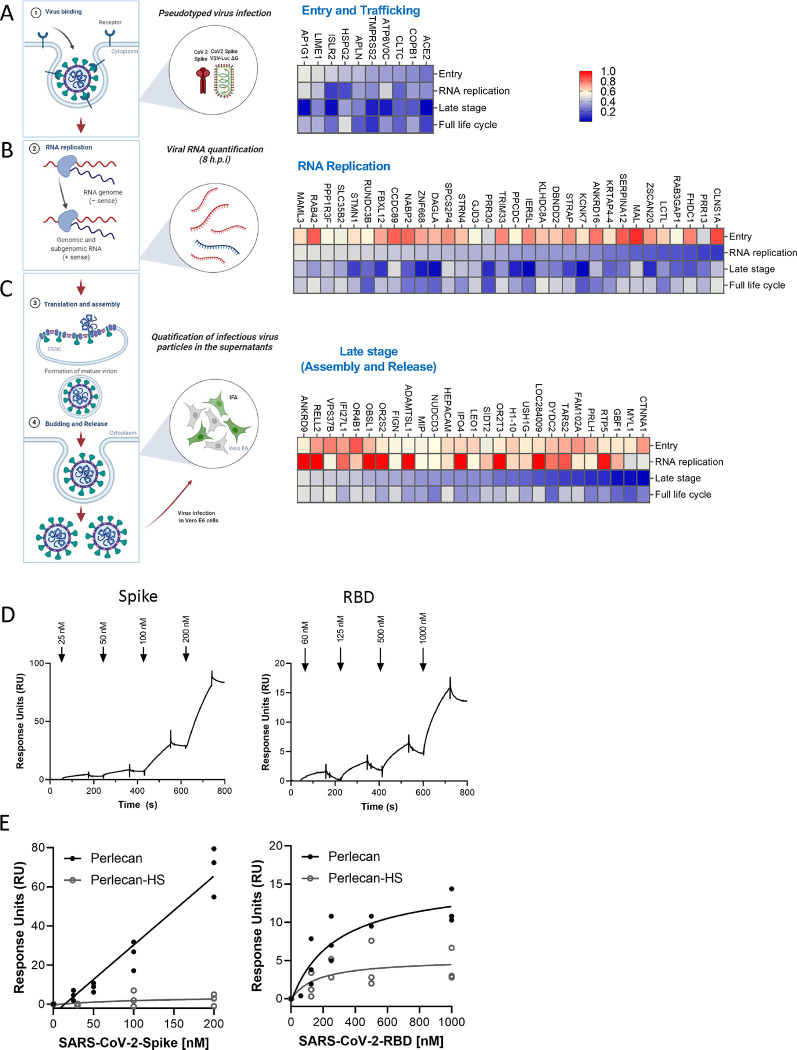
Figure 3 – Mapping of host factors into the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle reveals a direct interaction between entry factor perlecan and SARS-CoV-2 S protein.
(A) Caco-2 cells were subjected to siRNA-mediated knockdown of indicated host factors and then infected with SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped VSV luciferase virus (VSV-S-luc) for 18h prior to measurement of luciferase signal. (B) In parallel, cells were subjected to synchronized infection with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI = 5) for 8h prior to measurement of viral RNA, or (C) supernatants collected at 18h post-infection were used to infect naïve Vero E6 cells. The % of infected cells was then determined at 18h post-infection using immunostaining for viral N protein (3–4). In parallel to these experiments, the impact of depleting these factors on SARS-CoV-2 replication was evaluated at 24 h post-infection in Caco-2 cells (full replication cycle, Figure 3A–C). Results are summarized in the heat map and show the mean (n=2) of relative activities compared to cells treated with non-targeting scramble siRNA. (D and E) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to evaluate binding of S protein and RBD to perlecan or perlecan without HS spike binding to immunopurified perlecan isolated from human coronary artery endothelial cells. Control flow channels contained immobilized BSA. S protein at indicated concentrations was run across the flow channels for 120 s and dissociation was measured in the following 600 s. The RU values throughout the experiment for BSA were subtracted from the RU values for perlecan to determine the level of specific binding. This experiment was repeated with perlecan treated with heparinase III.