Abstract
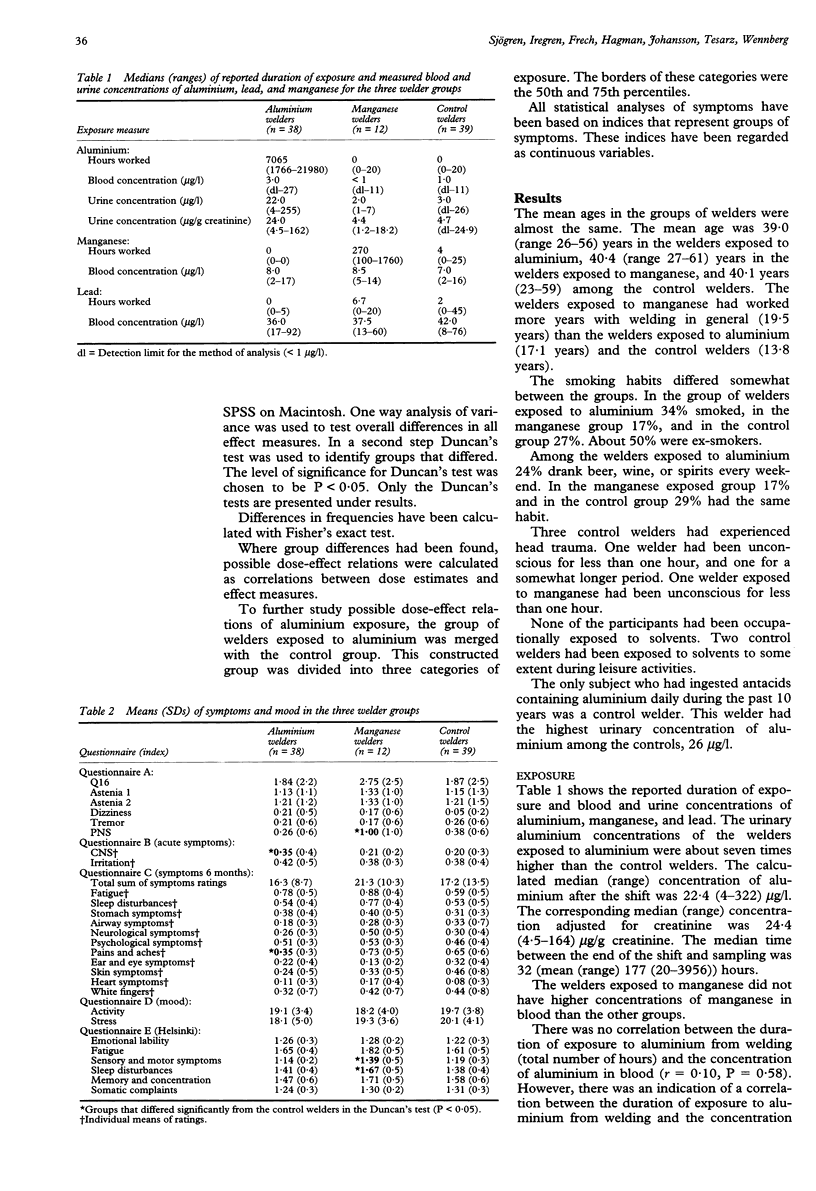
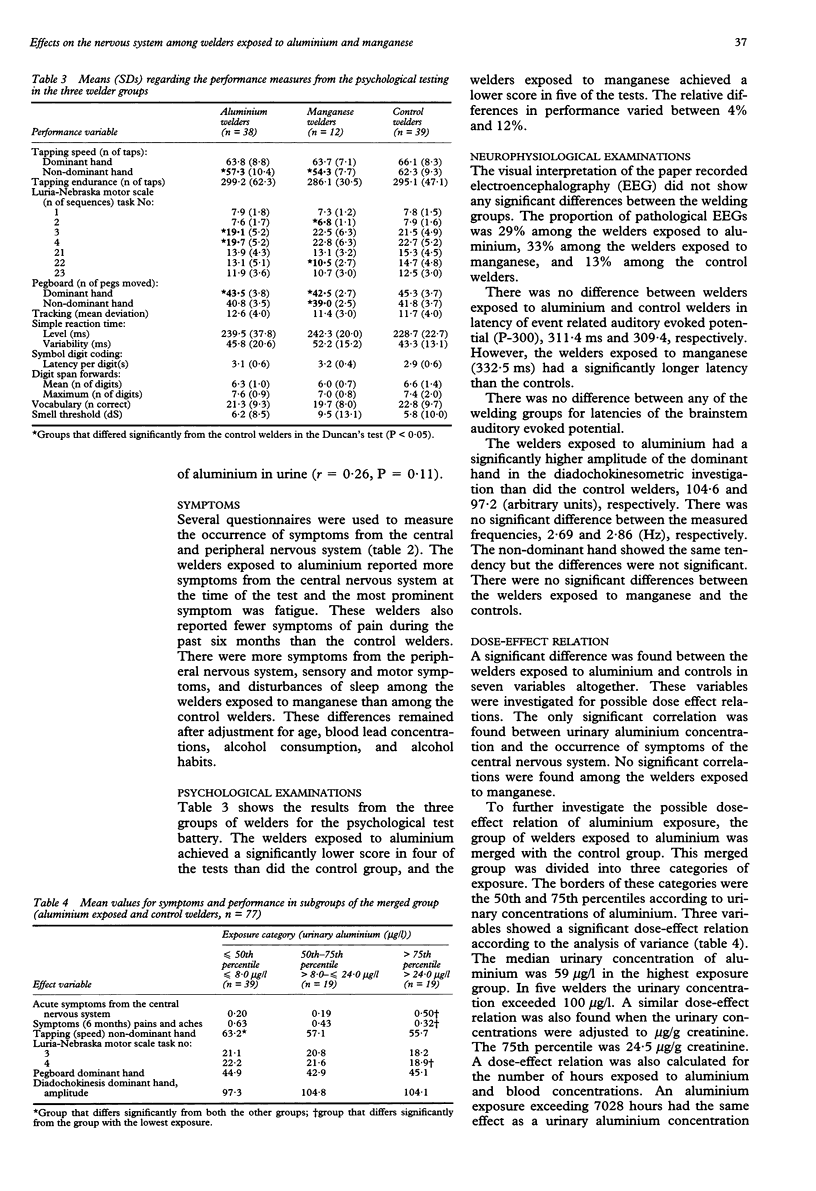
OBJECTIVES--The purpose was to study the effects on the nervous system in welders exposed to aluminium and manganese. METHODS--The investigation included questionnaires on symptoms, psychological methods (simple reaction time, finger tapping speed and endurance, digit span, vocabulary, tracking, symbol digit, cylinders, olfactory threshold, Luria-Nebraska motor scale), neurophysiological methods (electroencephalography, event related auditory evoked potential (P-300), brainstem auditory evoked potential, and diadochokinesometry) and assessments of blood and urine concentrations of metals (aluminium, lead, and manganese). RESULTS--The welders exposed to aluminium (n = 38) reported more symptoms from the central nervous system than the control group (n = 39). They also had a decreased motor function in five tests. The effect was dose related in two of these five tests. The median exposure of aluminium welders was 7065 hours and they had about seven times higher concentrations of aluminium in urine than the controls. The welders exposed to manganese (n = 12) had a decreased motor function in five tests. An increased latency of event related auditory evoked potential was also found in this group. The median manganese exposure was 270 hours. These welders did not have higher concentrations of manganese in blood than the controls. CONCLUSIONS--The neurotoxic effects found in the groups of welders exposed to aluminium and manganese are probably caused by the aluminium and manganese exposure, respectively. These effects indicate a need for improvements in the work environments of these welders.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfrey A. C., LeGendre G. R., Kaehny W. D. The dialysis encephalopathy syndrome. Possible aluminum intoxication. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 22;294(4):184–188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601222940402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann P., Dhanesha U., Hamon C., Cunningham J., Blair J., Marsh F. Disturbance of cerebral function by aluminium in haemodialysis patients without overt aluminium toxicity. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):7–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast-Pettersen R., Drabløs P. A., Goffeng L. O., Thomassen Y., Torres C. G. Neuropsychological deficit among elderly workers in aluminum production. Am J Ind Med. 1994 May;25(5):649–662. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700250505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder C. G., Ahrengart L., Lidums V., Pettersson E., Sjögren B. Evidence of aluminium accumulation in aluminium welders. Br J Ind Med. 1991 Nov;48(11):735–738. doi: 10.1136/oem.48.11.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hine C. H., Pasi A. Manganese intoxication. West J Med. 1975 Aug;123(2):101–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosovski E., Mastelica Z., Sunderić D., Radulović D. Mental abilities of workers exposed to aluminium. Med Lav. 1990 Mar-Apr;81(2):119–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H., Matikainen E., Kovala T., Valkonen S., Riihimäki V. Internal load of aluminum and the central nervous system function of aluminum welders. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1994 Aug;20(4):279–285. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iregren A. Using psychological tests for the early detection of neurotoxic effects of low level manganese exposure. Neurotoxicology. 1994 Fall;15(3):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. S., Williams H. E., Hinton D. Elevated plasma manganese levels in welders cutting manganese steel. N Z Med J. 1985 Oct 9;98(788):870–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristenson H., Trell E. Indicators of alcohol consumption: comparisons between a questionnaire (Mm-MAST), interviews and serum gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) in a health survey of middle-aged males. Br J Addict. 1982 Sep;77(3):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1982.tb02459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini R., Selis L., Folli D., Apostoli P., Mutti A., Vanoni O., Iregren A., Alessio L. Neurobehavioral effects of manganese in workers from a ferroalloy plant after temporary cessation of exposure. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1995 Apr;21(2):143–149. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLAUGHLIN A. I., KAZANTZIS G., KING E., TEARED, PORTER R. J., OWEN R. Pulmonary fibrosis and encephalopathy associated with the inhalation of aluminium dust. Br J Ind Med. 1962 Oct;19:253–263. doi: 10.1136/oem.19.4.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergler D., Huel G., Bowler R., Iregren A., Bélanger S., Baldwin M., Tardif R., Smargiassi A., Martin L. Nervous system dysfunction among workers with long-term exposure to manganese. Environ Res. 1994 Feb;64(2):151–180. doi: 10.1006/enrs.1994.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Golnick J., Korn T., Angle C. Manganese encephalopathy: utility of early magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Ind Med. 1993 Jun;50(6):510–513. doi: 10.1136/oem.50.6.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifat S. L., Eastwood M. R., McLachlan D. R., Corey P. N. Effect of exposure of miners to aluminium powder. Lancet. 1990 Nov 10;336(8724):1162–1165. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92775-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roels H. A., Ghyselen P., Buchet J. P., Ceulemans E., Lauwerys R. R. Assessment of the permissible exposure level to manganese in workers exposed to manganese dioxide dust. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Jan;49(1):25–34. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roels H., Lauwerys R., Buchet J. P., Genet P., Sarhan M. J., Hanotiau I., de Fays M., Bernard A., Stanescu D. Epidemiological survey among workers exposed to manganese: effects on lung, central nervous system, and some biological indices. Am J Ind Med. 1987;11(3):307–327. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700110308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreeder M. T., Favero M. S., Hughes J. R., Petersen N. J., Bennett P. H., Maynard J. E. Dialysis encephalopathy and aluminum exposure: an epidemiologic analysis. J Chronic Dis. 1983;36(8):581–593. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(83)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl P., Bergert K. D. Eine frühdiagnostische Uberwachungsmethode bei Manganexposition. Z Gesamte Hyg. 1982 Aug;28(8):524–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Elinder C. G., Lidums V., Chang G. Uptake and urinary excretion of aluminum among welders. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1988;60(2):77–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00381484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Gustavsson P., Hogstedt C. Neuropsychiatric symptoms among welders exposed to neurotoxic metals. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Oct;47(10):704–707. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.10.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Lidums V., Håkansson M., Hedström L. Exposure and urinary excretion of aluminum during welding. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Feb;11(1):39–43. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Ljunggren K. G., Almkvist O., Frech W., Basun H. Aluminosis and dementia. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1154–1154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90659-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slanina P., Frech W., Bernhardson A., Cedergren A., Mattsson P. Influence of dietary factors on aluminium absorption and retention in the brain and bone of rats. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1985 Apr;56(4):331–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1985.tb01299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lieben J. Manganese poisoning and exposure in Pennsylvania. Arch Environ Health. 1969 Nov;19(5):674–684. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1969.10666909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennberg A., Iregren A., Struwe G., Cizinsky G., Hagman M., Johansson L. Manganese exposure in steel smelters a health hazard to the nervous system. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1991 Aug;17(4):255–262. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. M., Longstreth W. T., Jr, Rosenstock L., Claypoole K. H., Brodkin C. A., Townes B. D. Neurologic syndrome in 25 workers from an aluminum smelting plant. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Jul;152(7):1443–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock C. M., Jr, Amuso S. J., Bittenbender J. B. Chronic neurological disease in two manganese steel workers. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1966 Sep-Oct;27(5):454–459. doi: 10.1080/00028896609342453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



