Abstract
Background
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy has achieved remarkable remission in patients with B-cell malignancies. However, its efficacy in treating solid tumors remains limited. Here, we investigated a combination therapy approach using an engineered long-acting interleukin (IL)-7 (rhIL-7-hyFc or NT-I7) and CAR-T cells targeting three antigens, glypican-2 (GPC2), glypican-3 (GPC3), and mesothelin (MSLN), against multiple solid tumor types including liver cancer, neuroblastoma, ovarian cancer, and pancreatic cancer in mice.
Methods
CAR-T cells targeting GPC2, GPC3, and MSLN were used in combination with NT-I7 to assess the anticancer activity. Xenograft tumor models, including the liver cancer orthotopic model, were established using NOD scid gamma mice engrafted with cell lines derived from hepatocellular carcinoma, neuroblastoma, ovarian cancer, and pancreatic cancer. The mice were monitored by bioluminescence in vivo tumor imaging and tumor volume measurement using a caliper. Immunophenotyping of CAR-T cells on NT-I7 stimulation was evaluated for memory markers, exhaust markers, and T-cell signaling molecules by flow cytometry and western blotting.
Results
Compared with the IL-2 combination, preclinical evaluation of NT-I7 exhibited regression of solid tumors via enhanced occupancy of CD4+ CAR-T, improved T-cell expansion, reduced exhaustion markers (programmed cell death protein 1 or PD-1 and lymphocyte-activation gene 3 or LAG-3) expression, and increased generation of stem cell-like memory CAR-T cells. The STAT5 pathway was demonstrated to be downstream of NT-I7 signaling, mediated by increased expression of the IL-7 receptor expression in CAR-T cells. Furthermore, CAR-T cells improved efficacy against tumors with low antigen density when combined with NT-I7 in mice, presenting an avenue for patients with heterogeneous antigenic profiles.
Conclusion
This study provides a rationale for NT-I7 plus CAR-T cell combination therapy for solid tumors in humans.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Chimeric antigen receptor - CAR, Monoclonal antibody, Solid tumor, Adoptive cell therapy - ACT
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies are generally unsuccessful in treating solid tumors due to the limited persistence of CAR-T cells and insufficient infiltration into the tumor microenvironment.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Our study demonstrates that a new immunotherapeutic approach, combining long-acting interleukin-7 (NT-I7) with three CARs that target tumor-associated antigens—glypican-3, glypican-2 and mesothelin—is efficient against mouse tumor models of liver cancer, pediatric cancer, ovarian cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
The significant therapeutic activity of CAR-T cells combined with NT-I7 suggests their potential as a novel treatment for solid tumors, warranting further exploration and clinical investigation.
Introduction
Genetically engineered T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) are an emerging immunotherapy for cancer.1 To date, six CAR-T cell products have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for subsets of B-cell leukemia or lymphoma.2 However, treating major solid tumors with CAR-T cells presents a significant challenge and yields only partial and transient responses.3,5 Importantly, these studies indicate potential mechanisms underlying why CAR-T therapy has limited effectivity on solid tumors, which include insufficient CAR-T cell persistence, restricted tumor trafficking and infiltration, and the presence of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME).6,8
Cytokines play a crucial role in T-cell activation, expansion, and polarization of subpopulations during the generation of CAR-T cells.9 Interleukin (IL)-2 is commonly used to support CAR-T cell maintenance. However, its predominant use in manufacturing CAR-T cells leads to variability in the potency and long-term effectiveness of the antitumor response by autologous CAR-T cells, thus restricting overall therapy success.10 11 Besides IL-2, IL-7 is implicated in fostering the proliferation and diversity of effector T cells in the TME with consequent superior antitumor effects.12 Accumulating preclinical and clinical data demonstrates that IL-7 extends CAR-T cell survival and enhances expansion and tumor elimination capabilities.13,16
To enhance the serum half-life and potency of IL-7, a non-cytolytic hybrid Fc (hyFc) fused human IL-7 known as rhIL-7-hyFc (NT-I7) has been developed and exhibits exceptional stability in humans.17 NT-I7 is safe at a single-dose injection (60 µg/kg) in healthy volunteers, resulting in increased T-cell count.18,20 Additionally, in preclinical and clinical testing, NT-I7 increases lymphocytes in murine tumor models, patients with glioblastoma, and patients with hard-to-treat gastrointestinal tumors.21,25 Furthermore, NT-I7 enhances the therapeutic efficacy of human CD19 CAR-T cells, CD2 CAR-T cells, and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) CAR-invariant natural killer T cells in murine models of hematological malignancy or multiple myeloma without increasing the risk of cytokine release syndrome.26,28 We hypothesize that incorporating NT-I7 into the culture of CAR-T cells may promote proliferation and improve the immune composition of the cell pool, prompting us to explore the potential of NT-I7 in improving CAR-T activity in the context of solid tumors.
In the present study, we produced clinic-ready CAR-T cells targeting three individual solid tumor antigens, including glypican-2 (GPC2),29 glypican-3 (GPC3),30 and mesothelin (MSLN),31 and cultured them with either IL-2 or NT-I7. NT-I7 significantly enhanced CAR-T cell proliferation, activity, and CD4+ stem memory CAR-T subpopulation compared with IL-2 in vitro. Moreover, in multiple mouse xenograft models including liver cancer, neuroblastoma, ovarian cancer, and pancreatic cancer, the combination therapy of CAR-T cells with NT-I7 exhibited improved antitumor activity and prolonged survival. Further analysis revealed that NT-I7 not only prolonged CAR-T cell persistence but also increased the percentage of tumor-infiltrated CAR-T cells, while reducing the expression of exhaustion markers, programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3). These findings underscored the potential of NT-I7 to improve the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy and its feasibility as a clinic-ready adjunct for patients with solid tumors.
Methods
Mouse and human specimens
Mice were housed at the NCI CCR/Leidos Animal Facility (Bethesda, USA) under a standard 12:12 hours light/dark cycle with standard food and water.
Human peripheral blood samples from healthy donors and patients with liver cancer were purchased from the Oklahoma Blood Institute (Oklahoma City, USA) and provided by Dr Tim Greten at the NCI (Bethesda, Maryland, USA), respectively. The use of de-identified human specimens was determined to be exempt by the NIH Institutional Review Board. Because the specimens and data were not collected specifically for our study and no one in our team has access to the subject identifiers linked to the specimens or data, our study is not considered a human subject research.
Cell culture
Hep3B (hepatocellular carcinoma) and HEK-293T cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. Ovarian cancer cell line OVCAR8 was obtained from the National Cancer Institute (Development Therapeutics Program). Neuroblastoma cell lines IMR5 and SKNSH were obtained from NCI Pediatric Oncology Branch (Bethesda, Maryland, USA). Pancreatic cancer cell line KLM-1 was obtained from Dr Christine Alewine at the NCI. Hep3B, OVCAR8, IMR5, SKNSH, and KLM-1 were transduced with lentiviruses expressing GFP and firefly luciferase (GL) in the laboratory. The luciferase-expressing Huh-7 cell line was kindly provided by Dr Andras Heczey at Baylor College of Medicine. OVCAR8, IMR5, SKNSH, and KLM-1 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institue 1640 (RPMI 1640) media supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS), 1% L-glutamine, and 1% penicillin–streptomycin; all other cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM). Cells were maintained in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37°C.
Generation of CAR-T cells
We generated the CAR lentiviral vectors targeting GPC2, GPC3, and MSLN respectively following the design principle of CAR construct published in our previous study.29,32 Briefly, the CAR construct consists of a recognition domain, CD8α or CD28 hinge, and CD8α or CD28 transmembrane, followed by a 4-1BB co-stimulatory domain and the CD3ζ signaling moiety. The recognition domain in this study consists of three single-chain variable fragments derived from monoclonal antibodies including humanized YP7 (hYP7), CT3, and humanized YP218 (hYP218), each used individually (named pMH289, pMH394, and pMH348). GPC3 CAR-T cells (NCT05003895) are being tested in patients in phase I clinical trials. The CAR-expressing lentivirus was produced as described previously.30 Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from donors were isolated using Ficoll (GE Healthcare) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The isolated PBMCs were stimulated for 24 hours using anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibody-coated beads (Invitrogen) at a bead:cell ratio of 2:1 according to manufacturer’s instructions in the presence of IL-2 (100 U/mL) or NT-I717 (10 ng/mL) or equimolar concentration of IL-7 compared with NT-I7.
Luciferase CAR-T cell killing assay
The cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells was determined by a luciferase-based assay. In brief, IL-2 or NT-I7 supported untransduced T cells (Mock) or CAR-T cells were co-incubated with GPC3-positive (Hep3B GL) and GPC3-negative tumor cells (Hep3B GPC3 knockout GL) for 24 hours at an effector:target (E/T) ratio of 5:1. The cytolytic activity of GPC2 CAR-T cells or MSLN CAR-T cells was measured by luciferase assay for 72-hour incubation with different tumor cell lines (IMR5 GL, SKNSH GL, OVCAR8 GL, and KLM-1 GL) at a series dilution of E/T ratios. The luciferase activity was measured using the luciferase assay system (Promega) on Victor (PerkinElmer).
Flow cytometry
The transduction efficiency of CARs on T cells was detected by anti-epidermal growth factor receptor human monoclonal antibody (mAb) cetuximab (Erbitux) and goat-anti-human IgG-PE, or allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch). The expression of antigens (GPC3, GPC2, or MSLN) on tumor cells was predicted by three monoclonal antibodies (YP7, CT3, and YP218) produced in the laboratory, respectively. To determine the absolute number of CAR-T cells in mouse blood, 100 µL of blood was collected from mice and 1× red blood cell lysis buffer (eBiosciences) was used to remove red blood cells. To detect the CD127 (IL-7Rα) expression on pre-infusion and post-infusion CAR-T cells, we obtained in vitro cultured CAR-T cells and CAR-T cells recovered from the Huh-7 mouse spleen. These cells were then stained with an APC-conjugated anti-human CD127 antibody (clone A019D5, BioLegend). BV711-conjugated anti-CD3, Erbitux, and goat-anti-human IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 (BioLegend) were used to stain CD3+ CAR-T cells. CAR-T cell count was measured using 123count eBeads (Thermo Fisher). For multiple color staining, antibodies including APC/Cy7-conjugated anti-CD4, FITC-conjugated anti-CD8, APC-conjugated anti-PD-1, APC-conjugated anti-LAG3, APC-conjugated anti-CD62L, BV421-conjugated anti-TIM3, BV421-conjugated anti-CD45RA, PE-conjugated anti-CD95 and BV711 conjugated anti-CD3 (eBioscience) were used. T-cell exhaustion was evaluated with PE-conjugated anti-PD-1, PE-conjugated anti-TIM-3, and PE-conjugated anti-LAG-3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The examination of CAR-T cell proliferation was evaluated using the CellTrace CFSE Cell Proliferation Kit (Invitrogen). To detect the cytokine expression in IMR5 mouse plasma, the LEGENDplex human CD8/NK panel (13-plex) V02 (BioLegend) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Data acquisition was performed using FACSCanto II (BD Biosciences) and Sony ID7000 (Sony). Data was analyzed using FlowJo software V.10.
ELISA
Supernatants were collected from CAR-T cell cytotoxicity assays for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-2, and interferon (IFN)-γ detection using an ELISA kit (BioLegend) according to the manufacturer’s manual. Mouse serum was collected at different time points during 6 weeks after 10 mg/kg NT-I7 infusion. The Human IL-7 Quantikine HS ELISA Kit (R&D systems) was used to detect the serum half-life of NT-I7.
Western blot
Equal masses of protein lysates were loaded onto a 4–20% SDS-PAGE gel for electrophoresis. Antibodies including anti-STAT5 (Cat#25656, 1:1,000), anti-phospho-STAT5 (Cat#4322, 1:1,000), anti-STAT3 (Cat#12640, 1:1,000), anti-phospho-STAT3 (Cat#9145, 1:2,000), anti-Erk1/2 (Cat#4695, 1:1,000), anti-phospho-Erk1/2 (Cat#4370, 1:2,000), anti-phospho-Akt (Cat#4060, 1:2,000), anti-Bax (Cat#5023, 1:1,000), anti-Bcl2 (Cat#15071, 1:1,000), and anti-GAPDH (Cat#2118, 1:1,000) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology.
Animal studies
5-week-old female NOD/SCID/IL-2Rgcnull (NSG) mice were provided by the NCI CCR Animal Resource Program/NCI Biological Testing Branch. The orthotopic Hep3B model was established by injecting 0.5×106 Hep3B GL tumor cells directly into the back of the frontal lobe of the liver through surgery. The Hep3B intraperitoneal (i.p.) model was established by i.p. injection of 3×106 Hep3B GL cells. The Hep3B subcutaneous (s.c.) model or Huh-7 s.c. model was established by s.c. injection of 5×106 Hep3B GL cells or Huh-7-luc cell, respectively. The IMR5 intravenous (i.v.) model was established by i.v. injection of 5×106 IMR5 GL cells. The KLM-1 i.p. model was created by i.p. injection of 5×106 KLM-1 GL cells. The OVCAR8 i.p. model was generated by i.p. injection of 5×106 OVCAR8 GL cells. Two tumor rechallenges were performed using the same dosage of tumor cells at weeks 4 and 9 after CAR-T cell infusion. Tumor volume was calculated as ½ (length×width2 or bioluminescent intensity (Xenogen IVIS Lumina). Mice were randomly allocated into several groups when the tumor signal or volume reached the range set (tumor signal above 1×108 p/sec/cm2/sr; tumor volume above 100 mm3). Mice were euthanized when they met any of the following endpoint criteria: tumor interfered with animals’ ability to eat or drink, 20% weight loss, or any sign of outward distress such as hunched posture, ruffled fur, and reduced motility. A body condition scoring system out of 5 was used.33 As well as a 2,500–3,000 mm3 tumor volume endpoint, a body condition score of <1.5/5, or a decreased activity level to the point of moribundity is used as a criterion for euthanasia. Ex vivo human T cells were isolated from Huh-7 mouse spleen using the Miltenyi Biotec tumor Dissociation Kit. Human CD3+ T cells were separated using anti-CD3 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec).
Histopathological and molecular pathology analysis
After the combination treatment of GPC3 CAR-T with NT-I7 for 1 week or 2 weeks, tumors were resected from the Hep3B s.c. mice, fixed with 10% neutral buffered formalin, and processed for sectioning (Histoserv). Immunohistochemistry staining was performed by the Molecular Histopathology Laboratory at the NCI. Briefly. After antigen retrieval with EDTA (Bond Epitope Retrieval 2) and endogenous peroxidase blocking, sections were incubated with anti-CD3 mAb (Bio-Rad, #MCA1477) and anti-GPC3 mAb (Abcam, #ab95363). Positive controls included human tonsils and human liver tissues. Negative controls included replacing the primary antibody with a non-specific antibody from the same species and of the same isotype. Images were captured using the Aperio Scanscope FL (or XT) whole slide scanner, and staining was interpreted by a board-certified veterinary pathologist. Cell detection algorithms were run to quantify positive cells, which were expressed as the number of positive cells per mm2 of tissue and the percent of positive cells.
Statistics
Experiments were performed at least three times to ensure the reproducibility of results. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism and were presented as mean±SEM. Results were analyzed using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test or two-way analysis of variance with Tukey (or Šidák)’s multiple-comparison test; ns, not significant. P value<0.05 was considered statistically significant. The number of repeats performed is described in legends.
Results
A long-acting IL-7 improves generation of GPC3 CAR-T cells in vitro
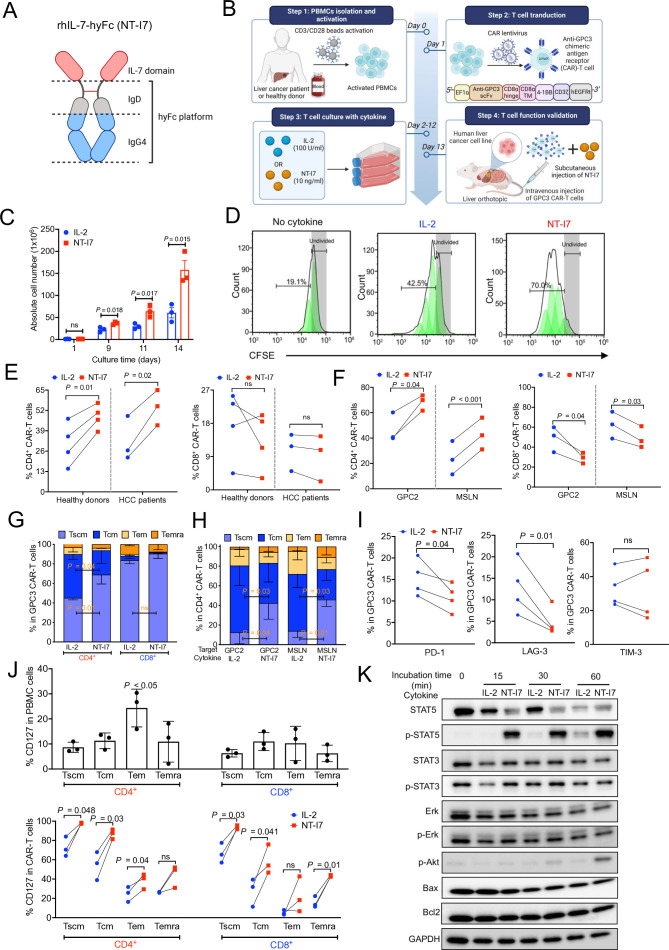
NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa) is an IL-7 fusion protein that combines two IL-7 domains with the hyFc platform, which consists of an IgD hinge and an IgG4 domain (figure 1A). To investigate the potency of NT-I7 on CAR-T cells, we cultured GPC3 CAR-T cells derived from human PBMCs of healthy donors (n=3) with either NT-I7 or IL-2 (figure 1B). In the 2-week in vitro culture system, we found that GPC3 CAR-T cells more efficiently expanded with NT-I7 than with IL-2 (figure 1C,D). In GPC3 CAR-T cells generated from PBMCs of healthy donors (n=4) and patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (n=3), NT-I7 increased the percentage of CD4+ CAR-T cells, while a slightly decreased or similar percentage was found in the CD8+ CAR-T subpopulation (figure 1E). Similar results were observed in the CAR-T cells targeting GPC2 or MSLN (figure 1F). NT-I7 also induced a higher proportion of stem cell-like memory T cells (Tscm) in the CD4+ CAR-T cell subset targeting GPC3, GPC2, and MSLN (figure 1G,H). After a 9-day culture period, NT-I7 reduced the expression of exhaustion markers, PD-1 and LAG-3, on all four donor-derived GPC3 CAR-T cells compared with IL-2, while the expression of T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3) was donor-dependent (figure 1I). In addition to IL-2, we assessed the effects of IL-7 and NT-I7 on the CAR-T cell culture system (online supplemental figure 1). The data revealed no significant difference in cell proliferation, memory T-cell differentiation, or exhaustion marker expression between IL-7 and NT-I7 cultured CAR-T cells. Additionally, compared with IL-7, NT-I7 induced a similar percentage of CD4+ CAR-T cells but a higher percentage of CD8+ CAR-T cells. These data suggest that the distinct impact of IL-2 and NT-I7 on CAR-T cell characteristics is attributable to IL-7 moiety rather than an artifact from the Fc fusion fragment or other engineering components, except the bivalent IL-7 in the NT-I7 molecule (online supplemental figure 1).
Figure 1. NT-I7 improved the generation of GPC3 CAR-T cells cultured in vitro. (A) NT-I7 is a homodimeric IL-7 fused to the hyFc platform, which consists of the IgD CH2 region followed by the C-terminal region of the IgG4 domain. (B) Schematic of GPC3 CAR-T cell production and evaluation in HCC mouse models. IL-2 100 U/mL or NT-I7 10 ng/mL were used to culture CAR-T cells in vitro. (C) In vitro proliferation of GPC3 CAR-T cells stimulated with NT-I7 or IL-2 during 14 days after transduction. n=3 healthy donors/group. (D) GPC3 CAR-T cells were labeled with CFSE before being cultured with NT-I7 or IL-2. CFSE dilution was determined by flow cytometry on day 5. n=3 independent experiments. (E–F) The percentage of CD4+ CAR-T and CD8+ CAR-T subpopulations targeting GPC3, GPC2, and MSLN cultured with NT-I7 or IL-2, by flow cytometry on day 9. The GPC3 CAR-T cells (E) were produced from individual healthy donors (n=4) and patients with HCC (n=3). GPC2 and MSLN CAR-T cells (F) were generated from three healthy donors. (G) Relative proportions of stem cell-like memory (Tscm: CD62L+CD45RA+CD95+), central memory (Tcm: CD62L+CD45RA−CD95+), effector memory (Tem: CD62L−CD45RA−CD95+), and terminally differentiated effector memory (Temra: CD62L−CD45RA+CD95+) subsets defined by CD62L, CD45RA, and CD95 expression in GPC3 CAR-T cell subpopulations cultured with NT-I7 or IL-2 on day 9 after transduction. n=3 donors/group. (H) Phenotype of memory CD4+ CAR-T cells targeting GPC2 or MSLN with NT-I7 or IL-2. n=3 donors/group. (I) Expression of exhaustion markers (PD-1, TIM-3, and LAG-3) across different healthy donor-derived GPC3 CAR-T cells cultured with NT-I7 or IL-2 on day 9. n=4 donors/group. (J) The CD127 expression in the relative proportions of Tscm, Tcm, Tem, and Temra subsets in the CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subpopulations of PBMCs or in vitro cultured GPC3 CAR-T cells. Three donors were used in this analysis. (K) Western blot analysis of T-cell signaling molecules of CAR-T cells on stimulation with NT-I7 or IL-2 at different time courses. Values represent mean±SEM. P value was calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test or two-way analysis of variance with Tukey (or Šidák)’s multiple-comparison test; ns, not significant. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; CFSE, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; GPC2, glypican-2; GPC3, glypican-3; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; hyFc, hybrid Fc; IL, interleukin; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; MSLN, mesothelin; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3.
The interaction between IL-7 and its receptor, IL-7R (CD127), activates pathways like JAK/STAT, regulating lymphocyte survival, proliferation, and differentiation.34,36 To understand IL-7 receptor modulation in CAR-T cells, we examined CD127 expression in PBMCs and memory GPC3 CAR-T cell phenotypes cultured with IL-2 or NT-I7. In the CD4+ T cells, CD127 expression was significantly higher in effector memory T cells (TEM) compared with other memory T phenotypes (figure 1J). Moreover, compared with IL-2, NT-I7 increased CD127 expression in Tscm, central memory T cells (Tcm), and Tem subpopulations of CD4+ CAR-T cells, and in Tscm, Tcm, and terminally differentiated effector memory T cells subpopulations of CD8+ CAR-T cells. These observations suggest that NT-I7 significantly enhances IL-7R expression on CAR-T cells, particularly in less differentiated states like Tscm and Tem subpopulations. Subsequently, we measured downstream phosphorylated (p-) and total STAT5 and STAT3 levels in CAR-T cells. Compared with IL-2, half dose of molecular quantity of NT-I7 significantly increased the levels of p-STAT5 after 15 min incubation and p-Akt after 60 min incubation (figure 1K). However, both IL-2 and NT-I7-treated T cells showed comparable levels of STAT3/p-STAT3 and Erk/p-Erk compared with T cells alone, resulting in similar expression of anti-apoptotic markers like Bax and Bcl2. This evidence suggests that the STAT5 pathway is downstream of NT-I7 signaling on CAR-T cells.
NT-I7 enhances the cytolytic activity of CAR-T cells in vitro
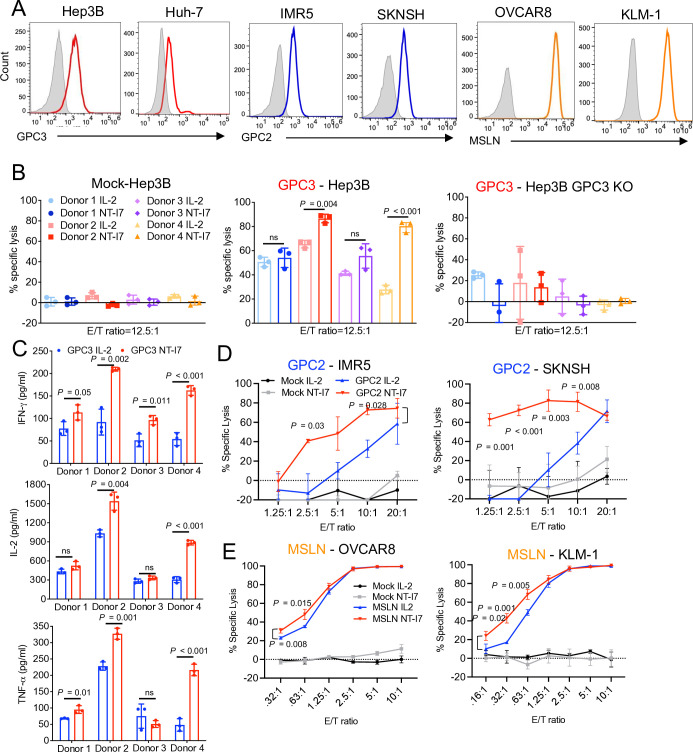
To examine the cytolytic activity of GPC3 CAR-T cells, we incubated them with GPC3-positive HCC cell line Hep3B (figure 2A) or Hep3B GPC3 knockout (KO) cells. GPC3 CAR-T cells derived from donor #2 and donor #4 with NT-I7, showed higher lytic activity than those stimulated with IL-2 on Hep3B but not Hep3B GPC3 KO cells, suggesting that NT-I7 could improve CAR-T potency without causing endotoxicity (figure 2B). In contrast, mock T cells stimulated with NT-I7 showed no cytotoxicity to Hep3B cells (figure 2B). Correlatively, higher levels of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α were released from GPC3 CAR-T cells cultured with NT-I7 when compared with IL-2 (figure 2C), with the expression of IL-2 and TNF-α appearing to vary depending on the donor. Moreover, NT-I7-stimulated GPC2 CAR-T cells also exhibited enhanced cytotoxicity against two GPC2-positive neuroblastoma cell lines, IMR5 and SKNSH, when compared with CAR-T cells cultured with IL-2 (figure 2A,D, and online supplemental figure 2). On incubation with two MSLN-positive tumor cell lines, OVCAR8 and KLM-1, a significantly increased cytotoxicity was observed in MSLN CAR-T cells supported by NT-I7, particularly at low E/T ratios (figure 2A,E, and online supplemental figure 2).
Figure 2. NT-I7 improved the cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells against tumor cells in vitro. (A) Cell surface antigens (GPC3, GPC2, and MSLN) expression in multiple human solid tumor cell lines by flow cytometry. (B) Cytolytic activity of GPC3 CAR-T cells and non-transduced mock-T cells against Hep3B and Hep3B GPC3 KO cells, at an E/T ratio of 12.5:1, for 24 hours of incubation. These cells were produced from four distinct donors. n=3 independent experiments. (C) Cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α) released by NT-I7 or IL-2 stimulated GPC3 CAR-T cells (the same four individual donors as in (B)) in the culture supernatant after 24 hours co-culture with Hep3B cells. n=3 independent experiments. (D) Cytolytic activity of GPC2 CAR-T cells against IMR5 and SKNSH cells at different E/T ratios for 72 hours. n=3 independent experiments. GPC2 CAR-T cells were sourced from a separate donor than those used for GPC3 CAR-T cells. (E) Cytolytic activity of MSLN CAR-T cells (derived from the same donor as used for GPC2 CAR-T cells) against OVCAR8 and KLM-1 cells at different E/T ratios for 72 hours. n=3 independent experiments. Values represent mean±SEM. P value was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test or two-way ANOVA with Šidák’s multiple-comparison test; ns, not significant. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; E:T, effector:target; GPC2, glypican-2; GPC3, glypican-3; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; KO, knockout; MSLN, mesothelin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Overall, we found that NT-I7 was more efficient in modulating CAR-T cell function than IL-2, by increasing CAR-T cell proliferation, a higher percentage of CD4+ CAR-T cells, reducing PD-1 and LAG-3 expression, and enhancing cytotoxicity.
Improved antitumor activity of GPC3 CAR-T cells stimulated with NT-I7 in orthotopic HCC mice
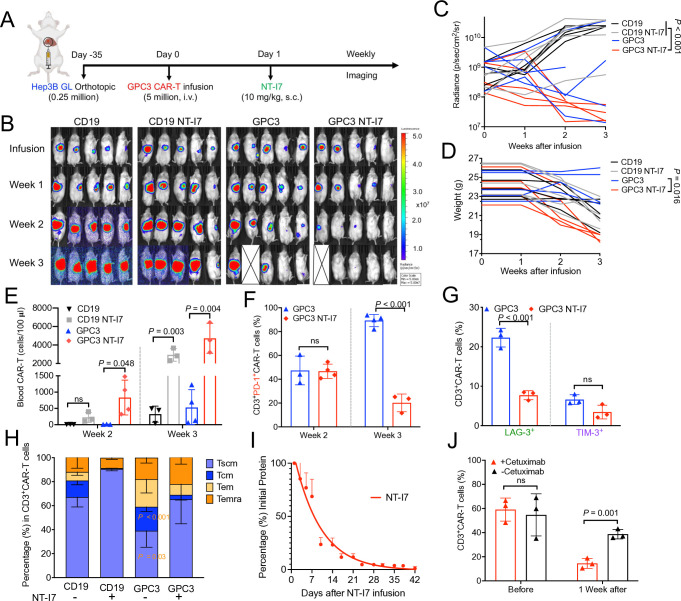
To further evaluate the antitumor efficacy of GPC3 CAR-T cells stimulated with NT-I7, we developed an orthotopic HCC mouse model via liver injection of Hep3B GL tumor cells in immunodeficient mice (NSG, NOD/SCID/IL2rγ−/−), and 35 days later, mice were treated with a single i.v. injection of 5×106 human GPC3 CAR-T or irrelevant CD19 CAR-T cells, followed by an s.c. injection of NT-I7 (10 mg/kg), 1 day after CAR-T infusion (figure 3A). During the 3 weeks after infusion, HCC tumors grew progressively in control mice infused with CD19 CAR-T cells alone or combined with NT-I7 (referred to as CD19 NT-I7), however, GPC3 CAR-T cells significantly regressed tumor burden in three out of five mice (figure 3B,C). Although a decreased body weight was observed in the treatment of GPC3 CAR-T cells combined with NT-I7 (referred to as GPC3 NT-I7), GPC3 NT-I7 significantly accelerated tumor regression in all five mice (figure 3B,C,D).
Figure 3. Enhanced antitumor activity of GPC3 CAR-T cells stimulated with NT-I7 in orthotopic HCC mice. (A) Experimental schema of the orthotopic HCC mouse model. Orthotopic Hep3B GL tumor-bearing NSG mice were intravenous infused with 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells or an equivalent amount of irrelevant CD19 CAR-T cells 35 days post tumor inoculation, followed by an s.c. injection of NT-I7 at 10 mg/kg 1 day after CAR-T infusion. n=5 mice/group. The CAR-T cells used in this figure were produced using donor 1’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells. (B–C) Representative tumor bioluminescence image of mice (B) and tumor growth curve (C) measured by bioluminescence in the treatment groups as shown in (A). (D) Individual mouse body weight. (E) Absolute CAR-T cell number (cells/100 µL blood) was identified in mouse peripheral blood after week 2 and week 3 of infusion. (F–G) PD-1 expression in circulating CD3+ CAR-T cells weeks after infusion (F) and the expression of LAG-3 and TIM-3 (G) at week 3 after infusion. (H) Relative proportions of circulating CAR-T cell immunophenotypes treated with or without NT-I7 after 3 weeks after infusion. (I) Mouse serum concentration-time profiles of the NT-I7. A single s.c. injection of NT-I7 10 mg/kg was administered on day 0. n=3 mice/group. (J) Percentage of mouse circulating GPC3 CAR-T cells before or after 1-week treatment with 0.5 mg cetuximab. n=3 mice/group. Values represent mean±SEM. P value was calculated by was calculated by two-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test; ns, not significant. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; GPC3, glypican-3; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; s.c., subcutaneous; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; Tcm, central memory T cells; Tem, effector memory T cells; Temra, terminally differentiated effector memory; Tscm, stem cell-like memory T cells.
Mice were euthanized due to xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) by the end of week 3 (online supplemental figure 3). A necropsy examination was subsequently performed on the four treatment groups (CD19 CAR-T, GPC3 CAR-T, NT-I7 alone, and GPC3 CAR-T plus NT-I7) to gain further insight into the impact of NT-I7 at this dose level (online supplemental table 1). A significant elevation in white blood cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils was observed in mice leukocytes (blood samples) that received combination treatment. While no significant disparity was detected in organ weights, the combination treatment group showed a reduced number of reticulocytes and an increased concentration of alanine aminotransferase.
To identify the factors contributing to the higher efficiency of combined GPC3 CAR-T cells with NT-I7, we analyzed circulating CAR-T cells at different time points post-infusion. A significant increase in GPC3 CAR-T cells stimulated with NT-I7 was found at weeks 2 and 3, while CD19 CAR-T cells treated with NT-I7 expanded only at week 3 (figure 3E). Moreover, NT-I7 significantly reduced the expression of T-cell exhaustion markers (PD-1 and LAG-3) on circulating GPC3 CAR-T cells at week 3 after treatment (figure 3F,G). We also observed a higher percentage of Tscm proportion in the persistent NT-I7-supported circulating CAR-T cells (figure 3H). To investigate the stability of NT-I7 in mice, we isolated mouse serum during a time course and estimated the serum half-life of NT-I7 to be approximately 6.37 days (figure 3I).
To avoid the toxic risk of T-cell hyperactivation, we previously designed a truncated human epidermal growth factor receptor tag expressed on CAR-T cells that functions as an OFF switch in the presence of the FDA-approved drug, cetuximab.30 A single dose of 0.5 mg cetuximab significantly reduced the number of circulated CAR-T cells after 1 week (figure 3J).
Lower NT-I7 dosage improvedGPC3 CAR-T cell therapy efficacy and reduced toxicity
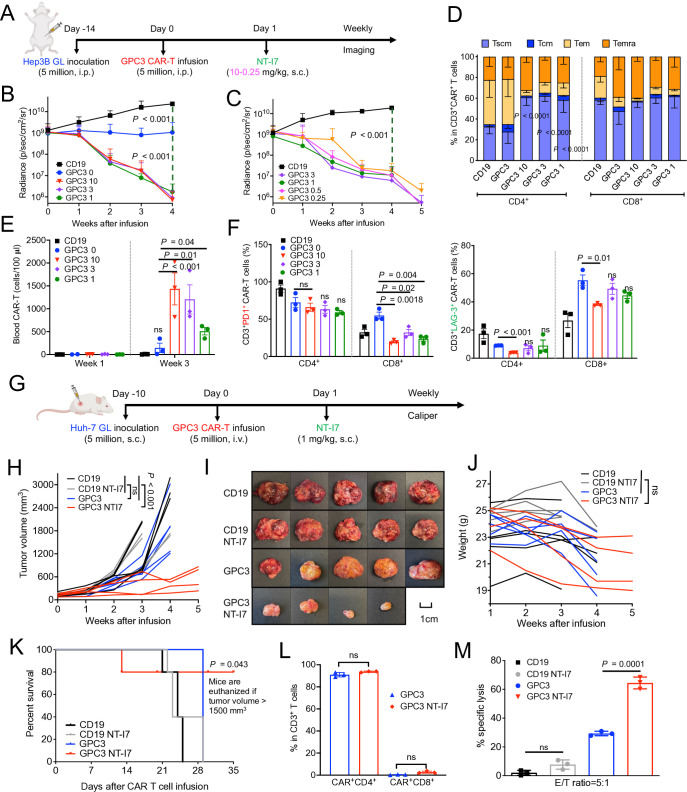
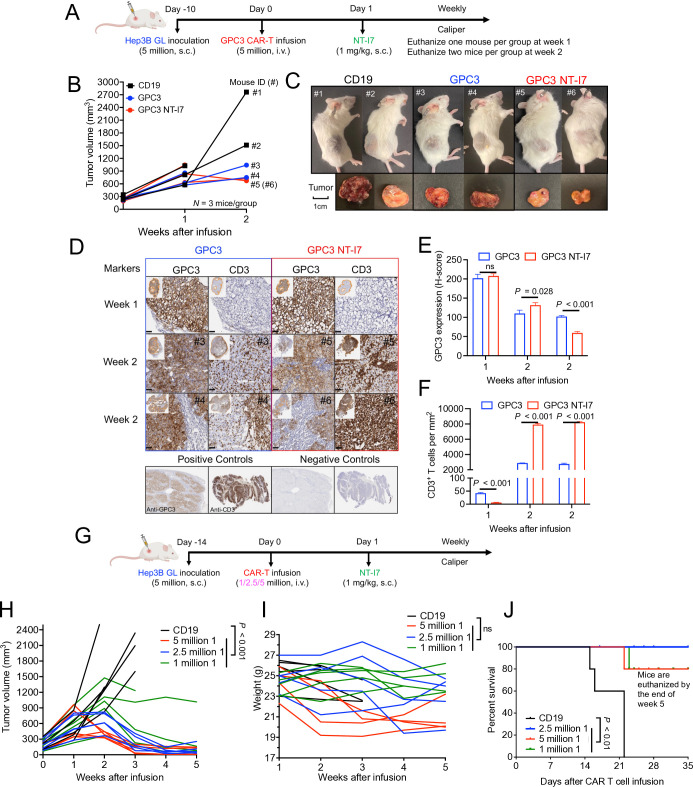
To determine the optimal dosage of NT-I7 combined with GPC3 CAR-T cells in vivo, we administered 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells followed by a gradually decreasing dose regimen (ranging from 10–3 mg/kg to 3–0.25 mg/kg) of NT-I7 in the Hep3B i.p. xenograft model (figure 4A). Compared with the CD19 CAR-T cells control group, mice infused solely with GPC3 CAR-T cells exhibited notable tumor inhibition, while mice infused with the same amount of GPC3 CAR-T cells and varying NT-I7 dose (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) further improved tumor regression, with comparable regression seen among different NT-I7 dose levels (figure 4B). Mice infused with NT-I7 at 0.5 mg/kg and 0.25 mg/kg, with 5×106 CAR-T cells, exhibited tumor shrinkage (figure 4C), and evidenced the potency of NT-I7 in enhancing the efficacy of CAR-T cells. In comparison to the CD19 control group, all GPC3 CAR-T treatment groups demonstrated prolonged mouse survival (online supplemental figure 4). Analyses of circulating CAR-T cells in mice 3 weeks post-infusion revealed a higher proportion of Tscm in the NT-I7-supported CD4+ GPC3 CAR-T subpopulation than in CAR-T alone (figure 4D). Moreover, we noted a progressive increase in GPC3 CAR-T cells exhibiting reduced expression of PD-1 and LAG-3 in the combination groups, particularly in the cohort receiving a dosage of 10 mg/kg NT-I7 (figure 4E,F).
Figure 4. Enhanced antitumor activity of GPC3 CAR-T cells and low dose NT-I7 against low antigen-density hepatocellular carcinoma tumors. (A) Experimental schema of the Hep3B i.p. xenograft model. The mice were intravenous infused with 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells or an equivalent amount of irrelevant CD19 CAR-T cells after 14 days of tumor inoculation, followed by a single s.c. injection of NT-I7 at a gradually decreasing dose regimen (ranging from 10 to 0.25 mg/kg). n=5 mice/group. The CAR-T cells were obtained from the NCI clinical center (source from a different donor). (B–C) Hep3B tumor growth curve measured by bioluminescence in the treatment groups of CAR-T combined with different dosages of NT-I7 at 10–3 mg/kg (B) or 3–0.25 mg/kg (C). (D) The relative proportion of the circulating CD4+ and CD8+ CAR-T cells immunophenotypes in combination with different doses of NT-I7 at week 3 after infusion. n=3 samples/group. (E) Absolute CAR-T number (cells/100 µL blood) was identified in mouse peripheral blood after week 1 and week 3 of infusion. n=3 individual samples/group. (F) The expression of PD-1 and LAG-3 in circulated CD4+ CAR-T and CD8+ CAR-T subpopulations at week 3 of infusion. n=3 samples/group. (G) Experimental schema of the Huh-7 s.c. xenograft model. The mice were intravenous infused with 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells, followed by a single s.c. injection of 1 mg/kg NT-I7. The CAR-T cells were obtained from the NCI clinical center (source from a different donor). (H) Huh-7 tumor growth curve was measured by caliper in the CAR-T treatment groups, as shown in (G). n=5 mice/group. (I) The sizes of Huh-7 tumors in individual mice from four different treatment groups at the end of the study. (J) Mouse body weight. (K) Kaplan-Meier survival curve in the Huh-7 s.c. mice. (L) The percentage of tumor-infiltrated CD4+ and CD8+ CAR-T subpopulations recovered from mice spleen. (M) Ex vivo cytotoxicity of mouse-recovered CD19 or GPC3 CAR-T cells against Huh-7 cells for 24 hours incubation. Values represent mean±SEM. P value was calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test or two-way analysis of variance with Tukey (or Šidák)’s multiple-comparison test; ns, not significant. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; E:T, effector:target; GPC3, glypican-3; i.p., intraperitoneal; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; s.c., subcutaneous; Tcm, central memory T cells; Tem, effector memory T cells; Temra, terminally differentiated effector memory; Tcm, stem cell-like memory T cells.
Superior antitumor activity of the GPC3 CAR-T NT-I7 combination treatment against low antigen-density tumor
A significant challenge in CAR-T cell treatment for solid tumors is antigen heterogeneity, hampering the eradication of tumor cells with low antigen expression. We demonstrated the variation in the GPC3 expression between two HCC cell lines, Hep3B (9.3×103 molecules/cell) and Huh-7 (5.7×102 molecules/cell) (figure 2A). To examine the potency of the combination treatment of GPC3 CAR-T cells and NT-I7, we constructed an Huh-7 s.c. model and intravenous infused 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells followed by s.c. infusion of low dose (1 mg/kg) NT-I7 1-day later (figure 4G). As depicted in figure 4H, tumors grew progressively in mice infused with either CD19 CAR-T cells alone or a combination of CD19 CAR-T and NT-I7. The administration of 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells alone failed to control tumor growth, whereas the addition of NT-I7 significantly enhanced the efficacy of GPC3 CAR-T cells, resulting in notable tumor inhibition and longer survival over 5 weeks post-treatment (figure 4H,I,K). While a slight decrease in body weight was observed in the GPC3 CAR-T and GPC3 CAR-T with NT-I7 groups, the decline remained within acceptable limits (<20% decrease), and mice remained active throughout the duration of the study (figure 4J). Regarding the persistent CAR-T cells on NT-I7 stimulation, we observed that the predominant population comprises CD4+ Tem (figure 4L and online supplemental figure 5A), exhibiting enhanced ex vivo cytotoxicity against Huh-7 tumor cells (figure 4M). Furthermore, we noted upregulation of CD127 expression across all memory T-cell phenotypes (online supplemental figure 5).
Therefore, administration of 1 mg/kg NT-I7 effectively enhanced the efficacy of GPC3 CAR-T cells, leading to successful inhibition of tumor growth in the Huh-7 s.c. mouse model, despite the low expression of GPC3 by tumor cells.
NT-I7 enhances GPC3 CAR-T cell efficacy via increased T-cell infiltration in HCC tumors
To determine the impact of NT-I7 treatment on GPC3 CAR-T infiltration of HCC tumors, we established an s.c. Hep3B model. Mice were intravenous infused with 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells, followed by s.c. administration of 1 mg/kg NT-I7 1 day later (n=3 mice/group) (figure 5A). In order to investigate tumor phenotype and CAR-T infiltration, we euthanized one mouse in the first week and two mice in the second week for each treatment group. By the end of week 2, both the GPC3 CAR-T cells alone and GPC3 CAR-T plus NT-I7 groups demonstrated smaller tumor volumes than the CD19 CAR-T cells group (figure 5B,C). We further examined the enrichment and spatial distribution of GPC3 CAR-T cells in the tumor by histology. GPC3 protein was highly expressed in tumor cells in both GPC3 CAR-T cells alone and the combination treatment groups. However, on comparison of weeks 1 and 2 samples, a decrease in GPC3 expression was evidenced in the combination treatment groups (figure 5D,E). The distribution of tumor-infiltrating CD3+ CAR-T cells spanned throughout the tumor, with a higher abundance of CAR-T cells observed in the group treated with NT-I7, especially at week 2 (figure 5D,F). These findings suggest that NT-I7 facilitates increased levels of infiltrating CAR-T cells, contributing to improved antitumor activity.
Figure 5. NT-I7 enhances GPC3 CAR-T cells efficacy via increased T-cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma tumors. (A) Experimental schema of the Hep3B s.c. xenograft model. Mice were intravenous infused with 5×106 CAR-T cells, followed by a single s.c. injection of 1 mg/kg NT-I7. n=3 mice/group. (B) Hep3B tumor growth curves measured by caliper during 2 weeks of treatment. Mouse ID (#) of individual mice from treatment groups is shown for week 2. The CAR-T cells were produced using donor 1’s PBMCs. (C) Visualization of mice and their respective tumors at week 2. (D) GPC3 CAR-T cell infiltration in Hep3B tumor tissues. Microscopic examination of immunochemical tissue sections were conducted and positive staining was quantified. The combination of anti-CD3 mAb and anti-GPC3 monoclonal antibody was used for primary staining. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E and F) Quantification of GPC3 expression (E) and number of CD3+ T cells (cell number/mm2) (F) in Hep3B tumor tissues in (D). n=3 independent calculation/group. (G) Experimental schematic of Hep3B i.p. model. Mice were intravenous infused with GPC3 CAR-T cells at different doses (5, 2.5, or 1×106), followed by a single s.c. injection of 1 mg/kg NT-I7. n=5 mice/group. The CAR-T cells were produced using donor 1’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells. (H–J) Tumor growth curves (H) and body weight (I) and Kaplan-Meier survival curves (J) of mice from different treatment groups during 5 weeks of treatment. Values represent mean±SEM. P value was calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test or two-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test; ns, not significant. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; GPC3, glypican-3; i.p., intraperitoneal; s.c., subcutaneous.
Low-dose CAR-T cell therapy has been recognized for its safety and efficacy in clinical settings.37 To assess the dose-dependent effectiveness of GPC3 CAR-T cell therapy in combination with NT-I7, we used the same Hep3B s.c. model. Mice were intravenous infused with three different doses (5, 2.5, or 1×106 cells) of GPC3 CAR-T cells, followed by s.c. administration of 1 mg/kg NT-I7 (figure 5G). As shown in figure 5H, the antitumor efficacy of the combination treatment is CAR-T cell dose-dependent, and even the lowest dose of GPC3 CAR-T cells in combination with NT-I7 displayed the ability to suppress tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, we observed that the number of CAR-T cells administered caused changes in the body weight of mice, particularly at the highest dose when combined with NT-I7 (figure 5I). However, a recovery in body weight was observed after week 3 of treatment, suggesting that combination therapy is safe. Notably, mice receiving the combination of GPC3 CAR-T cells and NT-I7 exhibited significantly extended survival compared with the CD19 CAR-T control group (figure 5J).
NT-I7 enhances the efficacy of GPC2 CAR-T cells against neuroblastoma
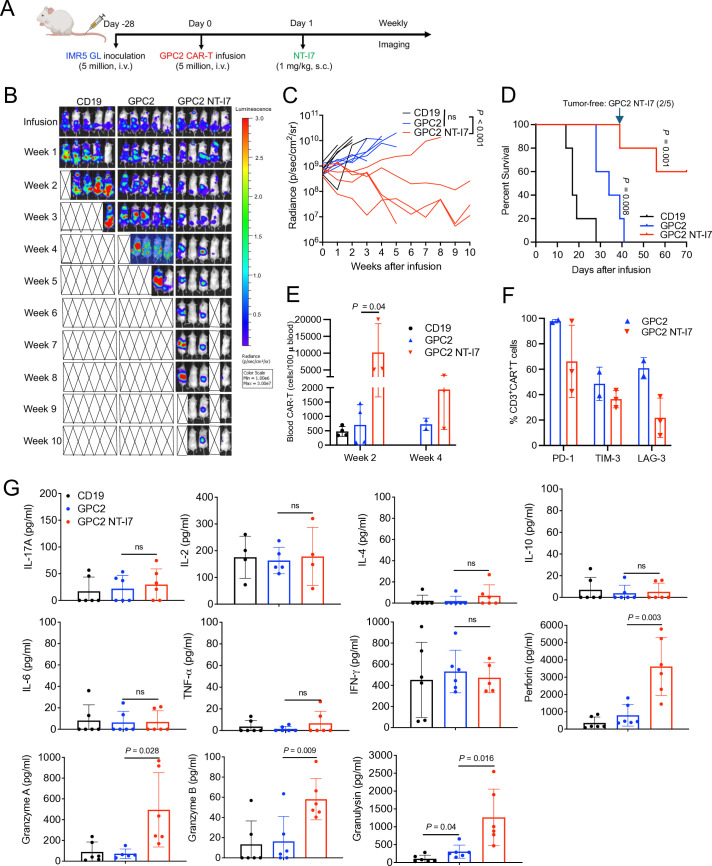
To explore the potential of NT-I7 as an adjunct to GPC2 CAR-T cells in neuroblastoma therapy, we established a metastatic neuroblastoma model by intravenous injection of the IMR5 tumor cell line. The IMR5 mice model was infused with 5×106 GPC2 CAR-T cells followed by 1 mg/kg NT-I7 1-day later (figure 6A). The administration of GPC2 CAR-T cells alone had limited effectiveness in tumor growth (figure 6B,C) or extending survival (figure 6D). However, when combined with NT-I7, tumor regression was observed in four out of five mice (figure 6B,C), leading to an extension of their survival (figure 6D) without decreased body weight (online supplemental figure 6). Furthermore, during 4 weeks of infusion, we observed a greater number of circulating GPC2 CAR-T cells expressing lower levels of LAG-3 in the combination group (figure 6E,F). In mouse circulation, GPC2 CAR-T combined with NT-I7 significantly increased the secretion of cytotoxic granular proteins (perforin, granzymes, and granulysin) compared with CAR-T cell treatment alone (figure 6G).
Figure 6. NT-I7 enhances GPC2 CAR-T efficacy against neuroblastoma. (A) Experimental schema of the IMR5 intravenous xenograft model. Mice were intravenous infused with 5×106 CAR-T cells, followed by a single s.c. injection of 1 mg/kg NT-I7. n=5 mice/group. The CAR-T cells were produced using donor 2’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells. (B–C) Representative tumor bioluminescence image of mice (B) and tumor growth curve (C) in the treatment groups as shown in (A). (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mice. (E) Absolute CAR-T cells number (cells/100 µL blood) was identified in mouse peripheral blood after week 2 and week 4 of infusion. n=2/3 samples/group. (F) Expression of PD-1, TIM-3, and LAG-3 in circulating CAR-T cells at week 4 after infusion. n=2/3 individual samples/group. (G) Mouse plasma cytokine detection at week 2 after infusion. n=3 individual mice/group from replicate assays. Values represent mean±SEM. P value was calculated by two-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test or a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test; ns, not significant. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; GPC2, glypican-2; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; s.c., subcutaneous; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Collectively, these findings provide evidence that the combination of GPC2-targeted CAR-T cells and NT-I7 enhances antitumor activity against neuroblastoma by promoting T-cell expansion and mitigating T-cell exhaustion, thereby facilitating persistent CAR-T cells in vivo.
NT-I7 enhances CAR-T cell efficacy against MSLN-positive ovarian cancer and pancreatic cancer
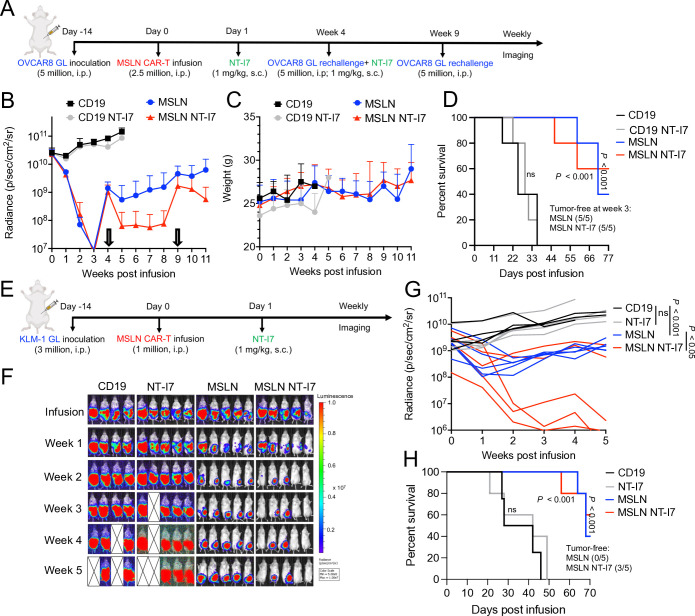
To assess the impact of NT-I7 on the antitumor efficacy of enduring CAR-T cells in the context of recurrent ovarian cancer, we administered MSLN CAR-T cells followed by NT-I7 in a murine model with two tumor rechallenges (figure 7A). While 2.5×106 MSLN CAR-T cells initially caused tumor regression, they failed to control regrowth after the first rechallenge at week 4 (figure 7B). However, when the mice who originally received the combination of CAR-T cells and NT-I7 were rechallenged at week 4 and treated with a second injection of NT-I7, they maintained antitumor activity (figure 7B). Even after a second rechallenge at week 9, tumor growth was controlled with no side effects (figure 7B–D).
Figure 7. NT-I7 enhances MSLN CAR-T cells efficacy against ovarian and pancreatic cancer. (A) Experimental schema of the OVCAR8 i.p. xenograft model. Mice were i.p. infused with 2.5×106 CAR-T cells, followed by a single s.c. injection of 1 mg/kg NT-I7. Two tumor rechallenges were performed at weeks 4 and 9 after CAR-T cells infusion. The second injection of NT-I7 was performed after tumor rechallenge at week 4. n=5 mice/group. The CAR-T cells were produced using donor 2’s PBMCs. (B) Tumor growth curves were measured by bioluminescence. (C) Mice body weight in the treatment groups. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of OVCAR8 mice. (E) Experimental schema of the KLM-1 i.p. xenograft model. Mice were i.p. infused with 1×106 CAR-T cells, followed by a single s.c. injection of 1 mg/kg NT-I7. n=4/5 mice/group. The CAR-T cells were produced using donor 2’s PBMCs. (F–G) Representative tumor bioluminescence image of mice (F) and tumor growth curve (G) measured by bioluminescence in the treatment group. (H) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of KML-1 mice. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; i.p., intraperitoneal; MSLN, mesothelin; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; s.c., subcutaneous.
To further evaluate the impact of NT-I7 using a low dosage of MSLN CAR-T cells, we established the KLM-1 pancreatic cancer model and treated mice with 1×106 MSLN CAR-T cells followed by 1 mg/kg NT-I7 (figure 7E). On comparison, the combination therapy exhibited superior efficacy over monotherapy treatment, resulting in continual tumor control in three out of five mice having persistent tumor control (figure 7F,G), and extending survival time (figure 7H) without any decrease in body weight (online supplemental figure 7).
Overall, NT-I7 shows significant potential in enhancing CAR-T cell persistence for MSLN-positive solid tumors.
Discussion
Despite extensive efforts in CAR construct engineering, the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy as a “living drug” for solid tumor treatment remains unsupported in clinical settings. To address this limitation, novel strategies to improve the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy without increasing the toxicity are needed. In the present study, we evaluated a combination therapy approach using a long-acting NT-I7 together with CAR-T cells targeting different antigens (GPC3, GPC2, or MSLN), across multiple human tumor types (liver cancer, neuroblastoma, ovarian cancer, and pancreatic cancer) in murine models. We demonstrated that adding NT-I7 to CAR-T cells enhanced the occupancy of the CD4+ CAR-T cell subpopulation and improved T-cell expansion. Furthermore, we identified that 1 mg/kg NT-I7 was safe and significantly improved CAR-T cell efficacy. This augmentation was attributed to the expansion of stem cell-like memory CAR-T cells, increased CAR-T cell persistence, and facilitated tumor infiltration. Notably, the synergistic effect of GPC3 CAR-T cells combined with NT-I7 was most pronounced in the low-antigen presenting HCC model. Our findings suggest that the integration of NT-I7 may serve as a crucial adjunct to CAR-T cell therapy for enhancing its efficacy in solid tumors.
As CAR-T cells are currently administered as an autologous therapy, each patient receives a distinct therapeutic agent derived from their own PBMCs. Under in vitro IL-2 incubation, we observed decreased expansion of HCC patients PBMC-derived GPC3 CAR-T cells and a gradual decline of CAR expression over time. Conversely, the application of NT-I7, which shares similar properties with IL-7,38 39 resulted in enhanced CAR-T cell proliferation and effectively mitigated exhaustion. Crucially, we have shown a substantially elevated percentage of CD4+ CAR-T cells supported by NT-I7, compared with those cultured with IL-2. This observation may be attributed to the potential role of IL-7 in promoting human CD4+ T-cell survival and proliferation, as well as providing signals required for TCR-induced activation.40 41 In a previously reported study, in vitro expansion of anti-CD19 CAR-T supported by NT-I7 revealed a higher proportion of Tcm and Tem compared with the input T cells in mice,26 which was validated throughflow cytometry staining with CD45RO and CCR7. To include the novel stem-like memory population within CAR-T cells, we expanded the flow cytometry markers to include CD95, CD62L, and CD45RA. Our findings demonstrated that NT-I7 treatment resulted in a higher proportion of stem cell-like memory CAR-T cells, both in vitro and in vivo, highlighting the potential for NT-I7 to enhance the therapeutic potential and consistency of CAR-T cell therapy in cancer treatment.
To minimize potential confounding effects from endogenous mouse T cells due to NT-I7 cross-reactivity, we established xenograft models using immunodeficient mice and evaluated the therapeutic impact of combining GPC3 CAR-T cells with NT-I7. The combination therapy significantly reduced HCC tumor size, due to a pronounced increase in CAR-T cell tumor infiltration and enhanced cell function. Notably, this combined approach demonstrated robust antitumor efficacy, particularly in the Huh-7 model with low-density GPC3 expression, presenting a promising avenue for patients with heterogeneous antigenic profiles in clinical cell-based immunotherapy. Despite the lack of toxicity in immunocompetent mice when administering a 10 mg/kg dose NT-I7 (equal to 813 µg/kg in humans) in combination with mouse anti-CD19 CAR-T cells, as previously reported,26 we noted a reduction in body weight in HCC mouse models when the same dosage of NT-I7 was combined with 5×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells. Besides body weight reduction, other symptoms of xenogeneic GvHD, such as fur loss and scaling skin, were observed, resulting from the heightened proliferation of 5 million GPC3 CAR-T cells on 10 mg/kg NT-I7 stimulation. To address this issue, we optimized the NT-I7 dosage and found that 1 mg/kg NT-I7 was equally effective for 5 million GPC3 CAR-T cells while minimizing toxicity in mice during liver cancer treatment. Importantly, this optimized dosage was also efficacious in treating neuroblastoma with GPC2 CAR-T cells and ovarian cancer with MSLN CAR-T cells, indicating broad applicability across cancer types.
Considering the potency of NT-I7 in increasing CAR-T cell numbers and addressing the issue of CAR-T-induced xenogeneic GvHD, we hypothesized that it could potentially reduce the minimum required dose of CAR-T cells. To explore this possibility, we optimized the dosage of GPC3 CAR-T cells by administering 1, 2.5, and 5×106 cells in combination with 1 mg/kg NT-I7 in a Hep3B subcutaneous mouse model. Remarkably, even the combination therapy involving a low dose of 1×106 GPC3 CAR-T cells with 1 mg/kg NT-I7 reduced Hep3B tumor size. These findings suggest that NT-I7 may be a cost-effective and safe strategy to address the financial and toxicity concerns associated with CAR-T cell therapy.
In a murine glioma model, when combined with radiotherapy, NT-I7 was observed to increase the number of tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic CD8+ murine T lymphocytes, resulting in improved survival.21 Conversely, in a murine leukemia model, NT-I7 was reported to have a more balanced impact on CD4+ and CD8+ endogenous T cells, with a notable effect on the CD4+ subset of CAR-T cells.26 In particular, in our xenograft model featuring various solid tumors, the persistent CAR-T cell population predominantly comprised CD4+ T cells. This observation aligns with a study involving two patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with CD19 CAR-T cells for over a decade, where a highly activated CD4+ population dominated the CAR-T cell population, which retained its cytotoxic characteristics.42 These findings suggest that the CD4+ population is closely related to the antitumor response and long-term remission of CAR-T cells and indicate that NT-I7 may hold clinical potential in enhancing such responses.
In summary, our data demonstrate that NT-I7 induces a remarkable enhancement in CAR-T cell proliferation, persistence, cytotoxicity, and tumor infiltration, culminating in a significant improvement in antitumor activity and survival in mice. These novel findings provide the rationale for NT-I7 plus CAR-T cell combination therapy in humans for treating multiple solid tumors.
supplementary material
Footnotes
Funding: This work was supported by US Department of Health and Human Services, the Intramural Research Program of National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI), Center for Cancer Research (CCR) (Z01 BC010891 and ZIA BC010891 to MH) and by a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with NeoImmuneTech.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Patient consent for publication: Not applicable.
Ethics approval: All mice were housed and treated under the protocol (LMB-059) approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the NIH.
Contributor Information
Dan Li, Email: dan.li2@nih.gov.
Tianyuzhou Liang, Email: TIL120@pitt.edu.
Laura E Hutchins, Email: laura.hutchins@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
Alexandra A Wolfarth, Email: awolfarth@neoimmunetech.com.
Sara Ferrando-Martinez, Email: sfm@neoimmunetech.com.
Byung Ha Lee, Email: blee@neoimmunetech.com.
Mitchell Ho, Email: homi@mail.nih.gov.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
References
- 1.Curran KJ, Pegram HJ, Brentjens RJ. Chimeric antigen receptors for T cell immunotherapy: current understanding and future directions. J Gene Med. 2012;14:405–15. doi: 10.1002/jgm.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen YJ, Abila B, Mostafa Kamel Y. CAR-T: what is next? Cancers (Basel) 2023;15:663. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thistlethwaite FC, Gilham DE, Guest RD, et al. The clinical efficacy of first-generation carcinoembryonic antigen (CEACAM5)-specific CAR T cells is limited by poor persistence and transient pre-conditioning-dependent respiratory toxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017;66:1425–36. doi: 10.1007/s00262-017-2034-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shi D, Shi Y, Kaseb AO, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-glypican-3 T-cell therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of phase I trials. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:3979–89. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hartmann J, Schüßler-Lenz M, Bondanza A, et al. Clinical development of CAR T cells-challenges and opportunities in translating innovative treatment concepts. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9:1183–97. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201607485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marofi F, Motavalli R, Safonov VA, et al. CAR T cells in solid tumors: challenges and opportunities. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:81. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02128-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Maalej KM, Merhi M, Inchakalody VP, et al. CAR-cell therapy in the era of solid tumor treatment: current challenges and emerging therapeutic advances. Mol Cancer. 2023;22:20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01723-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sengsayadeth S, Savani BN, Oluwole O, et al. Overview of approved CAR‐T therapies, ongoing clinical trials, and its impact on clinical practice. eJ Haem. 2022;3:6–10. doi: 10.1002/jha2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schluns KS, Lefrançois L. Cytokine control of memory T-cell development and survival. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:269–79. doi: 10.1038/nri1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang DKY, Adu-Berchie K, Iyer S, et al. Enhancing CAR-T cell functionality in a patient-specific manner. Nat Commun. 2023;14:506. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36126-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wrangle JM, Patterson A, Johnson CB, et al. IL-2 and beyond in cancer immunotherapy. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018;38:45–68. doi: 10.1089/jir.2017.0101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Silveira CRF, Corveloni AC, Caruso SR, et al. Cytokines as an important player in the context of CAR-T cell therapy for cancer: their role in tumor immunomodulation, manufacture, and clinical implications. Front Immunol. 2022;13:947648. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Adachi T, Kobayashi T, Sugihara E, et al. Hair follicle-derived IL-7 and IL-15 mediate skin-resident memory T cell homeostasis and lymphoma. Nat Med. 2015;21:1272–9. doi: 10.1038/nm.3962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhou J, Jin L, Wang F, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells expanded with IL-7/IL-15 mediate superior antitumor effects. Protein Cell. 2019;10:764–9. doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-0643-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pang N, Shi J, Qin L, et al. IL-7 and CCL19-secreting CAR-T cell therapy for tumors with positive glypican-3 or mesothelin. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:118. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Castella M, Caballero-Baños M, Ortiz-Maldonado V, et al. Point-of-care CAR T-cell production (ARI-0001) using a closed semi-automatic bioreactor: experience from an academic phase I clinical trial. Front Immunol. 2020;11:482. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lim JY, Kim NA, Lim DG, et al. Biophysical stability of hyFc fusion protein with regards to buffers and various excipients. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;86:622–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee SW, Choi D, Heo M, et al. HIL-7-hyFc, A long-acting IL-7, increased absolute lymphocyte count in healthy subjects. Clin Transl Sci. 2020;13:1161–9. doi: 10.1111/cts.12800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim S, Lee SW, Koh JY, et al. A single administration of hil-7-hyFc induces long-lasting T-cell expansion with maintained effector functions. Blood Adv. 2022;6:6093–107. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Naing A, Mamdani H, Barve MA, et al. Efficacy and safety of NT-I7, long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: results from the phase 2a study. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:2514. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.2514. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Campian JL, Ghosh S, Kapoor V, et al. Long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:1229–39. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ahn S, Park JS, Kim H, et al. Compassionate use of recombinant human IL-7-hyFc as a salvage treatment for restoring lymphopenia in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 2023;12:6778–87. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Butt O, Tao Y, Huang J, et al. 624 A phase I/II study evaluating the safety and efficacy of A novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy. J Immunotherap Cancer. 2022;10:A656. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-SITC2022.0624. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Naing A, Mamdani H, Barve M, et al. 652 NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting IL-7, in combination with pembrolizumab improves T cell fitness in heavily pretreated subjects with gastrointestinal tumors. J Immunotherap Cancer. 2023;11 doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-SITC2023.0652. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee M, Im SK, Baek S, et al. rhIL-7-hyFc and hil-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that improves antitumor efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2024;12:e008001. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim MY, Jayasinghe R, Devenport JM, et al. A long-acting interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, enhances CAR T cell expansion, persistence, and anti-tumor activity. Nat Commun. 2022;13:3296. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30860-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.O’Neal J, Cooper ML, Ritchey JK, et al. Anti-myeloma efficacy of CAR-inkt is enhanced with a long-acting IL-7, rhIL-7-hyFc. Blood Adv. 2023;7:6009–22. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xiang J, Devenport JM, Carter AJ, et al. An “off-the-shelf” CD2 universal CAR-T therapy for T-cell malignancies. Leukemia. 2023;37:2448–56. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-02039-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li N, Torres MB, Spetz MR, et al. CAR T cells targeting tumor-associated exons of glypican 2 regress neuroblastoma in mice. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li D, Li N, Zhang Y-F, et al. Persistent polyfunctional chimeric antigen receptor T cells that target glypican 3 eliminate orthotopic hepatocellular carcinomas in mice. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:2250–65. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tomar S, Zhang J, Khanal M, et al. Development of highly effective anti-mesothelin hYP218 chimeric antigen receptor T cells with increased tumor infiltration and persistence for treating solid tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21:1195–206. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun M, Cao Y, Okada R, et al. Preclinical optimization of a GPC2-targeting CAR T-cell therapy for neuroblastoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11:e005881. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ullman-Culleré MH, Foltz CJ. Body condition scoring: a rapid and accurate method for assessing health status in mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1999;49:319–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chetoui N, Boisvert M, Gendron S, et al. Interleukin-7 promotes the survival of human CD4+ effector/memory T cells by up-regulating Bcl-2 proteins and activating the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Immunology. 2010;130:418–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lin JX, Leonard WJ. The role of Stat5a and Stat5b in signaling by IL-2 family cytokines. Oncogene. 2000;19:2566–76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Palmer MJ, Mahajan VS, Trajman LC, et al. Interleukin-7 receptor signaling network: an integrated systems perspective. Cell Mol Immunol. 2008;5:79–89. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2008.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pan J, Yang JF, Deng BP, et al. High efficacy and safety of low-dose CD19-directed CAR-T cell therapy in 51 refractory or relapsed B acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Leukemia. 2017;31:2587–93. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cieri N, Camisa B, Cocchiarella F, et al. IL-7 and IL-15 instruct the generation of human memory stem T cells from naive precursors. Blood. 2013;121:573–84. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-431718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Li L, Li Q, Yan ZX, et al. Transgenic expression of IL-7 regulates CAR-T cell metabolism and enhances in vivo persistence against tumor cells. Sci Rep. 2022;12 doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16616-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lawson BR, Gonzalez-Quintial R, Eleftheriadis T, et al. Interleukin-7 is required for CD4(+) T cell activation and autoimmune neuroinflammation. Clin Immunol. 2015;161:260–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Silva SL, Albuquerque AS, Matoso P, et al. IL-7-induced proliferation of human naive CD4 T-cells relies on continued thymic activity. Front Immunol. 2017;8:20. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Melenhorst JJ, Chen GM, Wang M, et al. Decade-long leukaemia remissions with persistence of CD4+ CAR T cells. Nature New Biol. 2022;602:503–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04390-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.