R. A. et al. Risk Factors Associated With Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias by Sex and Race and Ethnicity in the US. JAMA Neurol 79, 584–591 (2022). 10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.0976 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gouveia N. et al. Short-term associations between fine particulate air pollution and cardiovascular and respiratory mortality in 337 cities in Latin America. Sci Total Environ 920, 171073 (2024). 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171073 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hierink F., Okiro E. A., Flahault A. & Ray N. The winding road to health: A systematic scoping review on the effect of geographical accessibility to health care on infectious diseases in low- and middle-income countries. PLoS One 16, e0244921 (2021). 10.1371/journal.pone.0244921 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hossin M. Z. International migration and health: it is time to go beyond conventional theoretical frameworks. BMJ Glob Health 5, e001938 (2020). 10.1136/bmjgh-2019-001938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Reitz C., Pericak-Vance M. A., Foroud T. & Mayeux R. A global view of the genetic basis of Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 19, 261–277 (2023). 10.1038/s41582-023-00789-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pardo J. V. et al. Where the brain grows old: decline in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal function with normal aging. Neuroimage 35, 1231–1237 (2007). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.12.044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tomasi D. & Volkow N. D. Aging and functional brain networks. Mol Psychiatry 17, 471, 549–458 (2012). 10.1038/mp.2011.81 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rempe M. P. et al. Spontaneous cortical dynamics from the first years to the golden years. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120, e2212776120 (2023). 10.1073/pnas.2212776120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hayflick L. Biological aging is no longer an unsolved problem. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mielke M. M. et al. Consideration of sex and gender in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders from a global perspective. Alzheimers Dement 18, 2707–2724 (2022). 10.1002/alz.12662 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mosconi L. et al. Sex differences in Alzheimer risk: Brain imaging of endocrine vs chronologic aging. Neurology 89, 1382–1390 (2017). 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Storsve A. B. et al. Differential longitudinal changes in cortical thickness, surface area and volume across the adult life span: regions of accelerating and decelerating change. J Neurosci 34, 8488–8498 (2014). 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0391-14.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Snyder H. M. et al. Sex biology contributions to vulnerability to Alzheimer’s disease: A think tank convened by the Women’s Alzheimer’s Research Initiative. Alzheimer’s & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association 12 (2016). 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.08.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Forsyth K. S., Jiwrajka N., Lovell C. D., Toothacre N. E. & Anguera M. C. The conneXion between sex and immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol (2024). 10.1038/s41577-024-00996-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Congdon E. E. Sex Differences in Autophagy Contribute to Female Vulnerability in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Neurosci 12, 372 (2018). 10.3389/fnins.2018.00372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wood E. M. et al. Development and validation of pedigree classification criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. JAMA Neurol 70, 1411–1417 (2013). 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.3956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Medina-Hernández E., Fernández-Gómez M. J. & Barrera-Mellado I. Gender Inequality in Latin America: A Multidimensional Analysis Based on ECLAC Indicators. Sustainability 13 (2021). 10.3390/su132313140 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Aranda M. P. et al. Impact of dementia: Health disparities, population trends, care interventions, and economic costs. J Am Geriatr Soc 69, 1774–1783 (2021). 10.1111/jgs.17345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Caldwell J. Z. K. & Isenberg N. The aging brain: risk factors and interventions for long term brain health in women. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 35, 169–175 (2023). 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.McKhann G. M. et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s and Dementia 7, 263–269 (2011). 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rascovsky K. et al. Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134, 2456–2477 (2011). 10.1093/brain/awr179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Prado P. et al. The BrainLat project, a multimodal neuroimaging dataset of neurodegeneration from underrepresented backgrounds. Scientific Data 10, 889 (2023). 10.1038/s41597-023-02806-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nieto-Castanon A. Handbook of functional connectivity Magnetic Resonance Imaging methods in CONN. 108 (2020). [Google Scholar]
- 65.Prado P. et al. Harmonized multi-metric and multi-centric assessment of EEG source space connectivity for dementia characterization. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 15, e12455 (2023). 10.1002/dad2.12455 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pion-Tonachini L., Kreutz-Delgado K. & Makeig S. ICLabel: An automated electroencephalographic independent component classifier, dataset, and website. Neuroimage 198, 181–197 (2019). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bigdely-Shamlo N., Kreutz-Delgado K., Kothe C. & Makeig S. EyeCatch: data-mining over half a million EEG independent components to construct a fully-automated eye-component detector. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2013, 5845–5848 (2013). 10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cruzat J. et al. Temporal Irreversibility of Large-Scale Brain Dynamics in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Neurosci 43, 1643–1656 (2023). 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1312-22.2022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Prado P. et al. Source space connectomics of neurodegeneration: One-metric approach does not fit all. Neurobiol Dis 179, 106047 (2023). 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ince R. A. et al. A statistical framework for neuroimaging data analysis based on mutual information estimated via a gaussian copula. Hum Brain Mapp 38, 1541–1573 (2017). 10.1002/hbm.23471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Li Y. et al. Brain Connectivity Based Graph Convolutional Networks and Its Application to Infant Age Prediction. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 41, 2764–2776 (2022). 10.1109/TMI.2022.3171778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhou Y., Huo H., Hou Z. & Bu F. A deep graph convolutional neural network architecture for graph classification. 18, PloS one (2023). 10.1371/journal.pone.0279604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kohavi R. A Study of Cross-Validation and Bootstrap for Accuracy Estimation and Model Selection. 14 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- 74.Selya A. S., Rose J. S., Dierker L. C., Hedeker D. & Mermelstein R. J. A Practical Guide to Calculating Cohen’s f(2), a Measure of Local Effect Size, from PROC MIXED. Frontiers in psychology 3 (2012). 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Friedman J. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. The Annals of Statistics 29 (2000). 10.1214/aos/1013203451 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Gini C. Variabilità e mutabilità: contributo allo studio delle distribuzioni e delle relazioni statistiche. [Fasc. I.]. (Tipogr. di P. Cuppini, 1912). [Google Scholar]
- 77.Selya A. S., Rose J. S., Dierker L. C., Hedeker D. & Mermelstein R. J. A Practical Guide to Calculating Cohen’s f(2), a Measure of Local Effect Size, from PROC MIXED. Front Psychol 3, 111 (2012). 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chen H., Lundberg S. M. & Lee S.-I. Explaining a series of models by propagating Shapley values. Nature Communications 13, 4512 (2022). 10.1038/s41467-022-31384-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Murphy K., Bodurka J. & Bandettini P. A. How long to scan? The relationship between fMRI temporal signal to noise ratio and necessary scan duration. Neuroimage 34, 565–574 (2007). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Zhao L. et al. Quantitative signal quality assessment for large-scale continuous scalp electroencephalography from a big data perspective. Physiol Meas 44 (2023). 10.1088/1361-6579/ac890d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All preprocessed data are openly available at: https://osf.io/8zjf4/. The fMRI and EEG datasets comprise sources (a) currently publicly available for direct download after registration and access application, (b) available after contacting the researcher, or (c) accessible after IRB approval of formal data-sharing agreement in a process that can last up to 12 weeks. The fMRI sources that are publicly available for direct download are the following: Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (USA) (ida.loni.usc.edu/collaboration/access/appLicense.jsp), Chinese Human Connectome Project (CHCP) (China) (scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=f512d085f3d3452a9b14689e9997ca94#p2), The frontotemporal lobar degeneration neuroimaging initiative (FTLDNI) (USA) (ida.loni.usc.edu/collaboration/access/appLicense.jsp), and Japanese Strategic Research Program for the Promotion of Brain Science (SRPBS) (Japan) (bicr-resource.atr.jp/srpbsopen/). The fMRI sources available after contacting the researcher include ReDLat USA by contacting Bruce Miller at UCSF through datasharing@ucsf.edu. The fMRI sources that require IRB approval and a formal data sharing agreement include: ReDLat pros (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, Peru) by contacting Agustín Ibañez at agustin.ibanez@gbhi.org, Centro de Gerociencia Salud Mental y Metabolismo (GERO) (Chile) by contacting Andrea Slachevsky at andrea.slachevsky@uchile.cl, ReDLat pre (Argentina) by contacting Agustín Ibañez at agustin.ibanez@gbhi.org, ReDLat pre (Peru) by contacting Nilton Custodio at ncustodio@ipn.pe, ReDLat pre (Colombia) by contacting Diana Matallana at dianamat@javeriana.edu.co, ReDLat pre (Colombia -II) by contacting Felipe Cardona at felipe.cardona@correounivalle.edu.co, ReDLat pre (Mexico) by contacting Ana Luisa Sosa at drasosa@hotmail.com, ReDLat pre (Chile) by contacting María Isabel Behrens at behrensl@uchile.cl, and ReDLat pre (Chile) by contacting Andrea Slachevsky at andrea.slachevsky@uchile.cl. The EEG sources that are publicly available for direct download are Centro de Neurociencias de Cuba (CHBMP) (Cuba) (www.synapse.org/Synapse:syn22324937). The EEG sources that are available after contacting the researcher include BrainLat (Argentina) by contacting Agustina Legaz at alegaz@udesa.edu.ar, BrainLat (Chile) by contacting Agustina Legaz at alegaz@udesa.edu.ar, Izmir University of Economics (Turkey) by contacting Gorsev Gener at gorsev.yener@ieu.edu.tr, Trinity College Dublin (Ireland) by contacting Francesca Farina at francesca.farina@northwestern.edu, Universidad de Antioquia (Colombia) by contacting Francisco Lopera at floperar@gmail.com, Universidad de Sao Paulo (Brazil) by contacting Mario Parra at mario.parra-rodriguez@strath.ac.uk, Universidad de Roma La Sapienza (Italy) by contacting Susana Lopez at susanna.lopez@uniroma1.it, University of Strathclyde (UK) by contacting Mario Parra at mario.parra-rodriguez@strath.ac.uk, Istanbul Medipol University (Turkey) by contacting Tuba Aktürk at takturk@medipol.edu.tr, and Takeda (Chile) by contacting Daniela Olivares at danielaolivaresvargas@gmail.com. For additional details, see Supplementary Data S1.


