Abstract
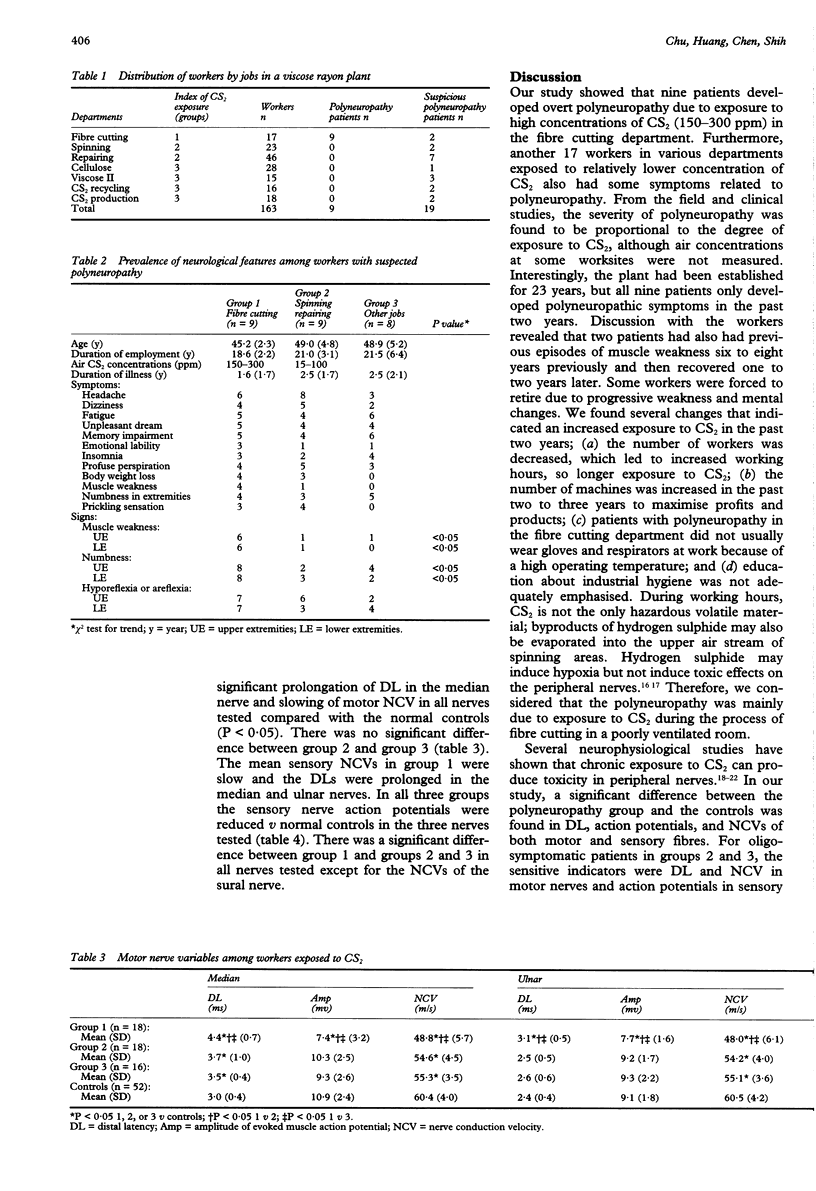
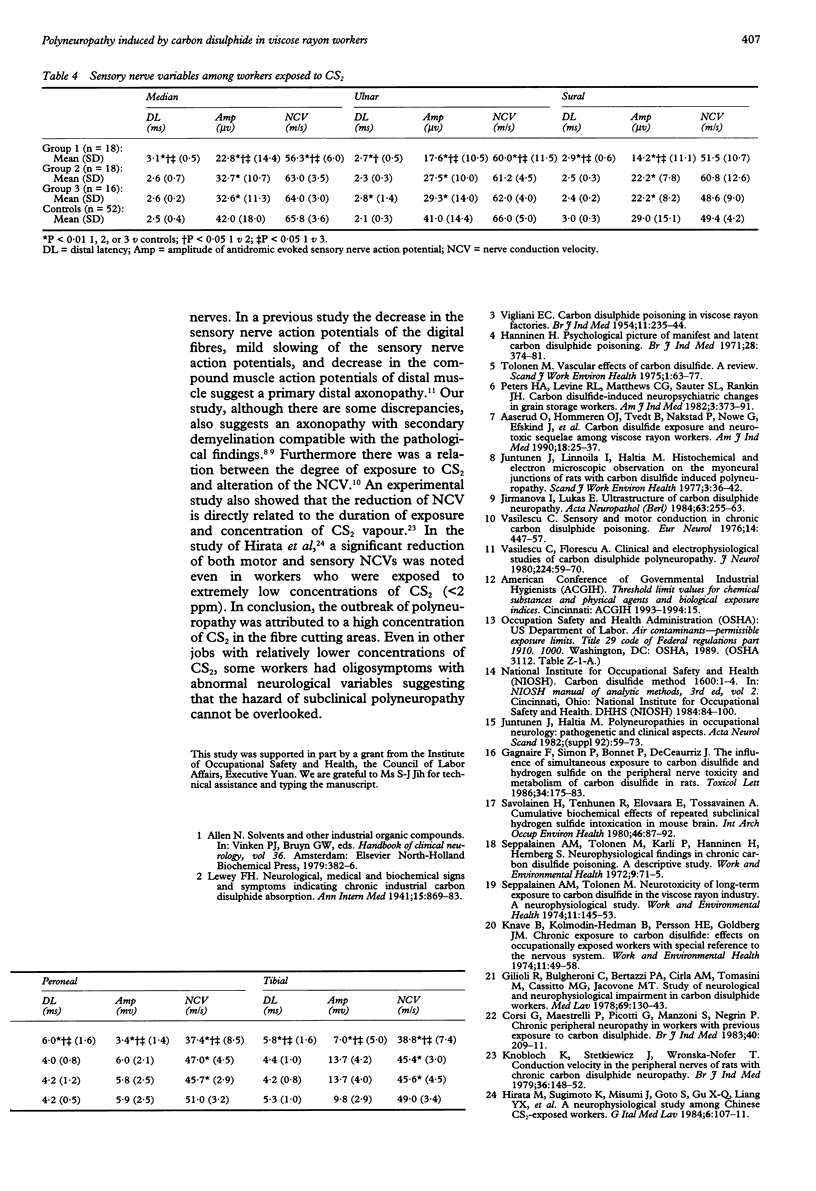
OBJECTIVES--To understand the prevalence of polyneuropathy and correlations among the clinical manifestations, electrophysiological findings, and degree of exposure to carbon disulphide (CS2) in workers who were exposed to variable concentrations of CS2 in a viscose rayon factory. METHODS--All the 163 workers received a detailed physical and neurological evaluation. Fixed point air samples were analysed for CS2. Nerve conduction velocity was studied in 26 workers with symptoms similar to neuropathy. RESULTS--Nine workers (53%) with overt polyneuropathy from the fibre cutting department and 19 workers (13%) with oligosymptoms similar to polyneuropathy from various jobs were noted. The fixed point air concentrations of CS2 were 150-300 ppm in the cutting areas and 15 to 100 ppm in the spinning areas. The estimated eight hour time weighted averages in the fibre cutting areas were 40-67 ppm. The occurrence of polyneuropathy was generally correlated with the degree of exposure to CS2. Nerve conduction velocities (NCVs) were significantly different in the overt polyneuropathy and subclinical polyneuropathy groups from the normal controls. The sensitive indicators for CS2 polyneuropathy were distal latency, motor NCV, and amplitude of sensory nerve action potentials in sensory NCVs. CONCLUSION--The outbreak of polyneuropathy was attributed to higher concentrations of CS2 in fibre cutting areas. Even in other jobs with relatively lower concentrations of CS2, the hazard of subclinical polyneuropathy cannot be overlooked.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaserud O., Hommeren O. J., Tvedt B., Nakstad P., Mowé G., Efskind J., Russell D., Jörgensen E. B., Nyberg-Hansen R., Rootwelt K. Carbon disulfide exposure and neurotoxic sequelae among viscose rayon workers. Am J Ind Med. 1990;18(1):25–37. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700180104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsi G., Maestrelli P., Picotti G., Manzoni S., Negrin P. Chronic peripheral neuropathy in workers with previous exposure to carbon disulphide. Br J Ind Med. 1983 May;40(2):209–211. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnaire F., Simon P., Bonnet P., De Ceaurriz J. The influence of simultaneous exposure to carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide on the peripheral nerve toxicity and metabolism of carbon disulfide in rats. Toxicol Lett. 1986 Dec;34(2-3):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(86)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilioli R., Bulgheroni C., Bertazzi P. A., Cirla A. M., Tomasini M., Cassitto M. G., Jacovone M. T. Study of neurological and neurophysiological impairment in carbon idsulphide workers. Med Lav. 1978 Mar-Apr;69(2):130–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Sugimoto K., Misumi J., Goto S., Gu X. Q., Liang Y. X., Jin X. P., Gu S. W., Chen Z. Q., Ding Z. L. A neurophysiological study among Chinese CS2-exposed workers. G Ital Med Lav. 1984 May-Jul;6(3-4):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H. Psychological picture of manifest and latent carbon disulphide poisoning. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Oct;28(4):374–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirmanová I., Lukás E. Ultrastructure of carbon disulphie neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;63(3):255–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00685252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juntunen J., Haltia M. Polyneuropathies in occupational neurology: pathogenetic and clinical aspects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1982;92:59–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juntunen J., Linnoila I., Haltia M. Histochemical and electron microscopic observations on the myoneural junctions of rats with carbon disulfide induced polyneuropathy. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1977 Mar;3(1):36–42. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knave B., Kolmodin-Hedman B., Persson H. E., Goldberg J. M. Chronic exposure to carbon disulfide: effects on occupationally exposed workers with special reference to the nervous system. Work Environ Health. 1974;11(1):49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch K., Stetkiewicz J., Wrońska-Nofer T. Conduction velocity in the peripheral nerves of rats with chronic carbon disulphide neuropathy. Br J Ind Med. 1979 May;36(2):148–152. doi: 10.1136/oem.36.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. A., Levine R. L., Matthews C. G., Sauter S. L., Rankin J. H. Carbon disulfide-induced neuropsychiatric changes in grain storage workers. Am J Ind Med. 1982;3(4):373–391. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700030404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen H., Tenhunen R., Elovaara E., Tossavainen A. Cumulative biochemical effects of repeated subclinical hydrogen sulfide intoxication in mouse brain. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1980;46(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00377463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolonen M. Vascular effects of carbon disulfide: a review. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1975 Jun;1(2):63–77. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIGLIANI E. C. Carbon disulphide poisoning in viscose rayon factories. Br J Ind Med. 1954 Oct;11(4):235–244. doi: 10.1136/oem.11.4.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu C., Florescu A. Clinical and electrophysiological studies of carbon disulphide polyneuropathy. J Neurol. 1980;224(1):59–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00313208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu C. Sensory and motor coduction in chronic carbon disulphide poisoning. Eur Neurol. 1976;14(6):447–457. doi: 10.1159/000114772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


