Abstract
Peripheral T‐cell lymphoma (PTCL) is a highly aggressive type of non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma with a poor prognosis. Pyroptosis is a newly discovered procedural cell death mode, which has been implicated to occur in both tumor cells and immune cells. However, the occurrence and effect of pyroptosis on PTCL remain unclear. Here, we found that pyroptosis occurred in interstitial macrophages of PTCL rather than in tumor cells. In clinical specimens, macrophage pyroptosis was associated with a poor prognosis of PTCL. In vitro experiments and gene sequencing results showed that pyroptotic macrophages could upregulate the expression of TLR4 through secreting inflammatory cytokines IL‐18. Upregulated TLR4 activated its downstream NF‐κB anti‐apoptotic signaling pathway, thus leading to malignant proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of tumor cells. Moreover, the expression of factors such as XIAP in the NF‐κB anti‐apoptotic pathway was downregulated after the knockdown of TLR4, and the malignant promotion effect of pyroptotic macrophages on PTCL cells was also reversed. Our findings revealed the mechanism of pyroptotic macrophages promoting the malignant biological behavior of PTCL and elucidated the key role of TLR4 in this process. In‐depth analysis of this mechanism will contribute to understanding the regulatory effect of PTCL by the tumor microenvironment and providing new ideas for the clinical treatment of PTCL.
Keywords: chemotherapy resistance, macrophage, peripheral T‐cell lymphoma, pyroptosis, Toll‐like receptor 4
This study is the first to find that pyroptosis occurs in interstitial macrophages of PTCL. We clarified the mechanism of pyroptotic macrophages promoting the malignant biological behavior of PTCL and elucidated the key role of TLR4 in this process. The results may contribute to understanding the regulatory effect of PTCL by tumor microenvironment, and providing a potential therapeutic target for the disease.
Abbreviations
- BPs
biological processes
- CCRPM
cell contents released from pyroptotic macrophages
- DDP
cisplatin
- DOX
doxorubicin
- GEM
gemcitabine
- IF
immunofluorescence
- IHC
immunohistochemistry
- IKK
inhibitory kappa B kinase
- IRAK
IL‐1‐related protein kinase
- OS
overall survival
- PFS
progression‐free survival
- PTCL
peripheral T‐cell lymphoma
- TLR4
Toll‐like receptor 4
- TNF
tumor necrosis factor
- WB
western blot
- XBP1
X‐box‐binding protein 1
- XIAP
X‐linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
1. INTRODUCTION
Peripheral T‐cell lymphoma is a heterogeneous disease originating from post‐thymic mature T lymphocytes. 1 Chemotherapy regimens based on cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) are the preferred treatment for PTCL, but the efficacy is limited. 2 In recent years, numerous novel molecule‐targeted drugs have been emerging with therapeutic potential and tolerability, including dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, histone deacetylase inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, antibody–drug conjugates, etc. Although the emergence of new drugs has improved the prognosis of patients with PTCL, the 5 years OS rate is still less than 40%. 3 Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore the specific mechanism of PTCL development and discover new therapeutic targets.
Pyroptosis is a recently identified form of programmed cell death that is different from apoptosis. 4 It is characterized by cell swelling and eventual rupture of the cell membrane, resulting in the release of cell contents and triggering a robust inflammatory response. 5 For cancers, pyroptosis can function on either promoting or inhibiting tumor growth. On the one hand, pyroptosis has been proven to directly inhibit tumor growth in solid tumors such as skin, colorectal, and liver carcinomas 6 , 7 . On the other hand, the release of inflammasomes after pyroptosis can create an inflammatory microenvironment that is conducive to the growth of tumor cells. In addition to tumor cells, immune cells in the tumor microenvironment can also undergo pyroptosis, thereby affecting the biological behavior of tumor cells 8 , 9 . However, whether pyroptosis occurs in PTCL tissue remains unclear and, if pyroptosis exists, its impact on the development of PTCL requires further research.
TLR4 is a protein that plays a key role in the innate immune system. 10 It has also been implicated in the development of various types of cancer. 11 Current studies have found that TLR4 on the surface of tumor cells can be activated by dozens of endogenous molecules such as angiotensin II, ceramide, IL‐18, SDF‐1α, etc. 12 Activated TLR4 is able to regulate TLR4/MyD88/NF‐κB signaling, promote the transcription of NF‐κB, and activate its downstream pathway, to affect the proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells. 13 In previous studies, we found that the expression of TLR4 was increased in PTCL. Upregulated TLR4 was closely related to a poor prognosis for PTCL patients. 14 Therefore, the reasons for the upregulation of TLR4 expression and the unique mechanism by which TLR4 promotes PTCL progression need to be explored.
Here, by analyzing the clinical specimens and prognostic information of PTCL patients, we found that pyroptosis occurred in interstitial macrophages and promoted the poor prognosis of PTCL. The co‐culture model of pyroptotic macrophages and tumor cells showed that pyroptotic macrophages upregulated the expression of TLR4 in PTCL cells through IL‐18 and activated its downstream anti‐apoptotic pathway, thereby promoting tumor proliferation and chemoresistance. In addition, the knockdown of TLR4 reversed the regulating effect of pyroptotic macrophages on PTCL cells. These results illustrated the role of pyroptotic macrophages in the poor prognosis of PTCL, explained the mechanism behind the malignant performance of PTCL, and provided a potential therapeutic target for the disease.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Patient samples
The PTCL tissues in this study were obtained from a total of 70 patients diagnosed with PTCL at the Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital during January 2006 and October 2015. Each enrolled patient had complete clinicopathological and follow‐up data. This experiment was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, and all patients provided informed consent for pathological examination and signed informed consent.
2.2. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence
IHC was performed on each of the specimens obtained from the 70 patients with PTCL. Paraffin‐embedded sections were washed and hydrated in xylene and different concentrations of alcohol. The slides were blocked and washed in PBS three times after antigen retrieval in 0.01 M citrate buffer (pH 6.0). The sections were then incubated with primary antibodies against NLRP3 (dilution 1:500, Abcam), Activated caspase‐1 (dilution 1:200, Abcam) and GSDMD (dilution 1:500, Abcam) at 4°C overnight. After washing with PBS three times, horseradish peroxidase‐conjugated secondary antibody was applied to reveal brown‐stained areas, and nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin.
For IF, frozen sections of PTCL tissues were fixed with paraformaldehyde, washed in PBS and blocked with normal goat serum at room temperature for 20 min. The sections were then incubated with primary antibodies against Activated caspase‐1 (dilution 1:200, Abcam) or CD11b (dilution 1:200, Abcam) at 4°C overnight and washed in PBS three times. Sections were incubated with Alexa Fluor® 488 Goat Anti‐Rabbit IgG diluted 1:200 at 37°C for 40 min, nuclei were stained with DAPI and images were acquired using a fluorescence microscope. The number of pyroptotic macrophages was counted by taking three high‐magnification fields of view for each sample, and the intermediate value of all samples was taken as the cutoff value to distinguish whether pyroptosis occurred. The cutoff value was 6.
2.3. Cell culture, treatment and transfection
Reagents for cell culture included 1640 medium and FBS, which were purchased from Gibco. PMA and nigericin were purchased from MedChemExpress, and LPS was purchased from SIGMA. Cell lines of monocytes including THP‐1 and U937, cell lines of T‐cell lymphomas including KARPAS‐299 and HUT78, and cell lines of T‐cell lymphocytic leukemia including Jurkat and MOLT‐4 were obtained from the ATCC. These cells were cultured in the same RPMI‐1640 medium containing 10% FBS to compare their response to supplementary agents. The cell lines were kept at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidification atmosphere. THP‐1 and U937 cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL PMA for at least 48 h to obtain mature macrophages. Matured macrophages were induced for pyroptosis by treatment with 1 μg/mL LPS for 4 h, and with 10 μM nigericin for 1 h. The cells were washed with PBS and cultured in fresh medium for the next 48 h to allow the pyroptosis. The CCRPM were collected to stimulate PTCL cell lines. Some PTCL cells were treated with DOX, GEM, or DDP at the IC50 level to investigate sensitivity to these drugs. Lipofectamine™ 3000 (Invitrogen, Shanghai, China) was used for transfection with the knockdown and expression vectors (Genepharma, Suzhou, China) of TLR4 and USP18 in PTCL cells.
2.4. RT‐PCR
Total RNA was extracted by TRIpure (BioTeke, Inc.). cDNA was obtained using Super M‐MLV reverse transcriptase (BioTeke, Inc.). The expression of RNA was detected by RT‐PCR using an Exicycler™ 96 fluorescence quantifier (BioNeer, Inc.). All of the reactions were run in quadruplicate. The data analysis employed the 2−ΔΔCt method.
2.5. Western blot
Cell lysates with total proteins of more than 20 μg were loaded onto SDS‐PAGE gels for electrophoresis and subsequently transferred onto a PVDF membrane. The membrane was blocked with 5% nonfat dried milk for 2 h at 37°C, followed by overnight incubation at 4°C with primary antibodies. Secondary antibodies at room temperature were then added to the membranes for the next incubation at 37°C for 2 h. The blots on the membranes were observed using an avidin/biotin/peroxidase complex (Vectastain ABC Elite kit; Vector Laboratories lnc.).
2.6. Proteome Profiler solid‐phase antibody chip and high‐throughput sequencing assays
CCRPM was centrifuged at 14,000 g for 5 min and the supernatant was transferred to a clean test tube. The supernatant was then mixed with several buffers provided by the Proteome Profiler™ Array Human XL Cytokine Array Kit (Youning Weisheng Technology Co., Ltd). A mixture containing more than 102 antibodies in the kit was added to the supernatant. Finally, the supernatant was added to Human XL Cytokine Array nitrocellulose membranes to analyze the proteins in the supernatant. KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells were homogenized for following RNA extraction using TRIzol® reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific). NanoDrop™ 2000 Spectrophotometers (Thermo Fisher Scientific) were utilized to test RNA quality. OD260/280 should range from 1.8–2.0 before use in subsequent studies. The RNA samples were sent to Aksomics Co., Ltd for high‐throughput sequencing.
2.7. Assessments of cell viability
Cell viability was evaluated using a CCK8 kit (Sigma, St. Louis) according to the manufacturer's instructions. For the measurement of cell viability, 10 μL CCK‐8 solution was added to each of 96 wells and these were incubated for 1 h in the cell incubator before OD values were determined by a microplate reader at 50 nm.
2.8. Analysis of cell apoptosis by flow cytometry
Annexin V‐FITC Staining kit (Beyotime) was used to determine cell apoptosis in cells subjected to different treatments. Briefly, cells subjected to different treatments were collected and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min. Cells were then washed with PBS, incubated with 5 μL of annexin V and 5 μL of propidium iodide for 5 min at room temperature in the dark, and analyzed using a dual laser flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson) for detection of apoptotic cells. Data were analyzed using ModFit LT software (Verity Software House).
2.9. Statistical analysis
Quantification results were statistically analyzed using two‐tailed Student's t‐tests and are shown as means ±SEM. Values of p < 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 were considered significant as *, ** and *** (or #, ##, ### in the control group), respectively.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Pyroptosis occurs in interstitial macrophages and promotes poor prognosis of PTCL
To explore whether pyroptosis existed in PTCL tissues, we obtained 70 tumor tissues from PTCL patients. IHC staining was used to detect the expression of major signaling molecules of pyroptosis including NLRP3, Activated caspase‐1, GSDMD, IL‐18, and IL‐1β in PTCL tissues (Figure 1A), which showed that pyroptosis occurred in 42 tissues. These pyroptosis‐related molecules were expressed in stromal cells that resembled macrophages under microscopic observation, rather than in tumor cells. We then conducted IF; the results showed that the fluorescence of pyroptotic indicators NLRP3, Activated caspase‐1, and GSDMD were largely co‐localized with CD11b (a surface marker of macrophages), suggesting that pyroptosis primarily existed in macrophages of the PTCL (Figure 1B).
FIGURE 1.
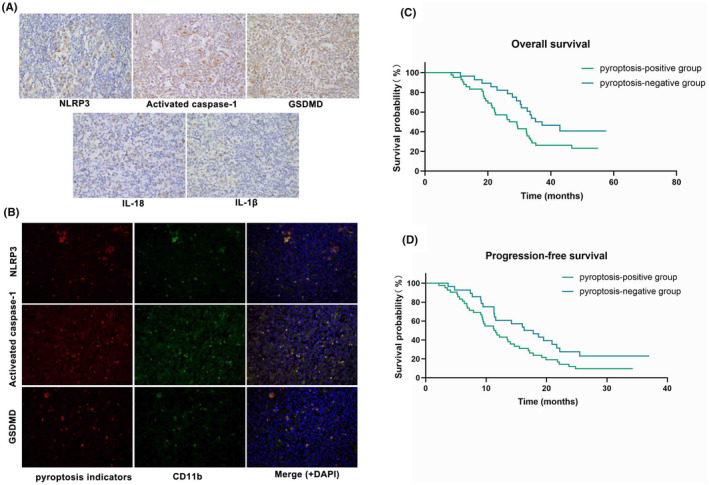
Correlation analysis of pyroptotic macrophages and prognosis of PTCLs. (A) Representative images of immunohistochemistry of NLRP3, Activated caspase‐1, GSDMD, IL‐18 and IL‐1β in PTCL sections. (B) Representative images of immunofluorescence of NLRP3, Activated caspase‐1, GSDMD, CD11b and DAPI in PTCL sections. (C) Kaplan–Meier overall survival (OS) curves of PTCLs patients with pyroptosis‐positive group (n = 42) and pyroptosis‐negative group (n = 28). (D) Kaplan–Meier progression‐free survival (PFS) curves of PTCLs patients with pyroptosis‐positive group (n = 42) and pyroptosis‐negative group (n = 28).
To investigate the effect of pyroptotic macrophages on the prognosis of PTCL, we collected prognostic information from 70 patients with PTCL, all of whom received CHOP first‐line chemotherapy. Compared with the pyroptosis‐positive group, patients' OS and PFS were found to be prominently longer in the pyroptosis‐negative group (Figure 1C,D; Table 1), which illustrated that pyroptotic macrophages might be related to the poor prognosis of PTCL.
TABLE 1.
OS and PFS of 70 PTCL patients with different pyroptosis status receiving first‐line chemotherapy.
| Pyroptosis‐positive group (n, %) | Pyroptosis‐negative group(n, %) | p‐value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OS(month) | 28.0 (42, 60%) | 36.2 (28, 40%) | 0.0459* |
| PFS(month) | 11.5 (42, 60%) | 17.1 (28, 40%) | 0.0477* |
Abbreviations: OS, overall survival; PFS, progression‐free survival.
3.2. Pyroptotic macrophages upregulate the expression of TLR4 in PTCL cells
To explore the influence of pyroptotic macrophages on PTCL cells, the monocyte cell lines THP‐1 and U937 were stimulated with PMA to induce differentiation into mature macrophages. The macrophages were further treated with LPS and nigericin to induce pyroptosis. WB results confirmed the successful establishment of pyroptotic macrophages (Figure 2A). The cell culture medium was used as CCRPM.
FIGURE 2.
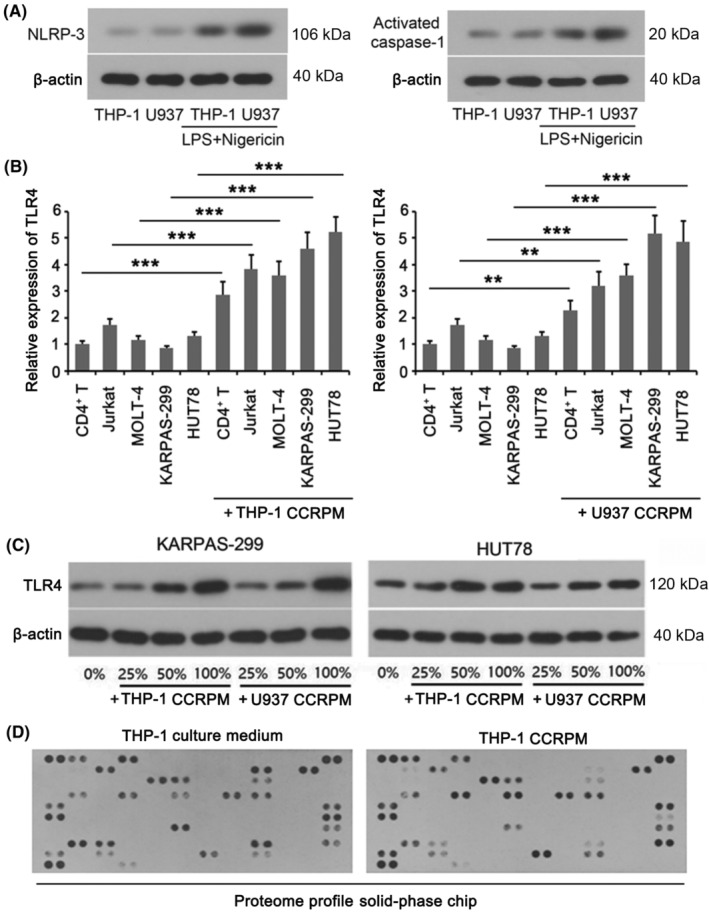
Cell contents released by pyroptotic macrophages (CCRPM) enhanced expression of TLR4 in PTCL cells. (A) Western blot (WB) of NLRP3 and Activated caspase‐1 in THP‐1 and U937 cells subjected to LPS plus nigericin stimulation or not. (B) Relative mRNA levels of TLR4 in KARPAS‐299, HUT78, Jurkat and MOLT‐4 cell lines subjected to pyroptotic supernatant treatment or not. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 (n = 3). (C) WB of TLR4 in THP‐1 and U937 cells incubated with various amount of pyroptotic supernatant. (D) Relative quantitation of cytokines in the culture medium of normal or pyroptotic macrophages through a Proteome Profiler chip assay.
Then we performed Proteome Profiler solid‐phase chip analysis to evaluate the variation in general cytokines in the culture medium of macrophages before and after pyroptosis, demonstrating that the expression levels of IL‐18, SDF‐1α and TGF‐α were markedly increased upon pyroptosis (fold change >3, p < 0.001; Table 2). Among them, IL‐18 has previously been confirmed to elevate the expression of Toll‐like receptors (TLRs; especially TLR4). We then analyzed the correlation between the expression of NLRP3, Activated caspase‐1, and GSDMD in the PTCL tissues and the expression of TLR4, TLR5, and TLR9, respectively. Our data showed that the levels of NLRP3, Activated caspase‐1, and GSDMD had a significant positive correlation with TLR4 expression (Table 3). This result revealed that pyroptotic macrophages might promote the expression of TLR4 in PTCL cells.
TABLE 2.
Variation of cytokines in supernatant of pyroptotic macrophages via analysis of Proteome Profiler solid‐phase chip.
| Analyte/Control | A Coordinate | IOD value in group A | IOD value in group B |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Reference Spots‐ Positive control |
A1 | 1226.4 | 1126.5 |
| A2 | 1349.9 | 1228.2 | |
| Adiponectin | A3 | 393.9 | 660 |
| A4 | 398.37 | 613.32 | |
| Angiogenin | A7 | 704.66 | 416.33 |
| A8 | 687.96 | 421.83 | |
| Reference Spots | A23 | 1282.1 | 1286.4 |
| A24 | 1275.9 | 1247 | |
| CD40 ligand | B3 | 12.04 | 53.62 |
| B4 | 9.35 | 39.1 | |
| Chitinase 3‐like 1 | B5 | 400.61 | 389.62 |
| B6 | 325.49 | 217.39 | |
| DPPIV | B17 | 544.15 | 44.14 |
| B18 | 502.97 | 42.52 | |
| EMMPRIN | B21 | 877.66 | 674.96 |
| B22 | 900.44 | 548.74 | |
| FGF basic | C9 | 513.9 | 989.4 |
| C10 | 626.49 | 933.01 | |
| FGF‐7 | C11 | 522.41 | 434.25 |
| C12 | 405.04 | 596.22 | |
| G‐CSF | C17 | 163.91 | 97.95 |
| C18 | 179.68 | 105.57 | |
| Growth hormone | D3 | 165.86 | 160.93 |
| D4 | 149.25 | 370.17 | |
| ICAM‐1 | D7 | 413.49 | 890.86 |
| D8 | 383.36 | 937.36 | |
| IGFBP‐2 | D11 | 142.35 | 1066.6 |
| D12 | 173.27 | 1073.9 | |
| IL‐1α | D15 | 400.95 | 736.18 |
| D16 | 467.8 | 734.44 | |
| IL‐1β | D17 | 346.22 | 530.8 |
| D18 | 293.45 | 451.63 | |
| IL‐4 | E1 | 211.85 | 477.08 |
| E2 | 322.74 | 560.8 | |
| IL‐18 | E23 | 346.72 | 768.59 |
| E24 | 355.39 | 759.26 | |
| IL‐19 | F1 | 774.22 | 733.49 |
| F2 | 738.21 | 819.82 | |
| Kallikrein 3 | F23 | 695.87 | 78.75 |
| F24 | 708.96 | 61.18 | |
| M‐CSF | G11 | 463.98 | 216.95 |
| G12 | 473.59 | 104.05 | |
| MMP‐9 | G23 | 274.97 | 395.82 |
| G24 | 251.52 | 357.28 | |
| Osteopontin | H3 | 832.75 | 346.91 |
| H4 | 782.83 | 471.17 | |
| PDGF‐AA | H5 | 475.82 | 107.75 |
| H6 | 495.96 | 125.75 | |
| RBP‐4 | H17 | 695.31 | 76.38 |
| H18 | 741.23 | 104 | |
| SDF‐1α | H23 | 372.84 | 893.57 |
| H24 | 286.19 | 915.43 | |
| Serpin E1 | I1 | 171.08 | 590.72 |
| I2 | 236.55 | 717.71 | |
| ST2 | I5 | 82.78 | 230.31 |
| I6 | 102.84 | 153.92 | |
| TGF‐α | I13 | 387.52 | 1140.8 |
| I14 | 296.45 | 1181.4 | |
| TNF‐α | I17 | 105.36 | 197.02 |
| I18 | 95.86 | 257.82 | |
|
Reference spots ‐Positive control |
J1 | 1212.6 | 1301.3 |
| J2 | 1215 | 1345.5 | |
| CD31 | J7 | 97.98 | 63.11 |
| J8 | 84.26 | 55.13 |
Note: Group A, analysis of non‐pyroptotic macrophages; group B, analysis of pyroptotic macrophages. Each protein was tested in two replicates.
TABLE 3.
Relationship between expression of NLRP‐3, Activated caspase‐1, or GSDMD and high/low expression of TLR4/5/9.
| Gene | Number of Cases | Low‐level TLR4 | High‐level TLR4 | p‐value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLRP‐3 | Low expression | 79 | 58 | 21 | <0.0001 |
| High expression | 65 | 26 | 39 | ||
| Activated caspase‐1 | Low expression | 68 | 52 | 16 | <0.0001 |
| High expression | 76 | 32 | 44 | ||
| GSDMD | Low expression | 80 | 55 | 25 | 0.004 |
| High expression | 64 | 29 | 35 | ||
| Low‐level TLR5 | High‐level TLR5 | ||||
| NLRP‐3 | Low expression | 79 | 41 | 38 | 0.2153 |
| High expression | 65 | 27 | 38 | ||
| Activated caspase‐1 | Low expression | 68 | 35 | 33 | 0.3341 |
| High expression | 76 | 33 | 43 | ||
| GSDMD | Low expression | 80 | 37 | 43 | 0.7939 |
| High expression | 64 | 31 | 33 | ||
| Low‐level TLR9 | High‐level TLR9 | ||||
| NLRP‐3 | Low expression | 79 | 43 | 36 | 0.5342 |
| High expression | 65 | 32 | 33 | ||
| Activated caspase‐1 | Low expression | 68 | 36 | 32 | 0.8455 |
| High expression | 76 | 39 | 37 | ||
| GSDMD | Low expression | 80 | 47 | 33 | 0.0734 |
| High expression | 64 | 28 | 36 |
Note: The significance for bold values is to indicate a p value of less than 0.05.
Then we cultured normal T cells, T‐cell lymphocytic leukemia cells (Jurkat and MOLT‐4), and T‐cell lymphoma cells (KARPAS‐299 and HUT78) with CCRPM and detected TLR4 expression levels of each cell line by RT‐PCR. Although there was little difference in baseline levels of various cells, TLR4 expression in all the cells was increased when cultured with CCRPM (Figure 2B). Among these cells, TLR4 expression in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 achieved the largest increase. Then we added different proportions of CCRPM (0%, 25%, 50%, 100%) to the medium of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78. WB results showed that the protein levels of TLR4 increased with the rising proportion of CCRPM (Figure 2C). Taken together, these findings implied that pyroptotic macrophages upregulated the expression of TLR4 in PTCL cells.
3.3. Pyroptotic macrophages activate the downstream anti‐apoptotic signaling pathway of TLR4 in PTCL cells
The effect of CCRPM on the differentially expressed genes of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells was analyzed a high‐throughput sequencing assay. Figure 3A,B shows the gene heat maps and volcano plots. Figure 3C shows the main stratification analysis of coding and non‐coding genes. The coding genes were used for the Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the BPs. As shown in Figure 3D, the upregulated genes were associated with BPs such as the immune response, cell activation, and defense response; and the downregulated genes were associated with BPs such as metabolic process and organelle organization.
FIGURE 3.
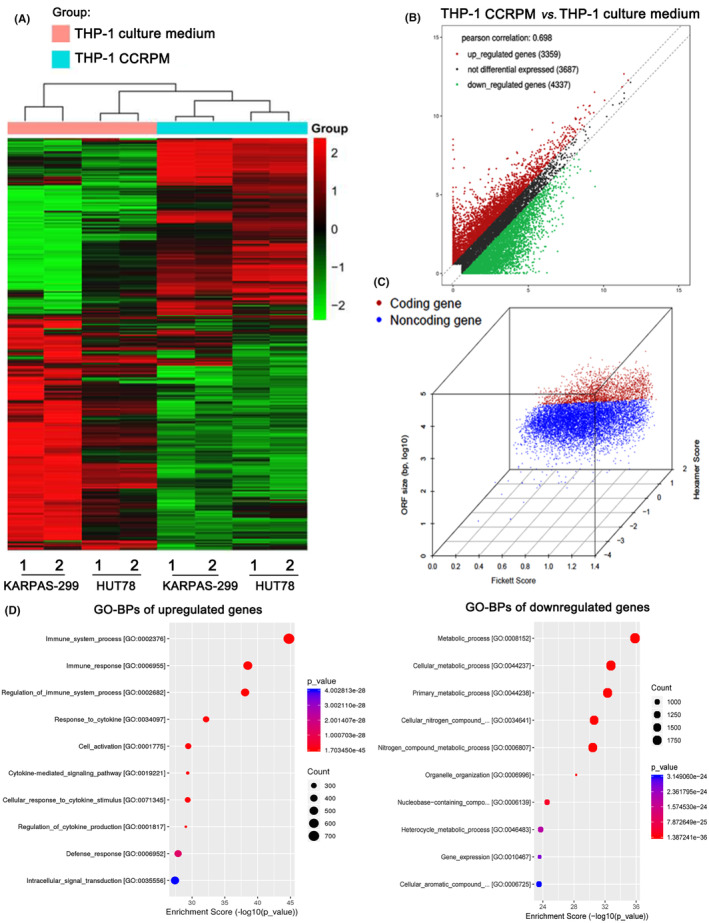
High‐throughput sequencing assay of differentially expressed genes in CCRPM and normal supernatant‐treated PTCL cells. (A) Heatmap illustration of differentially expressed genes of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells subjected to pyroptotic supernatant treatment or not. (B) Volcano plot illustrating differentially expressed genes in KARPAS‐299 cells subjected to pyroptotic supernatant treatment or not. (C) Principal component analysis of coding genes and non‐coding genes. (D) GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes in KARPAS‐299 cells subjected to pyroptotic supernatant treatment or not.
In addition, the significantly changed coding genes were used for Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis. Results showed that most genes in the TLR4 signaling pathway and its downstream NF‐κB pathways were upregulated, suggesting the stimulation of these pathways (Table S1). We noticed that many anti‐apoptotic genes (including BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1) in the NF‐κB pathway were upregulated with the stimulation of CCRPM. PCR, and WB results showed that both the gene and protein levels of BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1 were upregulated by CCRPM (Figure 4A,B). However, the knockdown of TLR4 resulted in the downregulation of key factors in the NF‐κB anti‐apoptotic signaling pathway (BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1), reversing the effect of CCRPM (Figure 4C,D). The results suggested that CCRPM could activate the anti‐apoptotic signaling pathway by regulating TLR4.
FIGURE 4.
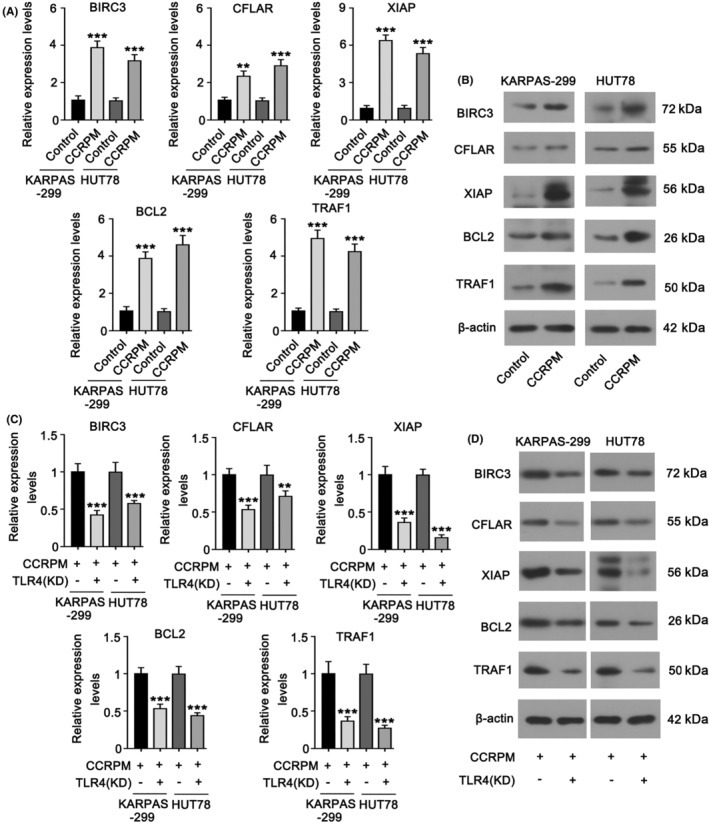
CCRPM activated the downstream anti‐apoptotic signaling pathway of TLR4 in PTCL cells. (A) RT‐PCR was conducted to detect mRNA levels of BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after stimulation with CCRPM (50%). ***p < 0.001 vs. Control (n = 3). (B) WB was conducted to detect protein levels of BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after the stimulation with CCRPM (50%). (C) mRNA levels of BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after the stimulation with CCRPM (50%) and knockdown of TLR4. ***p < 0.001 vs. CCRPM (50%) group (n = 3). (D) Protein levels of BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after the stimulation with CCRPM (50%) and knockdown of TLR4.
3.4. Pyroptotic macrophages induce malignant proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells
We further investigated the effect of CCRPM on the malignant proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of PTCL. Compared with the control group and 50% normal THP‐1 culture medium, the addition of 50% CCRPM increased the viability of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells. Then the cells were treated with chemotherapeutic drugs doxorubicin (DOX), Gemcitabine (GEM), and cisplatin (DDP), at their IC50 dosages. Treatment with 50% and 100% CCRPM both elevated the viability of chemotherapeutic drug‐treated tumor cells, and 100% CCRPM had a more significant effect. The results suggested that CCRPM could induce the resistance of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs (Figure 5A).
FIGURE 5.
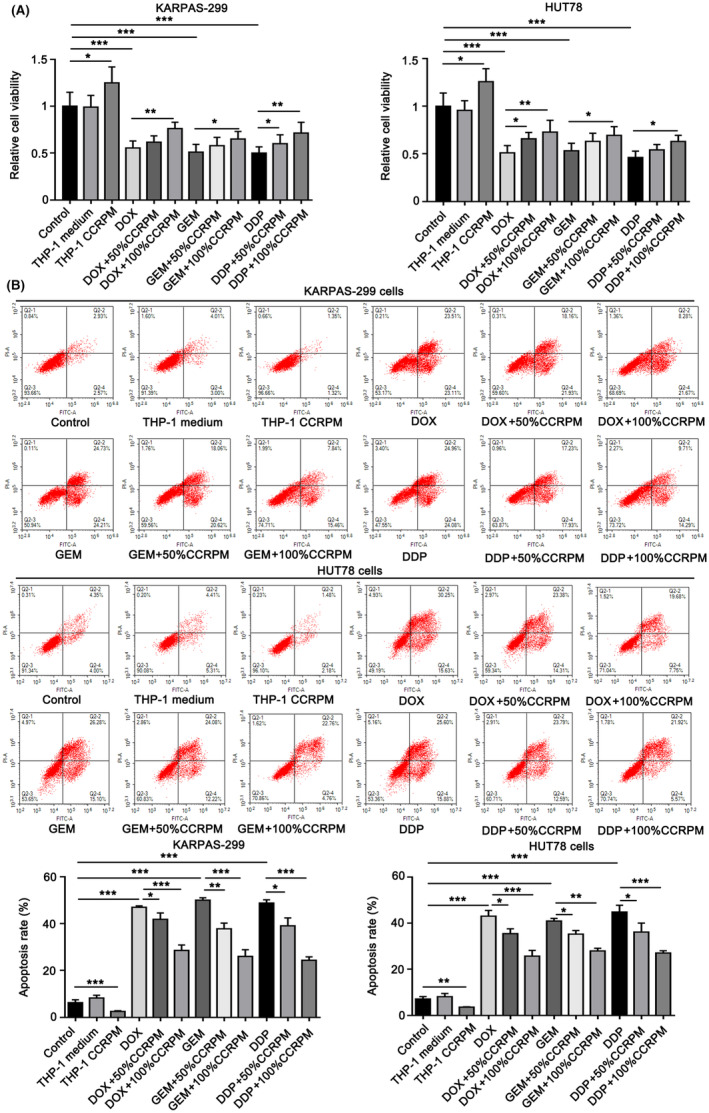
The effects of CCRPM on relative viability and chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells. (A). Relative viability of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells treated with 50% normal THP‐1 culture medium (as the control group), 50% CCRPM, chemotherapeutics including doxorubicin (DOX), gemcitabine (GEM) and cisplatin (DDP), chemotherapeutic+50% CCRPM and 100% CCRPM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (n = 3). (B). Apoptosis rate of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells treated with 50% normal THP‐1 culture medium (as control group), 50% CCRPM, chemotherapeutics including DOX, GEM and DDP, chemotherapeutic+50% CCRPM and 100% CCRPM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (n = 3).
As indicated by the flow cytometry assay, a 50% normal THP‐1 culture medium had no effect on the apoptosis rate of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells. However, 50% CCRPM reduced the apoptosis rate. The exposure to DOX, GEM, and DDP dramatically increased the apoptosis rate of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells, and treatment with 50% CCRPM suppressed the effect of chemotherapeutic drugs. Furthermore, 100% CCRPM had a stronger effect than 50% CCRPM in this way (Figure 5B).
In order to fully confirm the promoting effect of CCRPM on the chemoresistance of PTCL cells, we detected the expression of chemotherapy resistance‐related proteins MRP1, PCNA, P‐gp and their genes in PTCL cell lines treated with normal THP‐1 culture medium and 100% CCRPM, respectively (Figure 6A,B). 5‐Ethynyl‐2′‐deoxyuridine (EdU) assay was used to detect the cell proliferation in each group after DOX treatment (Figure 6C). The results showed that CCRPM treatment significantly upregulated the gene and protein expressions of MRP1 and P‐gp, but there was no significant change in PCNA. Meanwhile, CCRPM also increased the chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells.
FIGURE 6.
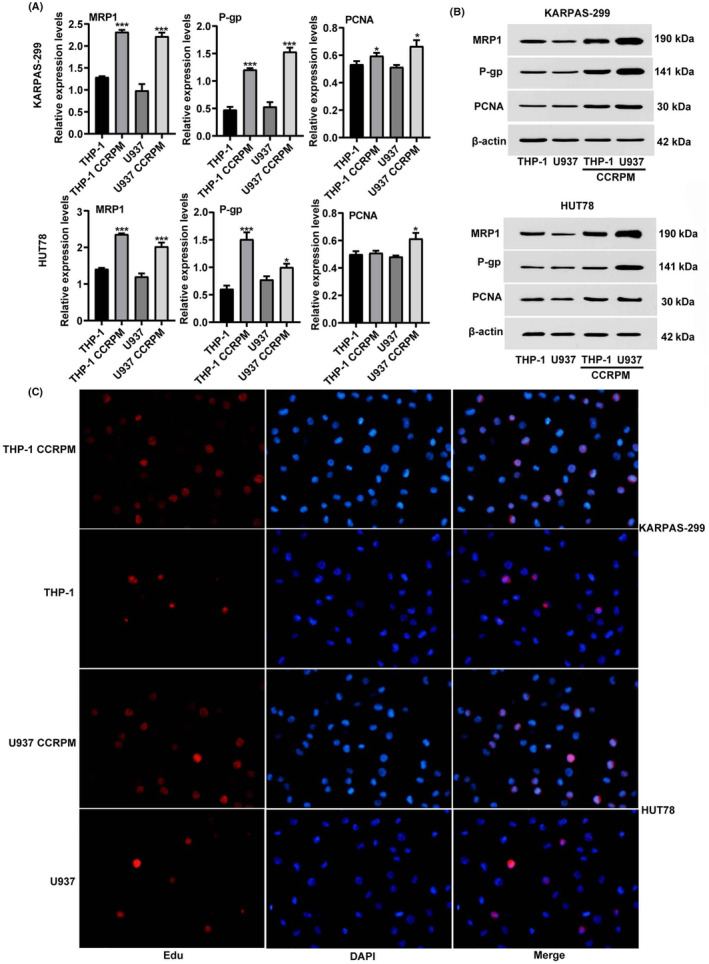
CCRPM promotes chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells. (A) mRNA levels of MRP1, P‐gp, and PCNA in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after the stimulation with THP‐1 culture medium, THP‐1 CCRPM, U937 culture medium and U937 CCRPM. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 vs. THP‐1 culture medium group or U937 culture medium (n = 3). (B) Protein levels of MRP1, P‐gp, and PCNA in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after the stimulation with THP‐1 culture medium, THP‐1 CCRPM, U937 culture medium and U937 CCRPM. (C) EdU assay was conducted to detect the proliferation of PTCL cells in each group (THP‐1 culture medium, THP‐1 CCRPM, U937 culture medium, and U937 CCRPM).
3.5. Knockdown of TLR4 reverses the effect of pyroptotic macrophages on PTCL cells
To further certify the role of TLR4 in the promotion of PTCL malignant proliferation by CCRPM, we knocked down TLR4 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells. According to the data from PCR and WB assays, compared with siRNA1 and siRNA2, siRNA3‐TLR4 showed the greatest efficiency in the downregulation of TLR4 (Figure 7A,B). So siRNA3‐TLR4 was used in the following assay for TLR4 knockdown. Then we analyzed the effects of TLR4 knockdown on cell proliferation and apoptosis. Results showed that the CCRPM‐induced proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of tumor cells was abolished with TLR4 knockdown (Figure 7C). Treatment with CCRPM also suppressed the apoptosis of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78, and this anti‐apoptotic effect was attenuated with TLR4 knockdown (Figure 7D). These results suggested that TLR4 played a key role in the regulation of the malignant behaviors of pyroptotic macrophage‐induced PTCL cells.
FIGURE 7.
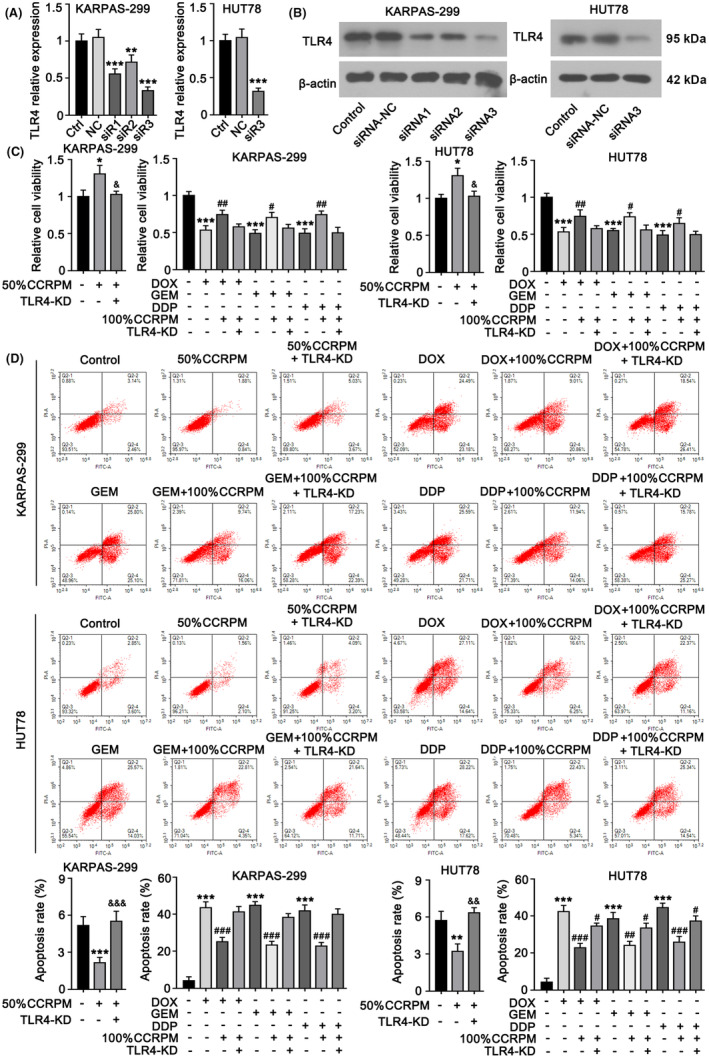
TLR4 mediates the malignancy‐promoting effects of CCRPM in PTCL cells. (A) KARPAS‐299 cells were transfected with three siRNAs individually to knockdown TLR4. RT‐PCR results showed that siRNA3 had the highest efficiency to downregulate TLR4 expression among the siRNAs. siRNA3 was also transfected to HUT78 cells to knock down TLR4. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. Control (n = 3). (B) WB was performed to detect TLR4 protein levels after transfecting the siRNAs. (C) KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells were transfected with siRNA3 to knock down TLR4. Cells with TLR4 knockdown or not were treated with 50% normal THP‐1 culture medium, 50% CCRPM, 100% CCRPM, and chemotherapeutics including DOX, GEM, and DDP. After the treatments, cell viability was tested. *p < 0.05 vs. Control (n = 3); &p < 0.05 vs. 50% CCRPM treatment group; #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 vs. Chemotherapeutics' groups (n = 3). (D) After the same treatments, apoptosis rate of cells were evaluated flow cytometry. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. Control (n = 3); &&p < 0.01 and &&&p < 0.001 vs. 50% CCRPM treatment group; ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001 vs. Chemotherapeutics' groups (n = 3).
3.6. Pyroptotic macrophages promote TLR4 expression and chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells through secreting IL‐18
The results of solid‐phase chip analysis showed that the secretion of IL‐18 increased significantly after macrophage pyroptosis (Table 2). Recent studies have shown that IL‐18 can activate TLR4. To explore whether the upregulation of TLR4 expression in PTCL cells by CCRPM relied on the release of IL‐18, we eliminated IL‐18 from CCRPM by magnetic beads cross‐linked with IL‐18 antibody, and then cultured PTCL cells with macrophage supernatant, macrophage supernatant supplemented with IL‐18 recombinant protein, CCRPM, or CCRPM with IL‐18 removed, respectively. Afterward, the cells were treated with DOX, GEM, or DDP, at their IC50 dosages. Through the detection by WB, CCK8 expression, and flow cytometry, we found that removal of IL‐18 from CCRPM significantly downregulated the expression of TLR4 in tumor cells (Figure 8A,B), decreased tumor cell viability (Figure 8C), and increased apoptosis rate (Figure 8D), while the addition of IL‐18 to macrophage supernatant had the opposite effect. These results suggested that pyroptotic macrophages might promote the expression of TLR4 and chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells by secreting IL‐18.
FIGURE 8.
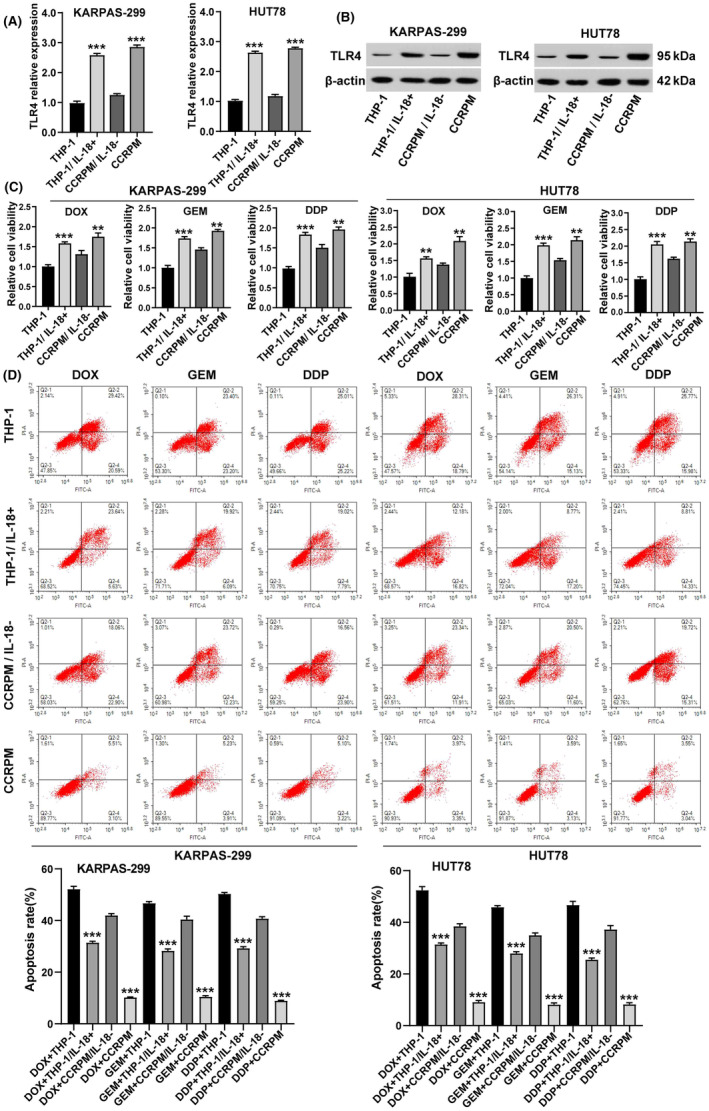
CCRPM promotes TLR4 expression and chemotherapy resistance in PTCL cells through secreting IL‐18. (A) mRNA levels of TLR4 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after stimulation with THP‐1 culture medium, THP‐1 supplemented with IL‐18 recombinant protein, CCRPM with IL‐18 removed, and CCRPM. ***p < 0.001 vs. THP‐1 culture medium or CCRPM‐IL‐18 (n = 3). (B) Protein levels of TLR4 in KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells after the stimulation with THP‐1 culture medium, THP‐1 supplemented with IL‐18 recombinant protein, CCRPM with IL‐18 removed and CCRPM. (C) Relative viability of KARPAS‐299 and HUT78 cells treated with THP‐1 culture medium, THP‐1 supplemented with IL‐18 recombinant protein, CCRPM with IL‐18 removed and CCRPM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (n = 3). (D) After the same treatments, apoptosis rate of cells was evaluated flow cytometry. ***p < 0.001 (n = 3).
4. DISCUSSION
In the present study, we demonstrated that pyroptosis occurred in interstitial macrophages of PTCL and was associated with poor prognosis, providing evidence that pyroptotic macrophages could upregulate TLR4 expression in tumor cells and activate its downstream NF‐κB anti‐apoptotic pathways, thereby promoting malignant proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of PTCL cells.
As a newly discovered form of cell death, pyroptosis differs from other cell death mechanisms such as apoptosis and necrosis in terms of morphological characteristics and regulatory mechanisms. 5 , 15 Increasing evidence suggests that pyroptosis has a complex regulatory relationship with cancers. In the case of solid tumors, pyroptosis has been shown to directly inhibit tumor growth. 16 , 17 In lymphoma, pyroptosis can affect the biological behavior of tumor cells. 18 Pyroptosis can also occur in immune cells, induce crosstalk between innate and adaptive immunity, modify the tumor microenvironment, and directly influence the development of tumor cells. 17 , 19 , 20 However, it has not been reported whether pyroptosis occurred in PTCL or its tumor microenvironment. In patients with Sjögren's syndrome, abnormal activation of NOD‐leucine rich repeat and pyrin containing protein (NLRPs) in macrophages led to the occurrence of pyroptosis in the blood and salivary glands, which contributed to a 15–20 times higher risk of developing lymphoma than the general population. 21 This inspired us to detect pyroptosis markers in tumors and adjacent tissues of PTCL patients. IHC and IF results confirmed that pyroptosis occurred in interstitial macrophages of PTCL. Based on clinical data, macrophage pyroptosis was proved to be relevant to the poor prognosis of PTCL patients.
To elucidate the mechanism of pyroptotic macrophages regulating PTCL cells, we induced macrophage pyroptosis in an in vitro model and analyzed the changes of cytokines secreted in the supernatant before and after pyroptosis. High‐throughput sequencing assay showed that pyroptotic macrophage supernatant significantly upregulated the expression of IL‐18, SDF‐1α and TGF‐α. Previous studies have reported that IL‐18 could promote the expression of TLR4 on monocytes in B lymphocytes. 22 , 23 Our previous studies have found that the expression of TLR4 was closely related to the poor prognosis of PTCL patients. 14 Combined with the results above, we speculated that pyroptotic macrophages upregulated the expression of TLR4 in tumor cells by secreting inflammatory cytokines such as IL‐18, which was confirmed by subsequent experiments.
TLR4 can regulate the classical TLR4/MyD88/NF‐κB signaling pathway, leading to the activation of NF‐κB transcription. 24 , 25 The regulation of apoptosis by NF‐κB has two sides: on the one hand, NF‐κB up‐regulates the expression of XIAP, which inhibits apoptosis and reduces the drug sensitivity of tumor cells 26 ; on the other hand, NF‐κB activates the Bax/Caspase‐3 and IRE1α/XBP1 signaling pathways to induce apoptosis. 27 Our results showed that, after treatment with pyroptotic macrophage supernatant, the expression of key factors in anti‐apoptotic pathways such as BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1 were significantly upregulated, suggesting that pyroptotic macrophage supernatant primarily activates NF‐κB anti‐apoptotic signaling pathway in tumor cells. Moreover, the knockdown of TLR4 inhibited the upregulation of BIRC3, CFLAR, XIAP, BCL2, and TRAF1, and also reversed the promotion of tumor cell proliferation and chemotherapy resistance, suggesting that TLR4 was the key target for pyroptotic macrophages to regulate the biological behavior of PTCL.
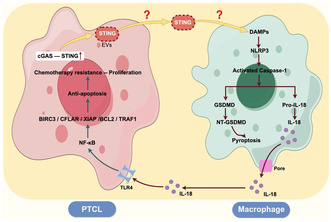
Another interesting phenomenon is that we did not observe plentiful macrophage pyroptosis in tumor tissues of other common types of lymphoma such as diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma. This may be related to the abundant macrophage infiltration in the PTCL tumor microenvironment but less macrophage infiltration in DLBCL. Another reason may be the specially altered signaling pathways of PTCL cells (such as cGAS–STING), which changes the mutual regulation of tumor cells and immune cells. Hui Jin et al. found that the cGAS–STING pathway was abnormally activated in PTCL and associated with a poor prognosis. 28 Some studies have shown that the cGAS–STING pathway was related to the activation of inflammatory factors and the occurrence of pyroptosis. 29 , 30 , 31 Ting et al. demonstrated that cGAS–STING–IFN1 pathway activation increases the AIM2 protein levels to induce a robust innate immune response. 32 Similarly, cGAS‐mediated IFN responses upregulated caspase‐1 and caspase‐11 expression, which in turn increased IL‐1β release and pyroptotic cell death. 33 These observations indicate that AIM2 activation and STING signaling amplified these responses. Therefore, we hypothesized that the cGAS–STING pathway in PTCL tumor cells was abnormally activated, leading to an increase in STING protein secretion. STING protein functioned as damage‐associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) to activate pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in macrophages, thereby inducing macrophage pyroptosis. In the follow‐up study, we will explore whether PTCL mediates macrophage pyroptosis through the activation of the cGAS–STING pathway, and explore the mechanism of cGAS–STING pathway activating macrophage pyroptosis.
At present, there are many clinical trials on new PTCL targets, such as PI3K inhibitors duvelisib 34 and linperlisib, 35 JAK inhibitor golidocitinib,36 and XPO1 inhibitor Selinexor. 37 But it is regrettable that the disclosed data have not yet made breakthroughs. Currently, TLR4 inhibitors are widely used in autoimmune diseases, acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological diseases, but are rarely used in the field of lymphoma. From the perspective of microenvironment immune cell regulation on tumor cells, our study revealed the key role of TLR4 and its downstream anti‐apoptotic pathways in the proliferation and chemoresistance of PTCL cells. It provided a theoretical basis for the application of TLR4 and related pathway inhibitors in the treatment of PTCL.
In conclusion, we are the first to identify the pyroptosis of macrophages in the PTCL microenvironment and verify that pyroptotic macrophages promoted the malignant biological behavior of PTCL. Our study suggests that there may be mutual regulation between tumor cells and immune cells in the microenvironment of PTCL, which plays an important role in regulating the development of PTCL (Figure 9). The comprehensive analysis of this mechanism will contribute to understanding the development of PTCL and offer new insights for clinical application.
FIGURE 9.
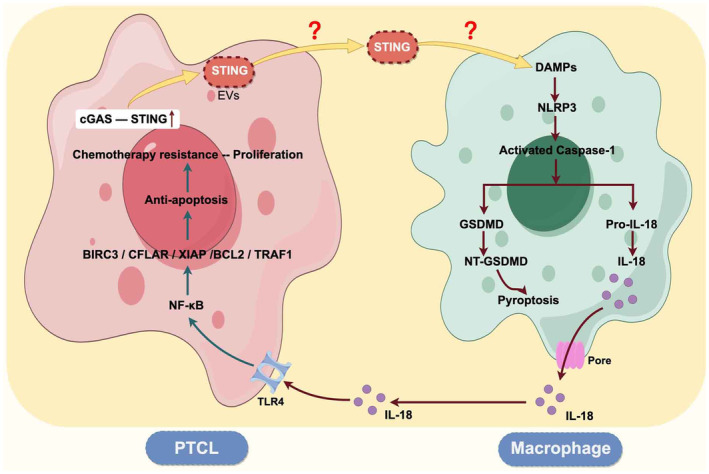
Schematic of the signaling pathways in which tumor cells and macrophages interact in the PTCL microenvironment.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Han Zhang: Data curation; investigation; writing – original draft; writing – review and editing. Liru Li: Data curation; investigation; writing – original draft; writing – review and editing. Zijian Zhang: Data curation; writing – review and editing. Shiqi Gao: Validation; writing – review and editing. Mingzhe Yang: Validation; writing – review and editing. Wenjie Ma: Writing – review and editing. Hongbin Li: Writing – review and editing. Wenhui Zhao: Writing – review and editing. Huike Yang: Conceptualization; writing – review and editing. Yue Zhang: Conceptualization; project administration; writing – review and editing. Shu Zhao: Conceptualization; funding acquisition; writing – review and editing.
FUNDING INFORMATION
This work was supported by the Beijing Medical Award Foundation (No. YXJL‐2020‐0785‐1072) (SZ), the Haiyan Foundation of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital (No. JJZD 2022‐10) (SZ), and the Haiyan Foundation of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital (No. JJQN 2023‐01) (HZ).
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors have no conflict of interest.
ETHICS STATEMENT
‐ This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, China (approval number: 2020–186), and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
‐ Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
‐ Registry and the Registration No. of the study/trial. N/A.
‐ Animal Studies. N/A.
Supporting information
Table S1.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The Haiyan Foundation of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, (Grant/Award Number: ‘No. JJQN 2023‐01’) the Haiyan Foundation of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, (Grant/Award Number: ‘No. JJZD 2022‐10’) the Beijing Medical Award Foundation, (Grant/Award Number: ‘No. YXJL‐2020‐0785‐1072’).
Zhang H, Li L, Zhang Z, et al. Pyroptotic macrophages promote proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of peripheral T‐cell lymphoma via TLR4 signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2024;115:2444‐2460. doi: 10.1111/cas.16180
Huike Yang, Yue Zhang and Shu Zhao are co‐corresponding authors and Shu Zhao is the major corresponding author.
Han Zhang, Liru Li are co‐first authors as they contributed equally to this study.
Contributor Information
Huike Yang, Email: huikeyang@hrbmu.edu.cn.
Yue Zhang, Email: zhangyue010@hotmail.com.
Shu Zhao, Email: zs_1881@163.com.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author (zs_1881@163.com) on reasonable request.
REFERENCES
- 1. Zhang P, Zhang M. Epigenetic alterations and advancement of treatment in peripheral T‐cell lymphoma. Clin Epigenetics. 2020;12(1):169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Timmins MA, Wagner SD, Ahearne MJ. The new biology of PTCL‐NOS and AITL: current status and future clinical impact. Br J Haematol. 2020. Apr;189(1):54‐66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Mina A, Pro B. T time: emerging and new therapies for peripheral T‐cell lymphoma. Blood Rev. 2022;52:100889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Frank D, Vince JE. Pyroptosis versus necroptosis: similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(1):99‐114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, Tang L, Peng C, Chen X. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ju A, Tang J, Chen S, Fu Y, Luo Y. Pyroptosis‐related gene signatures can robustly diagnose skin cutaneous melanoma and predict the prognosis. Front Oncol. 2021;11:709077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Song W, Ren J, Xiang R, Kong C, Fu T. Identification of pyroptosis‐related subtypes, the development of a prognosis model, and characterization of tumor microenvironment infiltration in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;10(1):1987636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Wei X, Xie F, Zhou X, et al. Role of pyroptosis in inflammation and cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(9):971‐992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hage C, Hoves S, Strauss L, et al. Sorafenib induces Pyroptosis in macrophages and triggers natural killer cell‐mediated cytotoxicity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2019;70:1280‐1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ciesielska A, Matyjek M, Kwiatkowska K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS‐induced pro‐inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(4):1233‐1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Chen CY, Kao CL, Liu CM. The cancer prevention, anti‐inflammatory and anti‐oxidation of bioactive phytochemicals targeting the TLR4 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9):2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Shetab Boushehri MA, Lamprecht A. TLR4‐based Immunotherapeutics in cancer: a review of the achievements and shortcomings. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(11):4777‐4800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Li C, Yang S, Ma H, Ruan M, Fang L, Cheng J. Influence of icariin on inflammation, apoptosis, invasion, and tumor immunity in cervical cancer by reducing the TLR4/MyD88/NF‐κB and Wnt/β‐catenin pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Zhao S, Sun M, Meng H, et al. TLR4 expression correlated with PD‐L1 expression indicates a poor prognosis in patients with peripheral T‐cell lymphomas. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:4743‐4756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Xia X, Wang X, Cheng Z, et al. The role of pyroptosis in cancer: pro‐cancer or pro‐"host"? Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(9):650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yu J, Li S, Qi J, et al. Cleavage of GSDME by caspase‐3 determines lobaplatin‐induced pyroptosis in colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(3):193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Wu J, Zhu Y, Luo M, Li L. Comprehensive analysis of Pyroptosis‐related genes and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in breast cancer. Front Immunol. 2021;12:748221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lim KH, Chen LC, Hsu K, et al. BAFF‐driven NLRP3 inflammasome activation in B cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Du T, Gao J, Li P, et al. Pyroptosis, metabolism, and tumor immune microenvironment. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(8):e492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Niu X, Chen L, Li Y, Hu Z, He F. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in the tumor microenvironment: perspectives for immunotherapy of SCLC. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86(Pt 3):273‐285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Vakrakou AG, Boiu S, Ziakas PD, Xingi E, Boleti H, Manoussakis MN. Systemic activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in patients with severe primary Sjögren's syndrome fueled by inflammagenic DNA accumulations. J Autoimmun. 2018;91:23‐33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Desbien AL, Dubois Cauwelaert N, Reed SJ, et al. IL‐18 and subcapsular lymph node macrophages are essential for enhanced B cell responses with TLR4 agonist adjuvants. J Immunol. 2016;197(11):4351‐4359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Dias‐Melicio LA, Fernandes RK, Rodrigues DR, Golim MA, Soares AM. Interleukin‐18 increases TLR4 and mannose receptor expression and modulates cytokine production in human monocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:236839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Xu GR, Zhang C, Yang HX, et al. Modified citrus pectin ameliorates myocardial fibrosis and inflammation via suppressing galectin‐3 and TLR4/MyD88/NF‐κB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126:110071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Prescott JA, Mitchell JP, Cook SJ. Inhibitory feedback control of NF‐κB signalling in health and disease. Biochem J. 2021. Jul 16;478(13):2619‐2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Jost PJ, Vucic D. Regulation of cell death and immunity by XIAP. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020;12(8):a036426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sadia K, Ashraf MZ, Mishra A. Therapeutic role of Sirtuins targeting unfolded protein response, coagulation, and inflammation in hypoxia‐induced thrombosis. Front Physiol. 2021;12:733453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Lu X, Wang S, Hua X, et al. Targeting the cGAS‐STING pathway inhibits peripheral T‐cell lymphoma progression and enhances the chemotherapeutic efficacy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;11:e2306092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Hu X, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Yao X, Ni W, Zhou K. Emerging role of STING signalling in CNS injury: inflammation, autophagy, necroptosis, ferroptosis and pyroptosis. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Li XQ, Yu Q, Fang B, Zhang ZL, Ma H. Knockdown of the AIM2 molecule attenuates ischemia‐reperfusion‐induced spinal neuronal pyroptosis by inhibiting AIM2 inflammasome activation and subsequent release of cleaved caspase‐1 and IL‐1β. Neuropharmacology. 2019;160:107661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Feltham R, Vince JE. Ion man: GSDMD punches pores to Knock out cGAS. Immunity. 2018. Sep 18;49(3):379‐381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Swanson KV, Junkins RD, Kurkjian CJ, et al. A noncanonical function of cGAMP in inflammasome priming and activation. J Exp Med. 2017;214(12):3611‐3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Webster SJ, Brode S, Ellis L, et al. Detection of a microbial metabolite by STING regulates inflammasome activation in response to chlamydia trachomatis infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13(6):e1006383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Wang Z, Zhou H, Xu J, Wang J, Niu T. Safety and efficacy of dual PI3K‐δ, γ inhibitor, duvelisib in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoid neoplasms: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of prospective clinical trials. Front Immunol. 2023;13:1070660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Jin J, Cen H, Zhou K, et al. A phase Ib study of linperlisib in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T‐cell lymphoma. Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):1386.34673948 [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kim WS, Yoon DH, Song Y, et al. Early safety and efficacy data from a phase I/II trial of DZD4205, a selective jak1 inhibitor, in relapsed/refractory peripheral T‐cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2021;39(S2):101. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Huang H, Gao Y, Zhang H, et al. XPO1 inhibitor (ATG‐010) plus chemotherapy per investigator's choice for heavily pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) peripheral T‐cell lymphoma (PTCL) and extranodal NK/T‐cell lymphoma (ENKTL): preliminary results from a multicenter, single‐arm, phase Ib study (TOUCH trial). Blood. 2021;138(Supplement1):2452. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author (zs_1881@163.com) on reasonable request.


