Abstract
The spliceosome executes pre-mRNA splicing through four sequential stages: assembly, activation, catalysis, and disassembly. Activation of the spliceosome, namely remodeling of the pre-catalytic spliceosome (B complex) into the activated spliceosome (Bact complex) and the catalytically activated spliceosome (B* complex), involves major flux of protein components and structural rearrangements. Relying on a splicing inhibitor, we have captured six intermediate states between the B and B* complexes: pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, and post-Bact. Their cryo-EM structures, together with an improved structure of the catalytic step I spliceosome (C complex), reveal how the catalytic center matures around the internal stem loop of U6 snRNA, how the branch site approaches 5′-splice site, how the RNA helicase PRP2 rearranges to bind pre-mRNA, and how U2 snRNP undergoes remarkable movement to facilitate activation. We identify a previously unrecognized key role of PRP2 in spliceosome activation. Our study recapitulates a molecular choreography of the human spliceosome during its catalytic activation.
Subject terms: Ribozymes, Cryoelectron microscopy
Here, the authors have captured the intermediate states of the human spliceosome during its activation through cryo-EM reconstruction of six distinct spliceosomal complexes.
Introduction
Pre-mRNA splicing is an essential process in eukaryotic gene expression, involving the excision of introns and ligation of exons1,2. RNA splicing consists of two reactions: branching and exon ligation3. The spliceosome, as one of the most dynamic molecular machines in eukaryotic cells, executes splicing in four sequential stages: assembly, activation, catalysis, and disassembly4–6. Each splicing cycle requires ten major functional states of the spliceosome: early spliceosome (E), pre-spliceosome (A), precursor to B complex (pre-B), B complex, Bact complex, B* complex, C complex, step II catalytically activated spliceosome (C*), post-catalytic spliceosome (P), and intron lariat spliceosome (ILS). The transition between two neighboring functional states requires major ribonucleoprotein (RNP) remodeling and is driven by a family of eight conserved RNA helicases7. During spliceosome assembly, the pre-B complex is converted to the B complex by the helicase PRP288–10.
The splicing active site is yet to be formed in the B complex. U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is sequestered by U4 snRNA and cannot form the internal stem loop (ISL). Activation of the spliceosome requires remodeling of the B complex to the Bact complex, which is driven by the helicase BRR211–13. During this process, U4 snRNP and the B-specific proteins are released; the PRP19/CDC5L complex (also known as the NineTeen Complex, or NTC) and NTC-related complex (NTR) are recruited. The Bact complex is then remodeled by the helicase PRP2 into the B* complex14–16, in which the branching reaction occurs, resulting in the C complex. PRP2 remodels the Bact complex by pulling the pre-mRNA14,15,17, which delivers the branch site (BS) into close proximity of the 5′-splice site (5′SS).
Mechanistic understanding of spliceosome activation requires detailed structural information on the activated spliceosome and related intermediate states. The B–Bact–B* transition involves extensive shuffling of spliceosomal components and constitutes the last and arguably the most important step prior to the splicing reaction. Cryo-EM structures have been obtained for the B18–21 and Bact22–25 complexes. The human Bact complex is thought to be highly dynamic, as evidenced by distinct conformations22,23,26. The human B* complex is yet to be structurally resolved. The B–Bact–B* remodeling process, which likely involves multiple intermediate states and additional roles of the RNA helicases27–29, remains poorly understood.
In this study, we have captured the intermediate states of the human spliceosome during its activation through cryo-EM reconstruction of six distinct spliceosomal complexes. These complexes, named pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, and post-Bact, bridge the critical gap between the B and B* complexes. We also re-determined the cryo-EM structure of the human C complex. Analysis of these structures reveals an ordered flux of spliceosomal components and conformational rearrangements that serve the purpose of organizing the catalytic center. We identify an unanticipated role of PRP2 in the activation of human spliceosome.
Results
Spliceosome isolation and cryo-EM analysis
To isolate the human spliceosome, we used the splicing inhibitor N-palmitoyl-l-leucine (NPL), which is known to selectively inhibit the late-stage assembly of the human spliceosome30 (Supplementary Fig. 1a). The human spliceosome was assembled on a synthetic pre-mRNA supplemented with NPL in the in vitro splicing reaction, followed by affinity purification and glycerol gradient centrifugation with chemical crosslinking (Supplementary Fig. 1b). The resulting sample was examined using urea–PAGE (Supplementary Fig. 1c) and subjected to cryo-EM analysis (Supplementary Fig. 1d). A total of ~4.6 million particles, generated from 17,070 micrographs, were applied to three rounds of three-dimensional (3D) classification. We identified seven classes of the spliceosome, which yielded seven distinct reconstructions (Supplementary Figs. 2–4).
The final cryo-EM reconstructions of the human pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, post-Bact, and C complexes display average resolutions of 3.4, 3.0, 4.2, 3.0, 3.3, 3.0, and 3.4 Å, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 3 and Supplementary Table 1). The local resolutions, which mostly reach 2.8–3.2 Å in the core regions (Supplementary Fig. 5), allow the identification of protein components and assignment of RNA elements (Supplementary Figs. 6–10). Each of the six distinct human Bact-like complexes contains a distinct set of protein components (Supplementary Table 2). In contrast, the newly determined human C complex is nearly identical to that reported previously31,32, corroborating the conclusion of our current investigation.
Overall structures of the intermediate-activated spliceosome
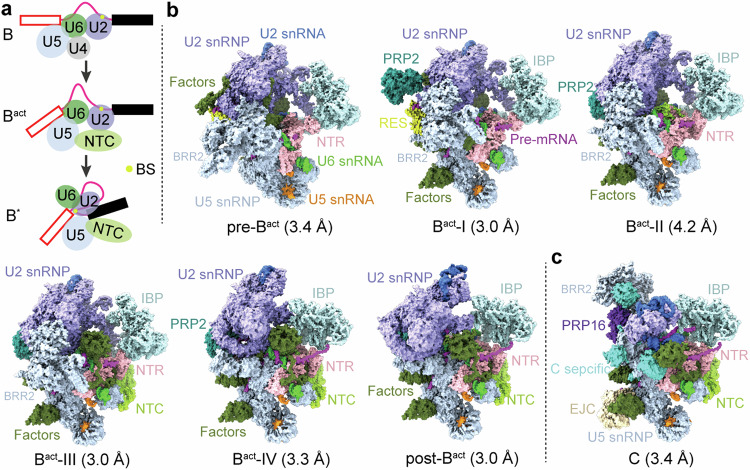
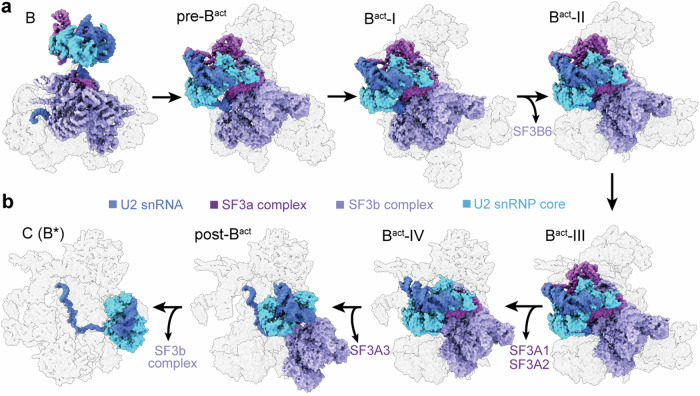
Activation of the spliceosome involves a major flux of components, including U4 snRNP, NTC, and NTR (Fig. 1a). The Bact complex already contains a splicing active site, which maintains the same configuration until spliceosome disassembly; but the BS is separated from 5′SS by a distance of ~50 Å22,23. This distance should be reduced presumably to ~4 Å in the B* complex to allow the branching reaction33. The six ordered human Bact complexes share a similar overall organization but exhibit pronounced differences in composition (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Table 2). At least 21 protein components are either recruited or released during the interchange of the six Bact complexes. For clarity, only key components are discussed here. The pre-Bact complex lacks PRP2 and the NTC core (PRP19 complex and SPF27) but still contains the retention and splicing (RES) complex, which is required for efficient B-to-Bact conversion34,35. In Bact-I, PRP2 is loaded together with the exchange of a number of splicing factors. In Bact-II, the RES complex is released, leaving a spatial vacancy to accommodate PRP2 translocation. In the latter three states, the NTC core is loaded and U2 snRNP undergoes marked translocations (Fig. 1b). In post-Bact, the BS is positioned close to 5′SS, which primes the branching reaction.
Fig. 1. Cryo-EM structures of six distinct conformational states of the human Bact complex.
a Schematic representation of the activation process of the human spliceosome. The B complex, containing U5.U4/U6 tri-snRNP, is remodeled by the RNA helicase BRR2, resulting in the release of U4 snRNP and recruitment of the NTC and NTR complexes. In the Bact-to-B* transition catalyzed by PRP2, the BS is brought into the close proximity of 5′SS for the branching reaction. b Cryo-EM structures of six distinct intermediate states between the B and B* complexes. These complexes, named pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, and post-Bact, are resolved at average resolutions of 3.4, 3.0, 4.2, 3.0, 3.3, and 3.0 Å, respectively. All complexes, with components displayed in color-coded surface representation, are shown in the same orientation. c Cryo-EM structure of the human C complex at an average resolution of 3.4 Å. All structural images in this manuscript were prepared using ChimeraX71 and PyMol72.
In addition to compositional differences, the six ordered Bact complexes also display marked conformational variation for a number of key protein components. For example, due to drastic translocation, BRR2 is unambiguously identified in pre-Bact through Bact-III, but not in Bact-IV or post-Bact (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Table 2). This is likely due to its mobile nature during spliceosome activation. Notably, BRR2 becomes ordered again in the reconstruction of the C complex (Fig. 1c), which is almost identical to that reported previously31,32. Based on these structures and additional evidence described below, we conclude that the six distinct conformations of the Bact complex represent intermediate states between the B and B* complexes.
Conformational changes of the RNA elements
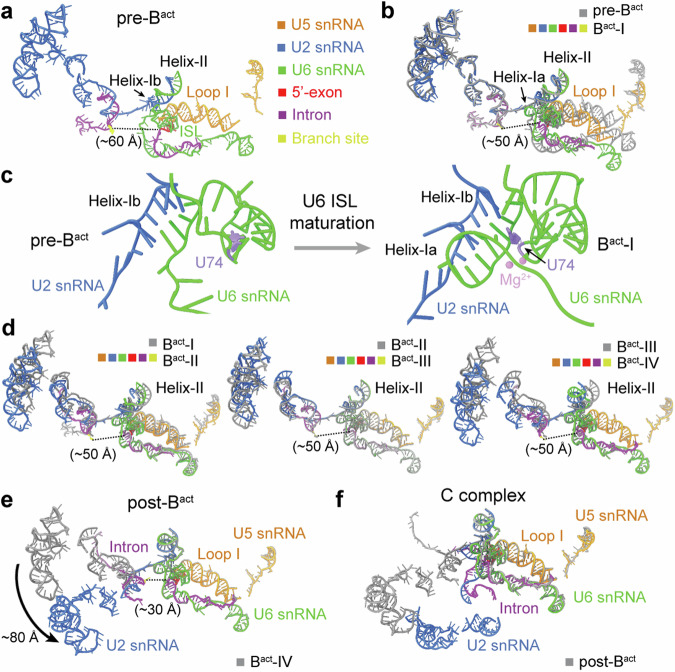
During spliceosome activation, 5′SS and the BS are gradually drawn together, with the formation of U6 ISL as the splicing active site3,36. All six activated complexes contain the same set of RNA components: U2, U5, and U6 snRNAs, and pre-mRNA; but these RNAs display notable differences in conformation. In all six complexes, 5′-exon is anchored on loop I of U5 snRNA, and 5′SS forms a duplex with U6 snRNA, whereas the BS is recognized by U2 snRNA (Fig. 2a–e and Supplementary Fig. 6).
Fig. 2. Conformational changes of the RNA elements.
a Overall structure of the RNA elements in the pre-Bact complex. The color-coding scheme is preserved throughout this manuscript. In pre-Bact, U6 ISL and helices Ib and II of U2/U6 duplex are initially formed; but helix Ia is yet to form. The BS is ~60 Å away from 5′SS. The 5′-exon remains anchored to loop I of U5 snRNA. b Structure comparison of the RNA elements between the pre-Bact and Bact-I complexes. The U2/BS duplex and helix II remain unchanged. Helix Ia appears in Bact-I. The 5′SS moves toward the BS by ~10 Å, with notable movements for U5 and U6 snRNAs. All structure alignments reported in this manuscript are based on PRP8, unless stated otherwise. c Close-up views on the maturation of U6 ISL. In the pre-Bact to Bact-I transition, helix Ia is formed, and the key nucleotide U74 of U6 snRNA is bulged out. d Pairwise comparison of the RNA elements among the Bact-I, -II, -III, and -IV complexes. The distance between 5′SS and the BS remains unchanged at about 50 Å. In the transition of Bact-I to Bact-II, U2 snRNA undergoes a marked translocation and helix II is shifted slightly. In the transition of Bact-III to Bact-IV, helix II moves to the position where it is found in the C complex. e Structure comparison of the RNA elements between Bact-IV and post-Bact. U2 snRNA undergoes notable movements with the BS moving towards 5′SS by about 20 Å. f Structure comparison of the RNA elements between the post-Bact and C complexes. After the branching reaction, the BS is linked to 5′SS in the C complex, and U2 snRNA undergoes a pronounced translocation.
In pre-Bact, U6 ISL, helices Ib and II of the U2/U6 duplex, but not helix Ia, are initially formed. These structural features reflect the premature nature of pre-Bact as an activated spliceosome. Consistently, the BS is positioned ~60 Å away from 5′SS (Fig. 2a), even farther apart compared to that in the published Bact complex22,23. During the transition of pre-Bact to Bact-I, the U2/BS duplex and helix II remain unchanged; but 5′SS moves toward the BS by about 10 Å, accompanied by notable shifts of U5 and U6 snRNAs (Fig. 2b). Importantly, helix Ia is formed in Bact-I, and the nucleobase of the key nucleotide U74 of U6 ISL (U80 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae)) is bulged out relative to its flanking nucleotides, which enables the positioning of two catalytic Mg2+ ions that directly participate in the splicing reaction37–40 (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Fig. 6c).
The 50-Å distance between 5′SS and the BS remains unchanged in Bact-I through Bact-IV; in contrast, U2 snRNA undergoes pronounced changes (Fig. 2d). Compared to Bact-I, U2 snRNA in Bact-II undergoes a marked translocation, with a slight shift of helix II. Compared to Bact-II, a portion of U2 snRNA in Bact-III continues to shift position. In the transition of Bact-III to Bact-IV, helix II moves to the position where it is found in the C complex. Each of these changes in U2 snRNA is accompanied by flux of specific protein components. In the transition of Bact-IV to post-Bact, U2 snRNA undergoes a translocation of ~80 Å, accompanied by a 20-Å movement of the BS toward 5′SS (Fig. 2e). This movement shortens the distance between the two reactive moieties on 5′SS and BS for the branching reaction. In the C complex, the BS is covalently linked to 5′SS (Supplementary Fig. 6f); U2 snRNA undertakes yet another marked translocation compared to post-Bact (Fig. 2f).
In summary, analysis of the RNA conformation in these six Bact intermediates reveals remarkable changes in U2 snRNA, which allow stepwise movement of the BS toward 5′SS for the branching reaction. In contrast to U2 snRNA, U5 and U6 snRNAs remain largely unchanged in the five intermediates Bact-I through post-Bact.
A key role by PRP2 during spliceosome activation
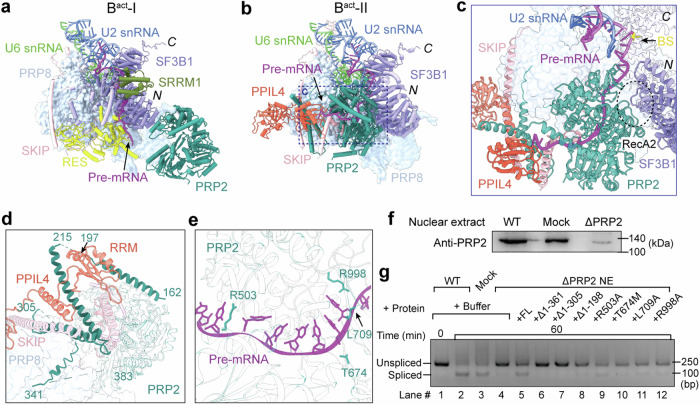
Spliceosome activation is triggered by the helicase BRR211–13; but compelling evidence also implicates a key role by another RNA helicase PRP214,16,41. PRP2 sequentially comprises six domains: an N-terminal extension, RecA1, RecA2, WH, HB, and OB (Supplementary Fig. 11a). PRP2 is absent in pre-Bact and is recruited to the peripheral region of Bact-I where it loosely contacts the N-terminal region of SF3B1 (Fig. 3a). In Bact-I, the splicing factor SRRM1 binds to the N-terminal HEAT repeats of SF3B1. The RES complex, located between SF3B1 and PRP8, associates with the N-terminal flexible helices of SF3B1 and the C-terminal flexible sequences of SKIP (Supplementary Fig. 9b).
Fig. 3. Structure and function of PRP2 in the human Bact complex.
a PRP2 in the Bact-I complex. PRP2 is attached to the peripheral region of the spliceosome and loosely contacts the N-terminal region of SF3B1. N the N-terminus of SF3B1, C the C-terminus of SF3B1. b PRP2 in the Bact-II complex. In the Bact-I to Bact-II transition, PRP2 undergoes a pronounced translocation, moving to the cavity vacated by the RES complex. The PPT sequences of pre-mRNA are loaded into PRP2. c A close-up view on PRP2 in Bact-II. The loop between the N-terminal HEAT repeats of SF3B1 interacts with the RecA2 domain of PRP2, and the BS is anchored on the C-terminal HEAT repeats of SF3B1. The PPT sequences of pre-mRNA are bound to PRP2. d The N-terminal helices of PRP2 directly associate with the C-terminal helices of SKIP, and the linker helix and RRM domain of PPIL4. e A close-up view on the interface between the PPT of pre-mRNA and PRP2. Residues Arg503, Leu709, and Arg998 directly contact the PPT sequences. f Depletion of endogenous PRP2 from the nuclear extract. Compared to the untreated sample, the amount of PRP2 in the nuclear extract is sharply reduced as confirmed by the western blot. g Deletion of the N-terminal extension or mutation of key residues in PRP2 impairs splicing. Shown here are the reverse transcription-PCR results of in vitro splicing reaction. These results have been repeated for three times to confirm the analysis. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
During the Bact-I to Bact-II transition, PRP2 is relocated through a distance of ~80 Å and a rotation of ~90° to the cavity vacated by dissociation of the RES complex (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 11b). The newly identified, extended helices from the N-terminal extension of PRP2 interact with PRP8, PPIL4, the C-terminus of SKIP and pre-mRNA (Fig. 3b). Meanwhile, SRRM1 is released, and the splicing factor PPIL4 is recruited. Most notably, the poly-pyrimidine-tract (PPT) sequences of pre-mRNA are loaded into PRP2 with its 3′-end reaching the RRM of PPIL4 (Supplementary Figs. 10 and 11c). The C-terminal flexible sequences of SKIP become ordered helices, contacting PRP2, PPIL4, and the 3′-end of PPT (Fig. 3c and Supplementary Fig. 11d). Furthermore, the N-terminal helices of SF3B1 become disordered in Bact-II, and the loop sequences connecting the N-terminal HEAT repeats interact with the RecA2 domain of PRP2. The BS is accommodated by the C-terminal HEAT repeats of SF3B1 (Fig. 3c).
The configuration of PRP2 in Bact-III and Bact-IV is nearly identical to that in Bact-II (Supplementary Fig. 12a, b). During the transition of Bact-IV to post-Bact, SF3B1 is relocated away from PRP8, helix II and U2 snRNA undergo obvious movements; but PRP2 remains unchanged. In contrast, SF3B1 undergoes dramatic conformational changes, resulting in the release of the BS from its C-terminal HEAT repeats (Supplementary Fig. 12c). U2 snRNA and U2/BS duplex also exhibit notable translocation in the transition.
One of the key structural findings is identification of the N-terminal helices of PRP2 (residues 162–341), which associate with the C-terminal helices of SKIP and the linker helix and RRM of PPIL4 (Fig. 3d). This finding suggests an important role by these PRP2 N-terminal helices and corroborates an earlier observation that the N-terminal extension of Prp2 in S. cerevisiae can be crosslinked to Prp45 (the SKIP homolog in S. cerevisiae)25. Interestingly, however, deletion of the yeast Prp2 N-terminal extension was reported to have little impact on splicing42.
In addition, three residues in PRP2 (Arg503, Leu709, and Arg998) already closely interact with the nucleobases of PPT in Bact-II, likely preventing the backward sliding of pre-mRNA toward its 5′-end (Fig. 3e). This structural feature is reminiscent of that in the yeast Bact complex43, underscoring a conserved mechanism from yeast to human16. Thr674 is located close to the binding groove for pre-mRNA (Fig. 3e); its mutation to methionine, predicted to cause a steric clash with the phosphate backbone of PPT, is thought to cause neuromuscular oculoauditory syndrome44.
To corroborate these structural findings, we depleted PRP2 (ΔPRP2) from nuclear extract (NE) using an anti-PRP2 antibody (Fig. 3f). Consistent with previous studies41, drastic reduction of PRP2 cripples splicing (Fig. 3g, lane 4). Compared to wide-type (WT) PRP2 (Fig. 3g, lane 5), deletion of its N-terminal 361 or 305 residues abrogated splicing (lanes 6 & 7); deletion of 198 residues also reduced splicing (lane 8) (Supplementary Fig. 13). These results identify a crucial role in splicing by the N-terminal extension of human PRP2. This conclusion is supported by our structural observation and potentially explains the low sequence conservation between the N-terminal extensions of human PRP2 and S. cerevisiae Prp2 (Supplementary Fig. 14a). In addition, each of four PRP2 missense variants (R503A, T674M, L709A, and R998A), which target conversed residues from yeast to human (Supplementary Fig. 14b), exhibits a reduced level of splicing (Fig. 3g, lanes 9–12).
Compositional changes during spliceosome activation
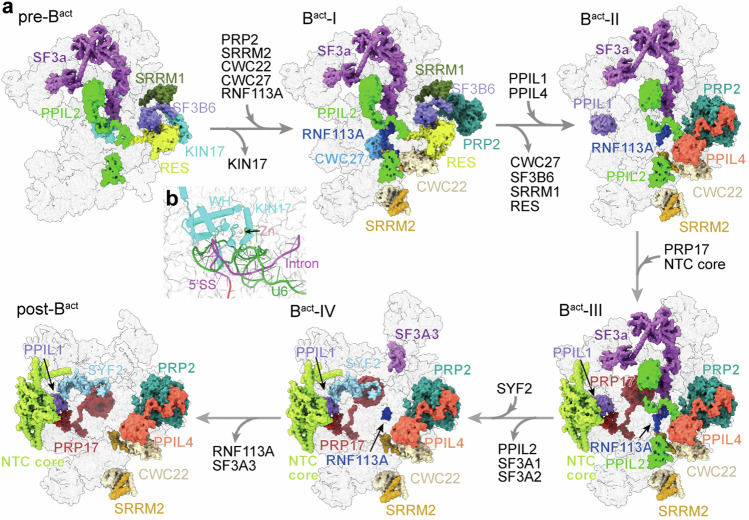
Our structures of six intermediate Bact complexes reveal stepwise compositional changes that occur during human spliceosome activation (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Table 2). In pre-Bact, the splicing factor KIN17 places its N-terminal zinc finger (ZnF) and WH domain above the U6/5′SS duplex (Fig. 4b), consistent with its involvement in 5′SS selection45. During the transition from pre-Bact to Bact-I, KIN17 is dissociated; the splicing factors CWC22, SRRM2, CWC27, RNF113A, and PRP2 are recruited. CWC22 is crucial for PRP2 function in promoting the release of the U2 components SF3a and SF3b46. SRRM2, which promotes the second step conformation and modulates 3′SS selection47,48, remains bound in the spliceosome until exon ligation and is released in the ILS complex49. Notably, CWC27, which was reported to form a heterodimer with CWC22 using its C-terminal region50, only transiently appears in Bact-I and is dissociated in Bact-II. RNF113A directly binds to 5′SS22. RNF113A is involved in the fidelity of 5′SS selection and may orchestrate spliceosome organization into an active configuration prior to PRP2-mediated remodeling51.
Fig. 4. Composition fluxes during activation of human spliceosome.
a The structures of six human Bact complexes, in surface representation with select components color-coded, reveal a series of compositional changes during activation of the human spliceosome. In the transition of pre-Bact to Bact-I, the splicing factor KIN17 is dissociated; CWC22, SRRM2, CWC27, RNF113A, and PRP2 are recruited. During the Bact-I to Bact-II transition, CWC27, SRRM1, SF3B6, and RES complex are released; PPIL1 and PPIL4 are recruited. In the transition of Bact-II to Bact-III, PRP17 and the NTC core are recruited. In the transition of Bact-III to Bact-IV, PPIL2 and the SF3a components SF3A1/SF3A2 are released; SYF2 is recruited. In post-Bact, RNF113A and SF3A3 are released. b A close-up view on the interface between the ZnF and WH domain of KIN17 and U6/5′SS duplex.
During the Bact-I to Bact-II transition, SRRM1, SF3B6, and the RES complex are released (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Table 2). SRRM1, found as a coactivator of pre-mRNA splicing by promoting critical interactions among pre-mRNA-bound splicing factors52,53, associates with pre-mRNA in Bact-I. SF3B6, also known as SF3B14 (p14), has no S. cerevisiae homolog and binds to the N-terminal sequences of SF3B1. Dissociation of the RES complex, which is required for efficient transformation of the B complex to Bact complex34, allows conformational rearrangement of PRP2. This conformation is stabilized by the freshly recruited PPIL4. PPIL1 is also engaged in Bact-II. Notably, PPIL4 associates with the N-terminal extension of PRP2 and the C-terminal fragments of SKIP; this structural feature persists in all later activated states.
Different from Bact-II, PRP17 and the NTC core are engaged in Bact-III. PRP17, which is required for the second step reaction54,55, stays in the spliceosome until its disassembly. In the transition of Bact-III to Bact-IV, PPIL2 and the SF3a components SF3A1/SF3A2 are released, and a major portion of RNF113A becomes disordered (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table 2). SYF2 is recruited in Bact-IV. In addition, RNF113A and SF3a complex are completely absent in the post-Bact complex.
Rearrangements of U2 snRNP
Activation of the human spliceosome involves substantial changes in the position and conformation of U2 snRNP, which consists of U2 snRNA, SF3a complex, SF3b complex, and the U2 snRNP core (U2-A′, U2-B″, and U2 Sm ring) (Fig. 5). U2 snRNP undergoes a stepwise translocation during spliceosome activation, moving to the main body of the spliceosome by a distance of ~150 Å in the B-to-pre-Bact transition (Supplementary Fig. 15a). During the transitions from pre-Bact to Bact-IV, U2 snRNP undergoes only slight conformational changes but marked compositional alterations. The SF3b component SF3B6 and the SF3a components SF3A1/SF3A2 are dissociated in the Bact-I to Bact-II and Bact-III to Bact-IV transitions, respectively. The last SF3a component SF3A3 is dissociated in the Bact-IV to post-Bact transition. Notably, U2 snRNP is translocated by about 50 Å during the transition from Bact-IV to post-Bact, with U2 snRNP core moving closer to the main body of spliceosome (Supplementary Fig. 15b). In the B*/C complexes, the SF3b complex is fully dissociated, and U2 snRNP core undergoes prominent movements.
Fig. 5. Rearrangements of U2 snRNP during human spliceosome activation.
a, b U2 snRNP, comprising U2 snRNA, SF3a, SF3b and the core, undergoes remarkable positional changes in a stepwise manner during spliceosome activation. In the B-to-pre-Bact transition, U2 snRNP undergoes a large translocation, moving toward the main body of spliceosome. U2 snRNP has a series of minor positional and conformational changes from pre-Bact to Bact-IV. Notably, the SF3b component SF3B6 and the SF3a components SF3A1/SF3A2 are dissociated in the transitions of Bact-I to Bact-II and Bact-III to Bact-IV, respectively. The last component SF3A3 of the SF3a complex is released in the Bact-IV to post-Bact transition. In the B*/C complexes, the SF3b complex is dissociated; U2 snRNP core undergoes prominent movements.
The local conformational changes of U2 snRNP during spliceosome activation are exemplified by SF3B1, the core component of the SF3b complex, which anchors the bulged BS using its C-terminal HEAT repeats56,57. The movement of SF3B1 generally coincides with the translocation of U2 snRNP, with the most significant changes occurring in the B to pre-Bact and Bact-IV to post-Bact transitions (Supplementary Fig. 16a). Notably, the BS is freed from the C-terminus of SF3B1 in post-Bact and moves closer to 5′SS, preparing for the branching reaction. In addition, the overall conformation of the superhelical SF3B1 becomes more extended and loosened during the activation process, getting ready for its release from the spliceosome (Supplementary Fig. 16b).
Discussion
Among all assembled spliceosomes, U4 snRNP is only present in the pre-B and B complexes; the splicing active site is only formed in the Bact complex and thereafter. These features allow unambiguous differentiation between the B-like and Bact-like complexes. Along this line, the spatial distance between the two reactive moieties (5′SS and the BS) of the branching reaction defines the Bact versus B* complexes: about 50 Å in the former and <4 Å in the latter. These considerations allowed us to unequivocally identify six intermediate states of the Bact complex, which bridge the critical gap between the B and B* complexes (Supplementary Fig. 2).
Ordering of these six intermediate Bact states is relatively straight forward. Pre-Bact represents a very early state, because helix Ia of the U2/U6 duplex is yet to be formed. In contrast, post-Bact represents a very late state, because the distance between 5′SS and the BS in this state is the shortest (~30 Å) among all six complexes and the SF3a complex has been released. The four intermediates between pre-Bact and post-Bact are differentiated on the basis of both prior experimental observations and rational analysis. Bact-I is ahead of Bact-II, because the RES is present in the former, but not the latter state. Bact-I and Bact-II are ahead of Bact-III, because the NTC core is only present in Bact-III. The SF3A components A1 and A2 are present only in Bact-III and prior states, but not in Bact-IV.
Structures of the six human intermediate Bact complexes reveal a cascade of coordinated rearrangements during spliceosome activation. Our results highlight the interplay between protein components and RNA elements in this process. One unanticipated finding is the gradual engagement of the BS to 5′SS (Fig. 2). Analysis of the six states, together with that of the newly resolved C complex, unveils a remarkable choreography of the RNA elements, leading to the branching reaction (Supplementary Movie 1). In the pre-Bact to Bact-I transition, helix Ia is formed, the key nucleotide U74 of U6 snRNA (U80 in S. cerevisiae) is flipped inside out, and two catalytic Mg2+ ions are appropriately loaded, resulting in the maturation of U6 ISL. U5 snRNA undergoes a notable translocation, delivering 5′-exon-5′SS to the correct location for nucleophilic attack by the BS. Meanwhile, driven by the remarkable movement of U2 snRNA, the BS is freed from SF3B1 and moves closer to 5′SS by about 20 Å during the transition of Bact-IV to post-Bact.
Actions of the conserved RNA helicases are the ultimate driving force for spliceosomal remodeling and the splicing reaction. However, due to the transient nature of such actions, mechanistic understanding can be achieved through the recapitulation of a series of static pictures. In this study, an unanticipated finding is the remarkable rearrangement of PRP2 in the process of engaging the PPT sequences (Fig. 3). PRP2 associates with Bact-I at the periphery but, following the release of SRRM1 and RES complex, is flipped into the central region of Bact-II. In addition, PPIL4 is engaged, and the C-terminus of SKIP is ordered into helices. In Bact-II, the N-terminal extension of PRP2 plays a previously unrecognized key role in splicing through interactions with PPIL4, SKIP, and PRP8. Similar to yeast Prp2, a few residues of PRP2 may prevent backward sliding of pre-mRNA. These structure-based conjectures are supported by biochemical analyses (Fig. 3).
The transition from B to Bact is thought to be mainly driven by the RNA helicase BRR2, which pulls U4 snRNA to trigger the dissociation of U4 snRNP11–13. However, once U4 snRNP is dissociated (as is the case in the intermediate Bact states), BRR2 can no longer exert its force to drive remodeling. Nonetheless, the conformation and composition of the spliceosome continue to change from pre-Bact to post-Bact. It is possible that the driving force for these changes is still the consequence of BRR2 action. Alternatively and perhaps more likely, PRP2 may play a key role. This conjecture is supported by the recruitment of PRP2 into Bact-I and pre-mRNA binding by PRP2 in Bact-II, both occurring at relatively early stages. The subsequent positional and conformational rearrangements of other components, as a result of continuous spliceosomal remodeling, are likely attributed to the RNA helicase activity of PRP2. Such an intricate role by PRP2 remains to be experimentally scrutinized.
The advent of the intermediate states of the human-activated spliceosome allows comparison with previously reported Bact complexes22,26. Our pre-Bact complex is reminiscent of the previously reported pre-Bact-2 complex, which was captured using another splicing inhibitor26. However, there are obvious differences in the overall architecture between our pre-Bact and the pre-Bact-2, especially in U2 and U5 snRNPs (Supplementary Fig. 17a). The B-specific proteins (PRP38, SNU23, MFAP1, and UBL5) together with CTNNBL1 are absent in our pre-Bact, suggesting that our pre-Bact may be downstream of pre-Bact-2 in the activation process. Notably, the previously reported pre-Bact-1 complex is more similar to the B complex26. In addition, Bact-I in this study resembles the previously described early Bact conformation22, but SYF3 and AQR are only present in Bact-I (Supplementary Fig. 17b), suggesting the previous early Bact lies intermediary between the pre-Bact and Bact-I. Through scrutinizing the protein components, the previously described mature Bact22 resembles the Bact-III and late Bact22 appears to bridge between the Bact-IV and post-Bact. As we were preparing this manuscript, an intermediate BAQR complex, enriched through the use of dominant negative AQR, was reported58; BAQR is structurally similar to our Bact-III complex (Supplementary Fig. 17c). The six distinct conformations reported in this study, together with those previously described22,26,58, collectively define the intermediate states of the spliceosome between the B and B* complexes.
We used the splicing inhibitor NPL, which is thought to affect the late assembly of the spliceosome30. The reported effect of the inhibitor is supported by particle distribution in the EM micrographs (Supplementary Fig. 2), which gives rise to six intermediate states of the Bact complex as well as the C complex. The use of the splicing inhibitor NPL likely allows the accumulation of the spliceosomal intermediate states that are otherwise transient during normal splicing. Structural and biochemical analysis strongly suggest that these conformational states may faithfully represent those in the splicing cycle. However, there is no obvious EM density for NPL. As such, the target of NPL remains to be identified. It is possible that this inhibitor may target a protein that regulates splicing through an enzymatic activity but makes no direct interaction with the spliceosome.
Methods
In vitro assembly of human spliceosomal complexes
The human spliceosomal complexes were assembled on the MINX pre-mRNA in vitro. The pre-mRNA with three tandem MS2 binding sites at its 3′-end was in vitro synthesized using the T7 run-off transcription method. The nuclear extracts of HeLa S3 cells were prepared as described59. The chemically synthesized small molecule NPL was incubated with the HeLa nuclear extract on ice at a concentration of ~600 μM for 1 h (Supplementary Fig. 1a). Meanwhile, the pre-mRNA was pre-incubated with the MS2-MBP fusion protein. The in vitro splicing reaction was performed at 30 °C for 1 h after mixing 15 nM pre-treated pre-mRNA with 50% (v/v) NPL bound-nuclear extract (diluted by a buffer containing 2 mM ATP, 20 mM creatine phosphate, 3 mM MgCl2, 20 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.9, and 50 mM KCl).
Purification of human spliceosomal complexes
The assembled human spliceosomal complexes were incubated with the amylose resin (NEB) at 4 °C for 2 h, and isolated using the MS2-MBP affinity chromatography. The amylose resin was rinsed using the G150 buffer (20 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.9, 150 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 4% glycerol). Eluted by the same buffer supplemented with 20 mM maltose, the spliceosomal complexes were further applied for a linear 10–30% (v/v) glycerol gradient with 0–0.1% EM-grade glutaraldehyde (Supplementary Fig. 1b). After centrifugation for 13 h at 4 °C at 110,000 × g, total RNA was extracted from the fractions and analyzed on a denaturing 8% urea–polyacrylamide gel (Supplementary Fig. 1c). The fractions containing spliceosomal complexes were pooled, concentrated, and dialyzed against the D150 buffer (20 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.9, 150 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2).
Cryo-EM sample preparation and data collection
The purified human spliceosomal complexes were used for cryo-EM sample preparation after examination by negative staining. Holey carbon grids (Quantifoil, Cu, 300-mesh, R1.2/1.3, 2 nm C) were glow-discharged in the Plasma Cleaner (HARRICK PLASMA Company) and each aliquot (4 μL) of the sample was applied to a glow-discharged grid. After blotting for 3.5 s, the grids were quickly plunged into liquid ethane cooled by liquid nitrogen using Vitrobot Mark IV (Thermo Fisher) at 8 °C and 100% humidity.
The cryo-grids were further transferred to a 300-kV Titan Krios electron microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) equipped with a Gatan K3 detector and GIF Quantum energy filter (slit width 20 eV). The micrographs were collected using a normal magnification of 81,000× in the super-resolution mode (Supplementary Fig. 1d). Each movie stack of 32 frames was automatically exposed for 2.56 s with a total dose of ~50 e−/Å2 using EPU (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The movies with the preset defocus range from −1.4 to −2.0 μm were aligned and summed using MotionCor260 with a binning factor of 2, resulting in a pixel size of 1.077 Å. Dose weighting was performed concurrently. The defocus value for each image was determined using Gctf61.
Cryo-EM image processing
The cryo-EM data processing is briefly described here (Supplementary Fig. 2). All steps were mainly carried out in RELION 3.062 unless stated otherwise. In total, 17,070 good micrographs were manually selected from 18,277 collected images, generating ~4.6 million particles using Gautomatch (developed by Kai Zhang, https://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/download/gautomatch-053/). Multi-reference guided 3D classifications were applied to the total particles, and two parallel runs were simultaneously performed. Multiple conformational states of the human-activated spliceosome were clearly present. Good particles were merged, and the duplicated particles were removed. The remaining ~1.5 million particles were re-extracted using a 2× binned pixel size of 2.154 Å. To further differentiate the different conformational states, we performed another round of multi-reference 3D classification. Three different conformational states of the human-activated spliceosomes were selected. The remaining particles were re-extracted using the unbinned pixel size of 1.077 Å. Good particles for each conformation were further analyzed using 3D classification with the skip_align option in RELION62. Finally, six distinct conformational states of the activated spliceosomes (Bact complex) and the catalytic step I spliceosome (C complex) were reconstructed. Based on differences of protein composition and conformation, the six conformational states of the Bact complex were unambiguously ordered and named as pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, and post-Bact. After final refinement using the Non-uniform Refinement in cryoSPARC63, the reconstructions for pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, post-Bact, and the C complexes were obtained at average resolutions of 3.4, 3.0, 4.2, 3.0, 3.3, 3.0, and 3.4 Å using 46,696, 136,665, 13,372, 111,205, 47,352, 92,596, and 18,223 particles, respectively (Supplementary Figs. 2, 3 and Supplementary Table 1).
Reported resolutions are calculated on the basis of the FSC value of 0.14364. The angular distributions of the particles used for the final reconstructions are reasonable (Supplementary Fig. 4). Local resolution variations were estimated using cryoSPARC63 (Supplementary Fig. 5). The EM density maps display clear features (Supplementary Figs. 6–10). Based on these results, we performed detailed structural and biochemical analysis on PRP2 (Supplementary Figs. 11–14), U2 snRNP (Supplementary Fig. 15), and the scaffolding component SF3B1 (Supplementary Fig. 16). We also made the structural comparison between the intermediate states reported in this manuscript and those reported previously (Supplementary Fig. 17).
Model building and refinement
The atomic models were generated by rigid docking of components with known structures and de novo modeling facilitated by AlphaFold65. For six different conformational states of the Bact complex, identification and docking of the known components were guided by the structures of previously reported human Bact complexes22,26. Protein components derived from these structures were fitted into the EM density maps using Chimera66 and manually adjusted using Coot67.
For the splicing factors KIN17 in pre-Bact, SRRM1 in pre-Bact and Bact-I, and PPIL2 in pre-Bact to Bact-III, individual domains from the predicated models were first docked into the respective EM density regions; the flexible linker sequences were de novo built. The N-terminal extension of PRP2 was assigned on the basis of its predicted helical feature and the positions of the bulky residues. Initially identified by mass spectrometry, the splicing factor PPIL4 was located through examination of the EM map and modeled on the basis of its AlphaFold-predicted structure. Based on our previously reported structures31 and the current 3.4-Å EM map, the atomic model of the human C complex in this study was improved.
The final atomic models of the human-activated spliceosomes and C complex were refined according to the cryo-EM maps using phenix.real_space_refine program in PHENIX with secondary structure restraints68. The structures were further validated through examination of the MolProbity scores and statistics of the Ramachandran plots. MolProbity scores were calculated as described69.
Expression and purification of PRP2
The cDNA sequences of human full-length PRP2 (DHX16, Uniprot ID: O60231), three truncated constructs (Δ1-198, Δ1-305, Δ1-361), and four missense variants (R503A, T674M, L709A, R998A) were generated using PCR-based strategy, and individually subcloned into a pCAG vector with an N-terminal 3xFlag tag70. The constructs were confirmed using DNA sequencing. Each plasmid was prepared with the GoldHi EndoFree Plasmid Maxi Kit (CWBio Inc., Cat# CW2104M). The purified plasmids were transiently transfected into Expi293F cells using 40K polyethyleneimines (PEIs, Polysciences) when the cell density reached about 2 × 106. The transfected cells were further cultured in SMM 293T-II medium at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for ~60 h.
The harvested cells were resuspended in the lysis buffer (25 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.9, 150 mM NaCl) supplemented with 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 2.6 μg/mL aprotinin, 1.4 μg/mL pepstatin, and 5 μg/mL leupeptin, and subsequently lysed through sonication. Cell debris was removed through centrifugation, and the supernatant was applied to the anti-Flag M2 affinity gel (Sigma). The washed resin was further rinsed with the buffer containing 25 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.9, 50 mM NaCl, 0.2 mg/mL Flag peptide. The protein eluent was applied to a heparin column (HiTrap Heparin HP, Cytiva) to remove endogenous nucleic acids. The desired fractions were concentrated, and subjected to a size-exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200 10/300 GL, Cytiva) using the lysis buffer. The peak fractions were examined using SDS–PAGE (Supplementary Fig. 13), and stored at −80 °C for further reconstitution assays.
Immuno-depletion of PRP2 and reconstitution assay
To deplete endogenous PRP2, 20 μL PRP2 antibody (Proteintech, Cat# 11021-1-AP) was incubated with 10 μL Protein A/G Magnetic beads (Pierce) at room temperature for 2 h in a buffer containing 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 0.01% NP-40. Four hundred microliters HeLa nuclear extract was successively incubated with three aliquots of 10-μL anti-PRP2-conjugated magnetic beads at 4 °C, each for 2–3 h. The PRP2-depleted (ΔPRP2) nuclear extract was collected. Depletion efficiency was examined through western blots using an anti-PRP2 antibody. For mock depletion, 20 μL of 0.35 mg/mL BSA were incubated with 10 μL of Protein A/G Magnetic beads.
The small-scale in vitro splicing assays were performed using 40% (v/v) WT, mock and PRP2-depleted (ΔPRP2) nuclear extracts supplemented with 2 mM ATP, 20 mM creatine phosphate, 3 mM MgCl2, 20 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.9. The splicing reaction was carried out at 30 °C for 1 h. The total RNA was isolated through phenol extraction and ethanol precipitation after proteinase-K digestion. The splicing efficiency was examined using reverse transcription-PCR.
For PRP2 reconstitution assay, each of the purified recombinant proteins of the PRP2 variants was pre-incubated with the ΔPRP2 nuclear extract on ice for 30 min at a concentration of 400 nM. Then the protein-supplemented ΔPRP2 nuclear extract was applied to the small-scale splicing assay, and the final concentration of reconstituted recombinant proteins was about 200 nM.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary information
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Source data
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yingjie Lei for his help in synthesizing and characterizing the small molecule NPL. We thank the Cryo-EM Facility, Mass Spectrometry & Metabolomics Core Facility, and High-Performance Computing Center of Westlake University for excellent services. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31930059 to Y. Shi), the “Pioneer” and “Leading Goose” R&D Program of Zhejiang (2024SSYS0029), and Start-up funds from Westlake University.
Author contributions
Y. Shi conceived and supervised the project. X. Zhan and Y. Lu designed and performed the experiments, and processed the EM data. X. Zhan built the atomic models. X. Zhan, Y. Lu, and Y. Shi wrote the manuscript.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Data availability
The atomic coordinates for human pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, post-Bact, and C complexes have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) under the accession codes 8I0P, 8I0R, 8I0S, 8I0T, 8I0U, 8I0V, and 8I0W, respectively. The EM maps of human pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, post-Bact, and C complexes have been deposited in the EMDB with accession codes EMD-35105, EMD-35107, EMD-35108, EMD-35109, EMD-35110, EMD-35111, and EMD-35113, respectively. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Xiechao Zhan, Yichen Lu.
Contributor Information
Xiechao Zhan, Email: zhanxiechao@westlake.edu.cn.
Yigong Shi, Email: syg@westlake.edu.cn.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41467-024-50785-0.
References
- 1.Shi, Y. Mechanistic insights into precursor messenger RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.18, 655–670 (2017). 10.1038/nrm.2017.86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wan, R., Bai, R., Zhan, X. & Shi, Y. How is precursor messenger RNA spliced by the spliceosome? Annu. Rev. Biochem.89, 333–358 (2020). 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shi, Y. The spliceosome: a protein-directed metalloribozyme. J. Mol. Biol.429, 2640–2653 (2017). 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yan, C., Wan, R. & Shi, Y. Molecular mechanisms of pre-mRNA splicing through structural biology of the spliceosome. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.11, a032409 (2019). 10.1101/cshperspect.a032409 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wilkinson, M. E., Charenton, C. & Nagai, K. RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem.89, 359–388 (2020). 10.1146/annurev-biochem-091719-064225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kastner, B., Will, C. L., Stark, H. & Luhrmann, R. Structural insights into nuclear pre-mRNA splicing in higher eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.11, a032417 (2019). 10.1101/cshperspect.a032417 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wahl, M. C. & Luhrmann, R. SnapShot: spliceosome dynamics I. Cell161, 1474.e1471 (2015). 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Staley, J. P. & Guthrie, C. An RNA switch at the 5′ splice site requires ATP and the DEAD box protein Prp28p. Mol. Cell3, 55–64 (1999). 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80174-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boesler, C. et al. A spliceosome intermediate with loosely associated tri-snRNP accumulates in the absence of Prp28 ATPase activity. Nat. Commun.7, 11997 (2016). 10.1038/ncomms11997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Strauss, E. J. & Guthrie, C. PRP28, a ‘DEAD-box’ protein, is required for the first step of mRNA splicing in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res.22, 3187–3193 (1994). 10.1093/nar/22.15.3187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Raghunathan, P. L. & Guthrie, C. RNA unwinding in U4/U6 snRNPs requires ATP hydrolysis and the DEIH-box splicing factor Brr2. Curr. Biol.8, 847–855 (1998). 10.1016/S0960-9822(07)00345-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maeder, C., Kutach, A. K. & Guthrie, C. ATP-dependent unwinding of U4/U6 snRNAs by the Brr2 helicase requires the C terminus of Prp8. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.16, 42–48 (2009). 10.1038/nsmb.1535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hahn, D., Kudla, G., Tollervey, D. & Beggs, J. D. Brr2p-mediated conformational rearrangements in the spliceosome during activation and substrate repositioning. Genes Dev.26, 2408–2421 (2012). 10.1101/gad.199307.112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim, S. H. & Lin, R. J. Spliceosome activation by PRP2 ATPase prior to the first transesterification reaction of pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell. Biol.16, 6810–6819 (1996). 10.1128/MCB.16.12.6810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu, H. L. & Cheng, S. C. The interaction of Prp2 with a defined region of the intron is required for the first splicing reaction. Mol. Cell. Biol.32, 5056–5066 (2012). 10.1128/MCB.01109-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ohrt, T. et al. Prp2-mediated protein rearrangements at the catalytic core of the spliceosome as revealed by dcFCCS. RNA18, 1244–1256 (2012). 10.1261/rna.033316.112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim, S. H., Smith, J., Claude, A. & Lin, R. J. The purified yeast pre-mRNA splicing factor PRP2 is an RNA-dependent NTPase. EMBO J.11, 2319–2326 (1992). 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05291.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhan, X., Yan, C., Zhang, X., Lei, J. & Shi, Y. Structures of the human pre-catalytic spliceosome and its precursor spliceosome. Cell Res.28, 1129–1140 (2018). 10.1038/s41422-018-0094-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bertram, K. et al. Cryo-EM structure of a pre-catalytic human spliceosome primed for activation. Cell170, 701–713.e711 (2017). 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Plaschka, C., Lin, P. C. & Nagai, K. Structure of a pre-catalytic spliceosome. Nature546, 617 (2017). 10.1038/nature22799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bai, R., Wan, R., Yan, C., Lei, J. & Shi, Y. Structures of the fully assembled Saccharomyces cerevisiae spliceosome before activation. Science360, 1423–1429 (2018). 10.1126/science.aau0325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang, X. et al. Structure of the human activated spliceosome in three conformational states. Cell Res.28, 307–322 (2018). 10.1038/cr.2018.14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Haselbach, D. et al. Structure and conformational dynamics of the human spliceosomal Bact complex. Cell172, 454–464 e411 (2018). 10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yan, C., Wan, R., Bai, R., Huang, G. & Shi, Y. Structure of a yeast activated spliceosome at 3.5 Å resolution. Science353, 904–911 (2016). 10.1126/science.aag0291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rauhut, R. et al. Molecular architecture of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae activated spliceosome. Science353, 1399–1405 (2016). 10.1126/science.aag1906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Townsend, C. et al. Mechanism of protein-guided folding of the active site U2/U6 RNA during spliceosome activation. Science370, eabc3753 (2020). 10.1126/science.abc3753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cordin, O., Hahn, D. & Beggs, J. D. Structure, function and regulation of spliceosomal RNA helicases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.24, 431–438 (2012). 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cordin, O. & Beggs, J. D. RNA helicases in splicing. RNA Biol.10, 83–95 (2013). 10.4161/rna.22547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu, Y. C. & Cheng, S. C. Functional roles of DExD/H-box RNA helicases in Pre-mRNA splicing. J. Biomed. Sci.22, 54 (2015). 10.1186/s12929-015-0161-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Effenberger, K. A. et al. The natural product N-palmitoyl-l-leucine selectively inhibits late assembly of human spliceosomes. J. Biol. Chem.290, 27524–27531 (2015). 10.1074/jbc.M115.673210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhan, X., Yan, C., Zhang, X., Lei, J. & Shi, Y. Structure of a human catalytic step I spliceosome. Science359, 537–545 (2018). 10.1126/science.aar6401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bertram, K. et al. Structural Insights into the roles of metazoan-specific splicing factors in the human step 1 spliceosome. Mol. Cell80, 127–139.e126 (2020). 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wan, R., Bai, R., Yan, C., Lei, J. & Shi, Y. Structures of the catalytically activated yeast spliceosome reveal the mechanism of branching. Cell177, 339–351.e313 (2019). 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bao, P., Will, C. L., Urlaub, H., Boon, K. L. & Luhrmann, R. The RES complex is required for efficient transformation of the precatalytic B spliceosome into an activated Bact complex. Genes Dev.31, 2416–2429 (2017). 10.1101/gad.308163.117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wysoczanski, P. & Zweckstetter, M. Retention and splicing complex (RES) – the importance of cooperativity. RNA Biol.13, 128–133 (2016). 10.1080/15476286.2015.1096484 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vidal, V. P., Verdone, L., Mayes, A. E. & Beggs, J. D. Characterization of U6 snRNA-protein interactions. RNA5, 1470–1481 (1999). 10.1017/S1355838299991355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yean, S. L., Wuenschell, G., Termini, J. & Lin, R. J. Metal-ion coordination by U6 small nuclear RNA contributes to catalysis in the spliceosome. Nature408, 881–884 (2000). 10.1038/35048617 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Huppler, A., Nikstad, L. J., Allmann, A. M., Brow, D. A. & Butcher, S. E. Metal binding and base ionization in the U6 RNA intramolecular stem-loop structure. Nat. Struct. Biol.9, 431–435 (2002). 10.1038/nsb800 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Butcher, S. E. The spliceosome and its metal ions. Met. Ions Life Sci.9, 235–251 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fica, S. M. et al. RNA catalyses nuclear pre-mRNA splicing. Nature503, 229–234 (2013). 10.1038/nature12734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gencheva, M., Kato, M., Newo, A. N. & Lin, R. J. Contribution of DEAH-box protein DHX16 in human pre-mRNA splicing. Biochem. J.429, 25–32 (2010). 10.1042/BJ20100266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Edwalds-Gilbert, G., Kim, D. H., Silverman, E. & Lin, R. J. Definition of a spliceosome interaction domain in yeast Prp2 ATPase. RNA10, 210–220 (2004). 10.1261/rna.5151404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bai, R. et al. Mechanism of spliceosome remodeling by the ATPase/helicase Prp2 and its coactivator Spp2. Science371, eabe8863 (2021). 10.1126/science.abe8863 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Paine, I. et al. Paralog studies augment gene discovery: DDX and DHX genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet.105, 302–316 (2019). 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.06.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Suzuki, J. et al. A genetic screen in C. elegans reveals roles for KIN17 and PRCC in maintaining 5′ splice site identity. PLoS Genet.18, e1010028 (2022). 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yeh, T. C. et al. Splicing factor Cwc22 is required for the function of Prp2 and for the spliceosome to escape from a futile pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol.31, 43–53 (2011). 10.1128/MCB.00801-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Grainger, R. J., Barrass, J. D., Jacquier, A., Rain, J. C. & Beggs, J. D. Physical and genetic interactions of yeast Cwc21p, an ortholog of human SRm300/SRRM2, suggest a role at the catalytic center of the spliceosome. RNA15, 2161–2173 (2009). 10.1261/rna.1908309 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gautam, A., Grainger, R. J., Vilardell, J., Barrass, J. D. & Beggs, J. D. Cwc21p promotes the second step conformation of the spliceosome and modulates 3′ splice site selection. Nucleic Acids Res.43, 3309–3317 (2015). 10.1093/nar/gkv159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang, X. et al. Structures of the human spliceosomes before and after release of the ligated exon. Cell Res.29, 274–285 (2019). 10.1038/s41422-019-0143-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Busetto, V. et al. Structural and functional insights into CWC27/CWC22 heterodimer linking the exon junction complex to spliceosomes. Nucleic Acids Res.48, 5670–5683 (2020). 10.1093/nar/gkaa267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wu, N. Y., Chung, C. S. & Cheng, S. C. Role of Cwc24 in the first catalytic step of splicing and fidelity of 5′ splice site selection. Mol. Cell. Biol.3710.1128/MCB.00580-16 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 52.Blencowe, B. J., Issner, R., Nickerson, J. A. & Sharp, P. A. A coactivator of pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev.12, 996–1009 (1998). 10.1101/gad.12.7.996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Blencowe, B. J. et al. The SRm160/300 splicing coactivator subunits. RNA6, 111–120 (2000). 10.1017/S1355838200991982 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ben Yehuda, S. et al. Identification and functional analysis of hPRP17, the human homologue of the PRP17/CDC40 yeast gene involved in splicing and cell cycle control. RNA4, 1304–1312 (1998). 10.1017/S1355838298980712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lindsey-Boltz, L. A., Chawla, G., Srinivasan, N., Vijayraghavan, U. & Garcia-Blanco, M. A. The carboxy terminal WD domain of the pre-mRNA splicing factor Prp17p is critical for function. RNA6, 1289–1305 (2000). 10.1017/S1355838200000327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tholen, J., Razew, M., Weis, F. & Galej, W. P. Structural basis of branch site recognition by the human spliceosome. Science375, 50–57 (2022). 10.1126/science.abm4245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang, X. et al. Structural insights into branch site proofreading by human spliceosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.31, 835–845 (2024). 10.1038/s41594-023-01188-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schmitzova, J., Cretu, C., Dienemann, C., Urlaub, H. & Pena, V. Structural basis of catalytic activation in human splicing. Nature617, 842–850 (2023). 10.1038/s41586-023-06049-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dignam, J. D., Lebovitz, R. M. & Roeder, R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase-II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res.11, 1475–1489 (1983). 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zheng, S. Q. et al. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods14, 331–332 (2017). 10.1038/nmeth.4193 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang, K. Gctf: real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol.193, 1–12 (2016). 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.11.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zivanov, J. et al. New tools for automated high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in RELION-3. Elife7, e42166 (2018). 10.7554/eLife.42166 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Punjani, A., Zhang, H. & Fleet, D. J. Non-uniform refinement: adaptive regularization improves single-particle cryo-EM reconstruction. Nat. Methods17, 1214–1221 (2020). 10.1038/s41592-020-00990-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chen, S. X. et al. High-resolution noise substitution to measure overfitting and validate resolution in 3D structure determination by single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Ultramicroscopy135, 24–35 (2013). 10.1016/j.ultramic.2013.06.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Jumper, J. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature596, 583–589 (2021). 10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF Chimera – a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem.25, 1605–1612 (2004). 10.1002/jcc.20084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D60, 2126–2132 (2004). 10.1107/S0907444904019158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Afonine, P. V. et al. Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol.74, 531–544 (2018). 10.1107/S2059798318006551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Davis, I. W. et al. MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res.35, W375–W383 (2007). 10.1093/nar/gkm216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Matsuda, T. & Cepko, C. L. Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA101, 16–22 (2004). 10.1073/pnas.2235688100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF ChimeraX: structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci.30, 70–82 (2021). 10.1002/pro.3943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.DeLano, W. L. The PyMOL molecular graphics system. http://www.pymol.org (2002).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Data Availability Statement
The atomic coordinates for human pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, post-Bact, and C complexes have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) under the accession codes 8I0P, 8I0R, 8I0S, 8I0T, 8I0U, 8I0V, and 8I0W, respectively. The EM maps of human pre-Bact, Bact-I, Bact-II, Bact-III, Bact-IV, post-Bact, and C complexes have been deposited in the EMDB with accession codes EMD-35105, EMD-35107, EMD-35108, EMD-35109, EMD-35110, EMD-35111, and EMD-35113, respectively. Source data are provided with this paper.