Graphical abstract
Key words: artificial intelligence, handout, patient education, patient-physician communication, skin cancer prevention, translation
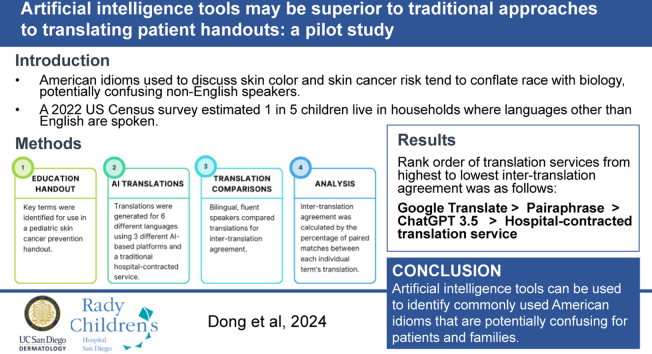
To the Editor: Idioms are phrases that have an intended meaning beyond the literal interpretation of the individual words. American idioms used to discuss skin color and skin cancer risk tend to conflate race with biology, potentially confusing non-English speakers.1,2 A 2022 US Census survey revealed that 1 in 5 children live in households where languages other than English are spoken, with Spanish, Chinese, Tagalog, Vietnamese, Arabic, and Korean among the most common non-English languages.3 For these children and families, artificial intelligence (AI)-powered tools offer promise in helping dermatologists with patient-provider communication and patient education.4
In this pilot study, we evaluated translations of a pediatric skin cancer prevention handout generated by AI. Our analysis focused on terms adopted from national medical organizations’ patient and clinician education materials. Terms included “skin of color,” “light skin,” “dark skin,” “lighter skin,” “darker skin,” “ethnic skin,” and “sunburn.” Translations of the handout were generated in Arabic, Korean, Mandarin, Spanish, Tagalog, and Vietnamese, using 3 different commercially available AI-based platforms (Google Translate, Pairaphrase, and ChatGPT; accessed May 2023) and a traditional hospital-contracted translation service. Bilingual individuals, fluent in both English and the language of interest, reviewed the handout and indicated whether translations of the terms matched. Intertranslation agreement for each language was calculated by the percentage of positive matches. For example, if one match was identified for a term (out of 6 possible matches), this would be calculated as 17% (1/6) (Table I).
Table I.
Intertranslation agreement by language (percentage of positive matches)
| Pairaphrase | Google Translate | ChatGPT | Hospital-contracted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabic | 57% | 71% | 67% | 62% |
| Mandarin | 48% | 48% | 38% | 29% |
| Korean | 38% | 43% | 24% | 10% |
| Spanish | 95% | 95% | 95% | 86% |
| Tagalog | 24% | 43% | 38% | 48% |
| Vietnamese | 38% | 43% | 10% | 14% |
Intertranslation agreement heat map legend.
| 0-20% | 21-40% | 41-60% | 61-80% | 81-100% |
Google Translate exhibited the highest intertranslation agreement across all languages. Translation services by ranking of highest to lowest intertranslation agreement were Google Translate (58%), Pairaphrase (50%), ChatGPT (45%), and the hospital-contracted translation service (41%). Across all languages, the term with the highest intertranslation agreement was “sunburn.” Terms by ranking of highest to lowest intertranslation agreement were “sunburn,” “dark skin,” “skin of color,” “light skin,” “ethnic skin,” “darker skin,” and “lighter skin.” Spanish translations displayed the highest inter-translation agreement. For Spanish translations, the terms “skin of color” and “ethnic skin” showed complete agreement across translations but were identified by reviewers as containing meanings different from the source handout (Table II).
Table II.
Intertranslation agreement by language for individual terms (percentage of positive matches)
| Skin of color | Lighter skin | Darker skin | Light skin | Dark skin | Ethnic skin | Sunburn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabic | 100% | 17% | 17% | 100% | 100% | 17% | 100% |
| Mandarin | 33% | 17% | 17% | 33% | 33% | 50% | 100% |
| Korean | 17% | 17% | 17% | 50% | 50% | 33% | 17% |
| Spanish | 100% | 50% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Tagalog | 50% | 17% | 33% | 0% | 50% | 17% | 100% |
| Vietnamese | 50% | 17% | 17% | 50% | 17% | 17% | 17% |
Intertranslation agreement heat map legend.
| 0-20% | 21-40% | 41-60% | 61-80% | 81-100% |
Commercially available AI platforms allow for inexpensive and quick translations. AI-powered tools can be used to recognize commonly used idioms that are potentially confusing for families and patients. Comparative analysis of translations in multiple languages provides a systematic approach for finding potential issues with the source material utilized for translations. While this pilot study recognized the potential of AI-based translation for patient education, it also raised potential pitfalls to their use. The idiom “skin of color” had high inter-translation agreement across all languages; however, when translated, the term was still confusing to non-English readers. Similarly, “ethnic skin” received high intertranslation agreement in Spanish, but in Mexico, the term “ethnic groups” specifically refers to indigenous communities living in Mexico, such as the Zapotecos.5 Our pilot study recognizes the potential value of AI-based approaches to generate translated patient materials but raises caution for potential inaccuracy, such as idioms whose meanings are lost in translation.
Conflicts of interest
None disclosed.
Acknowledgments
Thank you, Monica Guirgus, Katie Lock, and Sandra Yeoman, for providing translation help, preliminary statistical analysis, and critical feedback on the project.
Footnotes
Funding sources: Department of Dermatology at University of California San Diego, USA. Dr Hightower is the recipient of the Robert A. Winn Diversity in Clinical Trials: Career Development Award, which is partly funded by Bristol-Meyer Squibb Foundation.
Patient consent: Not applicable.
IRB approval status: Not applicable.
References
- 1.Jablonski N.G. Skin color and race. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2021;175(2):437–447. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.24200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tsai J. How should educators and publishers eliminate racial essentialism? AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(3):E201–E211. doi: 10.1001/amajethics.2022.201. English, Spanish. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dietrich S., Hernandez E. Nearly 68 Million People Spoke a Language Other than English at Home in 2019. US Census Bureau. 2022. https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2022/12/languages-we-speak-in-united-states.html
- 4.Ayers J.W., Poliak A., Dredze M., et al. Comparing physician and artificial intelligence chatbot responses to patient questions posted to a public social media forum. JAMA Intern Med. 2023;183(6):589–596. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pueblos indígenas en México : Sistema de Información Cultural-Secretaría de Cultura. https://sic.cultura.gob.mx/index.php?table=grupo_etnico