Abstract
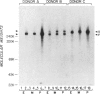
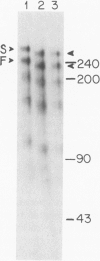
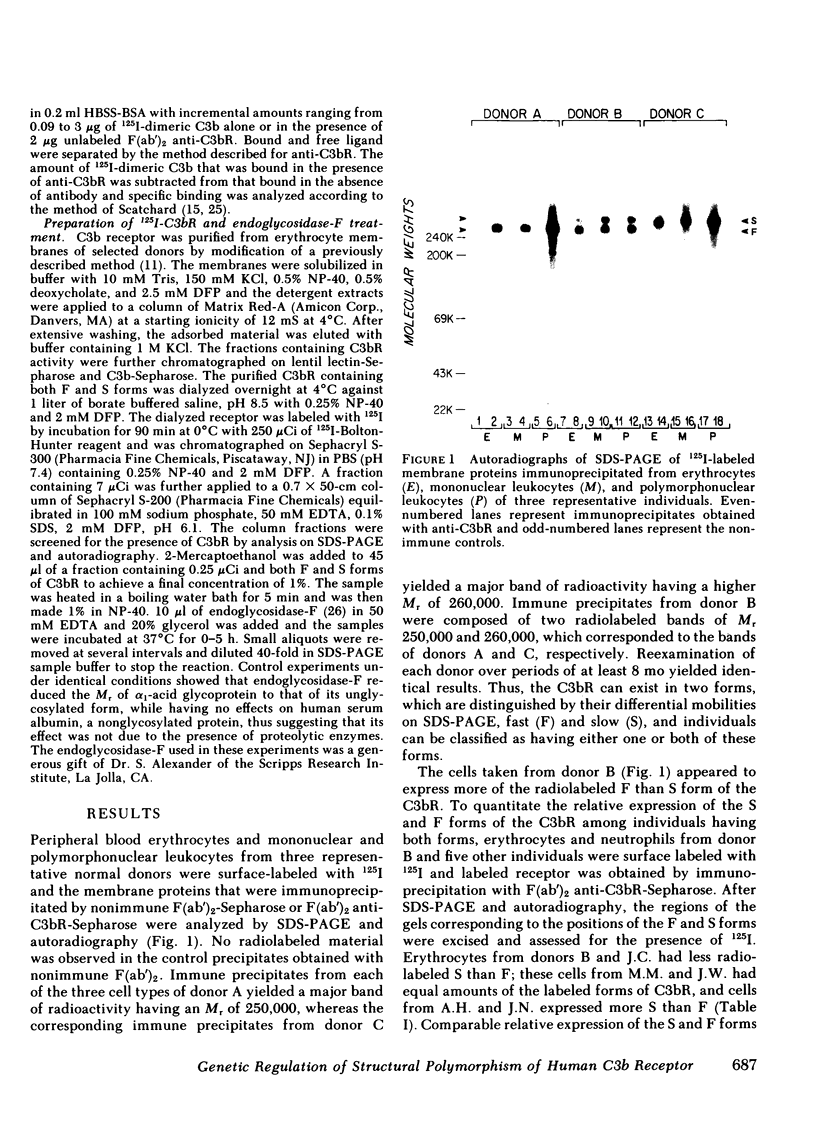
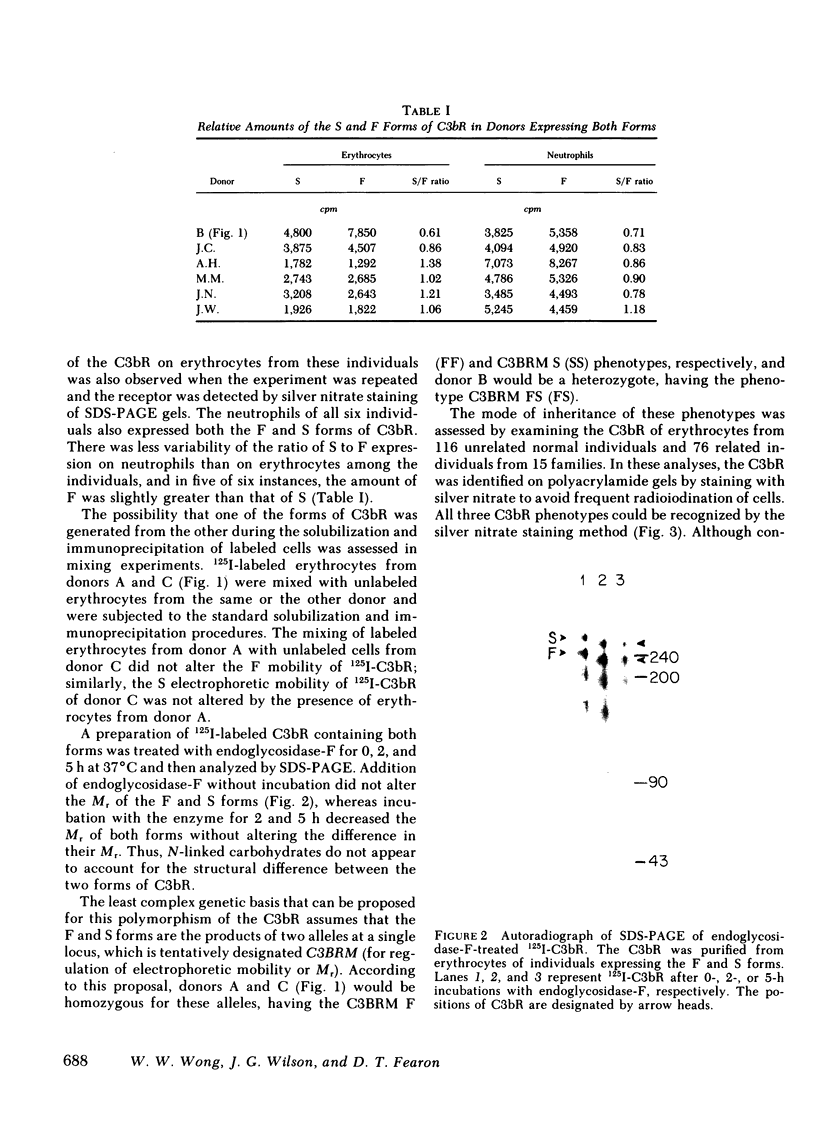
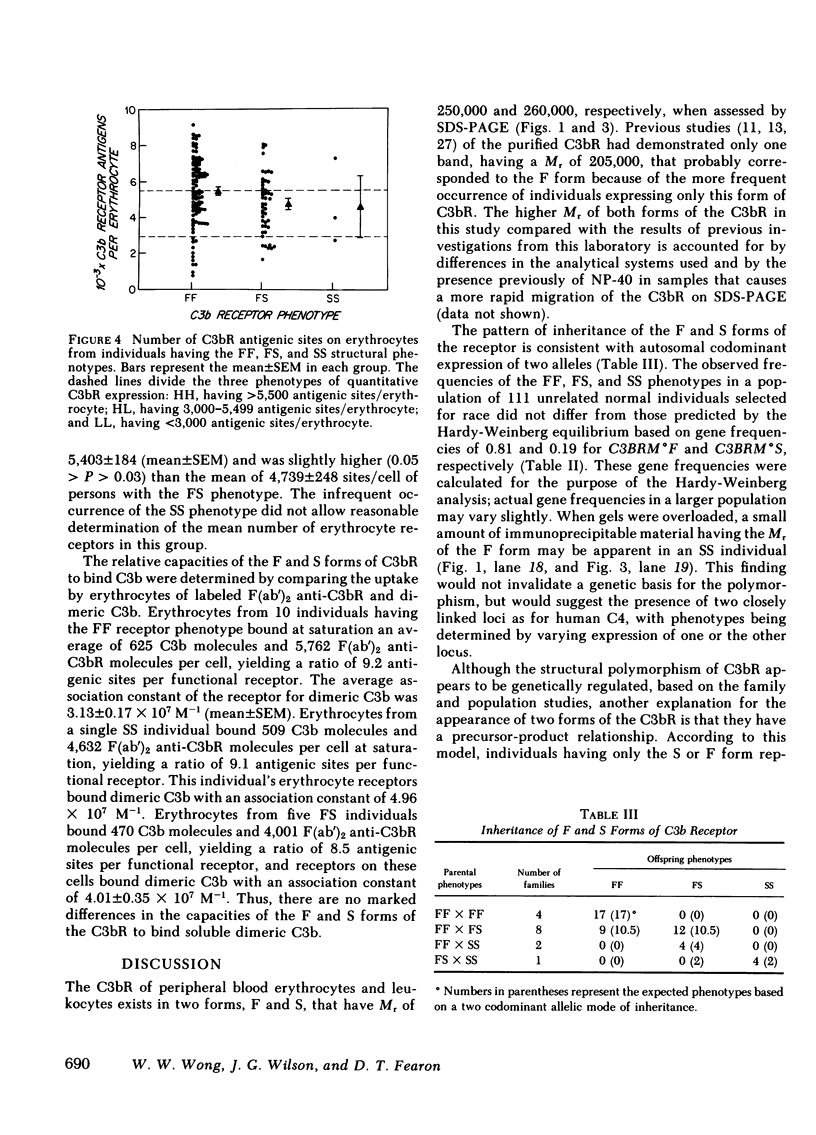
Two forms of the human C3b receptor (C3bR), which have relative molecular weights (Mr) of 250,000 and 260,000 and are designated F and S, respectively, have been identified in specific immunoprecipitates from erythrocytes and leukocytes by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Both forms of the receptor were visualized on gels by autoradiography of 125I-labeled antigen and by silver nitrate staining. Individual donors expressed one of three possible patterns of C3bR, either the F or S form alone or both, and these patterns represented stable phenotypic characteristics of their erythrocytes and polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes. Removal of N-linked oligosaccharides by endoglycosidase-F treatment decreased the Mr of both forms but did not abolish the difference in their electrophoretic mobilities. That both forms of the receptor were functional was indicated by the capacity of all antigenic C3bR sites on erythrocytes from individuals having any of the three phenotypes to bind dimeric C3b with affinities ranging from 3 to 5 X 10(7) M-1. Analyses of the occurrence of the F and S forms of C3bR in 76 individuals from 15 families revealed that this polymorphism was regulated by two alleles transmitted in an autosomal codominant manner. Of 111 normal unrelated individuals, 64.9% were homozygous for the F form (FF), 1.8% were homozygous for the S form (SS), and 33.3% were heterozygotes (FS). This distribution did not differ from that calculated by the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium based on two codominant alleles that regulate the expression of the F and S forms and that have frequencies of 81.5 and 18.5%, respectively. The locus regulating structural polymorphism of C3bR is designated C3BRM (M for mobility or Mr), and is distinct from the recently described locus regulating the quantitative expression of C3bR on erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Boenisch T., Watson L. Genetic polymorphism in human glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Propp R. P. Genetic polymorphism of the third component of human complement (C'3). J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2181–2191. doi: 10.1172/JCI105904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A., Melamed J., Tack B. F., Colten H. R. Characterization of the human complement (c3b) receptor with a fluid phase C3b dimer. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1348–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R. Immune adherence by the fourth component of complement. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):396–398. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson N. J., Lambris J. D., Ross G. D. Characteristics of isolated erythrocyte complement receptor type one (CR1, C4b-C3b receptor) and CR1-specific antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):693–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Collins L. A. Increased expression of C3b receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by chemotactic factors and by purification procedures. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Identification of the membrane glycoprotein that is the C3b receptor of the human erythrocyte, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, B lymphocyte, and monocyte. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):20–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Kaneko I., Thomson G. G. Membrane distribution and adsorptive endocytosis by C3b receptors on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1615–1628. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Frank M. M., Green I. A receptor for the third component of complement in the human renal glomerulus. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):1029–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Naiem M., Mason D. Y., Stein H. Human complement (C3b) receptors defined by a mouse monoclonal antibody. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):645–653. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Nelson R. A., Jr Complement dependent immune phagocytosis. I. Requirements for C'1, C'4, C'2, C'3. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jul;51(1):45–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Mornaghi R., Nussenzweig V. Complement receptor (CR1) deficiency in erythrocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1427–1438. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Genetic variation in glycosylation of the fourth component of murine complement. Association with hemolytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7330–7335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Appay M. D., Mandet C., Bariety J. Immunohistochemical study of the human glomerular C3b receptor in normal kidney and in seventy-five cases of renal diseases: loss of C3b receptor antigen in focal hyalinosis and in proliferative nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):900–912. doi: 10.1172/JCI110529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Yamada A., Kosaka K., Tsuda F., Kosugi E., Mayumi M. Defective immune-adherence (C3b) receptor on erythrocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1981 Sep 5;2(8245):493–497. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90882-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. The determination of the exposed proteins on membranes by the use of lactoperoxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:103–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON R. A., Jr The immune-adherence phenomenon; an immunologically specific reaction between microorganisms and erythrocytes leading to enhanced phagocytosis. Science. 1953 Dec 18;118(3077):733–737. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3077.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Atkinson J. P., Roos M. H., Shreffler D. C. Genetic and structural characterization of H-2-controlled allelic forms of murine C4. Immunogenetics. 1980 Jul;11(1):55–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01567769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Spence M. A., Balavitch D., Tideman S., Merritt A. D., Taggart R. T., Petersen B. H., Day N. K., Alper C. A. Genetic control of the eighth component of complement. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):858–865. doi: 10.1172/JCI109534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Atkinson J. P., Newball H. H., Frank M. M. Receptors for immunoglobulin and complement on human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1813–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Molecular characterization of the Ss and Slp (C4) proteins of the mouse H-2 complex: subunit composition, chain size polymorphism, and an intracellular (PRO-Ss) precursor. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1106–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Mollenhauer E., Démant P., Rittner C. A molecular basis for the two locus model of human complement component C4. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):854–856. doi: 10.1038/298854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2283–2292. doi: 10.1172/JCI106194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Alper C. A., Bootsma D., Dorf M., Douglas T., Huisman T., Kit S., Klinger H. P., Kozak C., Lalley P. A. International system for human gene nomenclature (1979) ISGN (1979). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;25(1-4):96–116. doi: 10.1159/000131404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., McAlpine P. J. The 1979 catalog of human genes and chromosome assignments. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;25(1-4):117–127. doi: 10.1159/000131405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranian G., Jr, Conrad D. H., Ruddy S. Specificity of C3 receptors that mediate phagocytosis by rat peritoneal mast cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2302–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. G., Wong W. W., Schur P. H., Fearon D. T. Mode of inheritance of decreased C3b receptors on erythrocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 14;307(16):981–986. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210143071604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]