Abstract
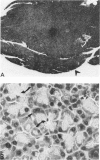
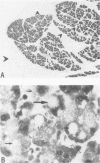
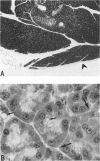
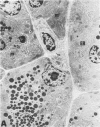
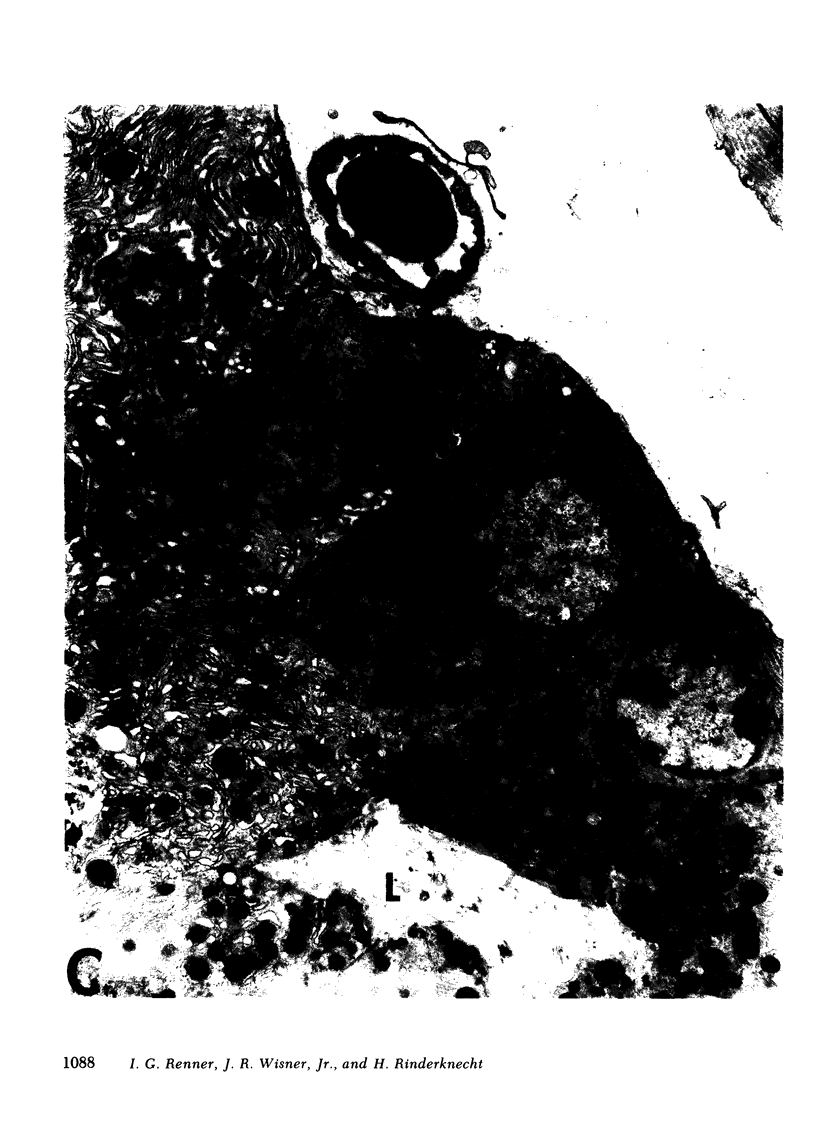
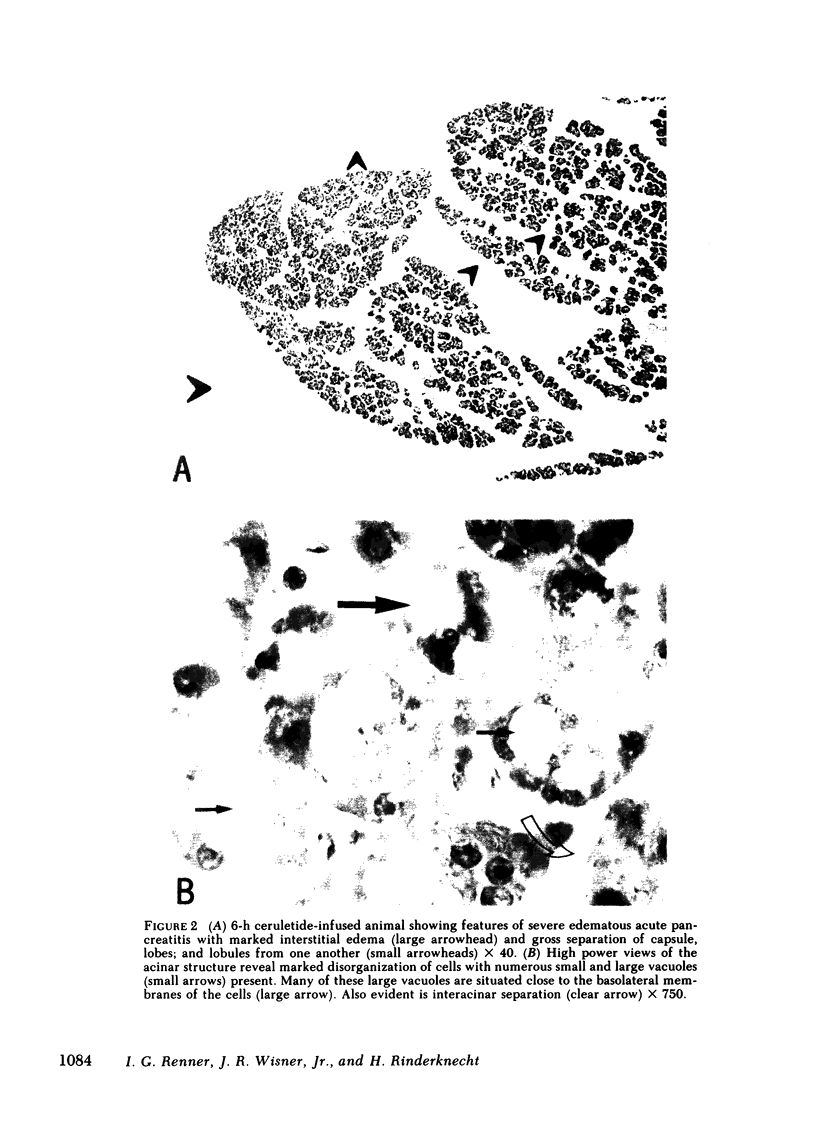
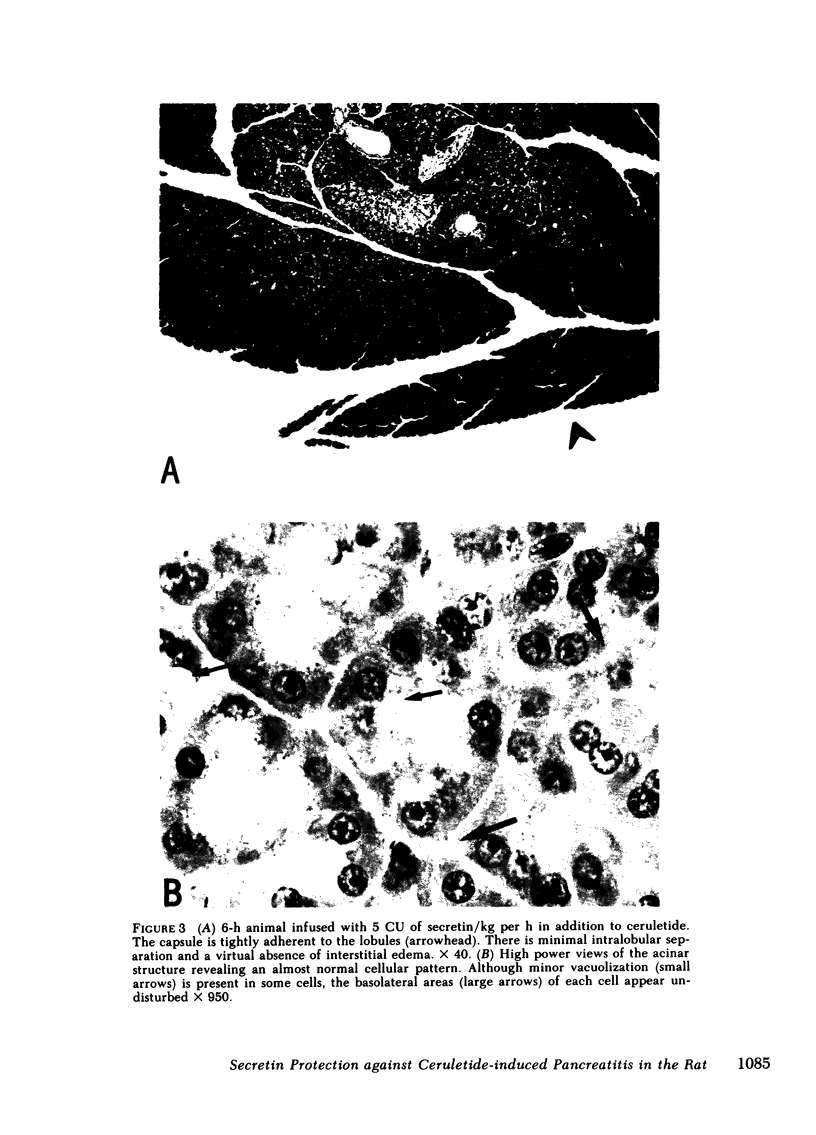
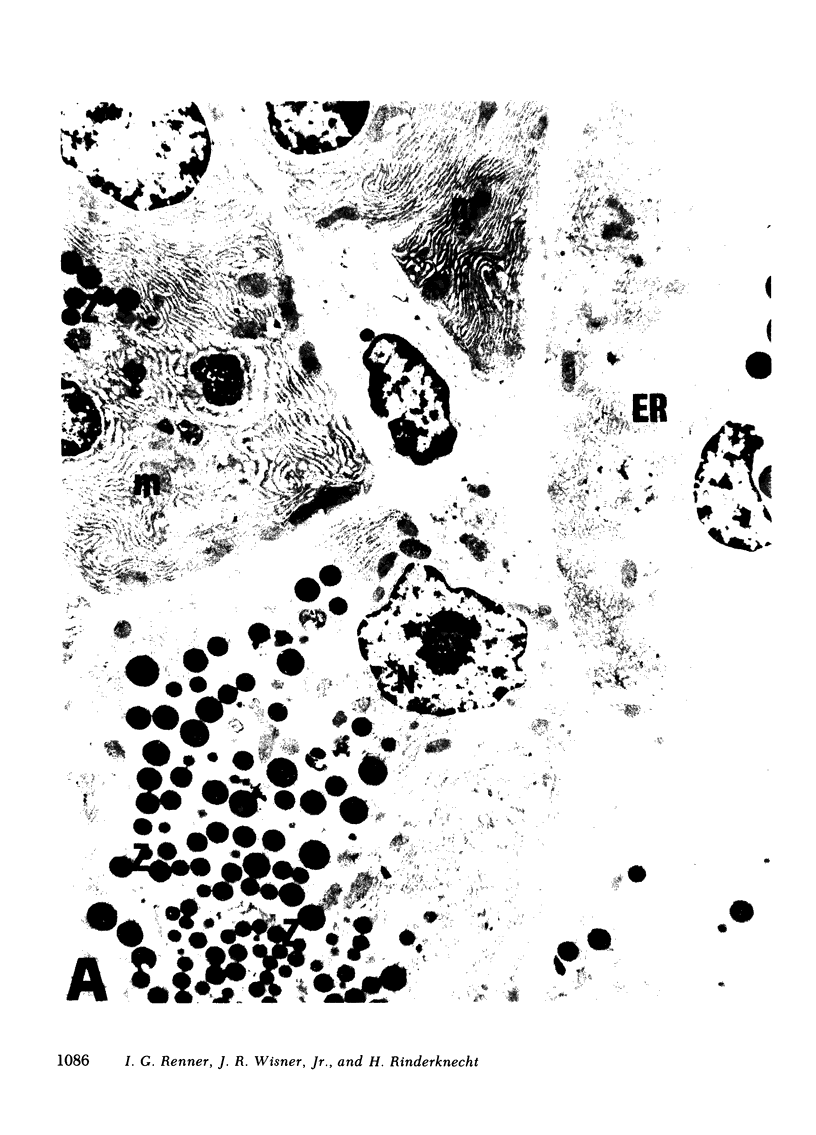
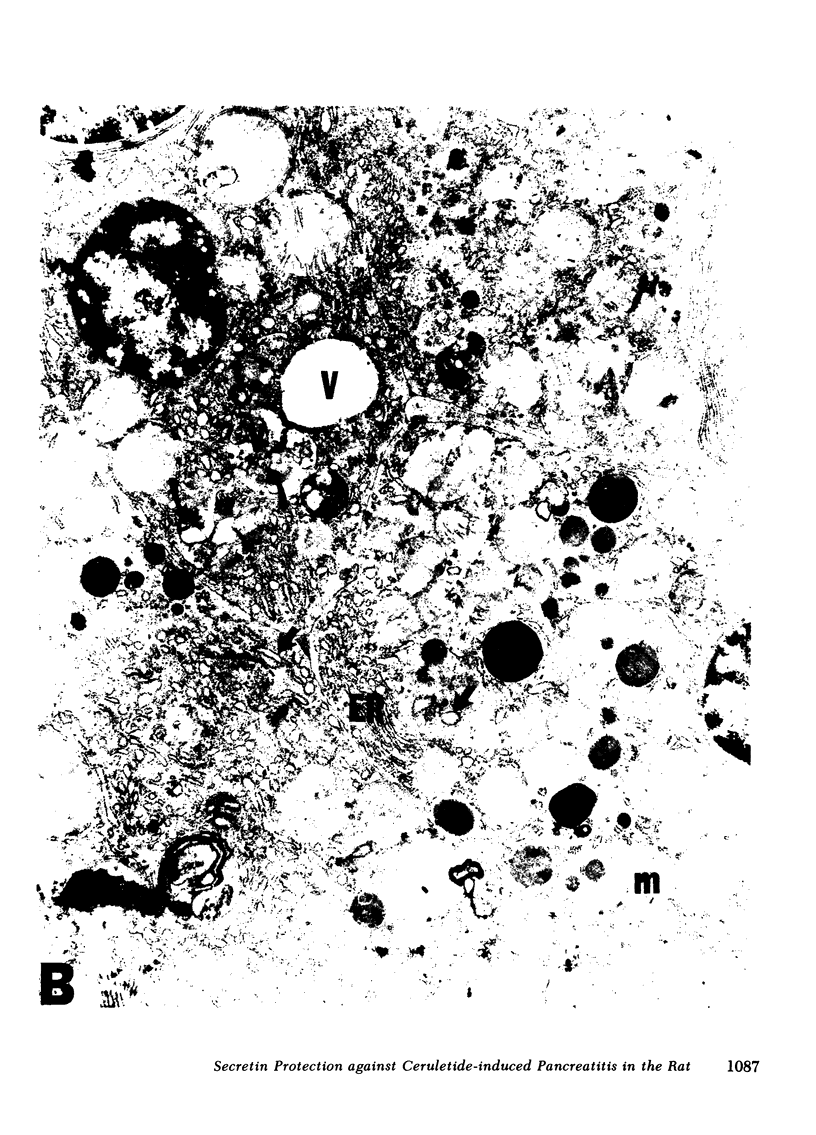
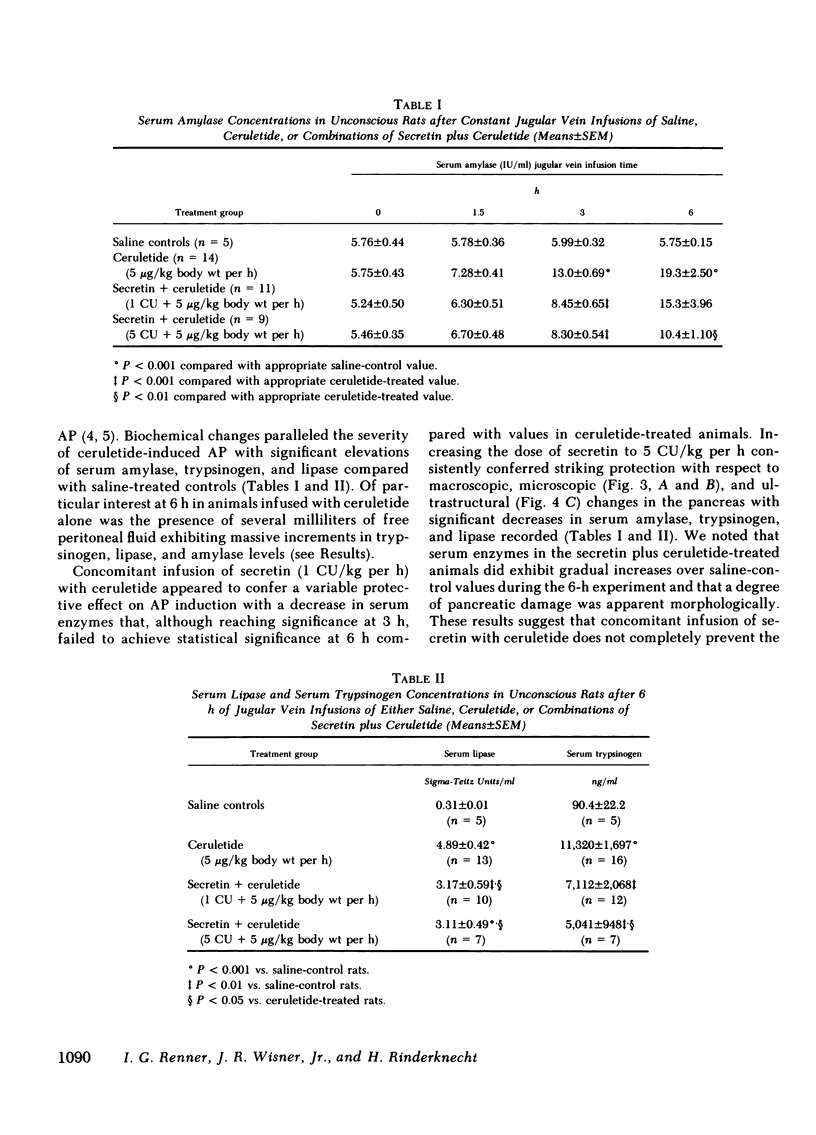
Unconscious rats given intravenous ceruletide (diethylamine salt of the decapeptide caerulein) in large pharmacologic doses consistently developed moderate acute pancreatitis by 3 h and florid pancreatitis by 6 h. Biochemical serum markers of acute pancreatitis tended to parallel the severity of the pancreatic damage. In 50% of the rats, mesenteric fat necrosis was present, free peritoneal fluid containing massive elevations of trypsinogen and amylase were noted in most animals. Intravenous secretion at a low dose given simultaneously with ceruletide exerted a variable protective effect on the pathological process. A high dose of secretin produced a striking macroscopic, microscopic, and biochemical protective effect on ceruletide-induced pancreatitis. High resolution light microscopy and electron microscopy showed a marked cellular disorganization in the acini of animals treated with ceruletide alone. By contrast, there was a striking apical redirection of zymogen granules in acini of the animals treated with secretin. The results of this study suggest that high dose intravenous secretin may exert a beneficial effect on acute pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler G., Hupp T., Kern H. F. Course and spontaneous regression of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1979 May 14;382(1):31–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01102739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyerman H. C., Grossman M. I., Scratcherd T., Solomon T. E., Voskamp D. On the instability of secretin. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 31;29(9):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imrie C. W., Whyte A. S. A prospective study of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1975 Jun;62(6):490–494. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. L., Daggett W. M., Civette J. M., Vasu M. A., Lawson D. W., Warshaw A. L., Nardi G. L., Bartlett M. K. Acute pancreatitis: analysis of factors influencing survival. Ann Surg. 1977 Jan;185(1):43–51. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197701000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Gardner J. D. Identification and characterization of receptors for secretagogues on pancreatic acinar cells. Fed Proc. 1981 Aug;40(10):2486–2496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Weinhold P. A., Calkins D. W., Hartog V. W. Comparative studies of the age-related changes in protein synthesis in the rat pancreas and parotid gland. Exp Gerontol. 1981;16(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(81)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampel M., Kern H. F. Acute interstitial pancreatitis in the rat induced by excessive doses of a pancreatic secretagogue. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1977 Mar 11;373(2):97–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00432156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja J. L., Renner I. G., Abramson S. B., Edmondson H. A. Production of acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis in the dog using venom of the scorpion, Buthus quinquestriatus. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 May;28(5):429–439. doi: 10.1007/BF02430532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen H., Grossman M. I. Pancreatic exocrine secretion in anesthetized and conscious rats. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):E530–E536. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.6.E530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Rifkind K. M., Turner J. W. Prognostic signs and nonoperative peritoneal lavage in acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Aug;143(2):209–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner I. G., Pantoja J. L., Abramson S. B., Douglas A. P., Russell F. E., Koch M. K. Effects of scorpion and rattlesnake venoms on the canine pancreas following pancreaticoduodenal arterial injections. Toxicon. 1983;21(3):405–420. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner I. G., Rinderknecht H., Douglas A. P. Profiles of pure pancreatic secretions in patients with acute pancreatitis: the possible role of proteolytic enzymes in pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1090–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Renner I. G., Douglas A. P., Adham N. F. Profiles of pure pancreatic secretions obtained by direct pancreatic duct cannulation in normal healthy human subjects. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Renner I. G., Stace N. H. Abnormalities in pancreatic secretory profiles of patients with cancer of the pancreas. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Feb;28(2):103–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01315138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]