Abstract
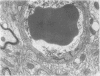
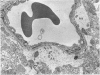
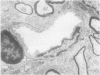
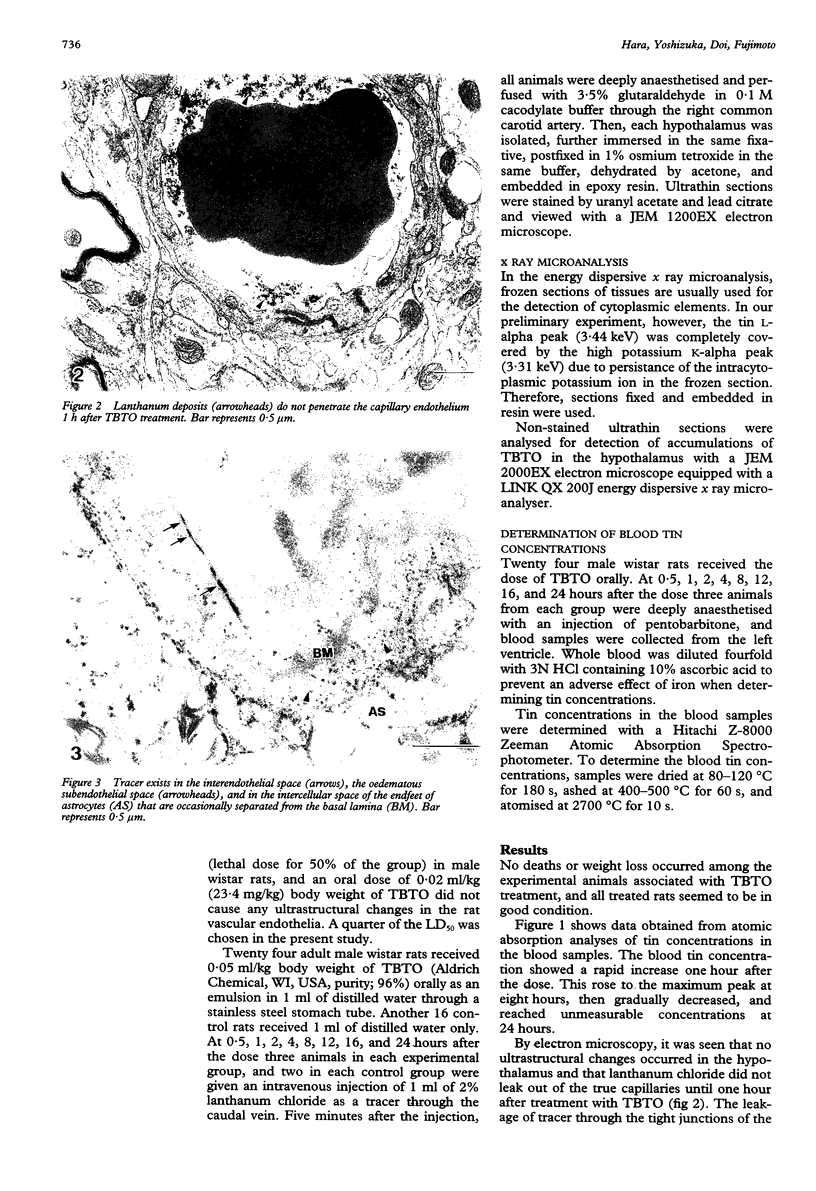
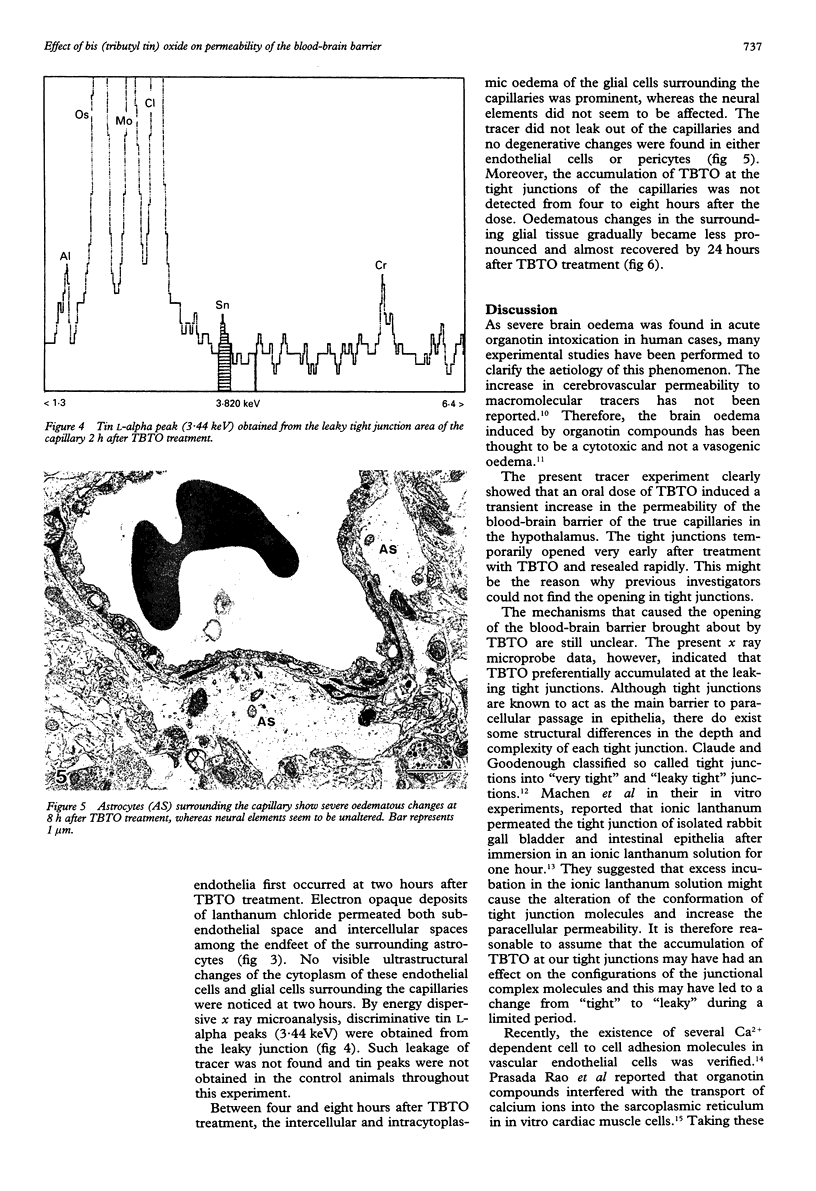
OBJECTIVES--To study the effect of bis (tributyl tin) oxide (TBTO) on permeability of the blood-brain barrier. METHODS--Electron microscopy and an x ray microanalyser with lanthanum chloride as a tracer were used, and blood tin concentrations were determined with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Adult male wistar rats received 0.05 ml/kg body weight of TBTO orally. RESULTS--A transient increase in paracellular permeability at the blood-brain barrier was found 2 h after the dose of TBTO. Electron dense lanthanum deposits penetrated tight junctions of the endothelia and permeated the subendothelial space. The x ray microprobe data showed an accumulation of TBTO at the tight junctions at 2 h. Leakage of tracer did not occur at 4 h, but oedematous changes in the surrounding glial cells were prominent between 4 and 8 h and had almost returned to normal by 24 h. By atomic absorption analysis, it was seen that blood tin concentrations rapidly increased at 1 h and rose to a maximum peak at 8 h, then gradually decreased to reach zero at 24 h. CONCLUSIONS--Accumulated TBTO at tight junctions could have caused the temporary replacement of calcium ion by tin, which induces a transient increase in paracellular permeability throughout the blood-brain barrier.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALAJOUANINE T., DEROBERT L., THIEFFRY S. Etude clinique d'ensemble de 210 cas d'intoxication par les sels organiques d'étain. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1958 Feb;98(2):85–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer I. J. Toxicity of dibutyltin, tributyltin and other organotin compounds to humans and to experimental animals. Toxicology. 1989 May 15;55(3):253–298. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(89)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Goodenough D. A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from "tight" and "leaky" epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):390–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Degner M., Schwartz S. M. Identification of a Ca2(+)-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecule in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1745–1756. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Zimmerman H. M., Levine S. Intramyelinic and extracellular spaces in triethyltin intoxication. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Oct;27(4):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultström D., Forssén M., Pettersson A., Tengvar C., Jarild M., Olsson Y. Vascular permeability in acute triethyltin-induced brain edema studied with FITC-dextrans, sodium fluorescein and horseradish peroxidase as tracers. Acta Neurol Scand. 1984 May;69(5):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1984.tb07810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Nagara H., Kondo A., Fukui M., Tateishi J. Effects of intracarotid hyperosmolar mannitol in triethyl tin (TET)-induced rat brain edema--preservation of blood-brain barrier (BBB) in TET edema. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 30;414(2):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodavanti P. R., Cameron J. A., Yallapragada P. R., Vig P. J., Desaiah D. Inhibition of Ca2+ transport associated with cAMP-dependent protein phosphorylation in rat cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum by triorganotins. Arch Toxicol. 1991;65(4):311–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01968965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machen T. E., Erlij D., Wooding F. B. Permeable junctional complexes. The movement of lanthanum across rabbit gallbladder and intestine. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):302–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. D., Emmett E. A., Steiner J., Tureen R. Neurotoxic effects of occupational exposure to organotins. Am J Psychiatry. 1981 Aug;138(8):1092–1095. doi: 10.1176/ajp.138.8.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizuka M., Hara K., Doi Y., Mori N., Yokoyama M., Ono E., Fujimoto S. The toxic effects of bis (tributyltin) oxide on the rat thoracic aorta. Histol Histopathol. 1992 Jul;7(3):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]