Abstract
To determine comparability of methods, postural sway was measured simultaneously with a force platform and a device that registers head (and trunk) movements (head tracking). The effects of age, sex, height, weight, shoe area, and grip strength on both measurements were examined in 162 subjects. To determine whether either method had advantages in detecting abnormal balance 46 reference subjects were compared with 116 people randomly selected from 500 residents whose well water was contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and trichloroethylene (TCE) from a metal casting plant. Speed, mean radius, and distance of sway were equally reproducible with both methods. Correlation coefficients were 0.672 with the eyes closed and 0.588 with the eyes open. The balance of those exposed to PCBs and TCE was significantly worse than that of unexposed subjects by both head tracking (1.50 + 71 cm/s v 1.27 + 0.36 cm/s; p < 0.034) and the force platform (4.93 + 1.56 N (kg force) v 4.29 + 1.14 N; p < 0.013) with the eyes closed and differences were also significant with the eyes open. Head tracking and the force platform produced equivalent results. Measurement by head tracking is recommended for field studies because the device is more portable and is less influenced by weight and height. Both methods showed impaired balance associated with years of exposure to PCBs and TCE.
Full text
PDF

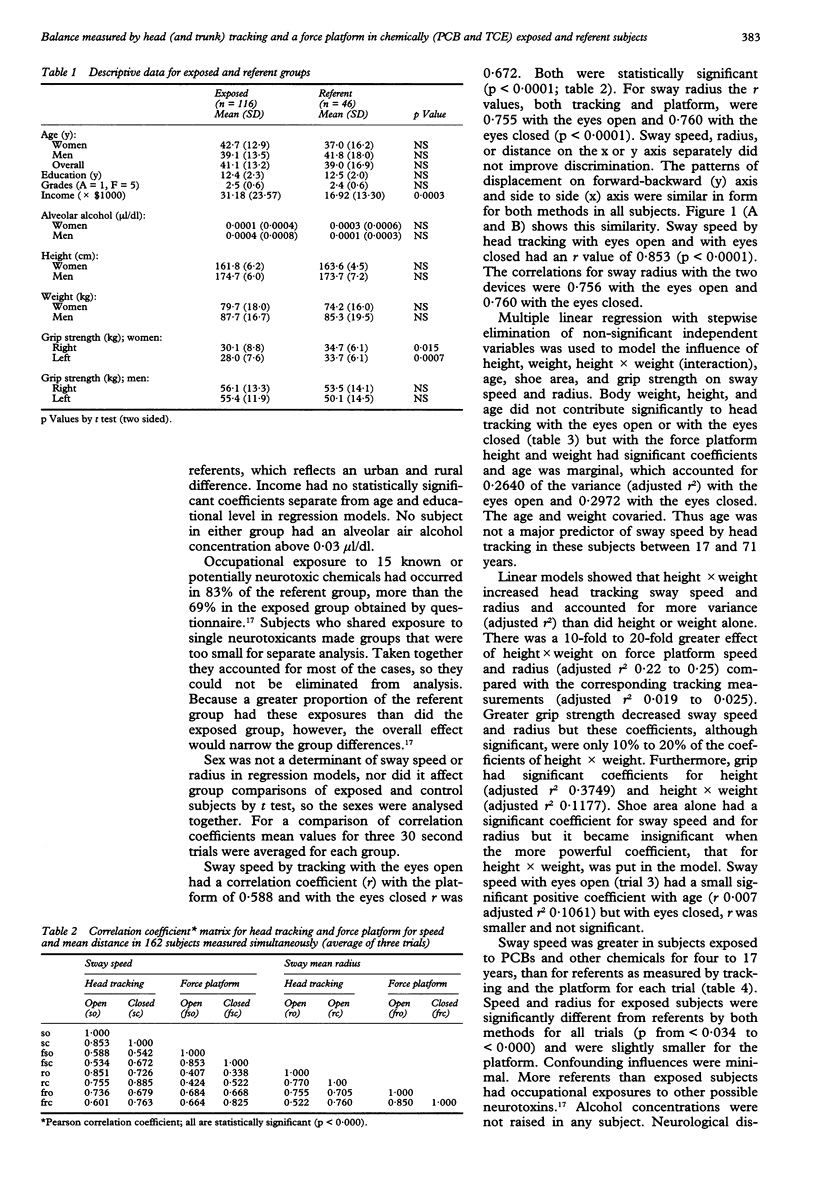
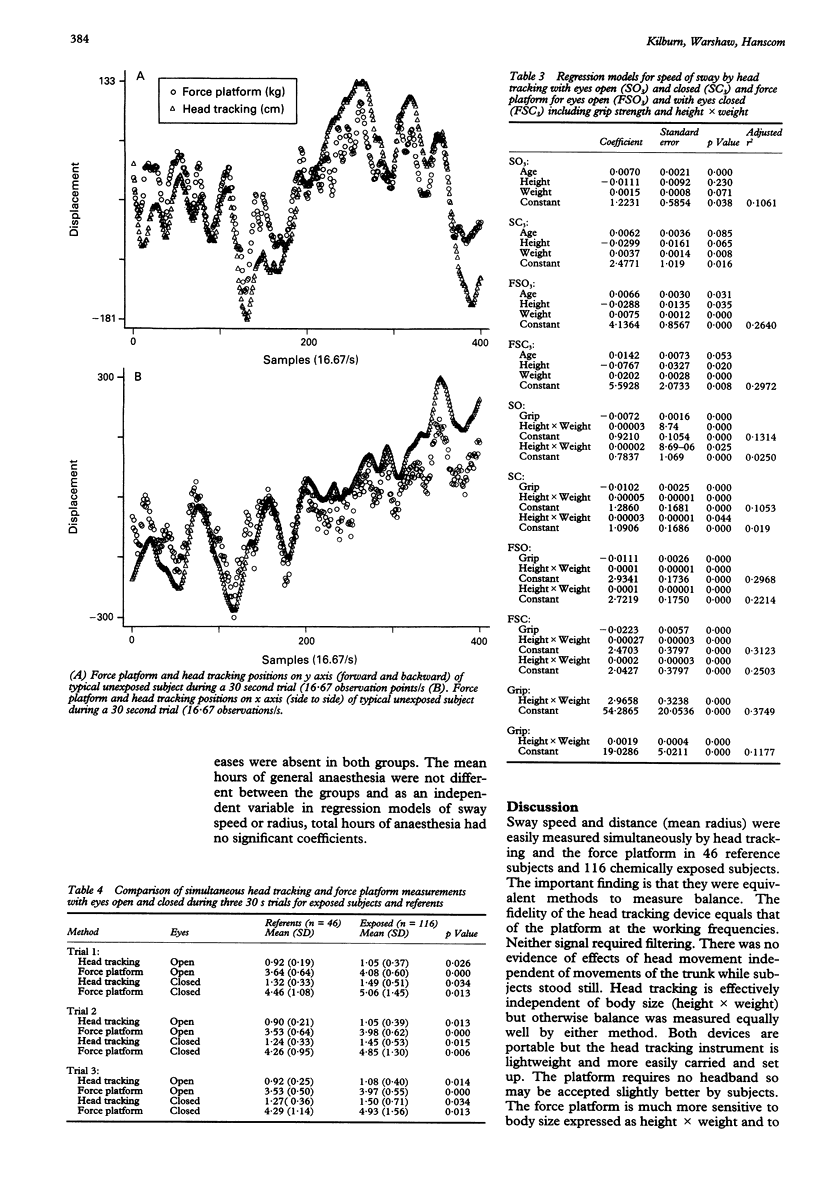

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya A., Morgan R., Shukla R., Ramakrishanan H. K., Wang L. Non-invasive estimation of afferent inputs for postural stability under low levels of alcohol. Ann Biomed Eng. 1987;15(6):533–550. doi: 10.1007/BF02364247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buser H. R. Formation, occurrence and analysis of polychlorinated dibenzofurans, dioxins and related compounds. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 May;60:259–267. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8560259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. C., Tang S. Y., Miyata H., Kashimoto T., Chang Y. C., Chang K. J., Tung T. C. Polychlorinated biphenyl poisoning: correlation of sensory and motor nerve conduction, neurologic symptoms, and blood levels of polychlorinated biphenyls, quaterphenyls, and dibenzofurans. Environ Res. 1985 Aug;37(2):340–348. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(85)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. M., Griffiths C. J., Murray A. Stability of the human body investigated by sway magnetometry. J Med Eng Technol. 1986 May-Jun;10(3):126–130. doi: 10.3109/03091908609022899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick R. B., Bhattacharya A., Shukla R. Use of a computerized postural sway measurement system for neurobehavioral toxicology. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(90)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald E. F., Standfast S. J., Youngblood L. G., Melius J. M., Janerich D. T. Assessing the health effects of potential exposure to PCBs, dioxins, and furans from electrical transformer fires: the Binghamton State Office Building medical surveillance program. Arch Environ Health. 1986 Nov-Dec;41(6):368–376. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1986.9935781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLORIG A., DAVIS H. Age, noise and hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1961 Jun;70:556–571. doi: 10.1177/000348946107000219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie P. A., Bach T. M., Evans O. M. Force platform measures for evaluating postural control: reliability and validity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989 Jul;70(7):510–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutzinger O., Choudhry G. G., Chittim B. G., Johnston L. E. Formation of polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dioxins during combustion, electrical equipment fires and PCB incineration. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 May;60:3–9. doi: 10.1289/ehp.85603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JALAVISTO E., LYBECK H., SALMI H. A., SUNDHOLM I. Bilirubin elimination from blood during acute hypoxia. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1953;31(4):437–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen E. C., Larsen R. E., Olesen M. B. Quantitative Romberg's test. Measurement and computer calculation of postural stability. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Jul;66(1):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Warsaw R. H., Shields M. G. Neurobehavioral dysfunction in firemen exposed to polycholorinated biphenyls (PCBs): possible improvement after detoxification. Arch Environ Health. 1989 Nov-Dec;44(6):345–350. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1989.9935904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Warshaw R. H., Hanscom B. Are hearing loss and balance dysfunction linked in construction iron workers? Br J Ind Med. 1992 Feb;49(2):138–141. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.2.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. P., Seireg A. A., Sepic S. B. Normal postural stability and steadiness: quantitative assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975 Jun;57(4):510–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogan W. J., Gladen B. C. Neurotoxicology of PCBs and related compounds. Neurotoxicology. 1992 Spring;13(1):27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON J. H. The effect of age on the control of sway. Gerontol Clin (Basel) 1963;5:129–138. doi: 10.1159/000244784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen K. Combined effects of xylene and alcohol on the central nervous system. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1980 May;46(5):366–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1980.tb02468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyssen H. H., Brynskov J., Jansen E. C., Münster-Swendsen J. Normal ranges and reproducibility for the quantitative Romberg's test. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Jul;66(1):100–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb03133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



