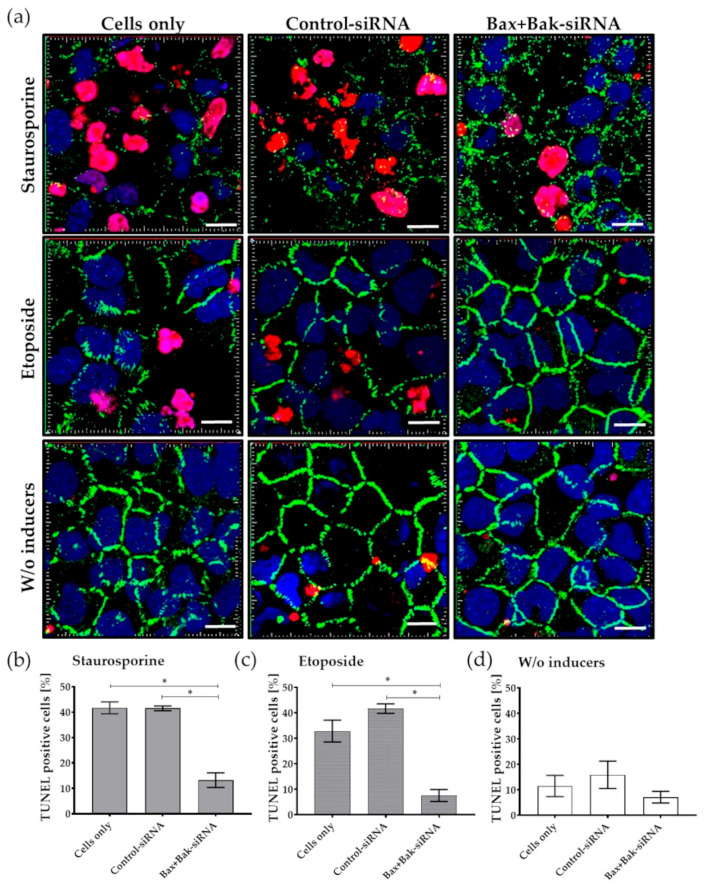
Figure 6.
Detection of apoptosis rate by TUNEL assay in human corneal endothelial cells (HCECs) after transfection with Accell Control-siRNA or Bax+Bak-siRNA compared to untransfected cells (Cells only). After incubation for 96 h, the apoptosis inducers staurosporine (250 nM for 6 h) or etoposide (42.5 µM for 21 h) were added. (a) Exemplary images of apoptosis rate and changes in cell morphology in HCECs labeled with TUNEL assay and staining of cell-cell contacts (ZO-1). Note that due to the induction of apoptosis, many nuclei of apoptotic cells (red) and gaps in the cell-cell barrier (green) could be detected in controls—Cells only and Control-siRNA. In contrast, almost no TUNEL-positive cells are found in Bax+Bak-siRNA-transfected cells, and tight cell-cell contact of HCECs can be observed, comparable to endothelial cells without (w/o) apoptosis induction for etoposide and to a lesser extent for staurosporine. (LSM780, Zeiss; red: TUNEL—apoptotic DNA fragmentation, blue: Dapi—cell nuclei, green: ZO-1—cell-cell contacts; 63× oil objective, zoom 2, 3D overlay, bar = 10 µm). Images were taken from five random fields, TUNEL-positive cells were counted, and the percentage for (b) staurosporine, (c) etoposide, and (d) cells treated without inducers was calculated. Quantification clearly shows that the apoptosis rate was reduced after the knockdown of Bax+Bak. (ImageJ; n = 3, mean ± s.e.m., RM one-way ANOVA posthoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test: * p < 0.05).