Abstract
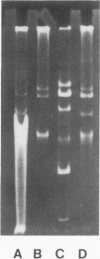
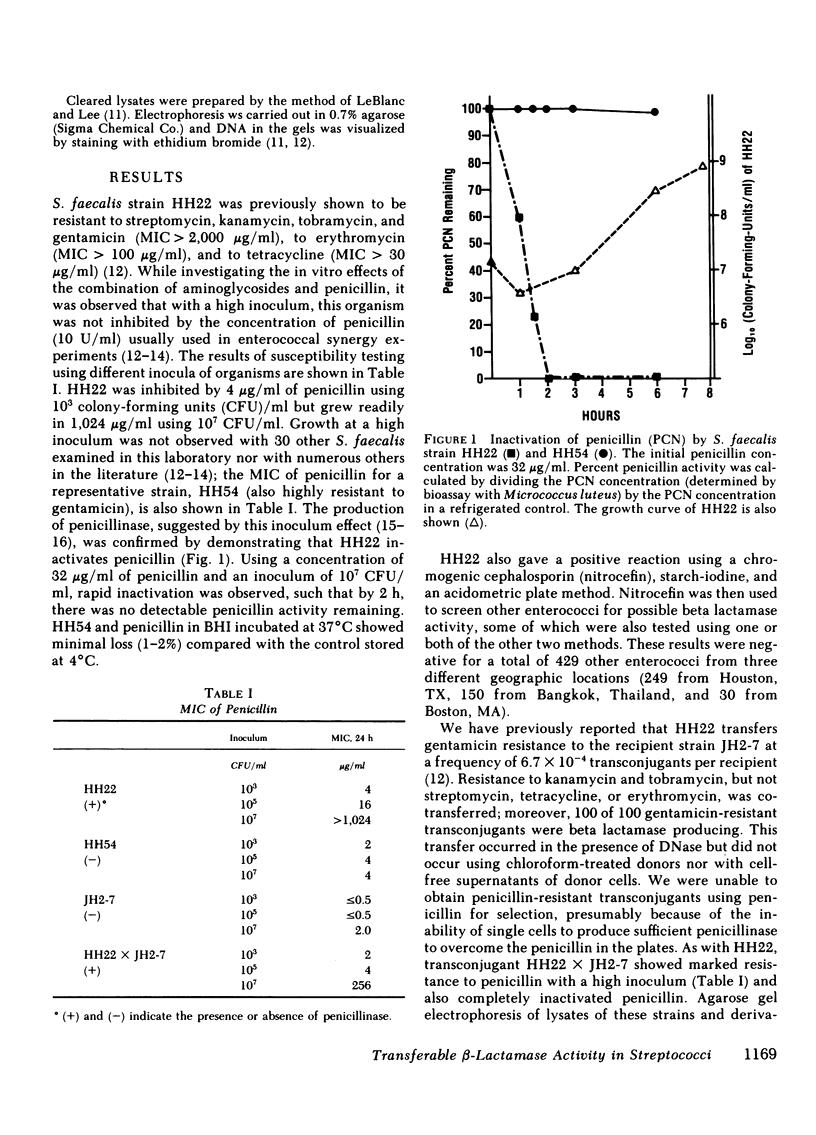
Although enterococci are relatively resistant to penicillin, the mechanism of resistance is largely unknown and enzymatic inactivation does not play a role. In this study, an isolate of Streptococcus faecalis was found to have beta lactamase activity resulting in complete inactivation of penicillin. With a high inoculum, this strain was resistant to greater than 1,000 micrograms/ml of penicillin. Penicillin resistance and beta lactamase activity were transferred by conjugation at a high frequency to an enterococcal laboratory recipient strain together with two plasmids of molecular size 34 X 10(6) and 56 X 10(6), thus demonstrating the emergence of plasmid-mediated penicillin resistance in the genus Streptococcus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calderwood S. A., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J., Krogstad D. J. Resistance to six aminoglycosidic aminocyclitol antibiotics among enterococci: prevalence, evolution, and relationship to synergism with penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):401–405. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel H. W., Soedirman N., Rost J. A., van Leeuwen W. J., van Embden J. D. Transferability of macrolide, lincomycin, and streptogramin resistances between group A, B, and D streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.407-413.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr, Gramling P. K. Antistaphylococcal activity and beta-lactamase resistance of newer cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):691–695. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finland M. I. Prevalence of extrachromosomal drug resistance. Changes in asusceptibility of selected pathogenic bacteria to widely used antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:5–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. E., Hobbs S. J. Conjugal transfer of plasmid-borne multiple antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):360–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.360-372.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D. J., Lee L. N. Rapid screening procedure for detection of plasmids in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1112–1115. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1112-1115.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas T. J. An evaluation of 12 methods for the demonstration of penicillinase. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):1061–1065. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mederski-Samoraj B. D., Murray B. E. High-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Synergy of penicillin and gentamicin against Enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S207–S209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Moellering R. C., Jr Patterns and mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Med Clin North Am. 1978 Sep;62(5):899–923. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31746-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Borst G. C., Mazur M. H., Iannini P., Klempner M. S., Moellering R. C., Jr, Anderson S. E. Endocarditis due to resistant viridans streptococci during oral penicillin chemoprophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Feb 8;300(6):296–300. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197902083000608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Brown R. M., Gaspar M. N., Ward J. I., Wachsmuth I. K., Koornhof H. J., Jacobs M. R., Thornsberry C. Resistance mechanisms of multiply resistant pneumococci: antibiotic degradation studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):470–474. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Effect of inoculum and of beta-lactamase on the anti-staphylococcal activity of thirteen penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):344–349. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of group D streptococcus (enterococcus) to 21 antibiotics in vitro, with special reference to species differences. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):416–430. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]