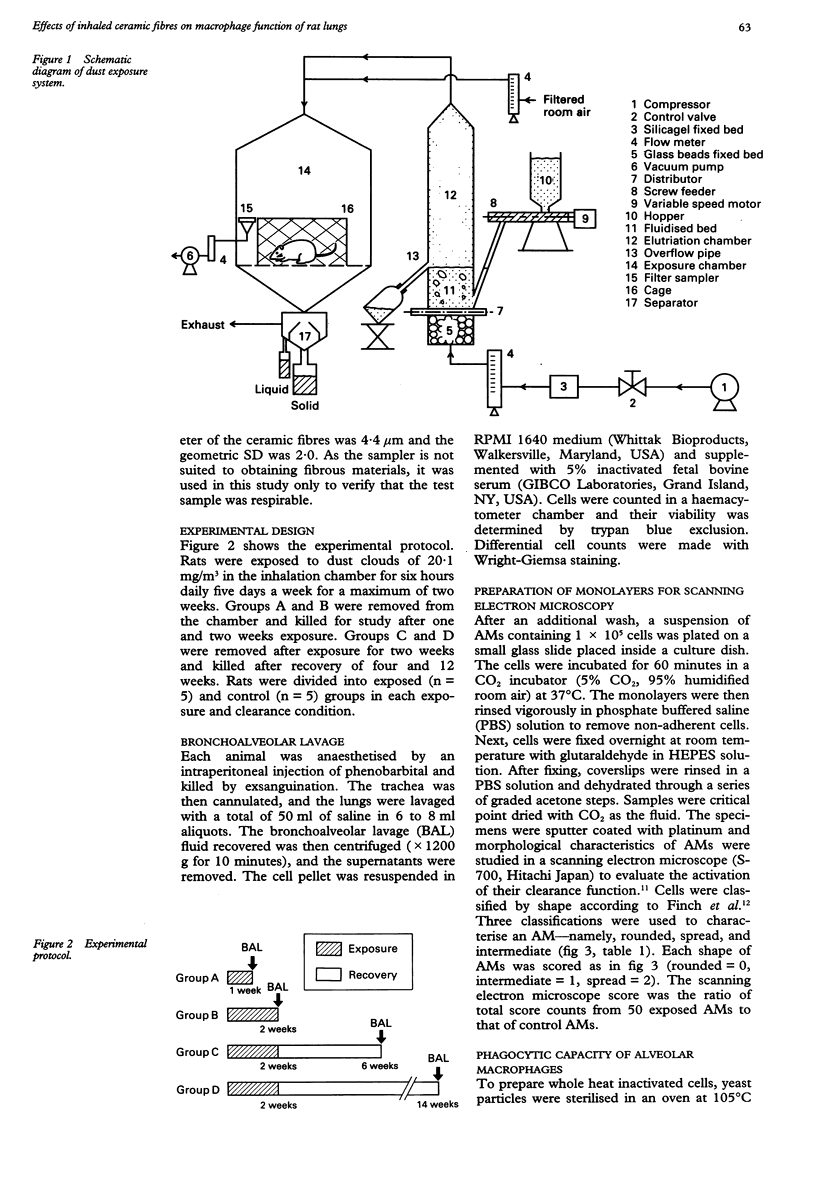
Abstract
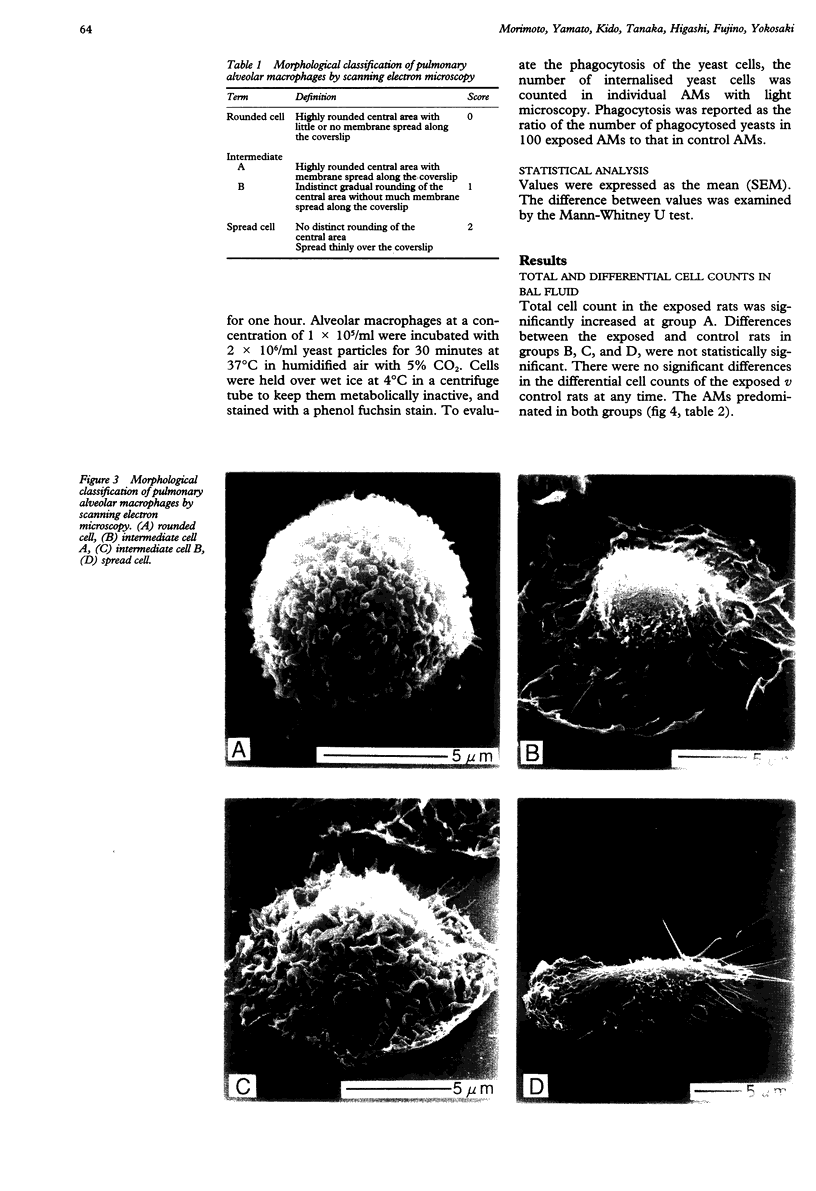
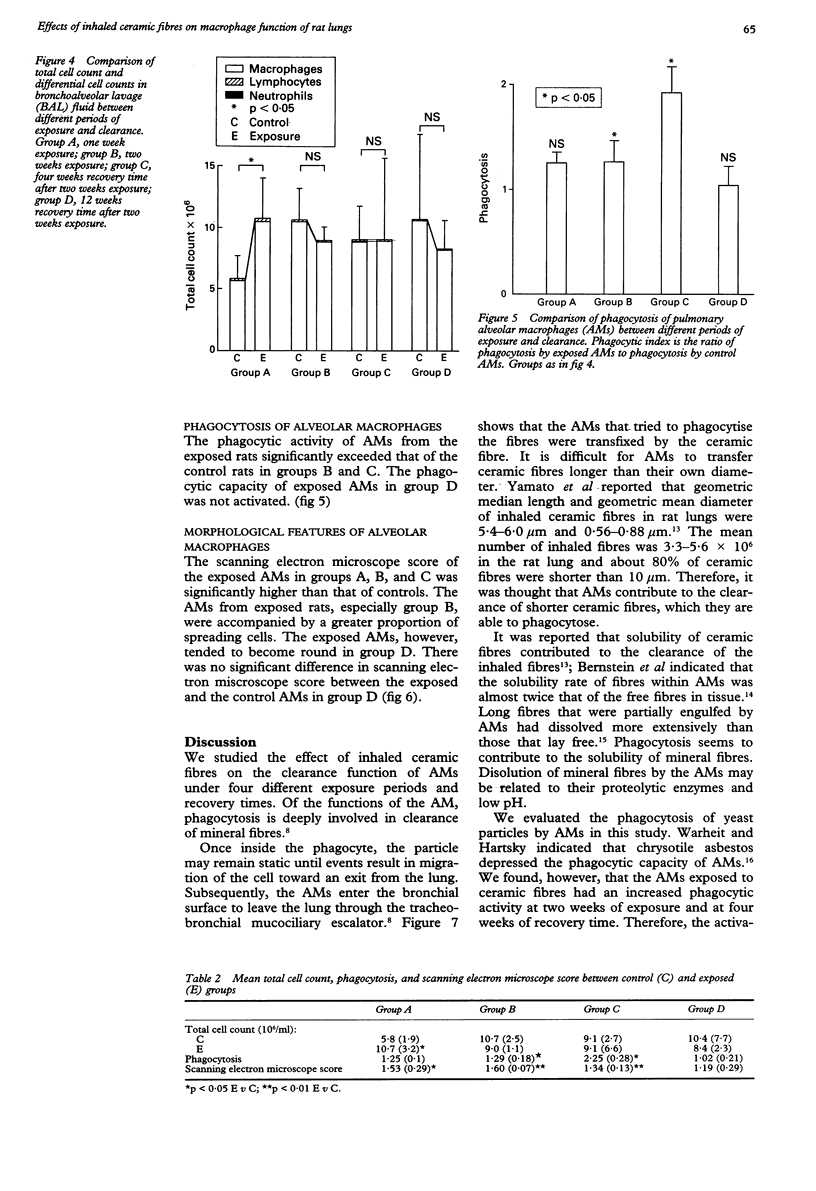
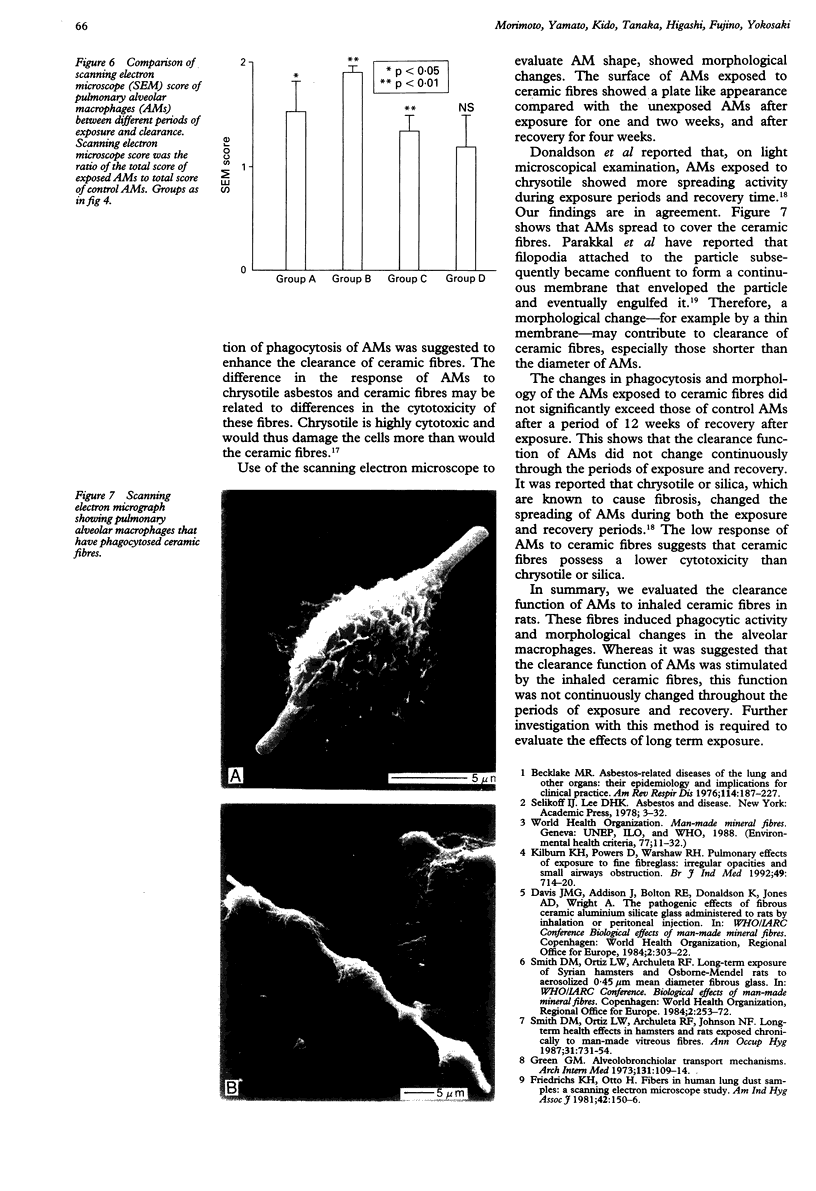
To evaluate the biological effect of ceramic fibres on the clearance function of alveolar macrophages (AMs) morphological changes and phagocytic activity of AMs were assessed. Rats were exposed to respirable ceramic fibres with a mass median aerodynamic diameter of 4.4 microns and a concentration of 20.1 mg/m3 in an exposure chamber. They were killed after one week (group A) and two weeks (group B) of exposure, and four weeks (group C) and 12 weeks (group D) after exposure for two weeks. The AMs recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) from each test group were incubated with yeast and phagocytic activity was determined by counting the number of yeast cells in AMs. Morphological features of AMs were assessed by scanning electron microscopy and quantified according to morphological changes. Total cell counts in BAL fluid from exposed rats in group A were higher than in control rats. Phagocytic activity of exposed AMs in group B and C exceeded that of control AMs. Morphological changes of the exposed AMs in groups A, B, and C were greater than those of control AMs. These findings suggest that ceramic fibres induced the phagocytic activity and morphological changes in AMs, and that the clearance function of AMs was stimulated by the inhaled ceramic fibres.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becklake M. R. Asbestos-related diseases of the lung and other organs: their epidemiology and implications for clinical practice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):187–227. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson K., Bolton R. E., Jones A., Brown G. M., Robertson M. D., Slight J., Cowie H., Davis J. M. Kinetics of the bronchoalveolar leucocyte response in rats during exposure to equal airborne mass concentrations of quartz, chrysotile asbestos, or titanium dioxide. Thorax. 1988 Jul;43(7):525–533. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.7.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
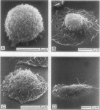
- Finch G. L., Fisher G. L., Hayes T. L., Golde D. W. Morphological studies of cultured human pulmonary macrophages. Scan Electron Microsc. 1980;(3):315–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichs K. H., Otto H. Fibers in human lung dust samples: a scanning electron microscope study. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1981 Feb;42(2):150–156. doi: 10.1080/15298668191419497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M. Alveolobronchiolar transport mechanisms. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Jan;131(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Holmes A., Davison W. Clearance of sized glass fibres from the rat lung and their solubility in vivo. Ann Occup Hyg. 1982;25(3):317–331. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/25.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parakkal P., Pinto J., Hanifin J. M. Surface morphology of human mononuclear phagocytes during maturation and phagocytosis. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Aug;48(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Jacoby F. Light microscope studies on the effects of chrysotile asbestos and fiber glass on the morphology and reticulin formation of cultured lung fibroblasts. Environ Res. 1976 Feb;11(1):112–121. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(76)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Ortiz L. W., Archuleta R. F., Johnson N. F. Long-term health effects in hamsters and rats exposed chronically to man-made vitreous fibres. Ann Occup Hyg. 1987;31(4B):731–754. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/31.4b.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Akiyama T. A new dust generator for inhalation toxicity studies. Ann Occup Hyg. 1984;28(2):157–162. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/28.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warheit D. B., Hartsky M. A. Assessments of pulmonary macrophage clearance responses to inhaled particulates. Scanning Microsc. 1988 Jun;2(2):1069–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warheit D. B., Hill L. H., Brody A. R. Pulmonary macrophage phagocytosis: quantification by secondary and backscattered electron imaging. Scan Electron Microsc. 1983;(Pt 1):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamato H., Tanaka I., Higashi T., Kido M. Determinant factor for clearance of ceramic fibres from rat lungs. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Mar;49(3):182–185. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.3.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]