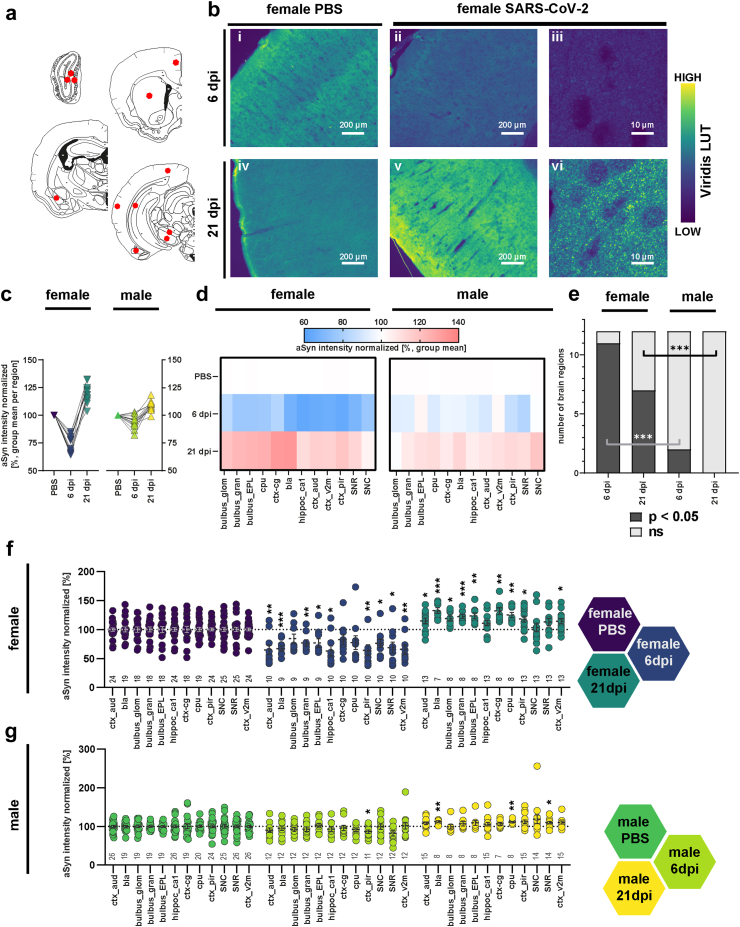
Fig. 1.
Biphasic response of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity following SARS-CoV-2 infection. (a). Schematic representation of the coronal hamster brain sections that were stained, red dots highlighting the regions of interest examined (Olfactory bulb glomerular, granular and external plexiform layers (bulbus_glom, gran, EPL), caudate putamen (cpu), cingulate cortex (ctx_cg), basolateral amygdala (bla), ca1 region of hippocampus (hippoc-ca1), and aud, v2m and pir regions of cortex, substantia nigra partes reticulata and compacta (SNR, SNC)). Modification of coronal brain illustrations of Wood et al., 2001.121 b. Representative histological stainings of aSyn recorded at a 10× magnification (i-ii, iv-v) and confocal laser scanning macroscopy at 160× (iii, vi) in the cortex from female animals with PBS or SARS-CoV-2 infection at 6 and 21 dpi. Scale bar in widefield images = 200 μm, in confocal images = 10 μm. The viridis lookup table was used for the histological images to increase the visibility of expression changes. (c) Group mean of the normalized aSyn-IR per region in sex/infection groups demonstrating the general biphasic tendency of the aSyn response to infection. (d) Heatmaps of group mean normalized aSyn-IR per brain region in female and male animals in the three groups PBS, 6 dpi and 21 dpi. (e) Distribution of brain regions where PBS and SARS-CoV-2 groups differ significantly. Statistics: fishers exact test between male and female groups at 6 and 21 dpi. (f–g) Quantification of mean aSyn-IR in relevant regions for female (f) and male (g) hamsters. Data normalized to female and male PBS control group. Circles depict individual animals. The mean ± SEM is additionally shown. Mark the different scales on the y-axes. Mixed-effect analysis of aSyn-IR across brain regions in female (f) and male (g) hamsters evaluating effects of region and infection followed by a Dunnett's multiple comparisons test to evaluate infection effects within brain regions. Further information on Mixed-effect statistics can be found in Supplementary data file 1. Differences are depicted as ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Sample sizes are shown at the bottom of the groups in the graphs. No experimental outliers were excluded, group differences originate from apriori quality control.