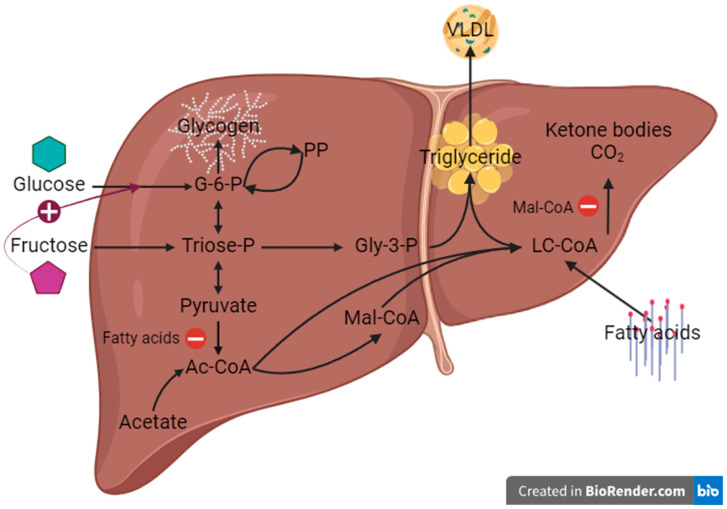
Figure 1.
Principal hepatic lipid and carbohydrate fluxes under postprandial conditions in relation to the availability of fatty acids, glucose and fructose. Selected key influences of one substrate on the metabolism of the other are highlighted with colors: in red the inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase by fatty acids, in purple the inhibition of lipid oxidation by malonyl-CoA, and in blue the activation of glucokinase by fructose. For simplicity, only the main metabolic intermediates are shown. Ac-CoA = acetyl-coenzyme A, G-6-P = glucose-6-phosphate, Gly-3-P = glycerol-3-phosphate, LC-CoA = long-chain fatty acid-coenzyme A, Mal-CoA = malonyl-coenzyme A, PP = pentose phosphates, VLDL = very low-density lipoprotein (Created in BioRender.com).