Abstract
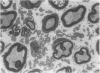
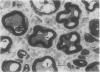
This study was conducted to clarify the effects of vibration on the peripheral nerves. Rat tails were exposed to vibration (acceleration 56.9 m/s2, frequency 60 Hz, amplitude 0.4 mm for two or four hours daily, six days a week. The maximum motor conduction velocity (MCV), the amplitude of evoked response, and the motor distal latency were measured on rat tail nerves every two months. Thin sections of tail nerves were examined under the electron microscope after 200, 500, and 800 hours of vibration. Neurophysiological and ultrastructural changes in tail nerves increased with the dose of vibration. In the groups exposed to vibration the MCVs were significantly reduced after a vibration time up to 400 hours, whereas the motor distal latency was not delayed significantly until 600 vibration hours. The ultrastructural changes were (1) detachment of the myelin sheath from the axolemma, (2) constriction of the axon, (3) protrusion of the myelin sheath into the axon, (4) accumulation of vacuoles in paranodal regions, and (5) dilatation of the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures. The ultrastructural changes induced by vibration in the paranodal regions and myelin sheaths were possibly responsible for the reduction in MCVs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cherniack M. G., Letz R., Gerr F., Brammer A., Pace P. Detailed clinical assessment of neurological function in symptomatic shipyard workers. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Aug;47(8):566–572. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.8.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Friedman P. L., Hamilton W. J. The localization of sodium and calcium to schwann cell paranodal loops at nodes of Ranvier and of calcium to compact myelin. J Neurocytol. 1980 Apr;9(2):185–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01205157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Dahlin L. B., Löwenadler B., Lundborg G., Paleus S., Skottner A. Transient increase in insulin-like growth factor I immunoreactivity in rat peripheral nerves exposed to vibrations. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Jan;132(1):35–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga H. [Studies of peripheral nerve conduction velocities in vibrating tool operators]. Sangyo Igaku. 1982 May;24(3):284–293. doi: 10.1539/joh1959.24.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. T., Yu H. S. Ultrastructural changes of the peripheral nerve induced by vibration: an experimental study. Br J Ind Med. 1989 Mar;46(3):157–164. doi: 10.1136/oem.46.3.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juntunen J., Matikainen E., Seppäläinen A. M., Laine A. Peripheral neuropathy and vibration syndrome. A clinical and neurophysiological study of 103 patients. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1983;52(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00380603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskimies K., Färkkilä M., Pyykkö I., Jäntti V., Aatola S., Starck J., Inaba R. Carpal tunnel syndrome in vibration disease. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Jun;47(6):411–416. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.6.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg G., Dahlin L. B., Danielsen N., Hansson H. A., Necking L. E., Pyykkö I. Intraneural edema following exposure to vibration. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1987 Aug;13(4):326–329. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg G., Dahlin L. B., Hansson H. A., Kanje M., Necking L. E. Vibration exposure and peripheral nerve fiber damage. J Hand Surg Am. 1990 Mar;15(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(90)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M. Morphology of the rat carotid sinus nerve. II. Number and size of axons. J Neurocytol. 1983 Jun;12(3):373–392. doi: 10.1007/BF01159381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi J., Nagano M. Experimental study on the enhancement of the neurotoxicity of methyl n-butyl ketone by non-neurotoxic aliphatic monoketones. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Mar;42(3):155–161. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.3.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Joyner R. W., Brill M. H., Waxman S. D., Najar-Joa M. Simulations of conduction in uniform myelinated fibers. Relative sensitivity to changes in nodal and internodal parameters. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):147–160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85515-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Araki S., Maeda K. Autonomic and peripheral nervous system dysfunction in workers exposed to hand-arm vibration: a study of R-R interval variability and distribution of nerve conduction velocities. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1991;63(3):205–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00381570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. [Vibration syndrome of vibrating tool users in a factory of steel foundry. Part 2. Disturbances of the cutaneous senses and the blood flow of fingers (author's transl)]. Sangyo Igaku. 1978 Sep;20(5):269–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Futatsuka M., Imanishi H., Yamada S. Pathological changes observed in the finger biopsy of patients with vibration-induced white finger. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1986 Aug;12(4 Spec No):280–283. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Takeya M., Imanishi H. Ultrastructural changes in peripheral nerves of the fingers of three vibration-exposed persons with Raynaud's phenomenon. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1988 Feb;14(1):31–35. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao-Cheng J. H., Rosenbluth J. Nodal and paranodal membrane structure in complementary freeze-fracture replicas of amphibian peripheral nerves. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 20;199(2):249–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tippe A., Müller-Mohnssen H. Further experimental evidence for the synapse hypothesis of Na+-current activation and inactivation at the Ranvier node. Naturwissenschaften. 1975 Oct;62(10):490–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00600513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng H. M., Yu H. S., Ho S. T., Yao T. H. Vibration syndrome--pathophysiological and electronmicroscopic studies. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi. 1986 Dec;2(12):732–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verberk M. M., Sallé H. J., Kempers O. Vibratory and tactile sense of the fingers after working with sanders. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1985;56(3):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00396599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Jean D. H., Whitaker J. N., McLaughlin B. J., Albers R. W. Immunocytochemical localization of the sodium, potassium activated ATPase in knifefish brain. J Neurocytol. 1977 Oct;6(5):571–581. doi: 10.1007/BF01205220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]